Mantidactylus delormei, ANGEL, 1938
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1096-3642.2010.00667.x |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0E4F87B3-E51B-C35B-FCA1-70F05A40FACF |
|
treatment provided by |
Valdenar |
|
scientific name |
Mantidactylus delormei |
| status |
|
MANTIDACTYLUS DELORMEI ANGEL, 1938 View in CoL
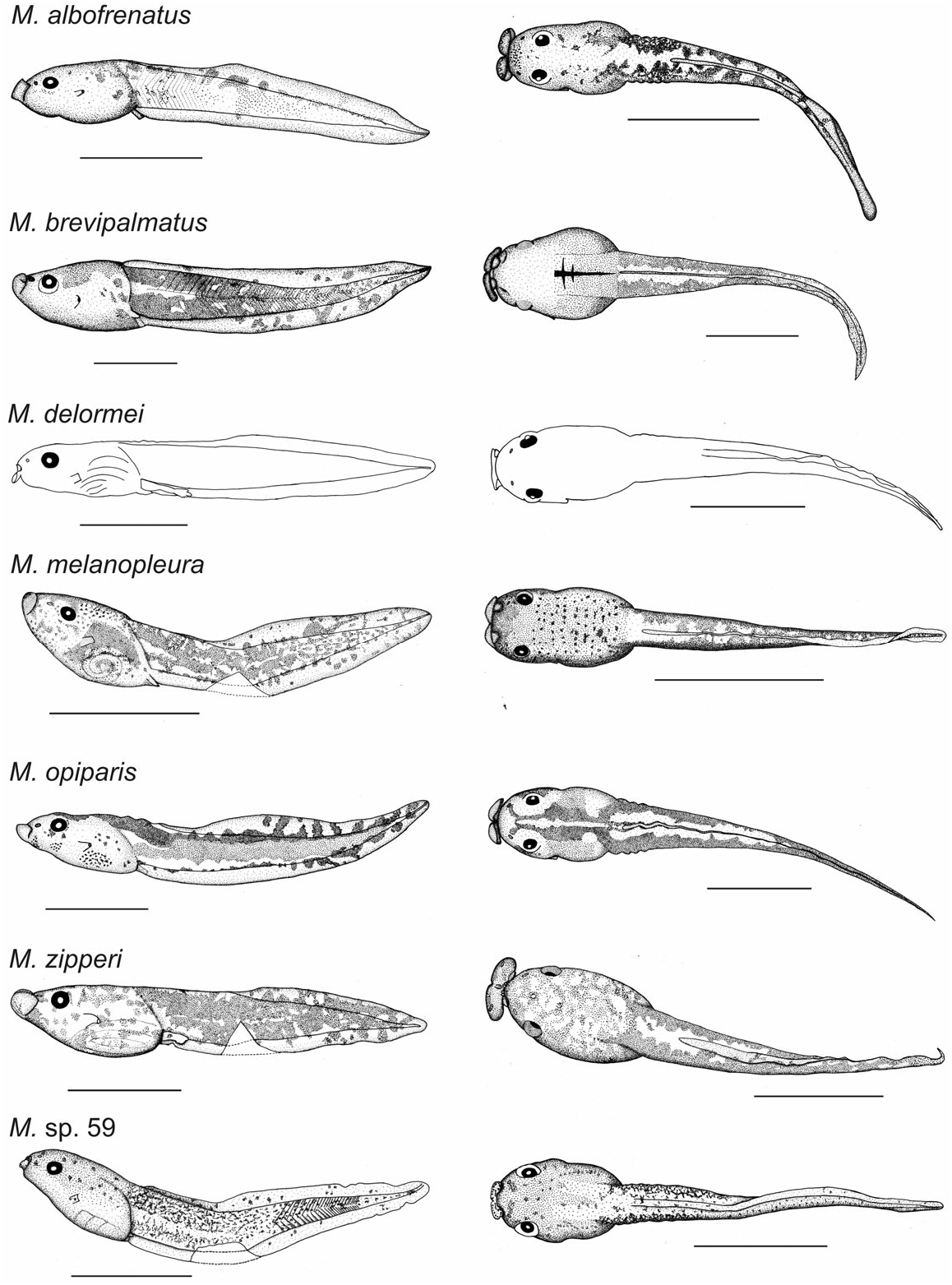
The tadpoles of M. delormei have no obvious diagnostic characters compared to those of other species of Chonomantis , except for some subtle details of uncertain diagnostic value, and except for M. aerumnalis and M. sp. 59, which can be distinguished, respectively, by their coloration and by the presence of rudimentary keratodonts (see accounts on these species for details).
The description of external morphology of the tadpoles of M. delormei is based on the DNA voucher specimen in stage 37, ZSM 440/2004 (field number FGMV 2002.1842; GenBank accession number GU808495 View Materials ) from a small stream in Ranomafana National Park, southern central east of Madagascar (BL 10.50 mm). A second specimen from the same batch, in stage 37/38, was used for the description of the tail, measurements, and the drawing of the oral disc (TL 39.8 mm, BL 10.9 mm). Buccopharyngeal features are described based on one tadpole at stage 40, ZSM 446/2004 (field number FGMV 2002.1875) and verified with a further specimen at stage 36, ZSM 437/2004 (field number FGMV 2002.1831), all from Ranomafana National Park.
