Paratranes monopticus ( Pascoe, 1870 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2021.767.1493 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:7BE2FA83-2717-4BE9-A540-F98BFAF5F7E1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5527164 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/311F2D1B-FFCA-FF91-0B7D-53EAFD539EE7 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Paratranes monopticus ( Pascoe, 1870 ) |
| status |
|
Paratranes monopticus ( Pascoe, 1870) View in CoL
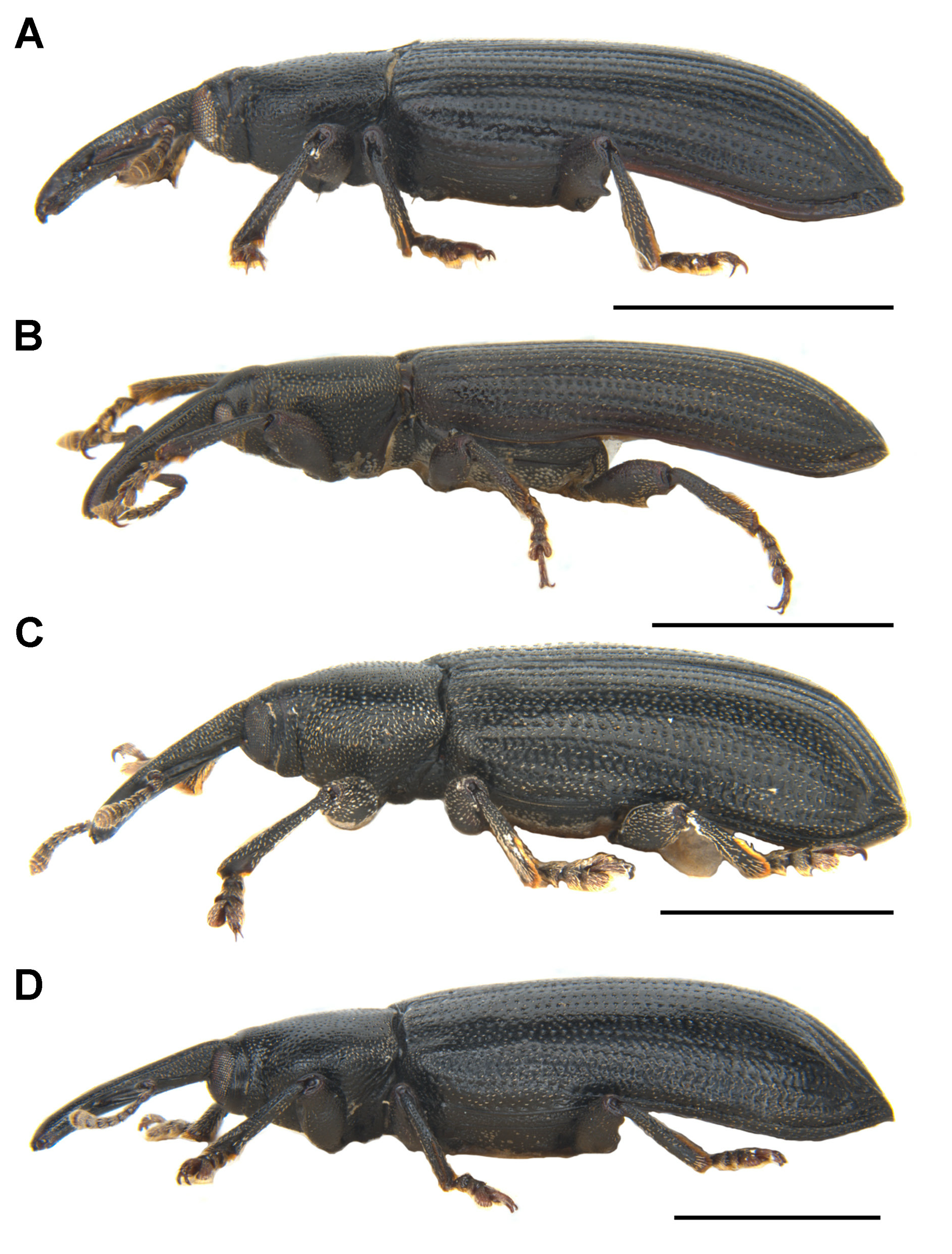
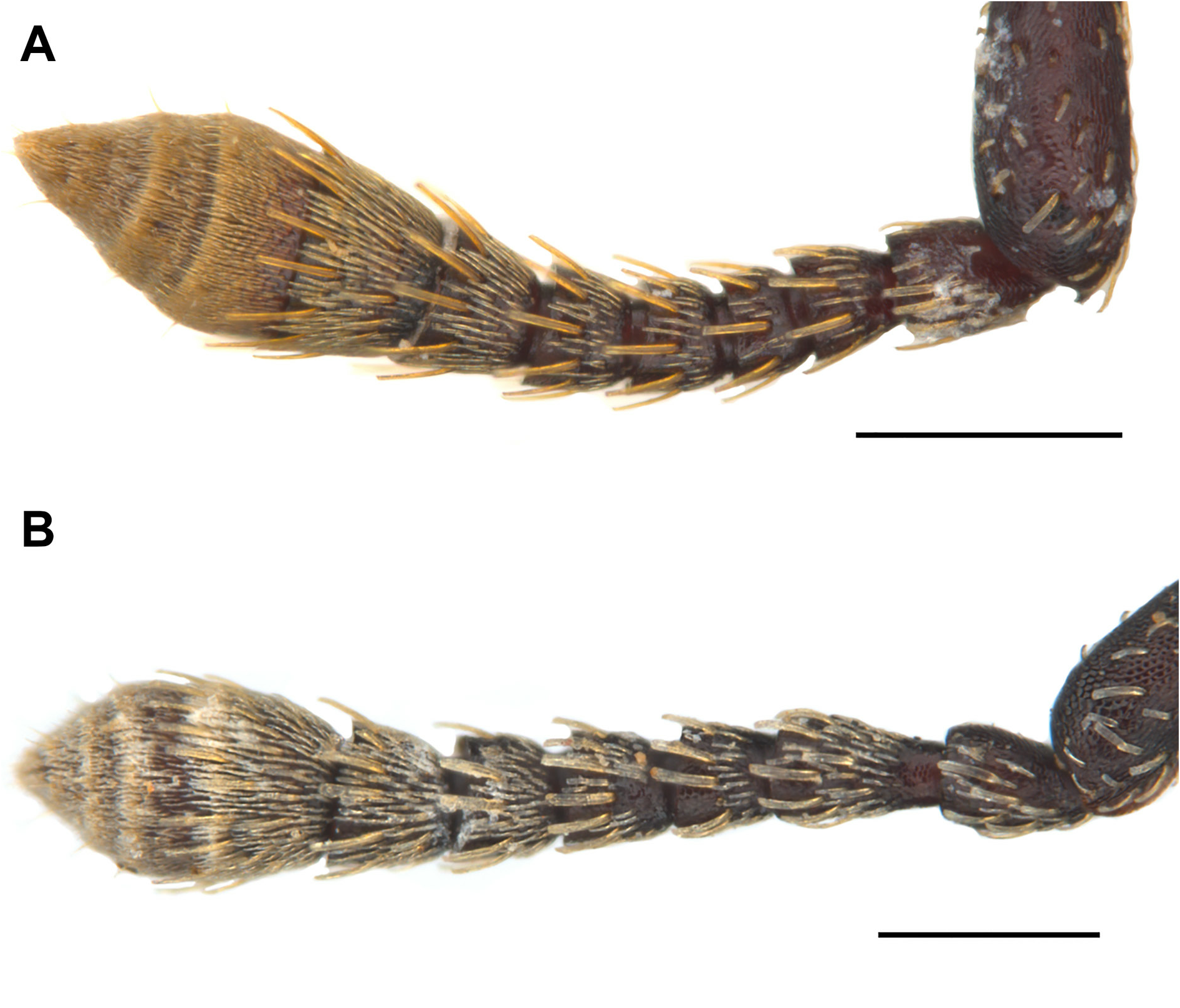
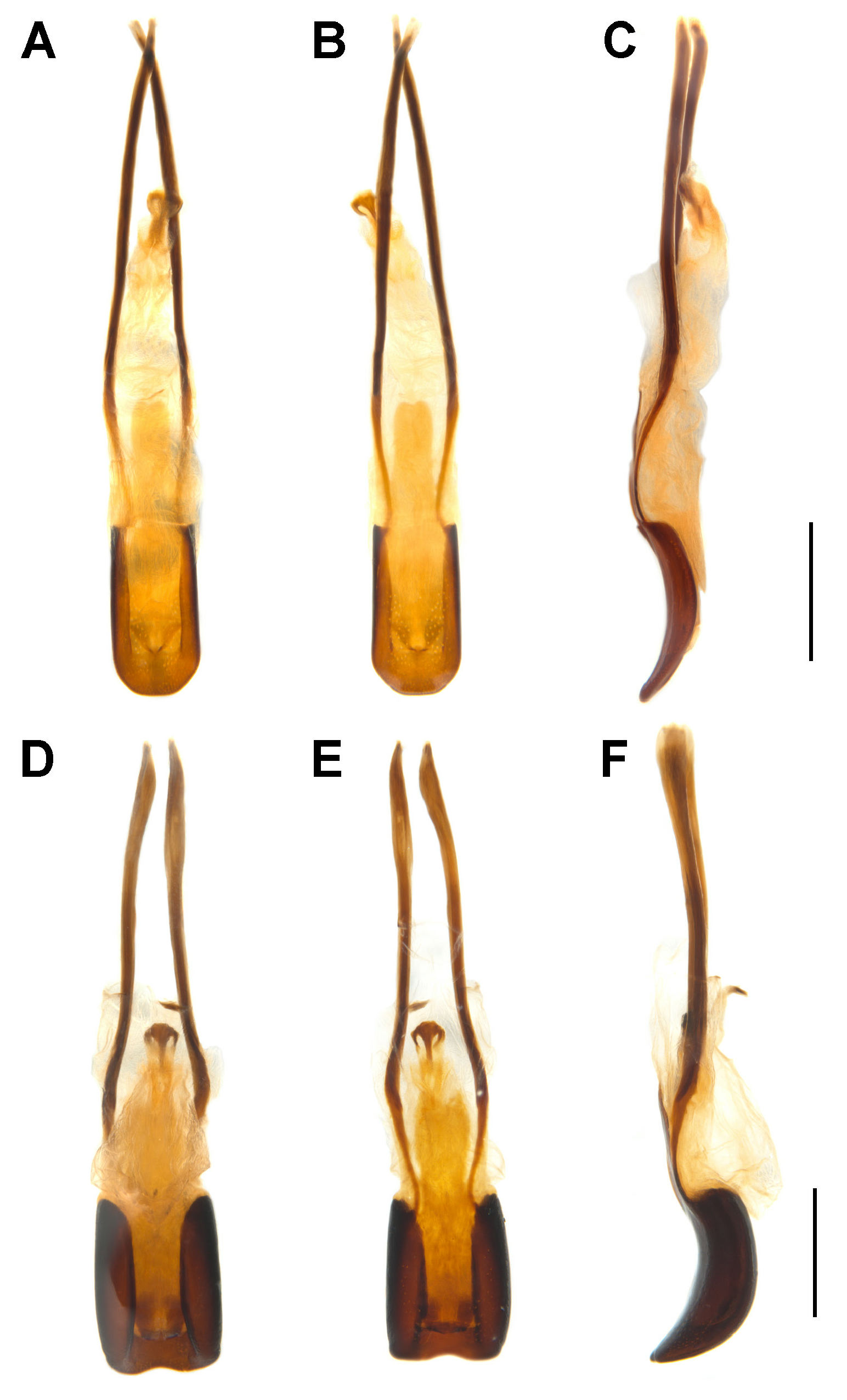
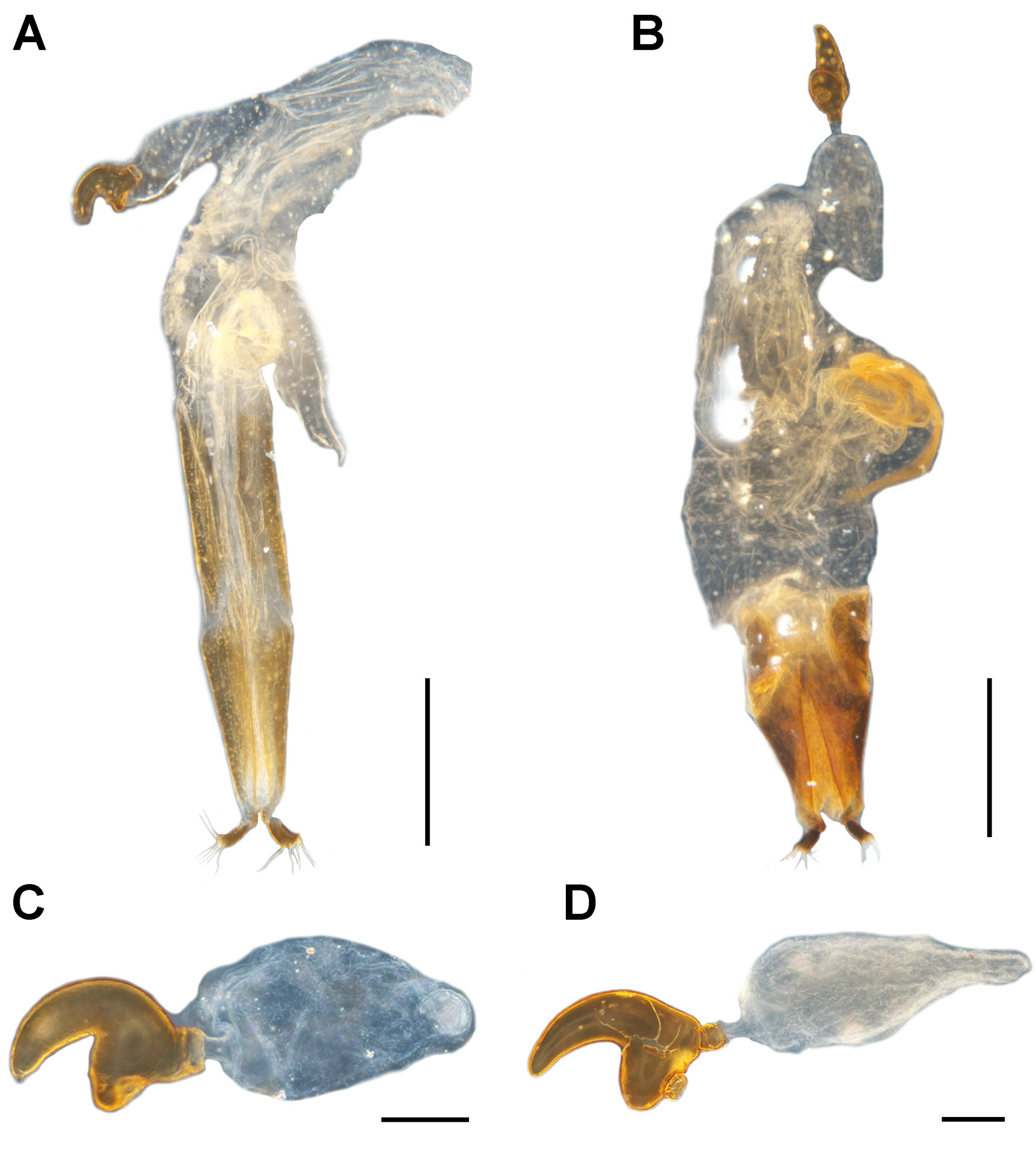
Figs 3A–B View Fig , 4A–B View Fig , 5A View Fig , 6A, C, E, G View Fig , 7A–B, E, G, I View Fig , 8A–C View Fig , 9A–C View Fig , 10A, C View Fig , 11–12 View Fig View Fig
Tranes monopticus Pascoe, 1870: 199 View in CoL . Type locality: Queensland, Australia.
Tranes xanthorrhoeae Lea, 1898: 592 View in CoL . Type locality: Darling Range, Western Australia, Australia.
Tranes monopticus View in CoL – Lea 1898: 594; 1929: 539. — Schenkling & Marshall 1936: 1. — Oberprieler 1995: 305.
Tranes xanthorrhoeae View in CoL – Froggatt 1907: 187. — Schenkling & Marshall 1936: 1. — Mulder 1964: 12. — Oberprieler 1995: 306. — Pullen et al. 2014: 289 (syn.).
Notiosomus (Tranes) xanthorrhoeae View in CoL – Hawkeswood 1985: 162, 164–165 (habits, distribution).
Paratranes monopticus View in CoL – Zimmerman1994: 696.— Alonso-Zarazaga &Lyal 1999: 210.— Oberprieler & Caldara 2012: 57; Pullen et al. 2014: 289.
