Philomedes assimilis Brady, 1907
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4141.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:6033C3F3-85B8-4665-A7AF-7C0E4B230ABC |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6069970 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/18659911-FFAA-C914-FF08-B00DFD5DFBD7 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Philomedes assimilis Brady, 1907 |
| status |
|
Philomedes assimilis Brady, 1907 View in CoL
( Figs. 17–22 View FIGURE 17 View FIGURE 18 View FIGURE 19 View FIGURE 20 View FIGURE 21 View FIGURE 22 )
1907 Philomedes assimilis Brady View in CoL ,: 5, pl. 1, Figs. 16–21 View FIGURE 16 View FIGURE 17 View FIGURE 18 View FIGURE 19 View FIGURE 20 View FIGURE 21 , pl. 2, Figs, 1–6. 1908 Philomedes assimilis Brady 1907 View in CoL —Müller: 87, pl. 6: Figs. 9–17 View FIGURE 9 View FIGURE 10 View FIGURE 11 View FIGURE 12 View FIGURE 13 View FIGURE 14 View FIGURE 15 View FIGURE 16 View FIGURE 17 ; pl. 7: Figs. 14–16 View FIGURE 14 View FIGURE 15 View FIGURE 16 . 1912 Philomedes assimilis Brady 1907 View in CoL —Müller: 26 [key], 31.
1912 Philomedes assimilis Brady 1907 View in CoL —Scott: 586.
1920 Philomedes assimilis Brady 1907 View in CoL —Skogsberg: 352, 413.
1921 Philomedes assimilis Brady 1907 View in CoL —Barney: 178.
1967 Philomedes assimilis Brady 1907 View in CoL —Lofthouse: 143
1971 Philomedes assimilis Brady 1907 View in CoL —Kornicker: 186, Fig. 14 View FIGURE 14 . 1975 Philomedes assimilis Brady 1907 View in CoL —Kornicker: 229–236, Figs. 128–130, 131, 132 (map). 1991 Philomedes assimilis Brady 1907 View in CoL —Hartmann: 212.
1986 Philomedes View in CoL cf. P. assimilis Brady 1907 View in CoL —Hartmann: 235.
1907 Philomedes antarctica Brady View in CoL : 5, pl. 5, Figs. 1–10 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 View FIGURE 7 View FIGURE 8 View FIGURE 9 View FIGURE 10 .
1971 Philomedes antarctica Brady, 1907 View in CoL —Kornicker: 189, Fig. 15 View FIGURE 15 .?1990 P. heptathrix Kornicker, 1975 View in CoL —Hartmann: 199, Abb. 1.
Studied material (coordinates, depth and sediment see Appendix). 16th Soviet (=Russian) Antarctic Expedition, sample 161: MIMB 18286—adult female (2.05 mm).
Sample 162: MIMB 18 287 and 18288—2 adult females (2.15 mm, other is deformed).
Sample 164: MIMB 18 291—adult male (2.16 mm).
Sample—unknown (depth 45 m), 18 February1972; MIMB 18293—adult male (2.30 mm).
Sample 166: MIMB 18 295—immature male (1.90 mm).
Sample 169: MIMB 18 292—adult male (2.05 mm); MIMB 18289—adult female (1.92 mm).
34th Soviet (=Russian) Antarctic Expedition, station 10, sample 1: MIMB 18294—adult male (2.10 mm).
RV “Polarstern”, ANT XIII/3, station 39/02: ZMH-K-42264—adult female (1.97 mm) and ZMH-K-42265— adult male (2.24 mm).
52th Russian Antarctic Expedition, station 8, sample 37: MIMB 18290—adult female (2.02 mm).
Additional material. See Appendix.
Diagnosis of female ( Kornicker 1975, with additional remarks). Carapace: with truncate posterior and angular caudal process, length 1.67–2.15 mm.
First antenna: 2nd joint with 5–7 setae, 3–4 ventral, 1 lateral and 1–2 dorsal.
Second antenna: 1st joint of endopodite with 5–6 setae, 4–5 proximal and 1 distal; 2nd joint with 1 long and 3 short ventral setae and 1 long recurved terminal seta.
Mandible: dorsal margin of basale with 4–6 setae, 2–4 near middle and 2 subterminal.
Sixth limb: epipodite with 3–5 setae.
Seventh limb: each limb with 8–10 (usually 9) setae, 4–5 distal and 3–5 proximal; 1–2 pegs present on opposite terminal comb.
Caudal furca: each lamella with 10 (very rarely 9) claws.
Bellonci organ: 1-jointed, with rounded tip.
Lateral eye: small with 2 divided ommatidia.
Anterior process (above upper lip): relatively developed and with rounded tip.
Diagnosis of male. Carapace: length 2.12–2.25 mm.
First antenna: 2nd joint with 4–5 setae, 2–3 ventral, 1 lateral and 1–2 dorsal.
Second antenna: 1st joint of endopodite with 6 seta, 5 proximal and 1 distal; proximal seta of 3rd joint somewhat longer than half of its length.
Mandible: dorsal margin of basale with 4 setae, 2 near middle and 2 subterminal; coxale endite present.
Sixth limb: epipodite with 3 (rarely with 2) setae.
Seventh limb: each limb with 8–10 (usually with 9) setae, 4–5 distal and 4–5 proximal; 2 pegs present on opposite terminal comb.
Caudal furca: each lamella with 9 (rarely with 10) claws.
Bellonci organ: 1-jointed, with rounded tip.
Anterior process (above upper lip): relatively developed with rounded tip.
