Contacyphon parvus ( Solier, 1849 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4767.4.6 |
|
publication LSID |
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:8C90FD99-8277-4728-A22B-3B9345C042C7 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3796651 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/617AC412-FFB9-5E12-FF4B-FCDB2E3D6424 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi (2020-04-29 06:42:40, last updated 2024-11-29 16:06:23) |
|
scientific name |
Contacyphon parvus ( Solier, 1849 ) |
| status |
|
Contacyphon parvus ( Solier, 1849)
( Figs 2C View FIGURE 2 , 3C View FIGURE 3 , 7 View FIGURE 7 )
Cyphon parvum Solier, 1849: 457 (locus typicus: Santa Rosa)
Helodes parvus Solier : Gemminger & von Harold 1869: 1619
Cyphon parvum: Blackwelder 1944: 267 (checklist; Chile); Moroni 1985: 174 (prov. de Aconcagua, Los Andes)
Cyphon parvus: Pic 1914: 34 (checklist; Chile)
Contacyphon parvus ( Solier, 1849) : Zwick et al. 2013: 345
Type material. Lectotype (present designation), “ Cyphon \ parvum Sol. \ Chili ” [handwritten with brown ink, prob- ably by Solier]; “9 \ 45: [handwritten on a green, round label]. The specimen is relatively well preserved but ventral portion is slightly damaged, and only anterior legs are preserved.
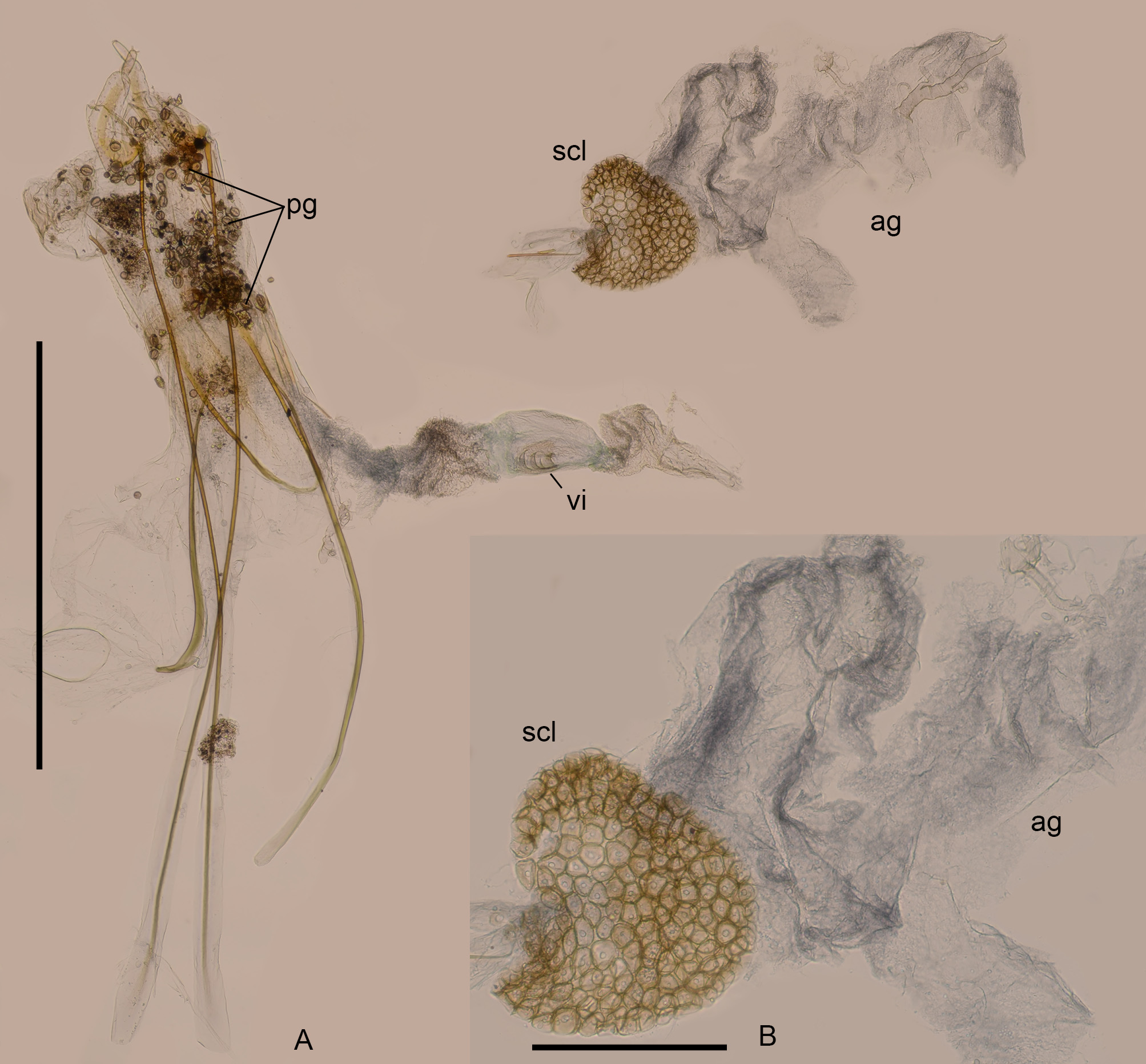
Description. Female, TL = 3.5 mm. Body uniformly light yellow. Punctures on elytra separated by ca. 0.5 di- ameter of a puncture. Anterolateral angles of pronotum slightly projecting anteriorly, posterolateral angles obtuse. Ovipositor with long apodemes and membranous coxites, coxites with styli; prehensor absent, only some invaginations (L 0.17 mm, W 0.13 mm) of membrane can be noticed in vagina ( Fig. 7A View FIGURE 7 ); sclerotized structure (diameter ca. 0.35 mm) present at base of accessory gland.
