Arcopotamonautes, (BOTT, 1955)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1093/zoolinnean/zlab082 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:A4C99333-FF4C-4857-9900-E3D743E03684 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6457209 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/7A4187EF-4F34-FF9B-0727-FE07FB41553B |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Arcopotamonautes |
| status |
|
GENUS ARCOPOTAMONAUTES ( BOTT, 1955) View in CoL STAT. NOV.
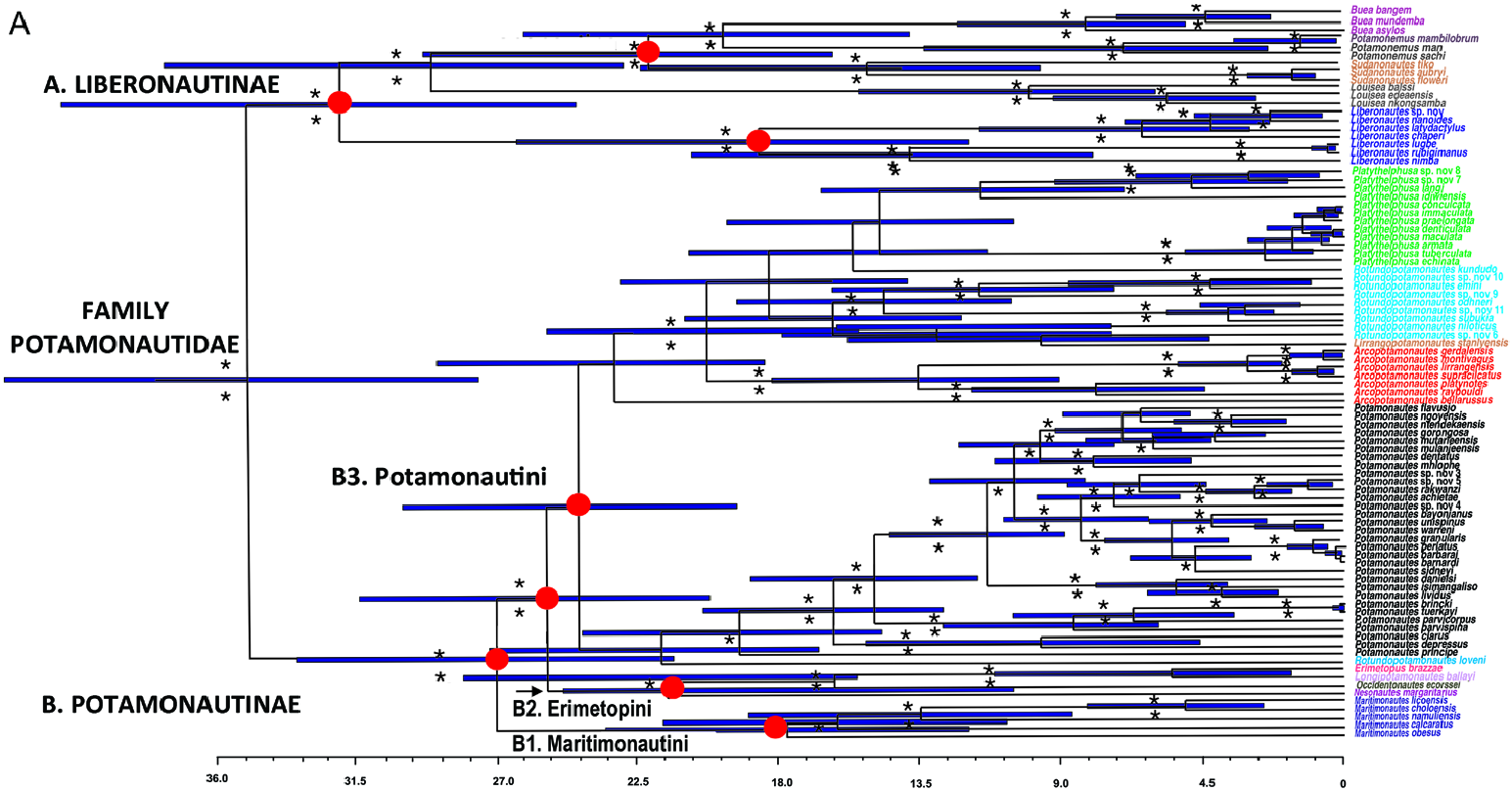
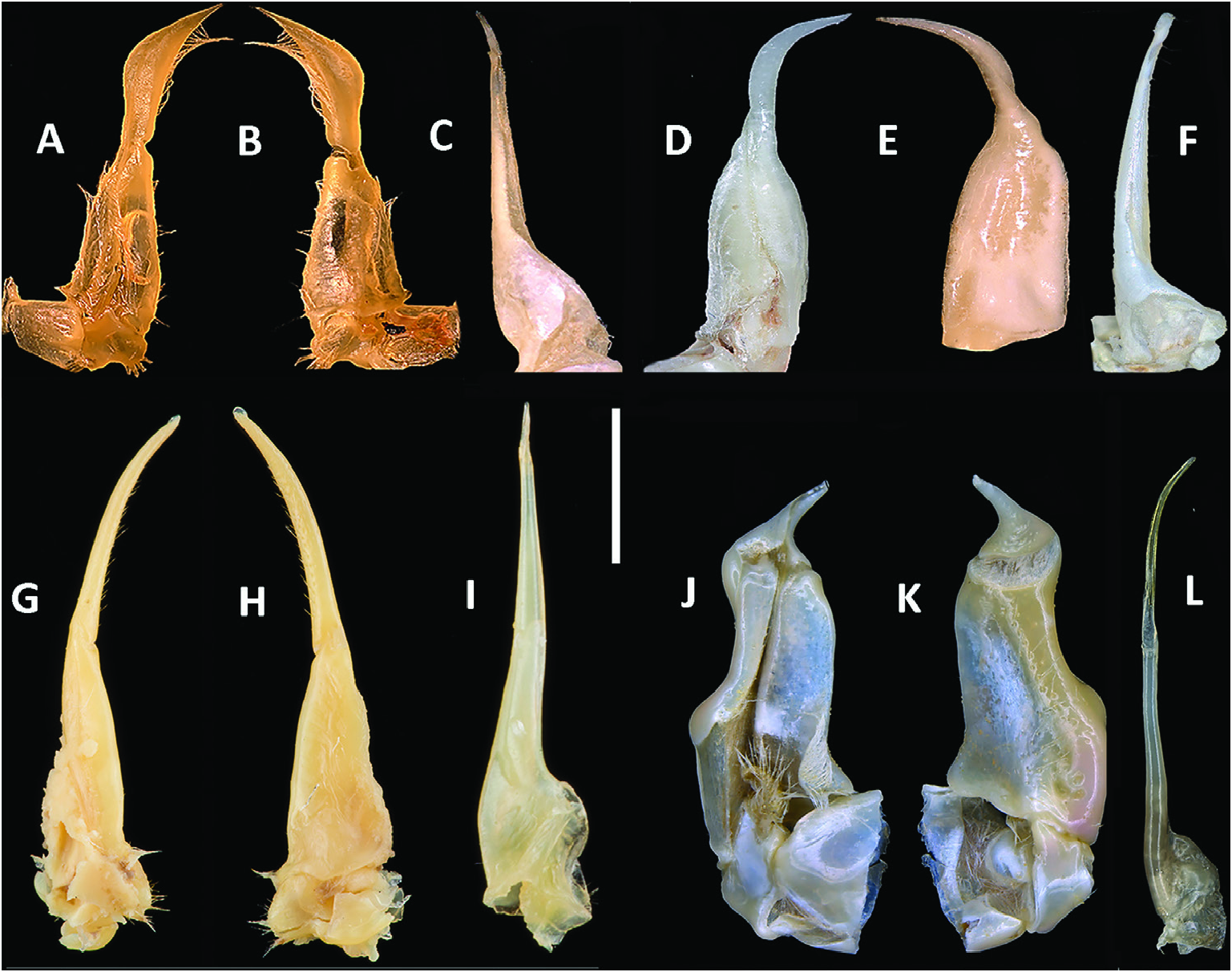
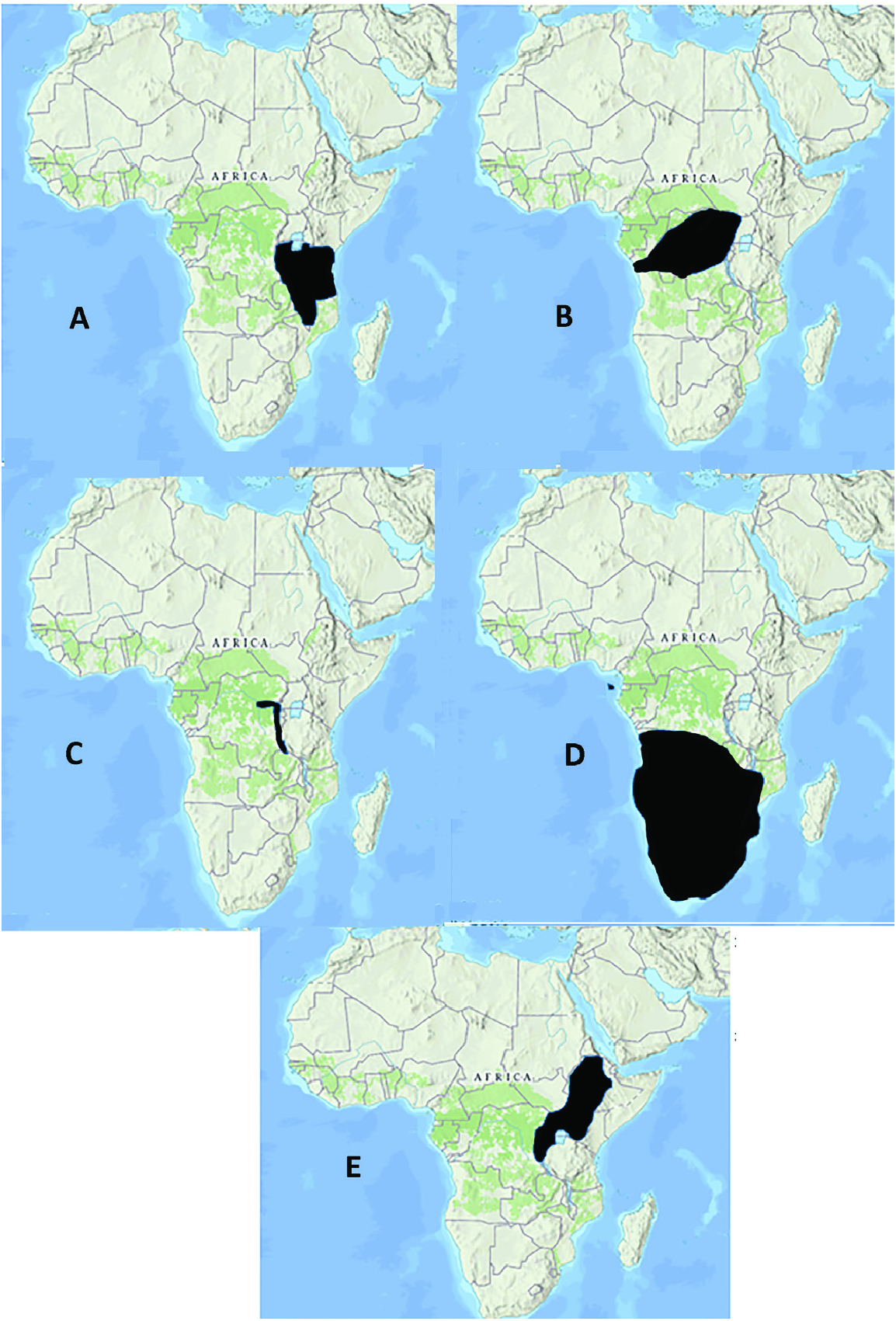
( FIGS 1B View Figure 1 3 View Figure 3 [1], 5D–F, 10A; TABLES 1–3 View Table 1 View Table 2 View Table 3 )
Zoobank registration: urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:187310FB-E397-49F6-A482-254C75929C62 .
Telphusa Hilgendorf, 1898: 8–9 View in CoL , fig. 5, 5a–d.
Potamon De Man, 1898: 438 View in CoL ; Chace, 1942: 222.