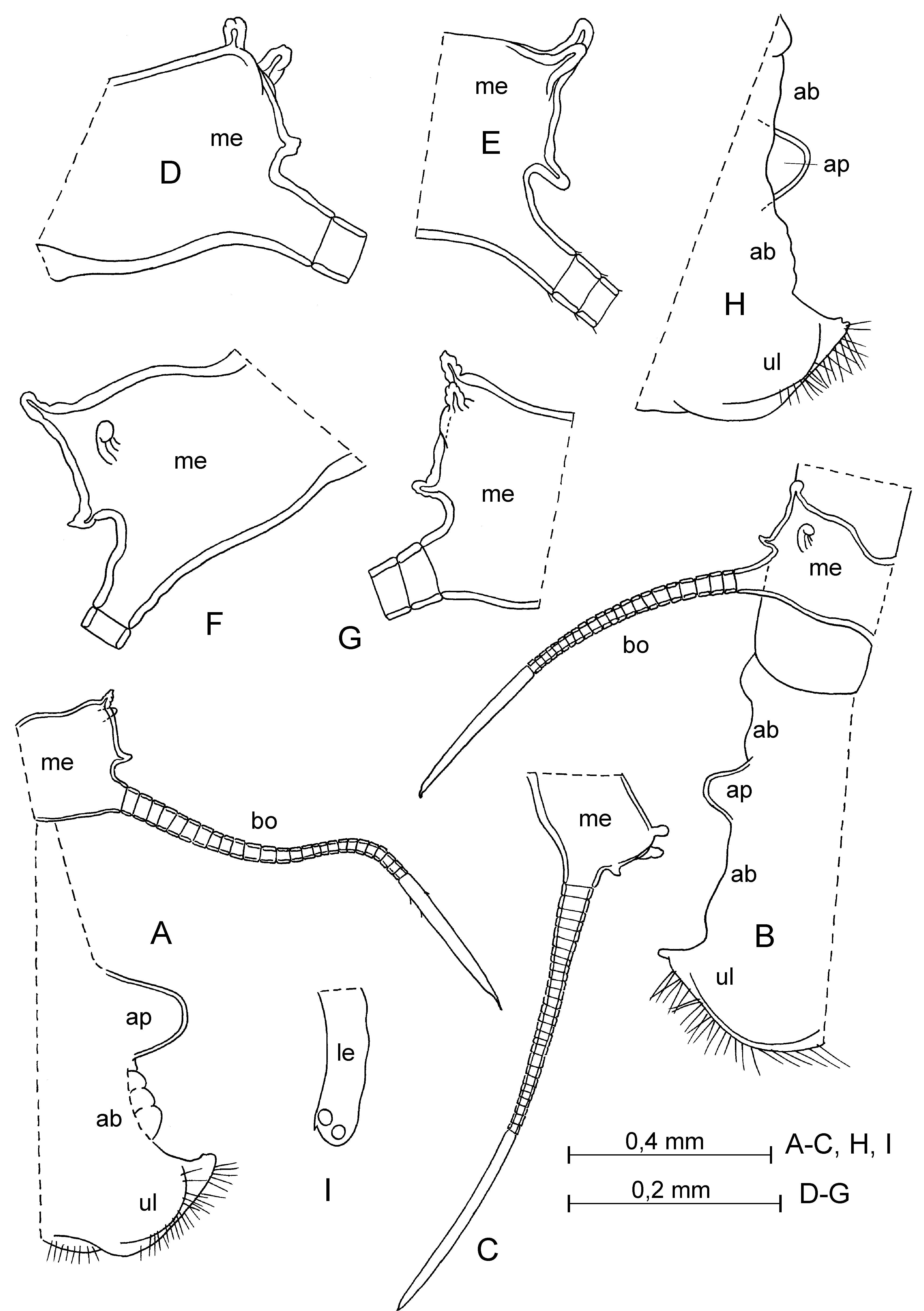
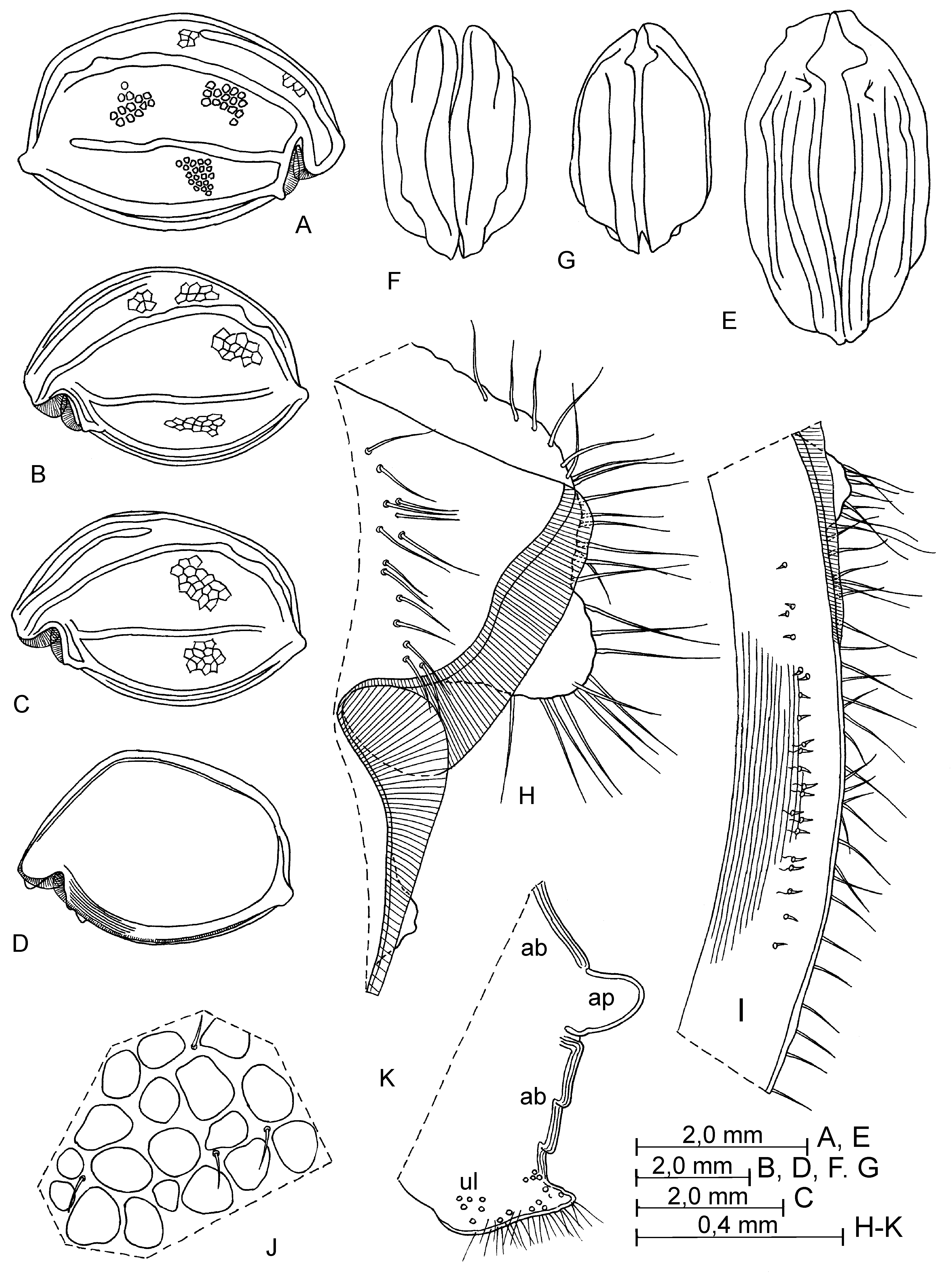
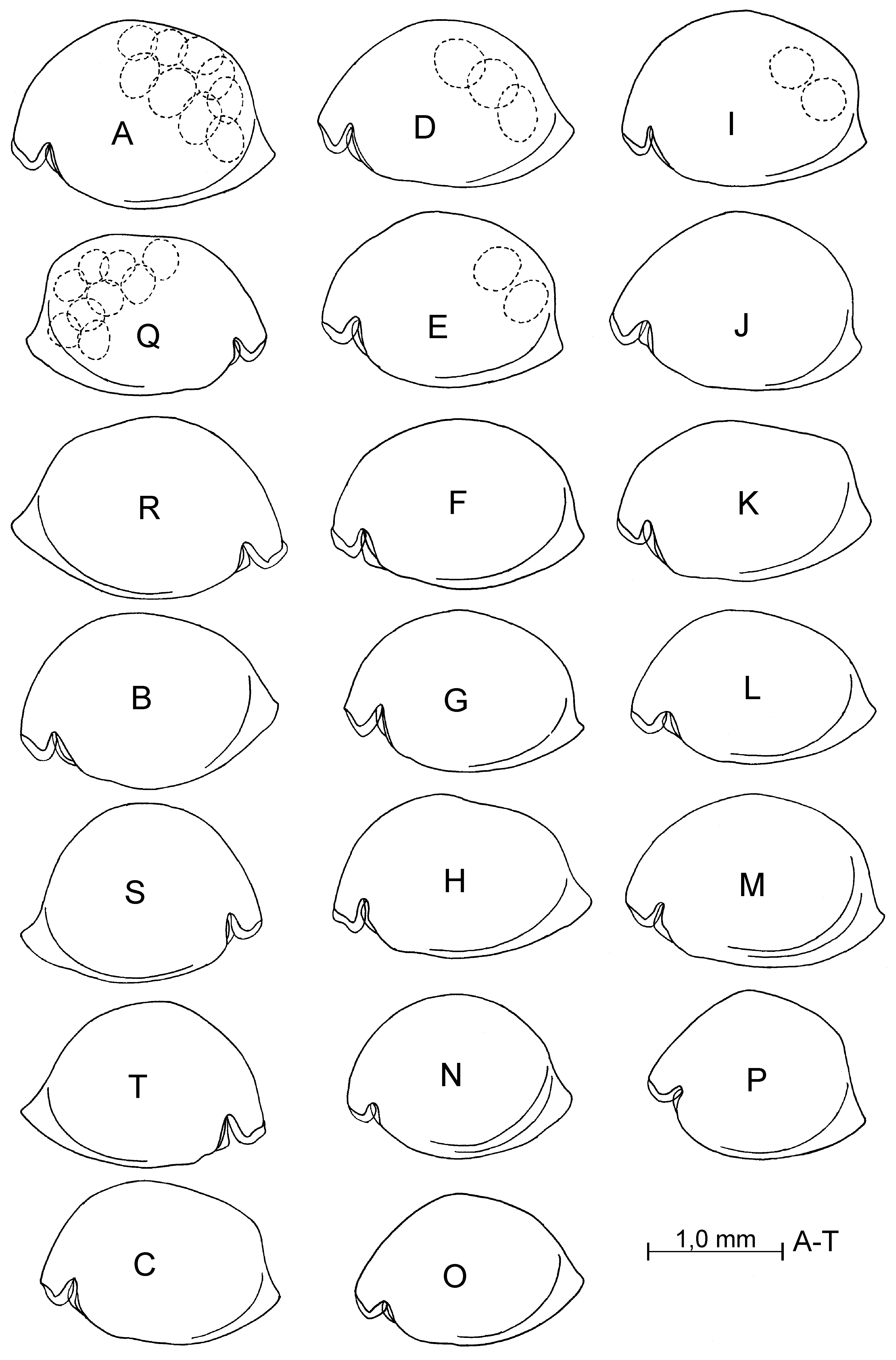
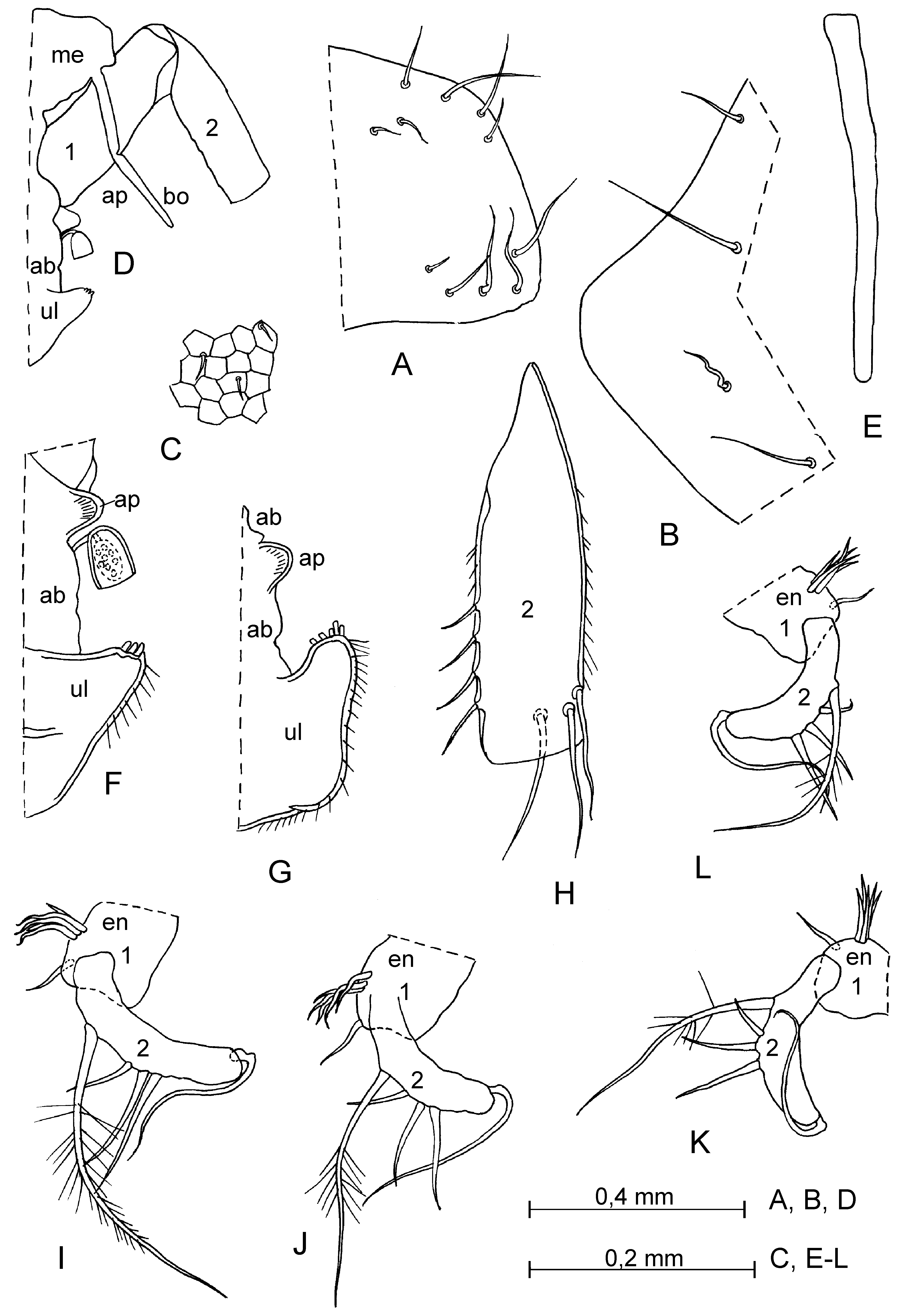
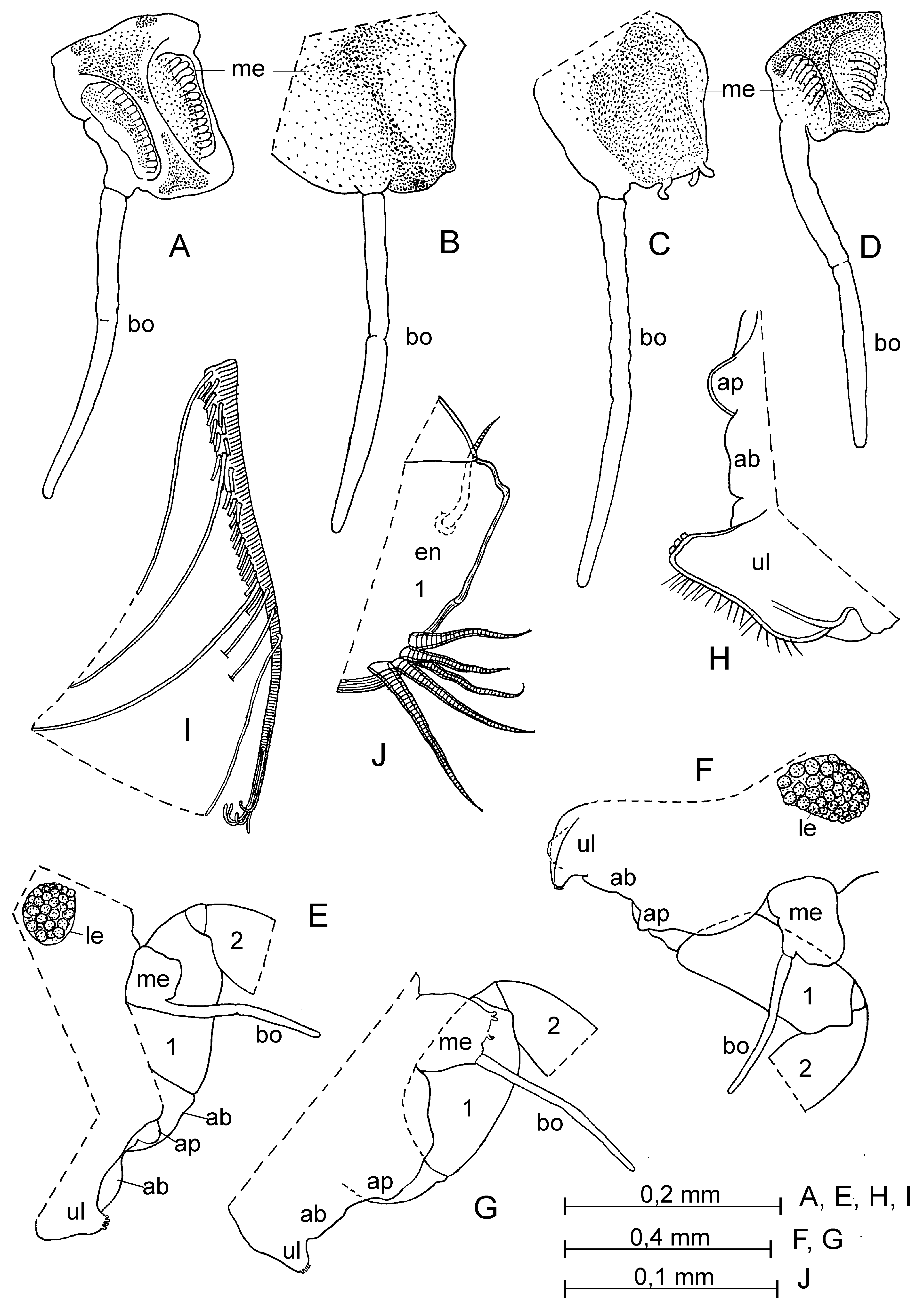
Supplementary description of adult female. Carapace ( Figs. 17 View FIGURE 17 A–L, R–T; 