Sibiota Casey, 1906
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.155701 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6277556 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/5B50E916-FF8F-3931-4D2D-FE5FFB97FB2C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Sibiota Casey, 1906 |
| status |
|
Subgenus Sibiota Casey, 1906
Sibiota Casey, 1906: 350 (Type species: Sibiota impressula Casey, 1906 View in CoL , by original designation) (as a genus in tribe Bolitocharini Thomson, 1859 View in CoL ).
Sibiota: Fenyes, 1920: 249 (as synonym of Sipalia Mulsant & Rey, 1853 ).
Sibiota: Bernhauer & Scheerpeltz, 1926: 599 (as synonym of Sipalia ).
Ditroposipalia Scheerpeltz, 1951: 172 (Type species: Leptusa bidens Baudi, 1869 , by original designation) (as subgenus of Sipalia ), syn. nov.
Sibiota: Seevers, 1978: 128 (as valid genus in subtribe Geostibina Seevers, 1978).
Sibiota: Lohse & Smetana, 1988: 270 (as synonym of Geostiba View in CoL ).
Sibiota: Ashe in Newton, Thayer, Ashe & Chandler, 2000: 371 (as subgenus of Geostiba View in CoL ).
(other references for Palaearctic Ditroposipalia are omitted)
Diagnosis. Sibiota differs from other subgenera of Geostiba in having two longitudinal carinae in the middle of male abdominal tergum 7 in front of posterior margin.
Synonyms. Ditroposipalia is placed in synonymy with Sibiota because the type species of both have two longitudinal carinae on the male tergum 7.
Discussion. Lohse and Smetana (1988) did not assign any of their four species to subgenera. Pace assigned his three species to subgenera Ditroposipalia (synonymized here with Sibiota ) and Lioglutosipalia Scheerpeltz, 1951 . The latter is now considered a synonym of Sipalotricha Scheerpeltz, 1931 ( Assing 1999) , which lacks modifications on male tergum 7.
The males of both western Nearctic species of Geostiba have male abdominal tergum with two carinae and are placed in the subgenus Sibiota (= Ditroposipalia ). Eight of the twelve Appalachian species have male secondary characters corresponding to Sibiota and four species are consistent with Sipalotricha . However there are good reasons to believe that all sixteen native Nearctic species of Geostiba (that is, excluding G. circellaris introduced to Newfoundland) form a monophyletic group in relation to Palaearctic species of Sibiota (= Ditroposipalia ) or Sipalotricha .