External morphology: In profile ( Fig. 1 View Figure 1 ), BW 124% of BH, flat above, snout rounded. In dorsal view ( Fig. 1 View Figure 1 ), body widest at level of gills. Eyes moderately large, ED 17% of BL, visible in ventral view. Pineal ocellus not observed. Nares oval, positioned almost dorsally, aperture directed ventrolaterally, RN 38% of NP, NN 55% of PP. Spiracle conical, moderately sized, attached to body wall except tip of inner wall thus giving to opening a posterolaterally direction, SS 52% of BL; spiracular opening situated on a plane going between the hindlimb insertion and apex of caudal myotomes. Tail musculature, TMH 77% of BH and 65% of MTH, TMW 59% of BW, proximal third parallel then gradually tapering. Upper fin almost nonexistent in first third then increasing suddenly in height just before halfway, then following caudal muscle, UF 22% of MTH, SU 118% of BL, lower fin almost straight until tip of tail when becomes convex to form end of tail, LF 26% of MTH; TAL 267% of BL, point of maximum height of tail located just before halfway, MTH 119% of BH, tail tip bluntly pointed. Anal tube moderately small, directed posterolaterally, mostly free from ventral tail fin. Lateral line organs not observed.
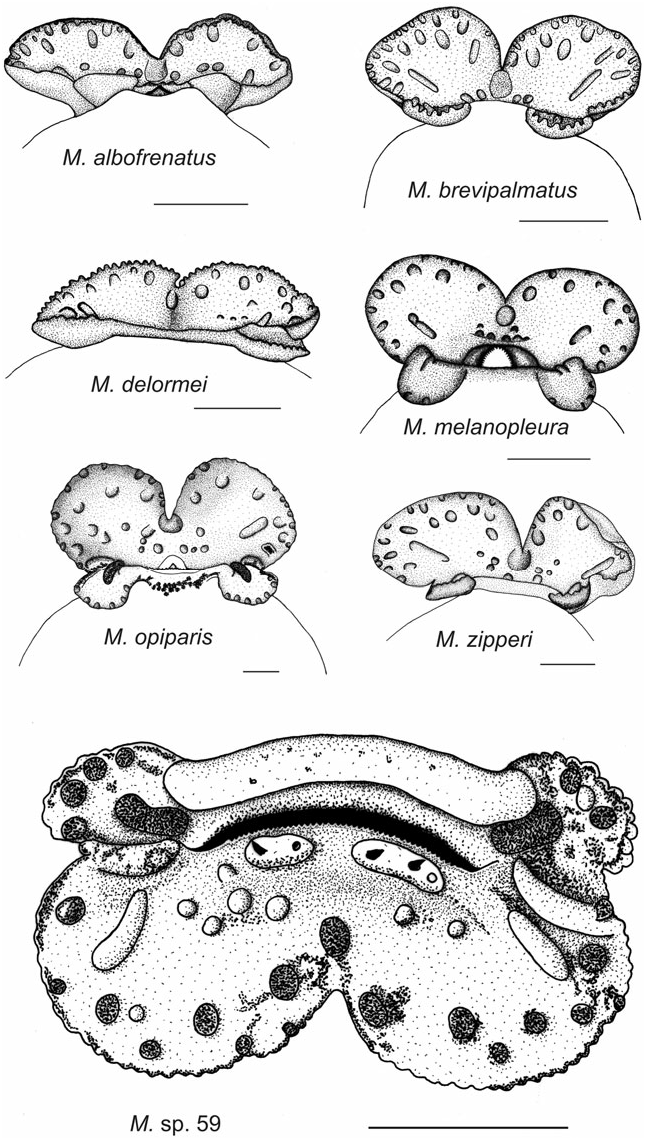
Oral disc ( Fig. 2 View Figure 2 ) ODW 28% of BL and 49% of BW. No real marginal papillae but crenulations on margin all around oral disc except on medial part of upper labium. The horizontal row of papillae on bottom of lower labium on a ridge interrupted in its centre and bearing three ‘papillae’ on each side, the large and round structure on the midline smaller than in other species. Upper jaw sheath white with dark serrations.
Coloration in preservative: Completely faded in the available specimen.
Variation: The ratios taken for five other tadpoles in stage 27–40/41 (ZSM 437/2004; ZSM 440/2004; ZSM 446/2004; TL 32.1–43.6 mm, BL 8.2–11.1 mm) vary in the following proportions: BW 116–132% of BH; ED 15–18% of BL; RN 41–50% of NP; NN 51–63% of PP; SS 48–54% of BL; TMH 68–79% of BH; TMH 62–69% of MTH; TMW 57–62% of BW; UF 25–28% of MTH; LF 25–28% of MTH; SU 107–127% of BL; TAL 272– 284% of BL, MTH 101–111% of BH; ODW 27–33% of BL; ODW 41–53% of BW. Maximum body width can be attained at the middle part of the intestinal coil.