18 A–C). Length 1.67–2.15 mm (in literature: 1.67–2.0 mm). Shape of carapace very various ( Fig. 17 View FIGURE 17 ). Infold on rostrum with about 13–28 setae forming a vertical row and on incisure with 3–4 setae near margin. Anterior-ventral inside with about 10–34 short setae and with 13–15 striations. Infold on caudal process with 3–11 short setae.
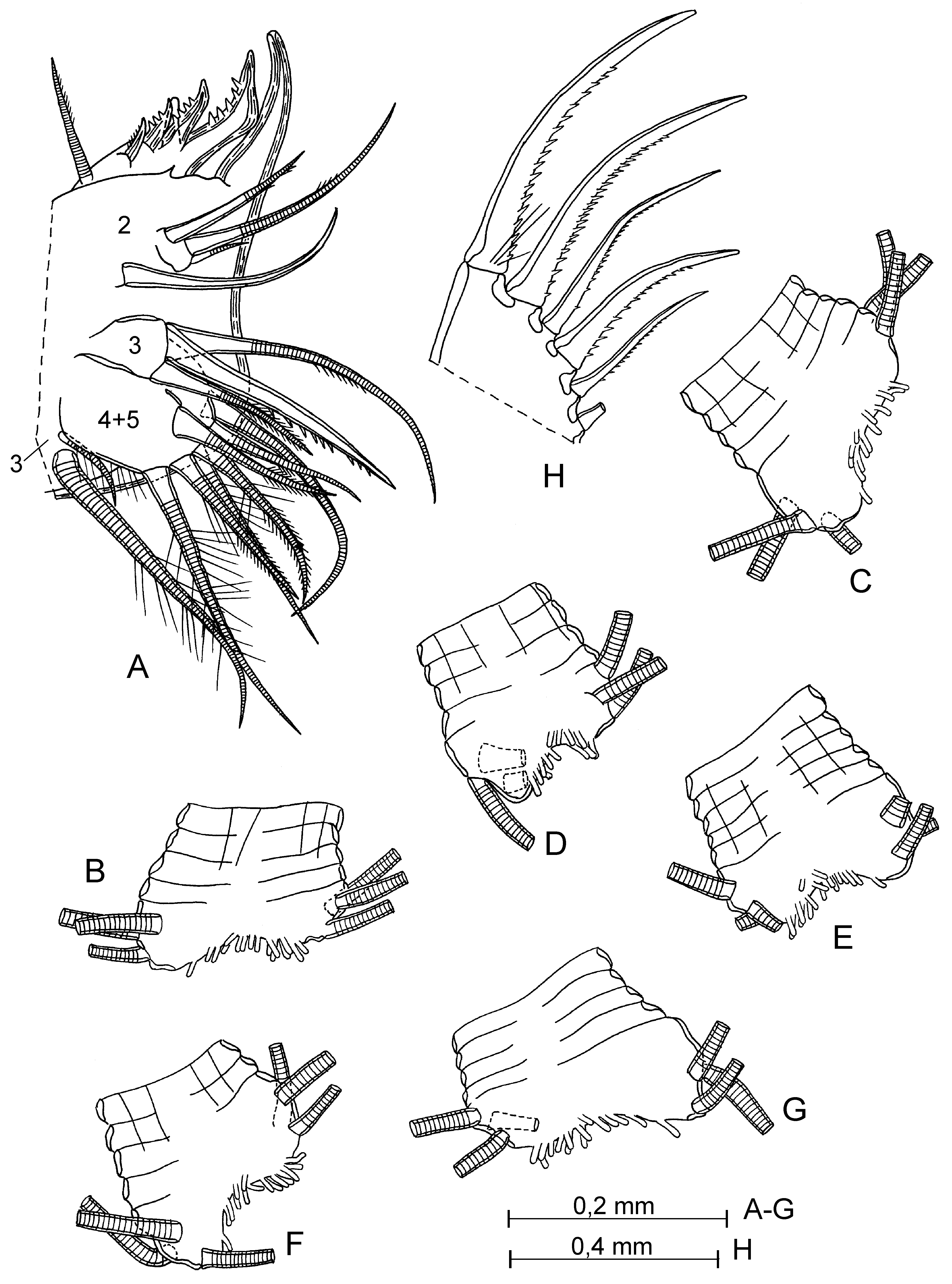
First antenna ( Fig. 18 View FIGURE 18 D, H). First joint with 4–5 setae in proximal group and 1 distal seta. Second joint with 5–7 setae, 1–2 dorsal, 1 lateral and 3 or 4 ventral.