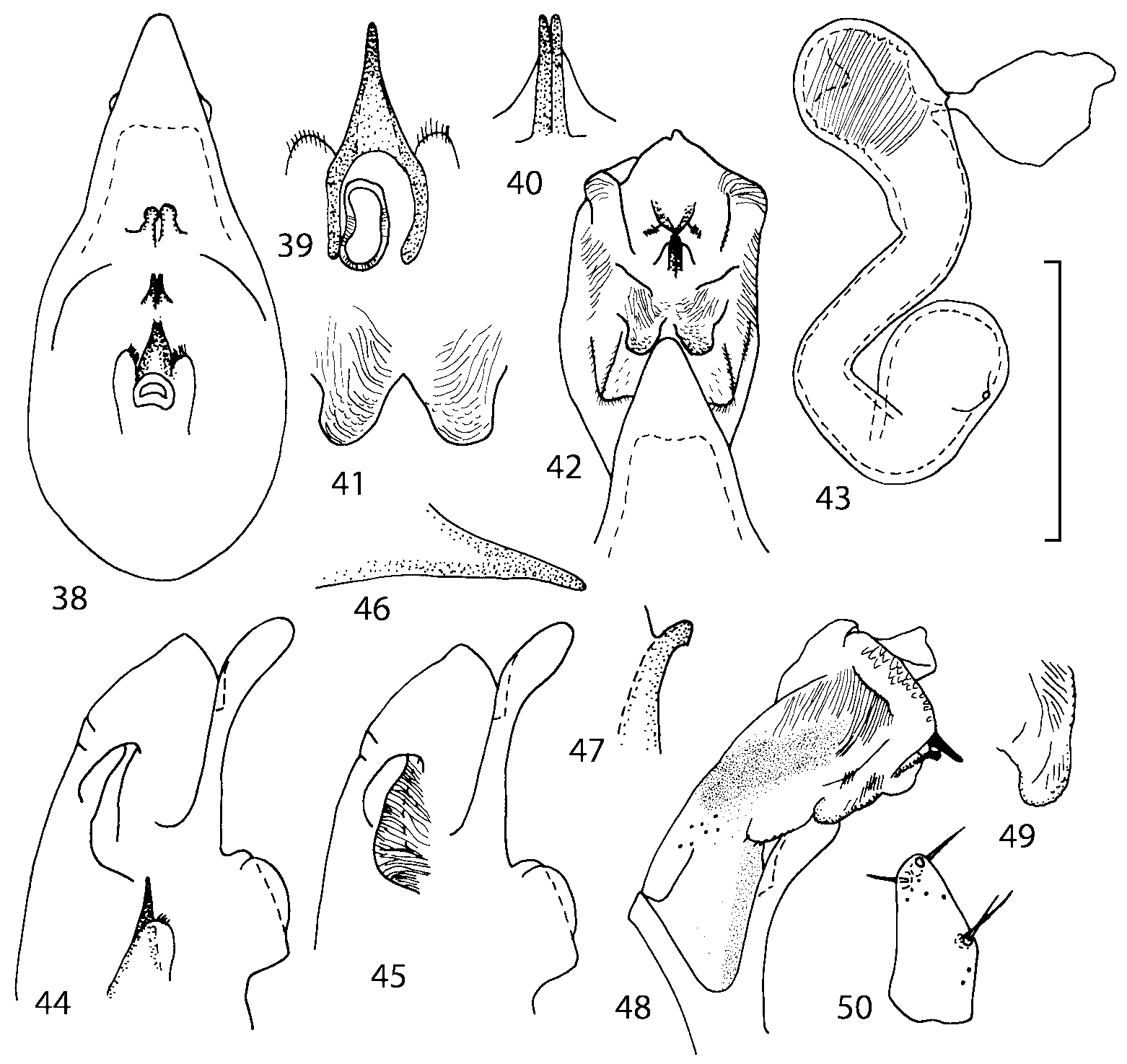
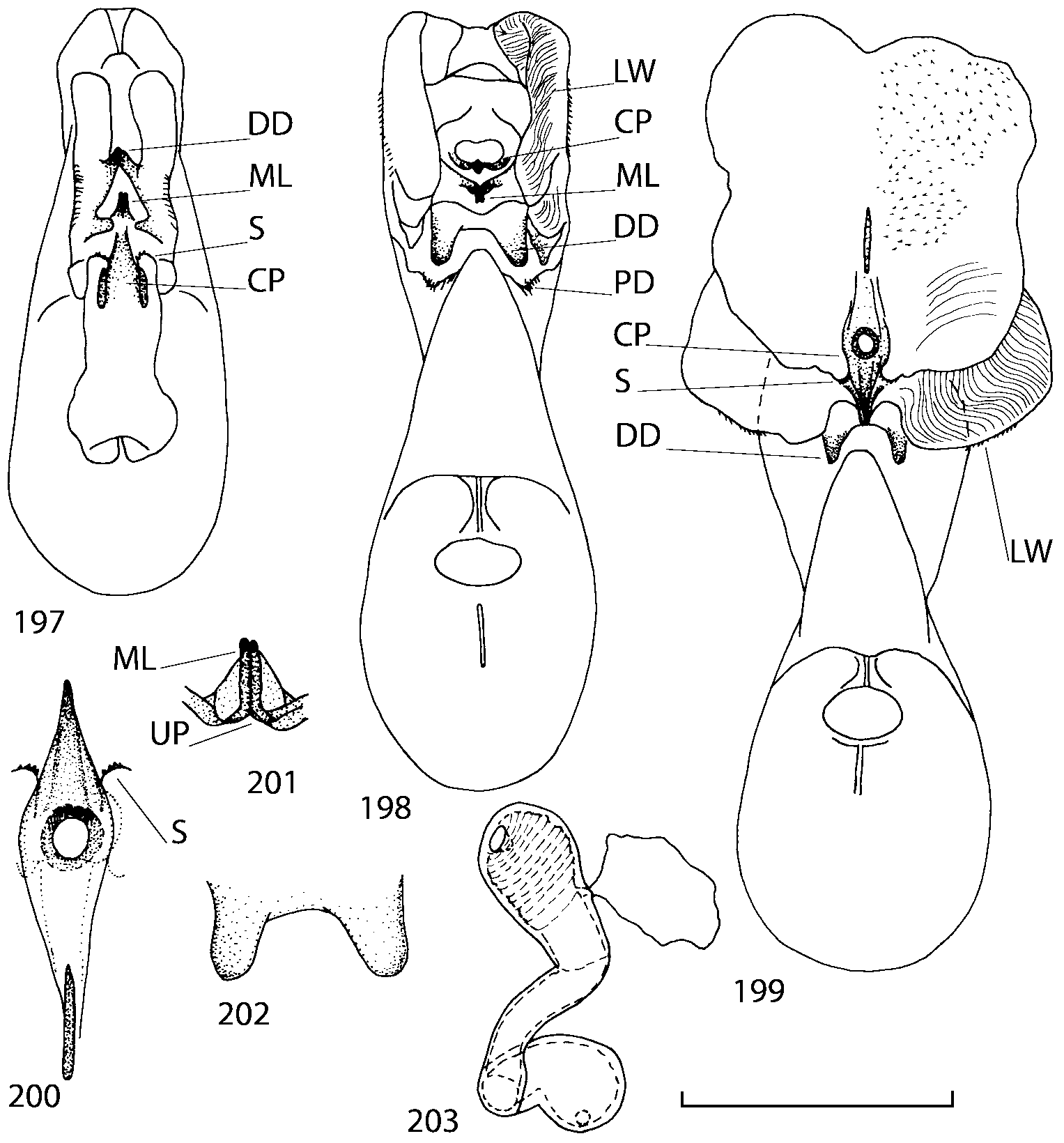
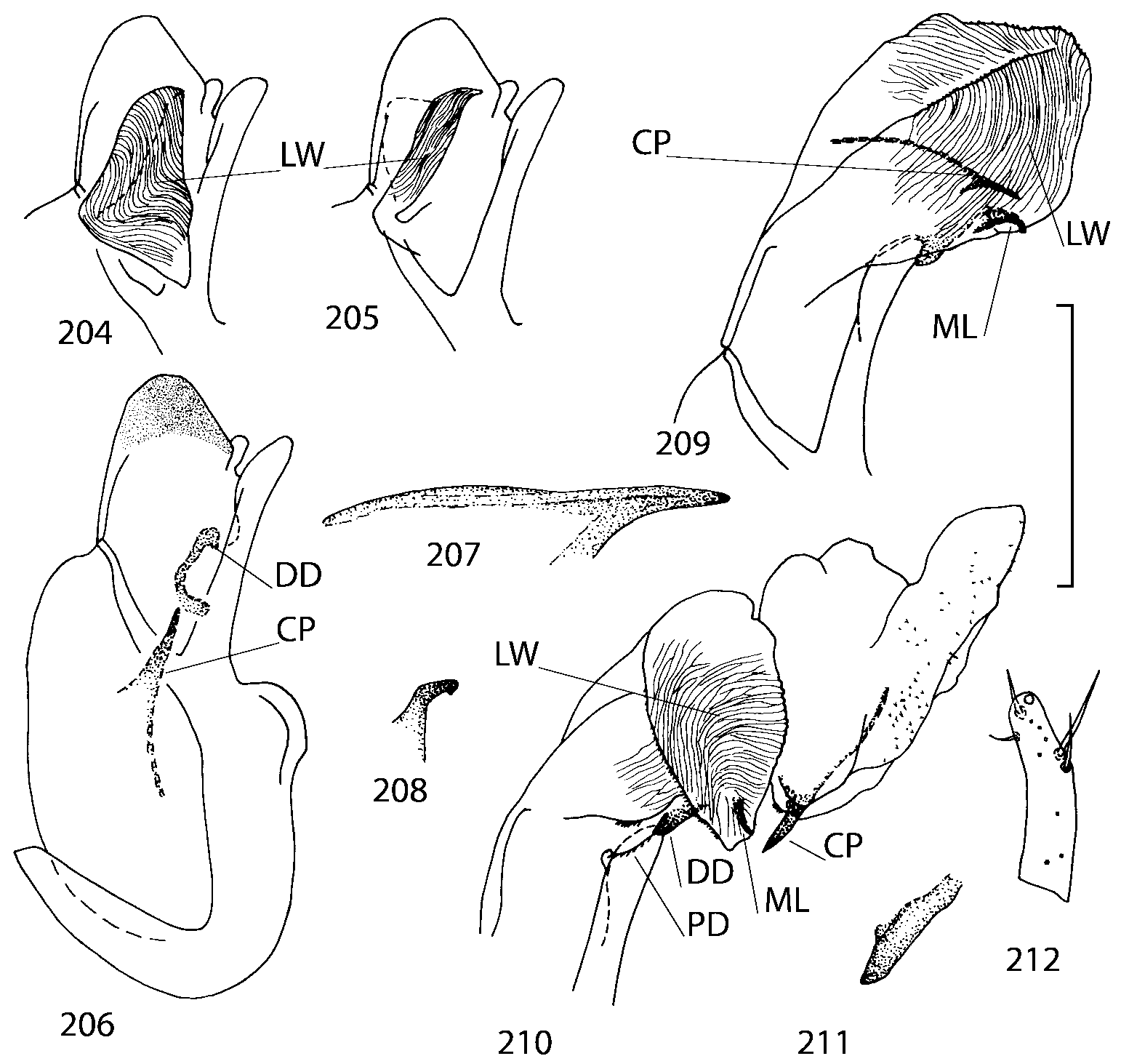
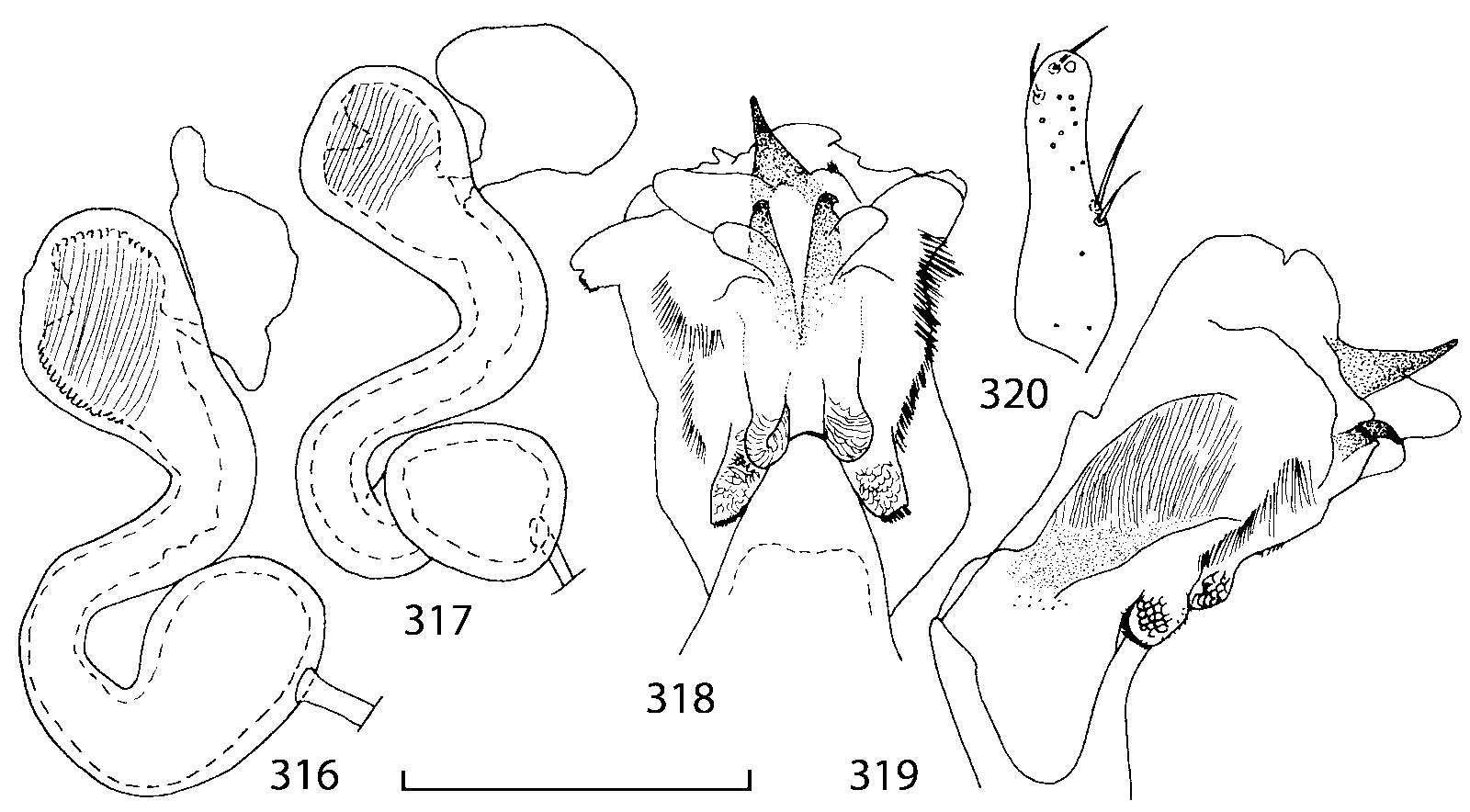
There are some characters shared by all native Nearctic species of Geostiba that may be autapomorphies for this group of species. These include: slightly raised elytral suture behind scutellum (except G. impressula ); the proximal seta on the external side of paramere apex is the longest; internal sac of the aedeagus has two pairs of diverticula ( Figs. 42, 48 View FIGURES 38 50 , 198 View FIGURES 197 203 , 210 View FIGURES 204 212 , 318 View FIGURES 316 320 ), medial lamellae are short, narrow and bent ventrally ( Figs. 40, 47 View FIGURES 38 50 , 201 View FIGURES 197 203 , 208 View FIGURES 204 212 ). This form of the internal sac is very different from the forms found in Palaearctic G. (s. str.) circellaris ( Figs. 2122 View FIGURES 21 25 ), G. (Sipalotricha) infirma ( Figs. 2425 View FIGURES 21 25 ), G. (Sibiota) padana ( Figs. 2627 View FIGURES 26 28 ) and G. (Sibiota) oertzeni ( Fig. 28 View FIGURES 26 28 ). The hypothesis of monophyly of the Nearctic group of species can be tested only if