Maritimonautes, Cumberlidge & Daniels, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1093/zoolinnean/zlab082 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:A4C99333-FF4C-4857-9900-E3D743E03684 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6461518 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/7A4187EF-4F3F-FF97-07DC-F93AFEDE54C3 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Maritimonautes |
| status |
gen. nov. |
MARITIMONAUTES View in CoL GEN. NOV.
( FIGS 1B1 View Figure 1 , 5A–C View Figure 5 , 8B; TABLES View Figure 8 1–3)
Zoobank registration: urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:29BB5EDB-5AB4-48E5-8B42-AA97939DDA7F
Thelphusa A. Milne-Edwards, 1868: 86 View in CoL , pl. 20, figs 1–4; 1869: 178; 1887: 146; Pfeffer, 1889: 33.
Telphusa Hilgendorf, 1879: 801 View in CoL ; 1891: 20; 1898: 16.
Potamon (Potamonautes) Ortmann, 1897: 303 , 305.
Potamon De Man, 1898: 434 View in CoL , 437; Chace, 1942: 190.
Potamon (Potamonautes) De Man, 1898: 262–270 , 436, fig. 3; Rathbun, 1904: pl. 15, figs 8, 9; 1905: 180, fig. 45; 1933: 258; 1935: 26; Sendler, 1912: 199; Bouvier, 1921: 49; Colosi, 1925: 2; Parisi, 1925: 98; Barnard, 1950: 192, fig. 34 f, g.