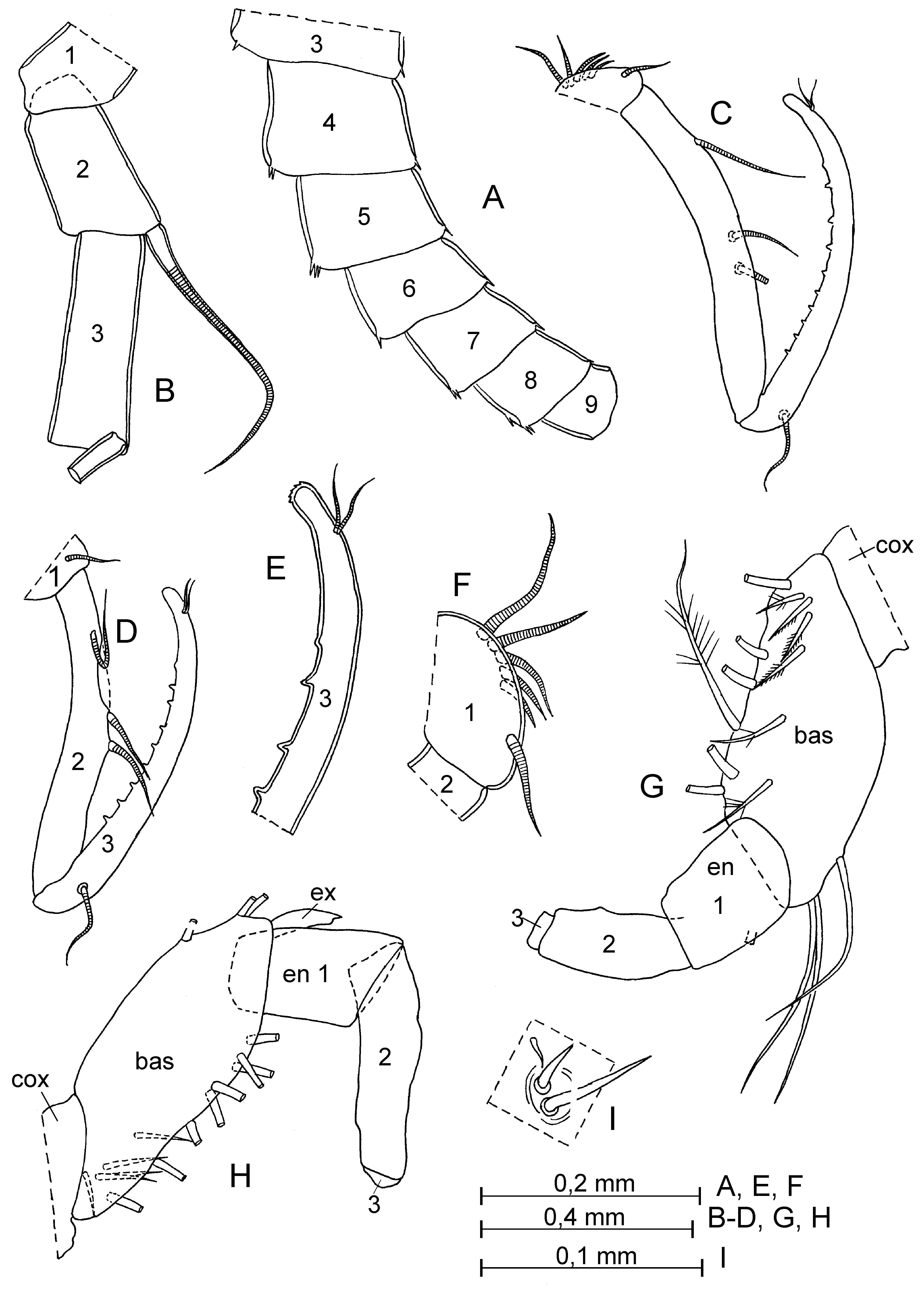
Second antenna ( Fig. 18 View FIGURE 18 I–L). Length of setae (1 long and 3 short ventral and 1 subterminal setae) on second endopodite joint varying.
Mandible ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 F). Basale: dorsal margin with 4–6 setae, 2–4 near middle and subterminal setae; medial side with 6 setae, 3 pectinate and 3 normal; lateral surface with 4–5 setae forming a row parallel to ventral margin; ventral margin with 3–4 distal setae. Endopodite: first joint with 3–4 ventral setae; dorsal margin of second joint with 2 setae in proximal group, 6 setae in distal group and 1 seta between these groups, ventral margin with 2–3 setae in subterminal group and 3 setae in terminal group.
Sixth limb. Endite I with 2–3 terminal and 1 medial setae, endite II with 3 terminal and 1 medial setae, endite III with 8–9 terminal and 1 medial setae, endite IV with 7–8 terminal and 1 medial setae, end joint with 24–30 setae, 3–5 setae present in place of epipodial appendage.
Seventh limb. Each limb with 8–10 setae, 4–6 distal (usually 2+3, rarely 2+2 and 3+3) and 4–5 setae (usually 2+2, rarely 3+2 and 1+3); each seta with 2–5 bells. Terminal comb with 10–11 teeth; 1–2 pegs present opposite comb.
Caudal furca. Each lamella usually with 10 claws and rarely 9 claws.
Bellonci organ ( Fig. 18 View FIGURE 18 D, E). 1-jointed, with rounded tip.
Upper lip ( Figs. 18 View FIGURE 18 D, F, G; 20 H). Lip ventrally hirsute and with several glandular processes at tip.
Anterior process of body ( Figs. 18 View FIGURE 18 D, F, G; 20 H). Relatively large and rounded.
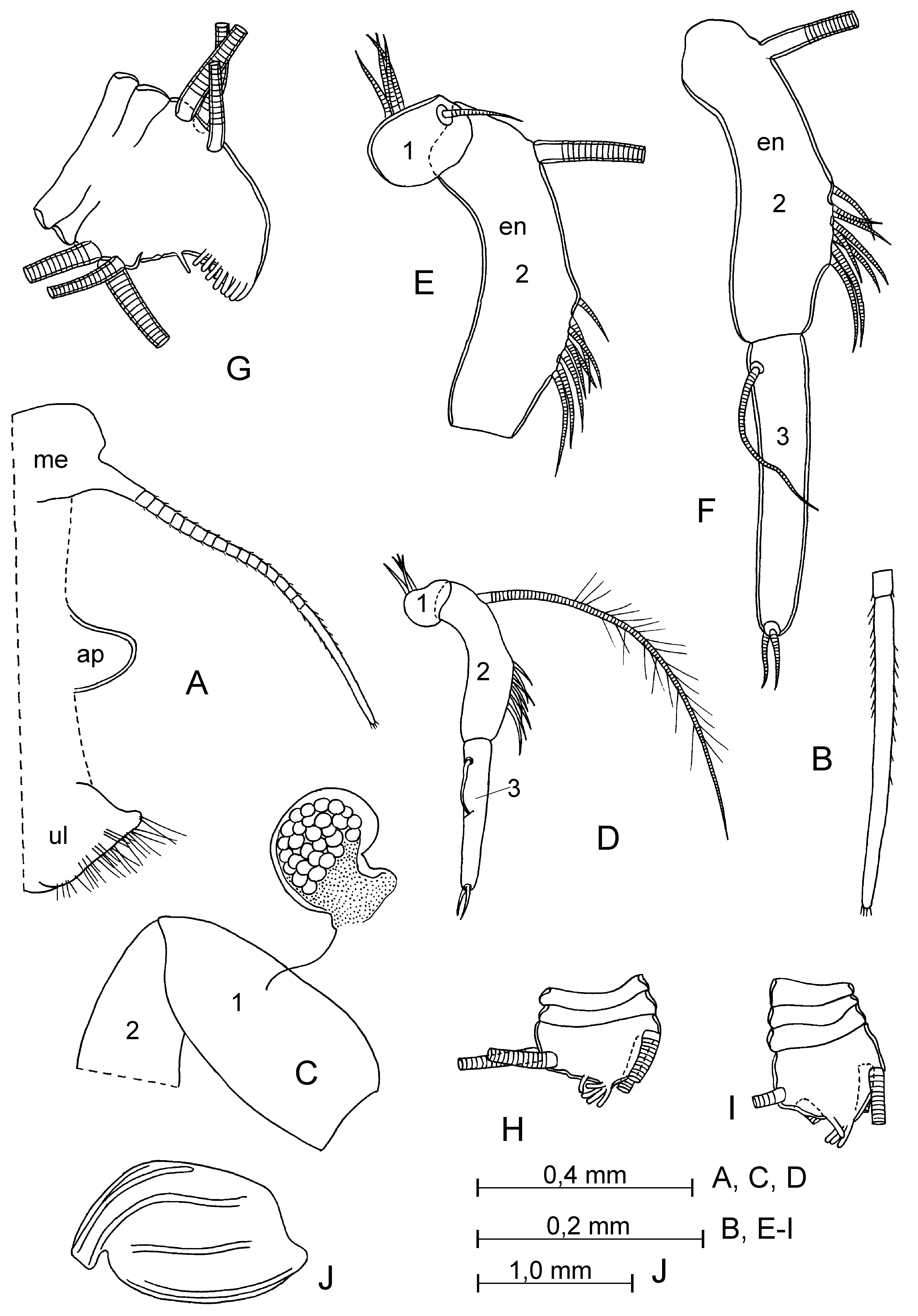
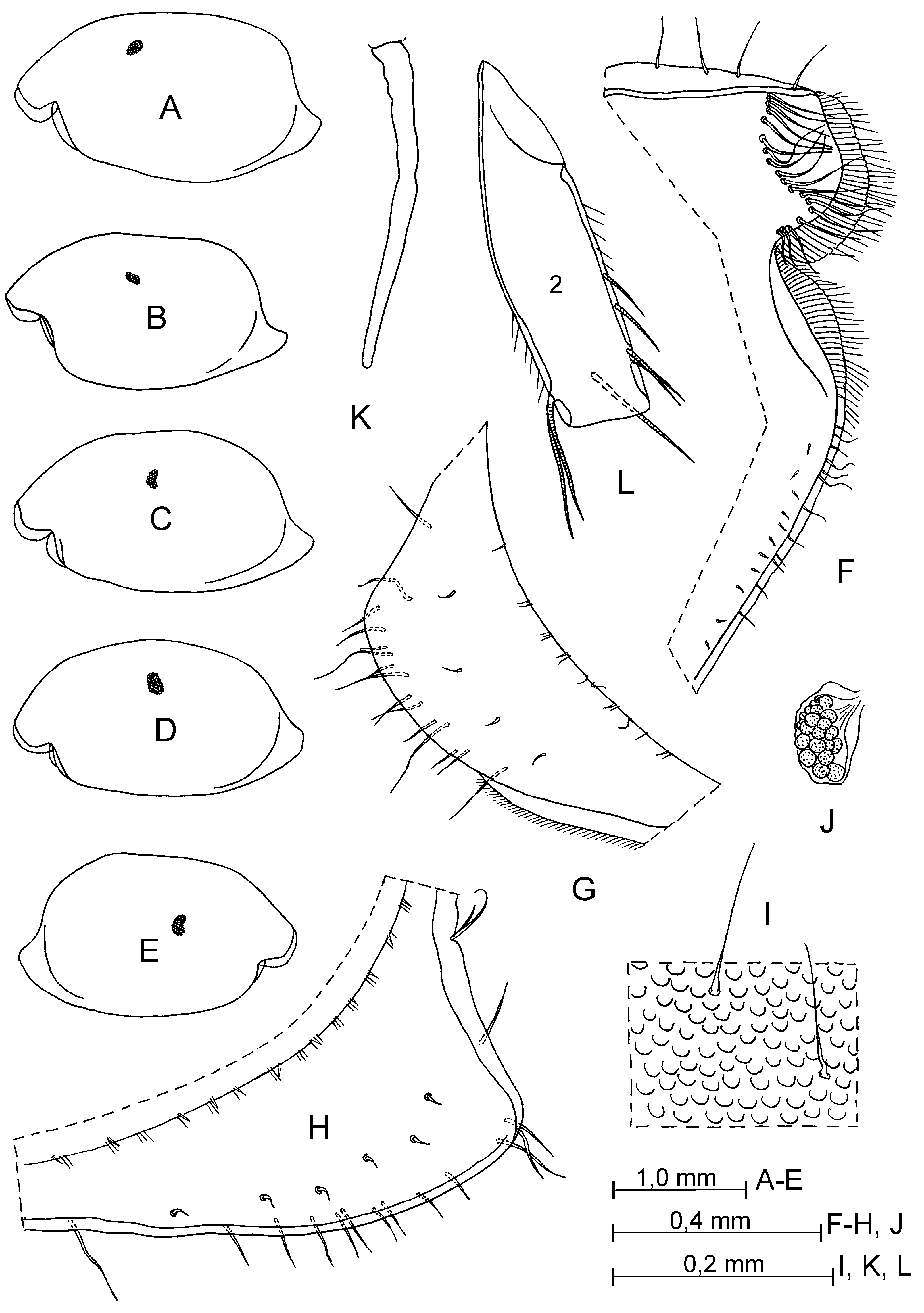
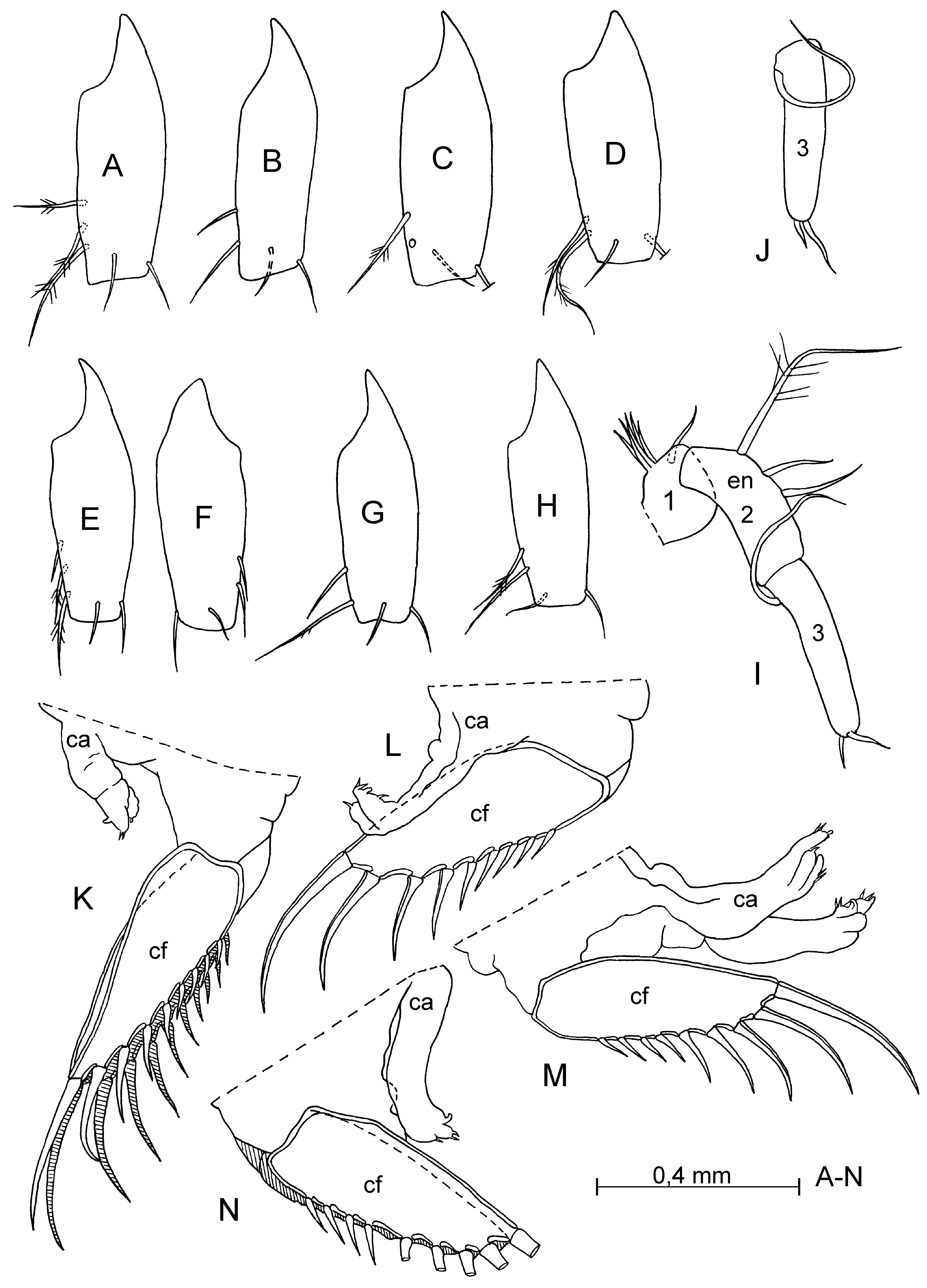