Diagnosis
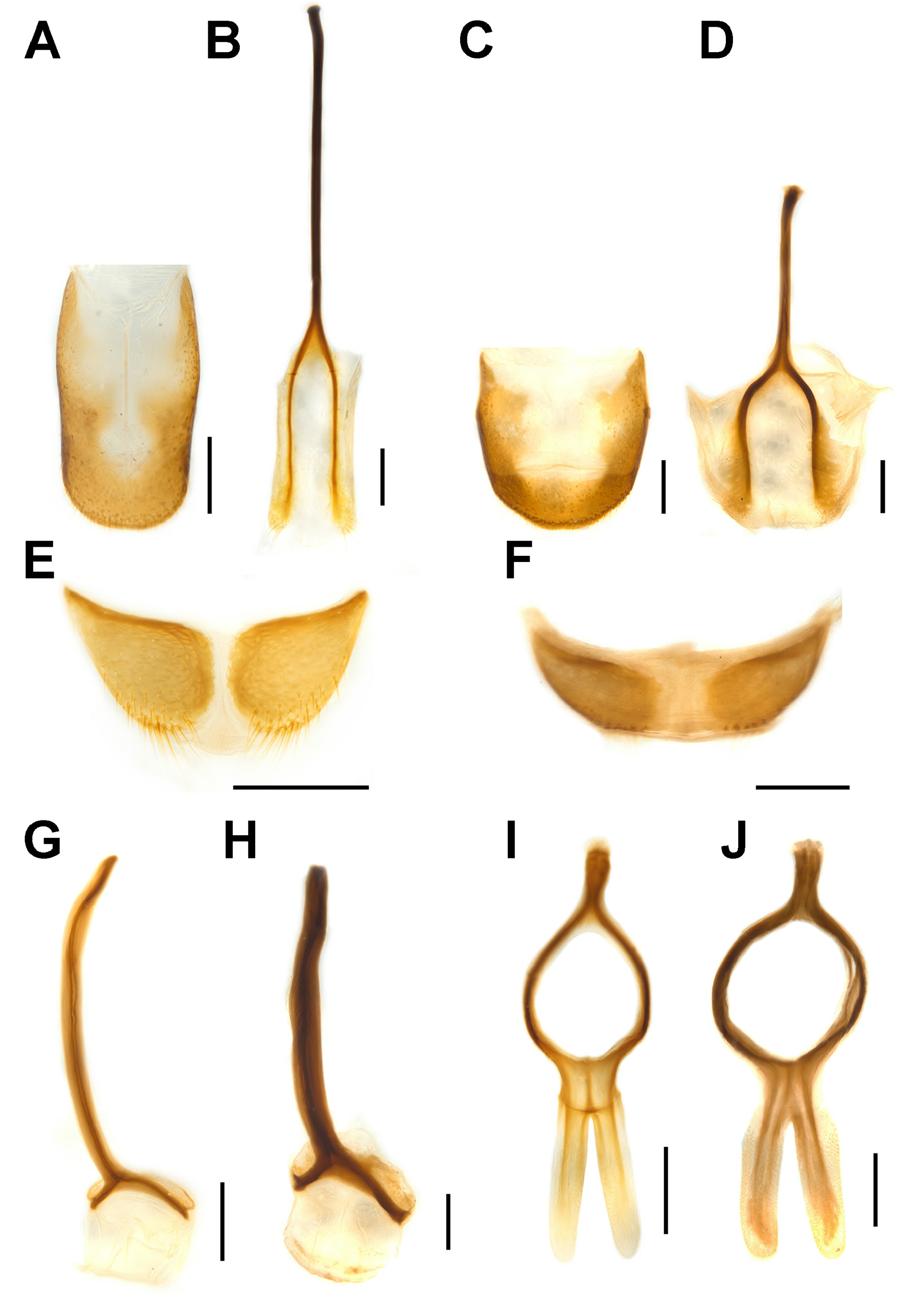
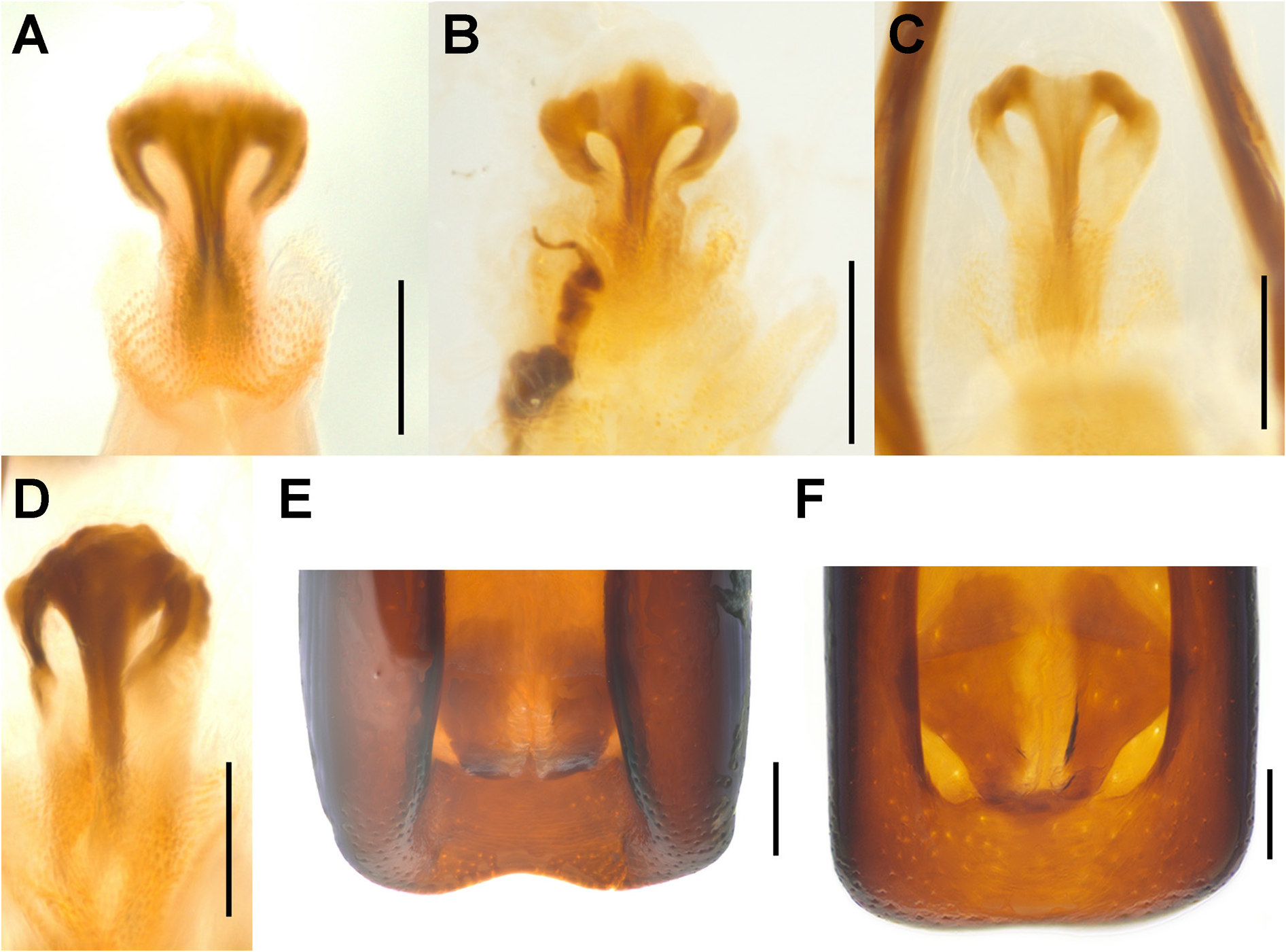
This species can easily be distinguished from P. zimmermani sp. nov. by the following characters (states of P. zimmermani sp. nov. in parentheses): body generally smaller, length 5.2–9.3 mm, width 0.40–0.42× length (body larger, length 7.3–10.1 mm, width 0.46–0.48 × length); rostrum shorter, ca 1.1–1.2 ×as long as pronotum ( Fig. 4A–B View Fig ) (ca 1.3–1.4× as long as pronotum; Fig. 4C–D View Fig ); funicles with segment 2 shorter than 1 ( Fig. 5A View Fig ) (longer than or subqual in length to 1; Fig. 5B View Fig ); pronotum narrower, sides weakly arcuate ( Fig. 3A–B View Fig ) (wider, sides distinctly arcuate; Fig. 3C–D View Fig ); elytra narrower and more slender, jointly ca 0.5–0.6 × as broad as long ( Fig. 3A–B View Fig ) (broader, jointly ca 0.6–0.7 × as broad as long; Fig. 3C–D View Fig ); glabrous region on prosternum oval, longitudinal, distinctly depressed ( Fig. 6A View Fig ) (wider, rounded, not so glabrous, with few sparse punctures, slightly depressed; Fig. 6B View Fig ); femora ventrally with subapical tooth ( Fig. 6C View Fig ) (edentate; Fig. 6D View Fig ); protibial uncus distinct ( Fig. 6E View Fig ) (minute; Fig. 6F View Fig ); tarsal claws