Potamonautes Balss, 1929: 348 View in CoL ; Barnard, 1935: 484; Capart, 1954: 841, fig. 36, 17; Cumberlidge, 1997: 580– 582; 1998: 198, 202–203.
Potamonautes (Obesopotamonautes) Bott, 1955: 257– 259 , pl. XXII, figs 2a–d, 19, 80; Pretzmann, 1977: 238, figs 7–12.
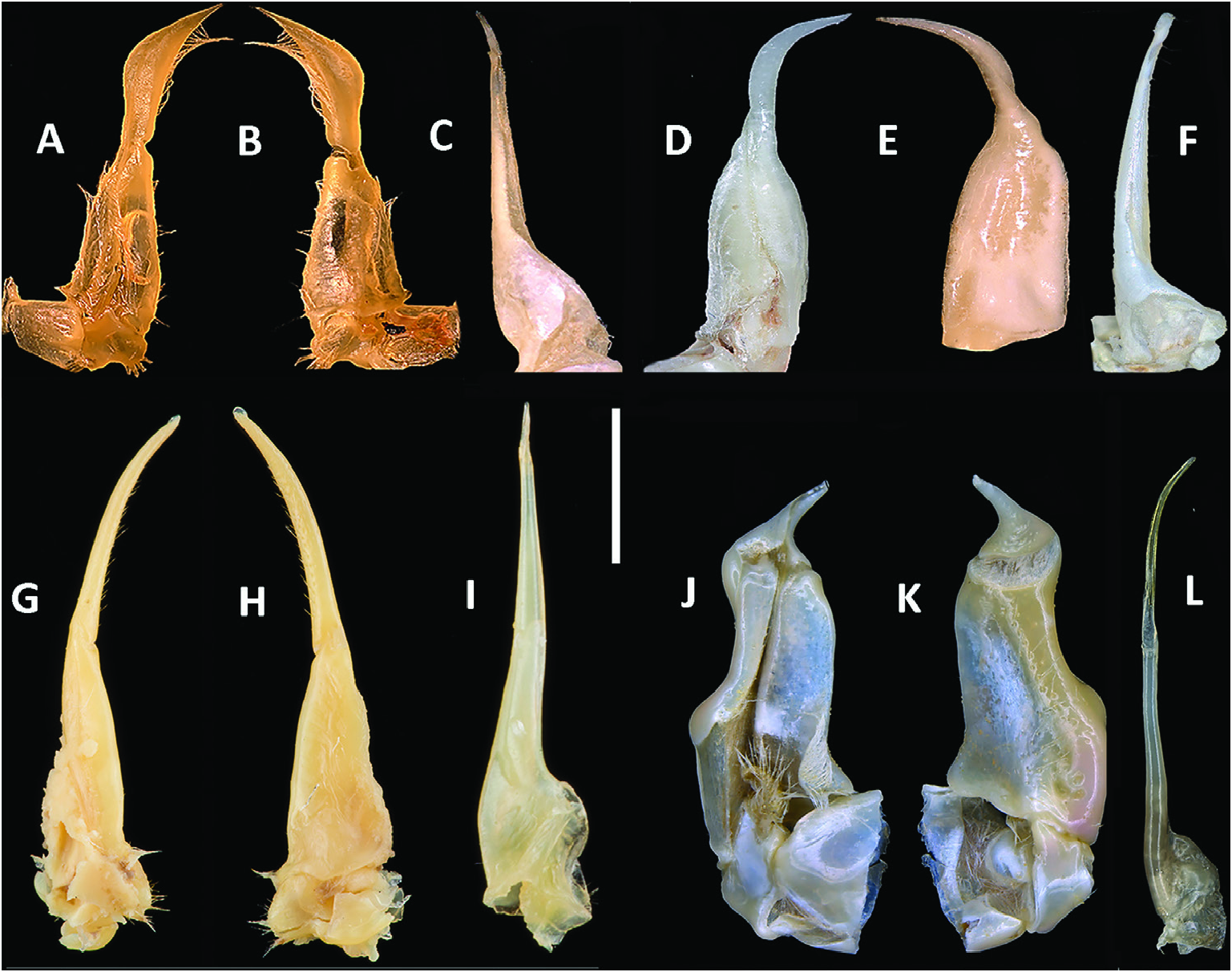
Diagnosis: S3/4 deep, V-shaped, completely traversing sternum (or deep at margins, faint in the middle); outer margins of S4 raised and thickened; third maxilliped ischium lacking vertical suture (or if present faint); anterolateral margin of carapace posterior to epibranchial tooth either smooth or granulated, but lacking teeth; G1 TA short (TA length 0.25 × SA length), slim, either not widened in midsection (or dorsal fold slightly higher than ventral fold), tapering evenly to pointed tip ( Fig. 5A, B View Figure 5 ).
Etymology: Maritimonautes is derived from the Latin maritimus, coastal, referring to the coastal plain of East Africa, east of the Rift Valley where this genus is found, and the Greek ναύτες, seamen, a common suffix for African freshwater crabs. Gender masculine.
Type species: Thelphusa obesa A. Milne-Edwards, 1868 , by original designation.