Supplementary description of adult male. Carapace ( Fig. 19 View FIGURE 19 A–I): Length 2.12–2.25 mm (in literature: 2.12–2.24 mm). Shape of carapace variable ( Fig. 19 View FIGURE 19 A–E). Infold on rostrum with about 17–18 setae forming a row. Antero-ventral inside with about 11–15 spine-like setae. Infold on caudal process with 4–6 spine-like setae. First antenna ( Figs. 19 View FIGURE 19 L; 20 E–G; 22 A–H). Second joint with 4–5 setae, 1 dorsal, 1 lateral and 2–3 ventral setae; length of setae varying ( Fig. 22 View FIGURE 22 A–H). Sensory seta on fifth joint evenly tapered from base to tip (without knee in middle) and with 5 terminal filaments ( Fig. 20 View FIGURE 20 I).
Second antenna ( Figs. 20 View FIGURE 20 J; 21 A–D). First endopodial joint with 6 setae, 5 proximal and 1 distal; second joint with 2 muscle bands, one extends from first joint to proximal margin of third joint and other from middle of dorsal margin of second joint to proximal margin of third joint ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 D). Proximal seta of third joint slightly longer than half of its length.
Mandible ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 E, G). Coxale endite bifurcate distally. Basale: dorsal margin with 4 setae, 2 near middle and 2 subterminal setae; medial side with 6 setae; lateral surface with 4 setae forming a row parallel to the ventral margin; ventral margin with 3 distal setae. Endopodite: first joint with 4 or 5 ventral setae; dorsal margin of second joint with 2 setae in proximal group, 6 setae in distal group and 1 seta between these groups, and ventral margin with 2–3 setae in subterminal group and 3 setae in terminal group.
Sixth limb. Endite I with 1–2 terminal and 1–2 medial setae; endite II with 2–3 terminal and 1 medial setae; endite III with 7–8 terminal and 1 medial setae; endite IV with 7–8 terminal and 1 medial setae; end joint with 21 setae (in all studied females); 2–3 setae present in place of epipodial appendage.