thinner ( Fig. 6G View Fig ) (thicker; Fig. 6H View Fig ); tergite VIII of female elongate ( Fig. 7A View Fig ), ca 1.6–1.8 × as long as wide (shorter, ca 0.9–1.1 × as long as wide; Fig. 7C View Fig ); sternite VIII of female more elongate ( Fig. 7B View Fig ) (shorter and thicker; Fig. 7D View Fig ); tegmen ring narrower ( Fig. 7I View Fig ) (broader; Fig. 7J View Fig ); penis slender, ca 1.9–2.0 × as long as wide ( Fig. 8A–C View Fig ) (thicker, ca 1.4–1.6 × as long as wide; Fig. 8D– F View Fig ); gonocoxites elongate, slender, ca 3.7–5.7 × as long as wide ( Fig. 10A View Fig ) (shorter and thicker, ca 1.5–2.0 × as long as wide; Fig. 10B View Fig ).
Material examined
Holotype AUSTRALIA • “ Holotype // Queensland // Tranes / monopticus / Type Pasc // Pascoe Coll. / 93–60. // Tranes / monopticus Pasc ”; NHMUK.
Lectotype of Tranes xanthorrhoeae Lea, 1898 (here designated) ( Fig. 11 B View Fig ) AUSTRALIA • ♂; “ Darling Rgs / W.A., Lea // Tranes / xanthorrhoeae / Lea ♂ // Co-type // LECTOTYPE / Tranes xanthorrhoeae / Lea, 1898 / Hsiao & Oberprieler des. 2021”; SAMA .
Paralectotype of Tranes xanthorrhoeae Lea, 1898 AUSTRALIA • 1 ♂; “ xanthorrhoeae / Lea Galston // PARALECTOTYPE / Tranes xanthorrhoeae / Lea, 1898 / Hsiao & Oberprieler des. 2021”; SAMA .