Remarks. The species is pollinophagous, as numerous pollen grains are preserved in intestines ( Fig. 7A View FIGURE 7 ). A similar sclerotization of basal portion of accessory gland was described in Ypsiloncyphon Klausnitzer ( Zwick 2016) and named dictyon. The original description includes no information on the number of specimens examined by Solier. A lectotype is designated in order to preserve the stability of nomenclature by selecting one specimen as the sole, name-bearing type of the taxon.
Blackwelder, R. E. (1944) Checklist of the coleopterous insects of Mexico, Central America, the West Indies, and South America. Bulletin of the United States National Museum, 185 (2), 266 - 268. https: // doi. org / 10.5479 / si. 03629236.185.2
Gemminger, M. & von Harold, E. (1869) Familia XLI. Dascillidae. In: Gemminger, M. & von Harold, E. (Eds.), Catalogus coleopterorum hucusque descriptorum synonymicus et systematicus. Tom. 6. Rhipidoceridae, Dascillidae, Malacodermidae, Cleridae, Lymexylonidae, Cupesidae, Ptinidae, Bostrychidae, Cioidae. Monachii, sumptu E. H. Gummi, Paris, pp. 1613 - 1625. https: // doi. org / 10.5962 / bhl. title. 9089
Moroni, J. C. (1985) Addenda y corrigenda al elenco sistematico, sinonimico y distribucion de coleopteros acuaticos chilenos. Revista chilena de entomologia, 12, 169 - 176.
Pic, M. (1914) Dascillidae, Helodidae, Eucinetidae. In: Junk, W. & Schenkling, S. (Eds.), Coleopterorum Catalogus, 10 (58), pp. 1 - 65.
Solier, A. J. J. (1849) Cyphonoideos. In: Gay, C. (Ed.), Historia fisica y politica de Chile segun documentos adquiridos en esta republica durante doce anos de residencia en ella y publicada bajo los auspicios del supremo gobierno. Zoologia. Tom. 4. Insectos. Orden III. Coleopteros. Chile, en el Museo de historia natural de Santiago, En casa del autor, Paris, pp. 454 - 461.
Zwick, P., Klausnitzer, B. & Ruta, R. (2013) Contacyphon Gozis, 1886 removed from synonymy (Coleoptera: Scirtidae) to accommodate species so far combined with the invalid name, Cyphon Paykull, 1799. Entomologische Blatter und Coleoptera, 109, 337 - 353.
Zwick, P. (2016) Australian Marsh Beetles (Coleoptera: Scirtidae). 9. The relations of Australasian Ypsiloncyphon species to their Asian congeners, additions, mainly to Petrocyphon and Prionocyphon, and a key to Australian genera of Scirtinae. Zootaxa, 4085 (2), 151 - 198. https: // doi. org / 10.11646 / zootaxa. 4085.2.1
FIGURE 2. Historical labels of Scirtidae specimens from the collection of A. Solier (A–I), and specimens collected by C. Gay (J–K). A) Contacyphon luteolineatus; B) Contacyphon maculicornis; C) Contacyphon parvus; D) Contacyphon testaceus; E) Contacyphon tristis; F) Elodes rousseli; G) Pseudomicrocara lunata; H) Pseudomicrocara obliquata; I) Pseudomicrocara tor- quata; J) an unidentified specimen; K) Contacyphon maculatus.
FIGURE 3. Lectotypes of species described by A. Solier, general view. A) Contacyphon luteolineatus (Solier, 1849); B) Con- tacyphon maculicornis (Solier, 1849); C) Contacyphon parvus (Solier, 1849); D) Contacyphon testaceus (Solier, 1849); E) Contacyphon tristis (Gemminger, 1869); F) Elodes rousseli Solier, 1849; G) Pseudomicrocara lunata (Solier, 1849); H) Pseudomicrocara obliquata (Solier, 1849); I) Pseudomicrocara torquata (Gemminger, 1869). Scale bars = 1.0 mm.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Contacyphon parvus ( Solier, 1849 )
| Ruta, Rafał 2020 |
Contacyphon parvus ( Solier, 1849 )
| Zwick, P. & Klausnitzer, B. & Ruta, R. 2013: 345 |
Cyphon parvum:
| Moroni, J. C. 1985: 174 |
| Blackwelder, R. E. 1944: 267 |
Cyphon parvus:
| Pic, M. 1914: 34 |
Helodes parvus
| Gemminger, M. & von Harold, E. 1869: 1619 |
Cyphon parvum
| Solier, A. J. J. 1849: 457 |