Seventh limb ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 H). Each limb with 8–10 setae, 4–5 distal (2+3 or 2+2) and 4–5 proximal (2+3 or 2+2); each seta with 3–6 bells. Terminal comb with 10 teeth; 2 pegs present on opposite comb.
Caudal furca ( Fig. 22 View FIGURE 22 K–N). Limb with 9+9 or 9+10 claws.
Copulatory appendage ( Fig. 22 View FIGURE 22 K–N). Elongate, with 2 lobes (long and short). Length of appendage varying, about half to 9/10 length of lamella of furca.
Medial eye ( Fig. 20 View FIGURE 20 A–G). Large, usual smooth (only in female ( Fig. 20 View FIGURE 20 C, G) eye with 3 anterior sclerotic tubercles.).
Bellonci organ ( Figs. 19 View FIGURE 19 K, 20 A–G). Elongate, unsegmented, with rounded tip and subequal, slightly longer, or shorter than length of first joint of first antenna.
Upper lip ( Fig. 20 View FIGURE 20 E–G). Tip with several glandular processes.
Anterior process of body ( Fig. 20 View FIGURE 20 E–G). Small or midsize and rounded.
Supplementary of A-1 male. Length 1.75 mm.
First antenna. Second joint with 1 dorsal, 1 lateral and 2 ventral setae; third joint with 2 dorsal and 1 ventral setae; fourth joint with 1 dorsal and 3 ventral setae.
Second antenna ( Fig. 22 View FIGURE 22 I, J). First joint with 6 setae, 5 proximal and 1 distal; second joint with 1 long spinous and 2 short ventral setae; third joint with 1 long dorsal and 2 short terminal setae.
Mandible. Similar to that of adult female.
Sixth limb. 4 setae present in place of epipodial appendage.
Seventh limb. Each limb with 9 setae (2+3 distal and 2+2 proximal). Terminal comb with 9 teeth; 1 peg present on opposite comb.
Caudal furca. Each lamella with 9 claws.