Other material
AUSTRALIA – Western Australia • 1 ♂; Pinjarra; “13574 / Tranes / xanthorrhoeae / W. Australia / TYPE [in Lea’s hand in red capital letters along right side of label]”, “ Tranes monopticus c.w.t. 1988, E.C. Zimmerman ”; SAMA • 1 ♀; WA; Ferguson Collection; ANIC • 1 ex.; Geraldton ; J. Clark leg.; NHMUK • 1 ♀; Bowring; ANIC • 1 ex.; same collection data as for preceding; NHMUK • 1 ♀; Denmark; ANIC • 1 ♂, 2 ♀♀; Mt Barker ; ANIC • 1 ex.; South Perth ; 5 Dec. 1903; H.M. Giles leg.; NHMUK • 2 exx.; North Sydney ; Oct. 1908; G.E. Bryant leg.; NHMUK • 1 ex.; same collection data as for preceding; 29 Nov. 1908; NHMUK • 1 ex.; same collection data as for preceding; 7 Dec. 1908; NHMUK • 2 exx.; Mt Barker ; 1919; A.H. Westley leg.; NHMUK • 2 ♀♀; Eradu ; Sep. 1926; H.J. Carter leg.; ANIC • 1 ♂; Deepdene, Karridale ; 17 Jan. 1967; M.S. Upton leg.; ANIC • 1 ♀; Applecross, Perth ; 7 May 1967; F.H. Uther Baker leg.; ANIC • 1 ♀; Mt Toolbrunup, Stirling Range National Park ; 25 Sep. 1975; F.H. Uther Baker leg.; ANIC • 1 ex.; same collection data as for preceding; E. Gowing-Scopes leg.; “ Tranes monopticus c.w.t. 1991”; NHMUK • 1 ♂; W of Bremer Bay ; 34°24.257′ S, 119°15.085′ E; 23 Oct. 2003; S. Neser leg.; ANIC GoogleMaps • 2 ♂♂, 3 ♀♀; 17 km E of Harvey ; 5 Jan. 1986; C. Reid and P.J. Gullan leg.; ANIC • 2 exx.; Stirling Range , 35 km NE of Kendenup; 34.383 S, 117.994 E; 287 m a.s.l.; 7 Sep. 2009; G.B. Monteith and F.Turco leg.; ANIC GoogleMaps . – South Australia • 1 ♀; Lucindale; ANIC • 1 ♂, 2 ♀♀; Lucindale ; A.M. Lea leg.; SAMA • 1 ex.; Melrose; Oct. ; A.M. Lea leg.; SAMA . – New South Wales • 2 ♂ ♂, 4 ♀♀, 1 ex.; NSW; ANIC • 2 exx.; NSW; Fry Collection; NHMUK • 2 exx.; NSW; G.A.K. Marshall Collection; NHMUK • 1 ex.; NSW; Sharp Collection; NHMUK • 2 ♂♂, 1 ♀, 1 ex.; Sydney; ANIC • 1 ex.; Sydney, Nat. Park ; H.J. Carter leg.; NHMUK • 1 ♀; Galston ; G.C. Champion Collection; NHMUK • 1 ex.; Gosford ; Dec. 1931; H.C. Davis leg.; ANIC • 1 ♀; Nr. Gosford ; 20 Dec. 1931; ANIC • 1 ex.; Palm Beach ; 24 Dec. 1933; ex collection A. Walford-Huggins, E. Gowing-Scopes Collection; NHMUK • 1 ♀; Homebush ; 26 Apr. 1941; ANIC • 1 ex.; Nat. Park, Engadine ; 8 Dec. 1961; P.L. Cook leg.; NHMUK ( BMNH ( E) 2016-227) • 1 ♂; 6 km N of Lennox Hd. ; 24 Nov. 1986; C. Reid and P.J. Gullan leg.; ANIC • 1 ♂, 1 ♀; Coonabarabran; ANIC • 1 ex.; Frenchs Forest [Sydney]; Jul. [19]30; ANIC • 1 ♀; Rivertree ; E. Sutton leg.; QM . – Queensland • 1 ex.; NQ; W.W. Froggatt Collection; ANIC • 1 ♂, 1 ♀; Queensland ; H. Hacker leg.; “ Tranes monopticus c.w.t. 1988, E.C. Zimmerman ”; ANIC • 1 ♂; Cooktown ; H. Hacker leg.; ANIC • 1 ex.; Coolangatta ; 8 Sep. 1919; F. Muir; ANIC • 1 ♀, 1 ex.; Yeppoon ; 24 Oct. H.J. C[arter] leg.; ANIC • 1 ♂; Bayfield ; 1924; ANIC • 1 ♂; South Keppel Island ; C. Vallis leg.; ANIC • 1 ♂; Mt Tozer Area, Iron Range ; 29 Apr.–1 May 1973; G.B. Monteith leg.; ANIC • 1 ♂, 1 ex.; Brisbane , Griffith Uni.; 1978; ANIC • 1 ♂, 1 ex.; 7 km NE of Tolga ; Mar. 1987; Storey and De Faveri leg.; ANIC • 1 ♀, 1 ex.; Isabella Falls ; 15.18° S, 145.00° E; 18 Jan. 1994; P. Zborowski and E.D. Edwards leg.; ANIC GoogleMaps • 2 ♂♂, 11 exx.; 14 km W by N of Hope Vale Mission ; 15.16° S, 144.59° E; 7–10 May 1981; A. Calder leg.; ANIC GoogleMaps • 7 ♂♂, 12 ♀♀, 17 exx.; 7 km N of Hope Vale Mission ; 15.14° S, 145.07° E; 4 Oct. 1980; T. Weir leg.; ANIC GoogleMaps • 9 ♂♂, 8 ♀♀; 14 km W by N of Hope Vale Mission ; 15.16° S, 144.59° E; 8–10 Oct. 1980; T.vWeir leg.; ANIC GoogleMaps • 2 ♂♂, 1 ♀; 5 km W by N of Rounded Hill ; 15.17° S, 145.10° E; 7 Oct. 1980; T. Weir leg.; ANIC GoogleMaps • 1 ex.; Heathlands ; 11.45° S, 142.35° E; 24–28 Feb. 1993; P. Zborowski leg.; ANIC GoogleMaps • 1 ♂; 91 km S of Coen ; 31 Nov. 1978; R.I. Storey leg.; QDPI • 1 ex.; Brisbane, Mt Alder ; 13 May 1912; QDPI • 3 exx.; same collection data as for preceding; QM • 1 ex.; Mt Tambourine ; QM • 5 exx.; Fletcher ; E. Sutton leg.; QM • 1 ♂; Beenleigh; 24 Apr. [19]28; [prob. E. Sutton leg.]; QM • 2 exx.; Moreton Is. ; E.vAllen; QM • 1 ex.; Gordonvale ; 1 Feb. 1923; QM • 1 ♀; Stradbroke Is. ; Jan. 1926; E. Kehon leg.; QM • 1 ex.; Mt Tambourine ; 18 Dec. 1929; QM • 2 exx.; same locality as for preceding; 14 Dec. 1930; E. Sutton; QM • 1 ex.; Hambledon ; 20 Jan. 1949; E. Sutton and A. Johnson leg.; QM • 1 ♀; Mt Cleveland Summit , 25 km E Townsville; 13 Jan. 1991; A. Graham leg.; QM • 1 ♀; Mcllwraith Nth end; 16°49′ S, 144°49′ E; 9 Jul. 1994; Potter, Ingram and Eddie leg.; QM GoogleMaps • 1 ex.; Mcllwraith Range , 8 km NE of Coen; 13°53.30′ S, 143°15.21′ E, 540 m a.s.l.; 29 Dec. 1994; G. and A. Daniels leg.; QM GoogleMaps • 1 ex.; Mt Nebo Road , powerline; 27°26′ S, 152°53′ E; 250 m a.s.l.; 23–26 Oct. 2004; G.B. Monteith leg.; QM GoogleMaps .