Potamon (Potamonautes) Rathbun, 1905: 172 ; 1933: 256; 1935: 26; Colosi, 1924: 4.
Potamonautes Balss, 1929: 348 View in CoL ; Barnard, 1935: 484; Cumberlidge, 1997: 581–582; 1998: 204; 2004: 418–423, figs 1–8, 17–25, 30; 2008: 72, 77, tab. 1; 2011: 79, 82–83, tabs 6.1, 6.3; Reed & Cumberlidge, 2006a: 34–37, figs 113–123, 167–168, 184, pl. XII; Ng et al., 2008: 171.
Potamonautes (Arcopotamonautes) Bott, 1955: 270– 272 , pl. XVII, figs 1a–d, 40 (for Telphusa suprasulcata, Hilgenforf, 1898 ; not Potamon (Potamonautes) alluaudi Bouvier, 1921 , Telphusa bipartite Hilgendorf, 1898 ).
Potamonautes (Gerdalopotamonautes) Bott, 1955 : pl. 13, figs 3a–d, 34, 82 (for Potamonautes (Gerdalopotamonautes) gerdalensis Bott, 1955 View in CoL ).
Potamonautes (Platypotamonautes) Bott, 1955: 229 , pl. IV, figs la–d, 12, 66 (for Potamon (Potamonautes) platynotus Cunnington, 1907 ; not Po. margaritarius View in CoL (= Nesonautes margaritarius View in CoL ), Po. ecorssei (= Occidensonautes ecorssei View in CoL ), Po. pilosus View in CoL (= Rotundopotamonautes pilosus View in CoL ) and Po. neumanni View in CoL (= Rotundopotamonautes neumanni View in CoL ).
Diagnosis: Postfrontal crest distinct, traversing entire carapace between epibranchial teeth; epibranchial tooth reduced to small granule; posterior carapace sulci deep, distinct; G1 TA distinctly widened in midsection (dorsal fold higher than ventral fold), tip curved upward; except for A. suprasulcatus whose G1 TA is a long, slim, curving and tapered and not widened in midsection.
Type species: Telphusa suprasulcata Hilgendorf, 1898 , by original designation.
Species included: Arcopotamonautes amosae ( Cumberlidge, Johnson, Clark & Genner, 2021) comb. nov., Arcopotamonautes bellarussus ( Daniels et al., 2014) comb. nov., Arcopotamonautes caputanatis (Cumberlidge, Clark & Fastiggi, 2019) comb. nov., Arcopotamonautes gerdalensis ( Bott, 1955) comb. nov., Arcopotamonautes infravallatus ( Hilgendorf, 1898) comb. nov., Arcopotamonautes johnstoni (Miers, 1885) comb. nov., Arcopotamonautes loveridgei (Rathbun, 1933) comb. nov.
Arcopotamonautes montivagus ( Chace, 1953) comb. nov., Arcopotamonautes orbitospinus (Cunnington, 1907) comb. nov., Arcopotamonautes platycentron (Hilgendorf, 1897) comb. nov.
Arcopotamonautes platynotus (Cunnington, 1907) comb. nov., Arcopotamonautes raybouldi ( Cumberlidge & Vannini, 2004) comb. nov., Arcopotamonautes suprasulcatus ( Hilgendorf, 1898) comb. nov., Arcopotamonautes unisulcatus ( Rathbun, 1921) comb. nov. and Arcopotamonautes xiphoidus (Reed & Cumberlidge, 2006) comb. nov.