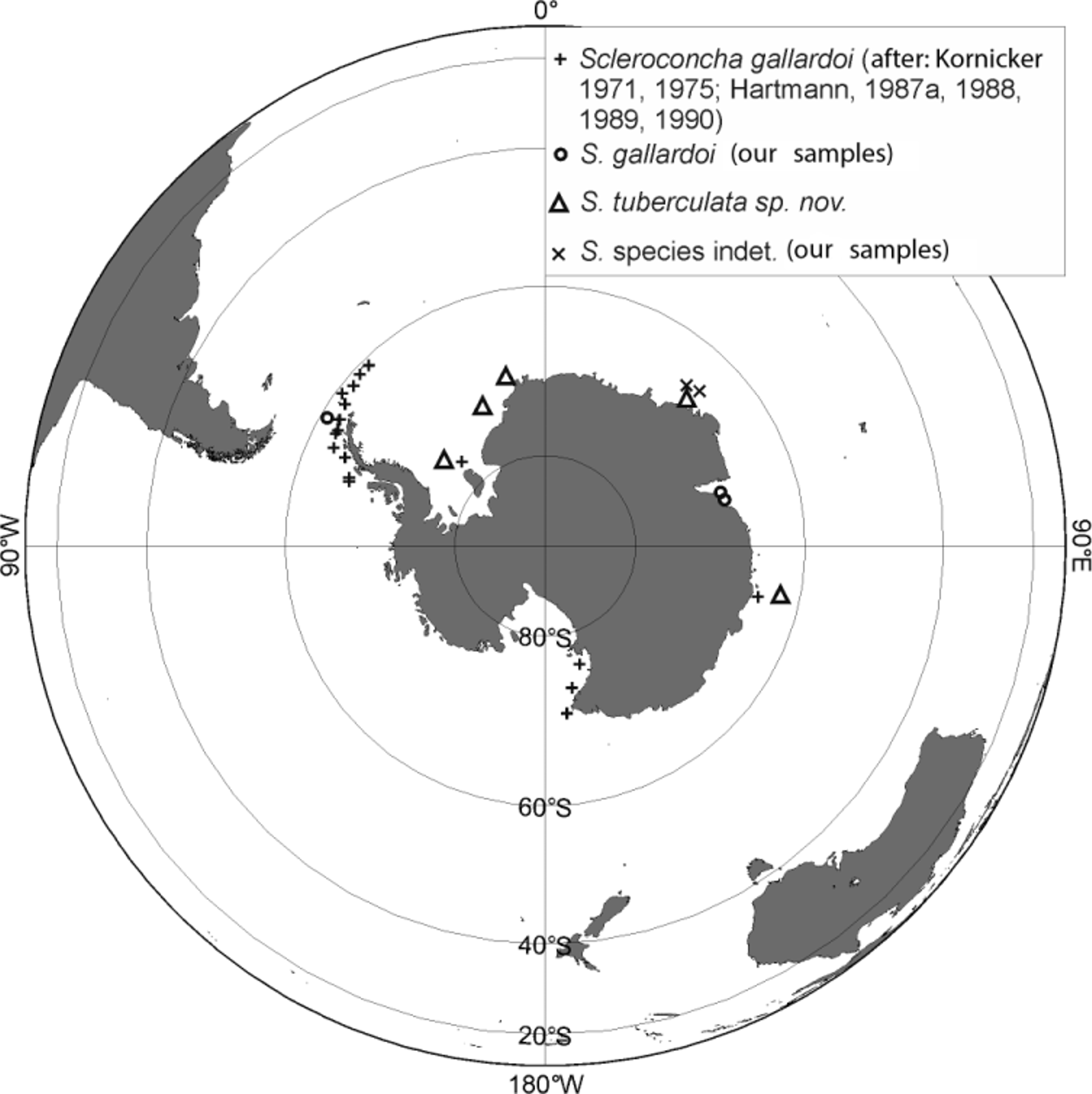
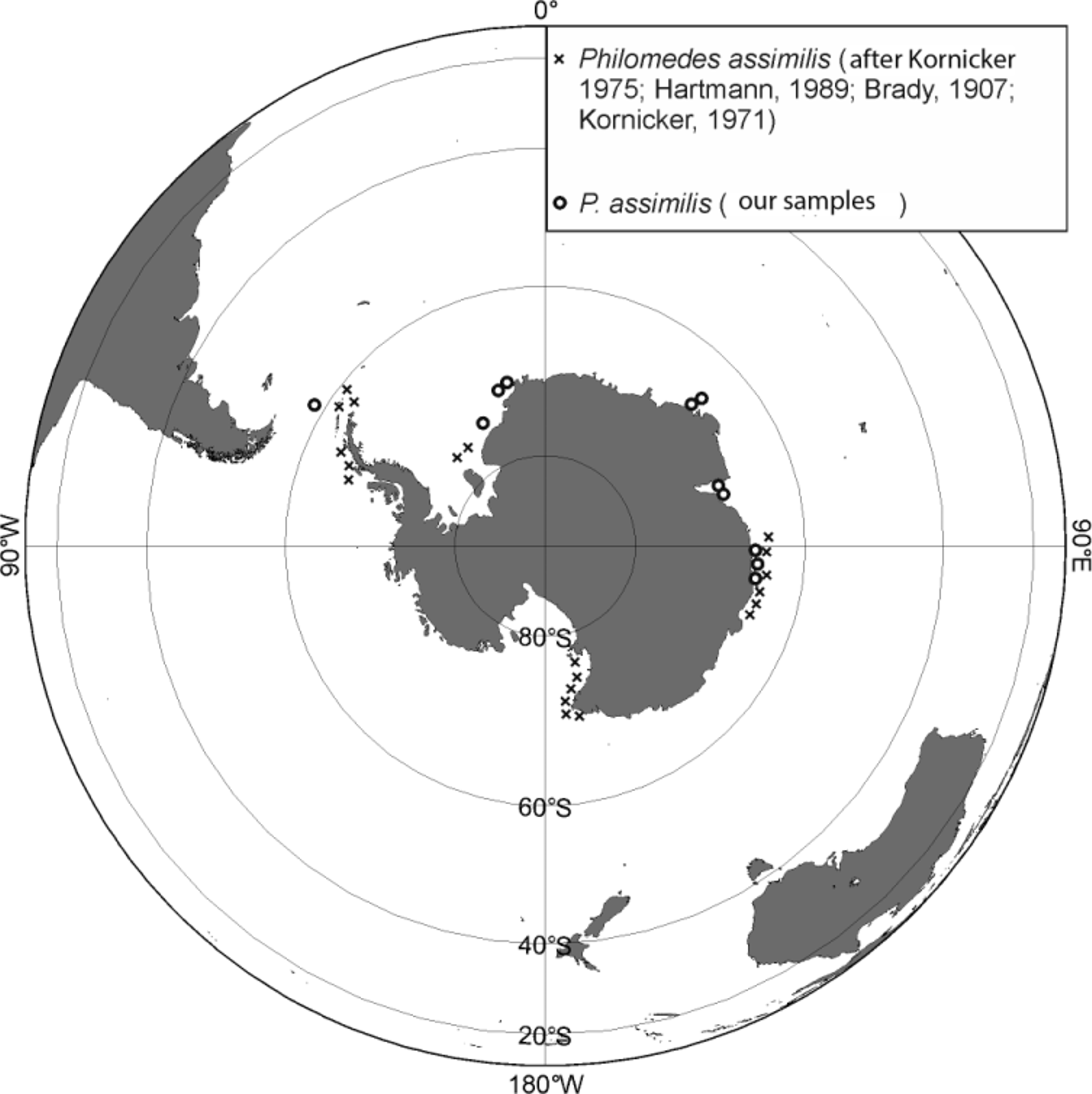
Distribution and ecology. Circumantarctic sublitoral-bathyal species. It has been collected almost around the whole Antarctic continent between 62° and 78°S (as rule to south of 65–66° S ( Fig. 16 View FIGURE 16 )) at depths of 7 to 876 m, temperature range of 0.57° to -1.53°C and on hard and soft substrates: rock, stone, gravel, sand, muddy sand ( Brady 1907; Kornicker 1971, 1975; Hartmann 1989).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
SubClass |
Myodocopa |
|
Order |
|
|
SubOrder |
Myodocopina |
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Philomedinae |
|
Genus |
Philomedes assimilis Brady, 1907
| Chavtur, Vladimir G. & Keyser, Dietmar 2016 |
heptathrix
| Kornicker 1975 |
Philomedes assimilis
| Brady 1907 |
Philomedes assimilis
| Brady 1907 |
Philomedes assimilis
| Brady 1907 |
Philomedes assimilis
| Brady 1907 |
Philomedes assimilis
| Brady 1907 |
Philomedes assimilis
| Brady 1907 |
Philomedes assimilis
| Brady 1907 |
Philomedes assimilis
| Brady 1907 |
Philomedes assimilis
| Brady 1907 |
P. assimilis
| Brady 1907 |
Philomedes antarctica
| Brady 1907 |