Redescription
SHAPE AND SIZE. Body elongate oval ( Fig. 3A–B View Fig ), length 5.2–9.3 mm in both sexes, width 0.40–0.42 × length; very flat in lateral view ( Fig. 4A–B View Fig ).
COLOUR AND VESTITURE. Body and legs shiny black, semilustrous; body, femora and tibiae sparsely covered with very short pale setae, setae on tibiae slightly longer than on body and femora; funicles, clubs and tarsi densely covered with yellowish setae, longer than short pale setae on body, femora and tibiae.
ROSTRUM. Moderately long, ca 1.1–1.2× as long as pronotum in both sexes, robust, faintly evenly curved ventrad, dorsoventrally flattened, slightly broadened apically in dorsal view, coarsely punctate dorsally, punctures very fine in distal half, proximal half with paired dorsomedian and dorsolateral carinae, the latter lower than the former.
EYES. Subcircular in outline, slightly convex but not protruding ( Fig. 4A–B View Fig ).
ANTENNAE. Inserted at about distal third of rostrum in both sexes ( Fig. 4A–B View Fig ); scapes not reaching eye; funicles with segment 1 ca 1.5–1.6×, 1.7–3.2 ×, 2.0–3.2 ×, 2.0–2.7×, 1.7–2.0 × and 1.2–1.5 × as long as segments 2 to 7, respectively; clubs stout, fused with segment 7 of funicle, ca 1.7–1.9 × as long as wide, densely and finely pubescent ( Fig. 5A View Fig ).
PRONOTUM. Roundly trapezoidal, apex ca 0.6 × as broad as base; anterior margin slightly emarginate medially, posterior margin protruding medially, forming obtuse median lobe, sides weakly arcuate; disc nearly flat; surface densely and coarsely punctate, with elongate longitudinal impunctate region medially, punctures separate but confluent and vague laterally; prosternum with oval longitudinal impunctate depressed region medially ( Fig. 6A View Fig ).
SCUTELLAR SHIELD. Roundly pentagonal to subcircular.
ELYTRA. Ca 3.0× as long as pronotum, jointly ca 0.5–0.6× as broad as long, distinctly broader than base of pronotum; humeri broadly rounded, slightly protruding; surface nearly flat, shallowly and coarsely punctate in rows, forming shallowly depressed striae.
LEGS. Femora distinctly sulcate beneath, ventrally with subapical tooth ( Fig. 6C View Fig ); tibiae with arcuate premucro smaller than uncus ( Fig. 6E View Fig ); tarsi with claws free, divergent ( Fig. 6G View Fig ).
TERMINALIA. Tergite VIII of female subtrapezoidal ( Fig. 7A View Fig ), ca 1.6–1.8 × as long as wide; sternite VIII of male broadly crescentic, sclerotised, apical margin rounded to truncate, basal margin strongly sclerotised ( Fig. 7E View Fig ); spiculum gastrale widely concave apically, base weakly sclerotised ( Fig. 7G View Fig ). Tegmen with complete, oval ring, manubrium slender, distinctly shorter than parameroid lobes ( Fig. 7I View Fig ); penis elongate (ca 1.9–2.0 × as long as wide), sides straight, parallel or merely slightly diverging apicad, dorsum flat, laterally distinctly sclerotised, medially broadly grooved, apical margin subtruncate ( Fig. 8A–C View Fig ); endophallus with apical sclerite varying from slightly sinuate, emarginate to protuberant ( Fig. 9A–C View Fig ). Gonocoxites narrow, elongate, apically bluntly rounded ( Fig. 10A View Fig ), ca 3.7–5.7 × as long as wide, proximal gonocoxite ca 1.0–1.4 × as long as distal gonocoxite; gonostyli cylindrical; bursa copulatrix without bands of spicules; spermatheca thick, right-angled, gland thick, swollen, narrowing apicad ( Fig. 10C View Fig ).
Distribution
This species is disjunctly distributed in coastal regions from northern Queensland to central New South Wales (Sydney) and in southeastern South Australia and southwestern Western Australia ( Fig. 12 View Fig ). Based on our survey of museum collections, the Queensland population of Paratranes monopticus is the largest and eastern Australia appears to be the main distribution range of this species.
Natural history
Paratranes monopticus has been reported occurring at the base of flower stalks and leaves and amongst young leaves of Xanthorrhoea ( Froggatt 1896, 1907; Mulder 1964; Hawkeswood 1985). Mulder (1964) indicated that the species can attack the green leaves of grasstrees at the base, and the presence of a brownish, mucous secretion at the leaf bases may be linked with the occurrence of this species, although the larvae have apparently not yet been found. According to label data, specimens can be attracted by mercury-vapour lamps, but this does not necessarily indicate a nocturnal behaviour and may just relate to specimens disturbed from grasstrees growing near the lights, as happens with Tranes weevils and cycads. Based on records by Hawkeswood (1985) and label data, P monopticus is associated with at least three species of grasstrees ( X. australis R.Br. , X. johnsonii A.T.Lee and X. preissii Endl. ), but it probably occurs on others as well and is likely not host-specific.