Distribution: Arcopotamonautes species are found in the southern and central parts of the Rift Valley around Lake Malawi and Lake Tanganyika ( Malawi, Tanzania and Zambia) ( Fig. 10A View Figure 10 ). Eight species, A. unisulcatus , A. xiphoidus , A. gerdalensis , A. infravallatus , A. johnstoni , A. loveridgei , A. platycentron and A. raybouldi , have a distribution in Tanzania ( Reed & Cumberlidge, 2006a), with the range of A. platycentron and A. raybouldi extending just across the border into southern Kenya ( Cumberlidge & Vannini, 2004; Reed & Cumberlidge, 2006a). One species, A. amosae , is found in the basins of rivers draining into Lake Tanganyika in Tanzania and also in Lake Kivu, in Nord-Kuvi Province in the D.R. Congo (Cumberlidge et al., 2021). Three species, A. montivagus , A. suprasulcatus and A. loveridgei , are found in southern Tanzania (Iringa, Mbeya and Ruvuma provinces) and in Malawi (Northern Region) ( Chace, 1953; Reed & Cumberlidge, 2006a) and one species A. caputanatis is found in Zambia (Northern Province) ( Cumberlidge et al., 2019). Four species in this genus are found in large lakes such as A. platycentron (Lake Chala) ( Reed & Cumberlidge, 2006a), A. amosae (Lake Kivu) (Cumberlidge et al., 2021), A. platynotus (Lake Tanganyika) ( Reed & Cumberlidge, 2006a) and A. orbitospinus (Lake Malawi) (Cumberlidge et al., 2021).
Remarks: The subgenus Potamonautes (Arcopotamonautes) Bott, 1955 is given generic status and revised. Arcopotamonautes is recognized here to accommodate 14 species from the African Rift Valley. Bott (1955) established P. ( Arcopotamonautes ) for P. (A.) suprasulcatus suprasulcatus , P. (A.) s. alluaudi and P. (A.) bipartitus . Arcopotamonautes includes Telphusa suprasulcata Hilgendorf, 1898 , the type species of P. ( Arcopotamonautes ) as well as P. (Gerdalopotamonautes) gerdalensis Bott, 1955 , the type species of P. (Gerdalopotamonautes) Bott, 1955. The latter subgenus becomes a junior synonym of Aropotamonautes under the rule of priority because Telphusa suprasulcata Hilgendorf, 1898 , is the senior name. Similarly, Arcopotamonautes also includes Potamon (Potamonautes) platynotus Cunnington, 1907 , which is the type species of the subgenus P. (Platypotamonautes) Bott, 1955. The latter subgenus becomes a junior synonym of Aropotamonautes under the rule of priority because Telphusa suprasulcata Hilgendorf, 1898 is the senior name.
DNA data are available for six of these species: A. gerdalensis , A. montivagus , A. orbitospinus (as Po. lirrangensis in Fig. 1B View Figure 1 3 View Figure 3 [2]), A. platynotus , A. raybouldi and A. suprasulcatus . These species group together in a well-supported lineage within the large clade for the Potamonautini ( Daniels et al., 2015, fig. 2; Daniels & Klaus, 2018: fig 1; Wood et al., 2019: fig 1; Fig. 1B View Figure 1 3 View Figure 3 ). In the absence of DNA data, the other eight species assigned here to this genus ( A. amosae , A. caputanatis , A. infravallatus , A. johnstoni , A. loveridgei , A. platycentron , A. suprasulcatus and A. unisulcatus ) are included based on shared morphological characters that conform to the generic diagnosis.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Arcopotamonautes
| Cumberlidge, Neil & Daniels, Savel R. 2022 |
Nesonautes margaritarius
| Cumberlidge & Daniels 2022 |
Occidensonautes ecorssei
| Cumberlidge & Daniels 2022 |
Rotundopotamonautes pilosus
| Cumberlidge & Daniels 2022 |
Rotundopotamonautes neumanni
| Cumberlidge & Daniels 2022 |
Potamonautes (Arcopotamonautes)
| Bott 1955: 270 - 272 |
Potamonautes (Gerdalopotamonautes)
| Bott 1955 |
Potamonautes (Gerdalopotamonautes) gerdalensis
| Bott 1955 |
Potamonautes (Platypotamonautes)
| Bott 1955: 229 |
Potamonautes
| Balss 1929: 348 |
Potamon (Potamonautes) alluaudi
| Bouvier 1921 |
Po. margaritarius
| Balss 1914 |
Potamon (Potamonautes) platynotus
| Cunnington 1907 |
Potamon (Potamonautes)
| Rathbun 1905: 172 |
Po. ecorssei
| , Marchand 1902 |
Telphusa
| Hilgendorf 1898: 8 - 9 |
Potamon
| De Man 1898: 438 |
Telphusa suprasulcata
| Hilgenforf 1898 |
Telphusa bipartite
| Hilgendorf 1898 |