S p e c i e s i n c l u d e d: M a r i t i m o n a u t e s c a l c a r a t u s ( Gordon, 1929) comb. nov., Maritimonautes choloensis ( Chace, 1953) comb. nov., Maritimonautes licoensis (Daniels, Bittencourt-Silva, Muianga, & Bayliss, 2020) comb. nov., Maritimonautes namuliensis ( Daniels & Bayliss, 2012) comb. nov. and Maritimonautes obesus (A. Milne-Edwards, 1868) comb. nov.
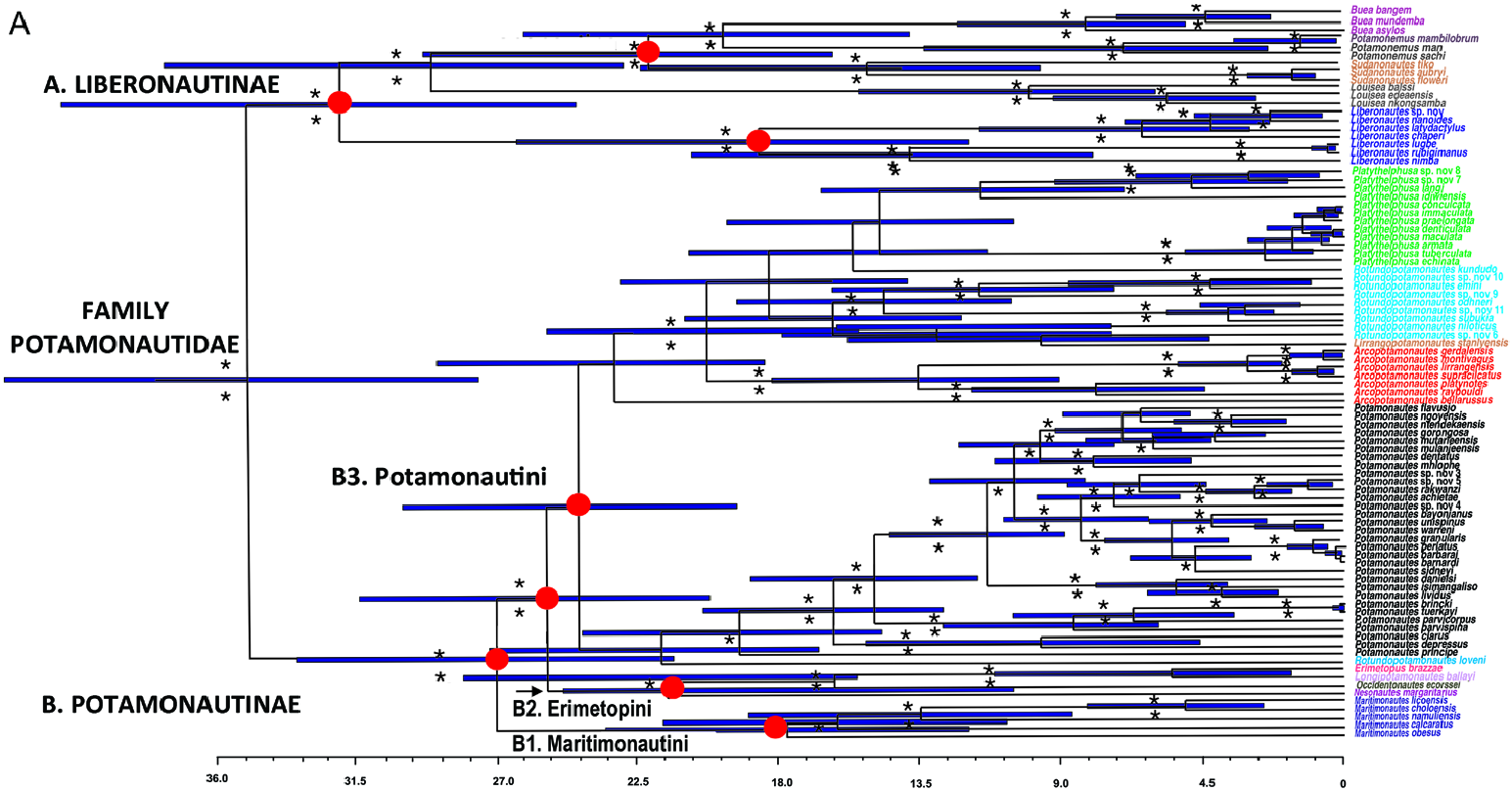
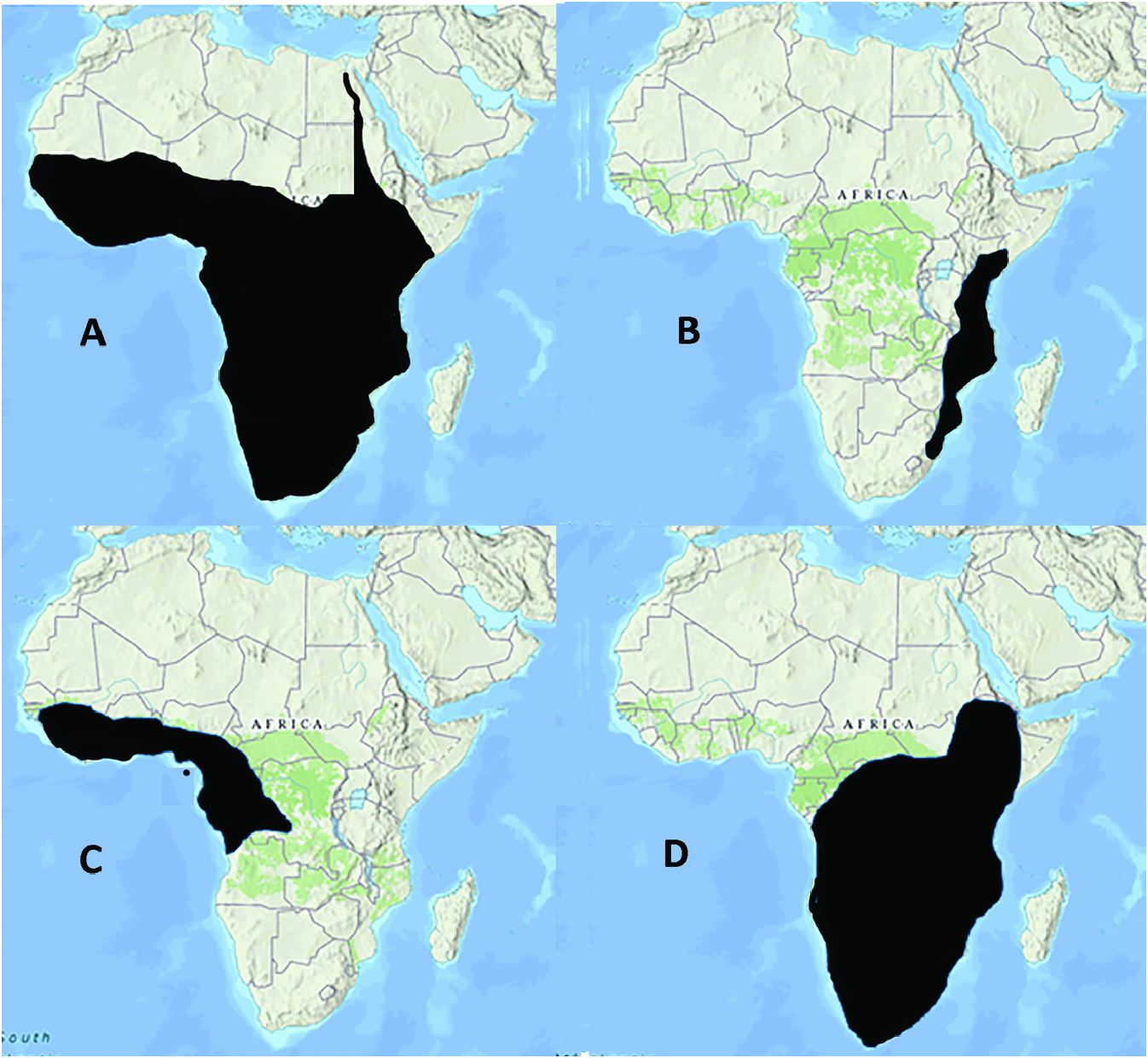
Distribution: Maritimonautes is found in the lowlying coastal plains of Somalia, Kenya and Tanzania (plus Zanzibar and Pemba islands), including the north coast of Lake Malawi in Tanzania (Ruvuma, Iringa and Mbeya Provinces), Mounts Inago, Mabu, Namuli and Lico in northern Mozambique, Mount Nyangoni (Manicaland Province) in eastern Zimbabwe and the Kruger National Park in Mpumapanga Province, South Africa ( Chace, 1953; Reed & Cumberlidge, 2004; Daniels & Bayliss, 2012; Daniels et al., 2014, 2020; Fig. 8B View Figure 8 ).
Remarks: Maritimonautes is established for five species formerly assigned to Potamonautes s.l. DNA data are available for five of these species that are grouped together in a well-supported clade ( Daniels et al., 2015: fig. 2; Daniels & Klaus, 2018: fig. 1; Wood et al., 2019: fig. 1; Fig. 1B1 View Figure 1 ). The most recently-described species of this genus ( M. licoensis ) from Mozambique is included based on morphology and the phylogeny published with the description ( Daniels et al., 2020). Two of the species transferred here to Maritimonautes ( M. calcaratus and M. obesus ) were assigned by Bott (1955) to Potamonnautes (Obesopotamonautes) Bott, 1955. The latter subgenus is not recognized here, because it is not monophyletic: two of its three taxa belong to the new genus Maritimonautes ( Fig. 1B1 View Figure 1 ), but the third species, Platythelphusa langi , is positioned in a separate lineage for Platythelphusa ( Fig. 1B View Figure 1 3 View Figure 3 [3]).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Maritimonautes
| Cumberlidge, Neil & Daniels, Savel R. 2022 |
Potamonautes (Obesopotamonautes)
| Pretzmann G 1977: 238 |
| Bott R 1955: 259 |
Potamonautes
| Cumberlidge N 1998: 198 |
| Cumberlidge N 1997: 580 |
| Capart A 1954: 841 |
| Barnard KH 1935: 484 |
| Balss H 1929: 348 |
Potamon
| Chace FA 1942: 190 |
| De Man JG 1898: 434 |
Potamon (Potamonautes)
| Bouvier EL 1921: 49 |
| De Man JG 1898: 270 |
Potamon (Potamonautes)
| Ortmann AE 1897: 303 |
Telphusa
| Hilgendorf F 1879: 801 |
Thelphusa A. Milne-Edwards, 1868: 86
| Pfeffer G 1889: 33 |
| Milne-Edwards A 1868: 86 |