Remarks
The taxonomy and nomenclature of P. monopticus is complicated, because the type series of the synonymic name xanthorrhoeae comprises two different species and its author ( Lea 1898) did not validly (in the description) designate a primary type, so that all specimens of the type series are syntypes. Lea also did not specify the number of specimens on which he based the description of xanthorrhoeae , but he cited the specimens as having been collected at seven localities, as “ Hab.— Darling Ranges, Mt. Barker, Bridgetown, Swan River, W.A.; Galston, Gosford, Sydney, N.S.W.”. There are seven specimens from these locations in Lea’s collection (in SAMA) and the ANIC (see Material examined), but there are two from Sydney and none from Bridgetown, and only the three specimens from WA (Darling Ranges, Mt Barker and Swan River) are labelled as ‘Co-types’ by Lea. A further specimen in his collection is labelled “xanthorrheae [sic] / Lea TYPE / Pinjarrah” and also carries a large label with Lea’s handwriting “ Tranes / xanthorrhoeae / W Australia ” and “TYPE” in red lettering along its right side, as is typical of specimens that Lea regarded as the primary types of his species names. However, as Pinjarra is not mentioned as a locality in the description of Tranes xanthorrhoeae , it appears that Lea may not have had this specimen when he described the species and it cannot therefore be regarded as belonging to the type series and be treated or designated as the name-bearing type of Tranes xanthorrhoeae .
In his description of the species, Lea (1898) noted that some of his specimens were larger and wider (especially the elytra), had a longer and thinner rostrum, the glabrous region on the prosternum wider and less noticeable and, most notable, edentate femora, and he regarded these specimens as representing the female of his new species. Zimmerman later recognised that these so-called females actually represent a different species, and he noted this on a copy of Lea’s description (kept among his notes on the Tranes group in the ANIC), and later he even regarded these specimens as representing a new genus “allied to Paratranes ” ( Zimmerman 1994). On his copies of the descriptions of Tranes monopticus and T. xanthorrhoeae he further wrote that he had borrowed the type specimen of monopticus from Pascoe’s collection in the Natural History Museum in London in 1988 and, comparing it with the “male” types of Lea’s xanthorrhoeae (in particular the specimen from Pinjarra, which he accepted as the “ holotype ”), he concluded that the types of monopticus and xanthorrhoeae represent the same species. According to his notes, the synonymy of these two names had in fact earlier been suggested to him by John Balfour- Brown (of the Natural History Museum, London) — although a specimen so labelled by Balfour-Brown, from the Stirling Range in WA, is in fact P. zimmermani sp. nov. (see there). Zimmerman did not, however, effect this synonymy in his description of Paratranes ( Zimmerman 1994) , and it was only published much later by Pullen et al. (2014) (although it was actually not possible to synonymise the names without designating a lectotype for xanthorrhoeae and fixing the name to one of the two species represented in Lea’s type series).
From our thorough examination of all available material of Paratranes , including of the male genitalia of many specimens, we conclude that the type series of xanthorrhoeae indeed comprises two distinct species, as Zimmerman had recognised, and furthermore that the syntypes from the Darling Range in WA and Galston in NSW represent P. monopticus (as determined by comparison with the holotype of monopticus ( Fig. 11A View Fig ) and specimens “c.w.t.” (compared with the type) of monopticus by Zimmerman) and that those from Mt Barker, Swan River, Gosford and Sydney belong to a different species. In order to fix the name xanthorrhoeae to one of these two species, we here designate the male syntype from the Darling Range ( Fig. 11B View Fig ), which agrees well with Lea’s description, as the lectotype of xanthorrhoeae and the other six specimens of the type series as paralectotypes. This lectotype designation and comparison of the lectotype with the holotype of monopticus enable us to validate the synonymy of monopticus and xanthorrhoeae published by Pullen et al. (2014) and to describe the other species as new, here named P. zimmermani sp. nov. The paralectotypes of xanthorrhoeae from Mt Barker, Swan River, Gosford and Sydney are further designated as paratypes of P. zimmermani sp. nov. Specimens of P. monopticus from Western Australia and South Australia differ slightly from those from Queensland (the type locality) and New South Wales by having the apical margin of the genital sclerite of the endophallus medially not straight ( Fig. 9A View Fig ) but slightly emarginate (WA) or lobed (SA) ( Fig. 9B–C View Fig ). Based on the records available to us, the WA and SA populations also appear to be geographically separated from those in eastern Australia, but in the absence of significant morphological differences we interpret all populations to represent a single, somewhat variable species.
| SAMA |
Australia, South Australia, Adelaide, South Australian Museum |
| ANIC |
Australia, Australian Capital Territory, Canberra City, CSIRO, Australian National Insect Collection |
| BMNH |
United Kingdom, London, The Natural History Museum [formerly British Museum (Natural History)] |
| QM |
Australia, Queensland, South Brisbane, Queensland Museum |
| QDPI |
Australia, Queensland, Indooroopilly, Queensland Department of Primary Industries |
| NHMUK |
Natural History Museum, London |
| SAMA |
South Australia Museum |
| ANIC |
Australian National Insect Collection |
| QDPI |
Queensland Department of Primary Industries |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Paratranes monopticus ( Pascoe, 1870 )
| Hsiao, Yun & Oberprieler, Rolf G. 2021 |
Notiosomus (Tranes) xanthorrhoeae
| Hawkeswood 2014: 162 |
Paratranes monopticus
| Pullen et al. 2014: 289 |
| Oberprieler & Caldara 2012: 57 |
| Alonso-Zarazaga &Lyal 1999: 210 |
| Zimmerman 1994: 696 |
Tranes xanthorrhoeae
| Pullen et al. 2014: 289 |
| Oberprieler 1995: 306 |
| Mulder 1964: 12 |
| Schenkling & Marshall 1936: 1 |
| Froggatt 1907: 187 |
Tranes xanthorrhoeae
| Lea A. M. 1898: 592 |
Tranes monopticus
| Oberprieler 1995: 305 |
| Schenkling S. & Marshall G. A. K. 1936: 1 |
| Lea A. M. 1929: 539 |
| Lea A. M. 1898: 594 |
Tranes monopticus
| Pascoe F. P. 1870: 199 |