representatives from other lineages are included in the analysis, which is outside the scope of the present paper. However, if this hypothesis is accepted and both Sibiota and Sipalotricha are monophyletic groups, then all native Nearctic species must be placed in the same subgenus of Geostiba .
Among the twelve Appalachian species, G. appalachigena is the least adapted to cryptic habitats such as soil and leaf litter and has the following plesiomorphies: well developed wings, long elytra (longer than pronotum), large eyes (temple length / eye length ratio 2.32.7) and large body (pronotal width 0.400.47 mm). Geostiba appalachigena has well developed carinae on the male tergum 7 and could be considered a typical representative of the subgenus Sibiota . The four species of Geostiba without carinae can be considered as more adapted to cryptic habitats. In comparison to G. appalachigena they have the following apomorphies: reduced wings, short elytra (shorter than pronotum), small eyes (temple length / eye length ratio 3.86.0) and smaller body (pronotal width 0.340.44 mm). One can hypothesize that the four species without carinae on male tergum 7 originated from an ancestor or ancestors with carinae. Two arguments confirm that this scenario is possible. Geostiba balsamensis , one of the smaller species (pronotal width 0.36 0.39), has weak enough carinae on tergum 7 that Pace (1997) overlooked them and placed this species in Lioglutosipalia . The state of the carinae in G. balsamensis can be considered intermediate between the well developed and the absent states. In many species of Geostiba the small males are known to lack secondary sexual characters present in the large males ( Assing 2000). The same trend may take place when species evolve to a smaller size.
Taking into account the above arguments, I place all sixteen native Nearctic species of Geostiba in the subgenus Sibiota . This subgenus is also represented in the Palaearctic region from Europe to the Caucasus, Central Asia, Siberia and the Far East.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Aleocharinae |
Sibiota Casey, 1906
| Gusarov, Vladimir I. 2002 |
Sibiota:
| Newton 2000: 371 |
Sibiota:
| Lohse 1988: 270 |
Sibiota:
| Seevers 1978: 128 |
Ditroposipalia
| Scheerpeltz 1951: 172 |
Sibiota:
| Bernhauer 1926: 599 |
Sibiota:
| Fenyes 1920: 249 |
Sibiota
| Casey 1906: 350 |