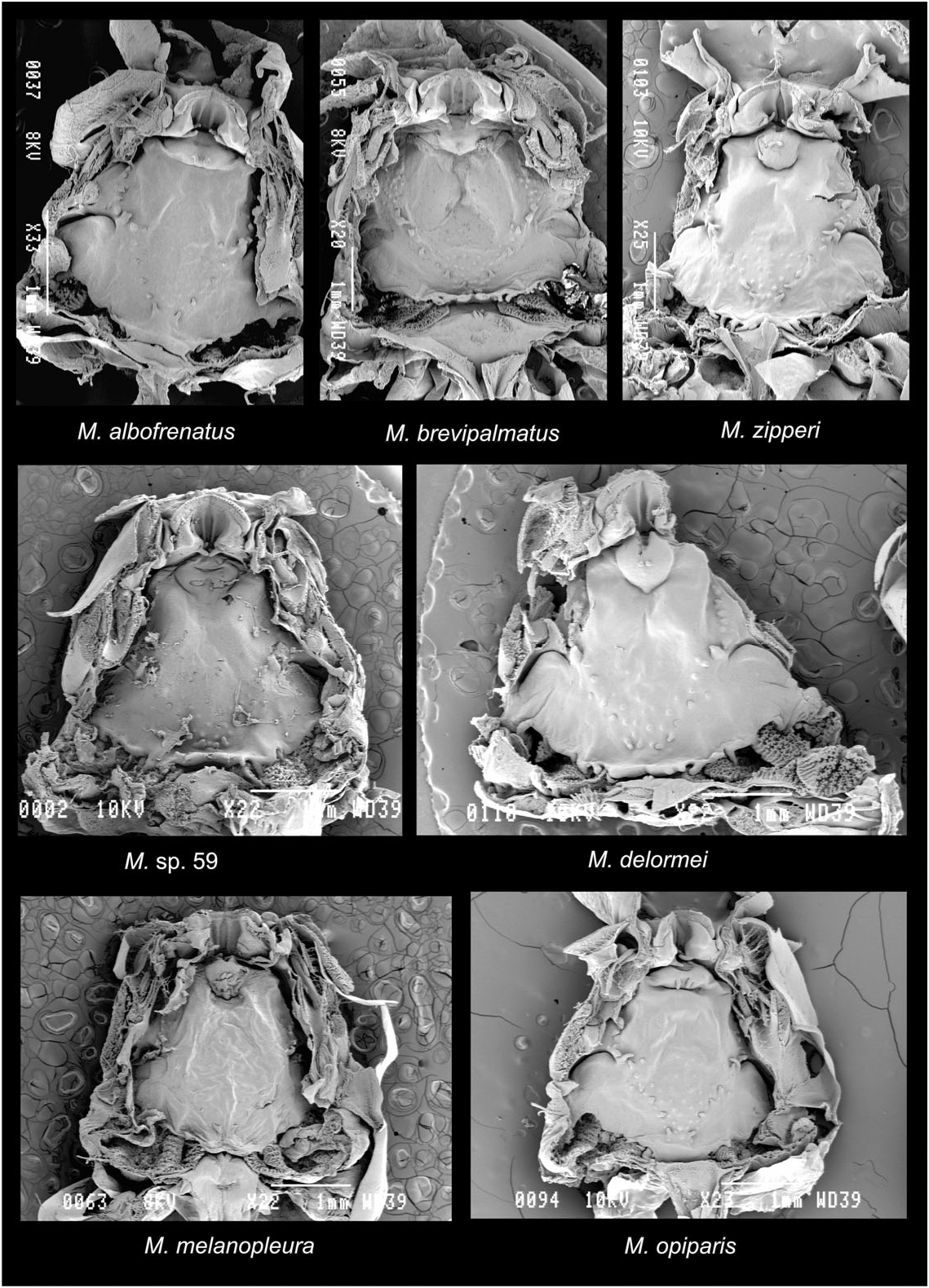
Buccal floor ( Fig. 3 View Figure 3 ): Prelingual arena very small and deep, two vertical ridges on inner side of lower beak, ridges continuing on anterior part of tongue anlage forming a longitudinal notch after being interrupted in bottom of arena. Two pairs of small and simple prelingual papillae on lateral wall of arena, the anterior-most lowest, both directed dorsomedially. Tongue anlage very prominent, lemon-shaped; one pair of relatively long and simple lingual papillae orientated dorsally. Buccal floor arena triangular, delimited by a row of about eight stocky and very small papillae on each side, the biggest in front of buccal pocket bearing some stubs, the two or three posterior-most finest; interior of arena with fewer than 20 pustules. Buccal pockets narrow, curved anteriorly, obliquely orientated; a longitudinal row of six to eight prepocket papillae in continuity with buccal floor arena papillae running up to level of posterior end of tongue anlage. Ventral velum with spicular support, slightly wavy, bearing a big projection above both second and first filter plates and four to six big projections medially (which can be more or less fused), the two median forming median notch; glottis covered by velum except for its posterior end; medial part of velum and glottis vertical; secretory pits present on projections and on velum margin. Branchial baskets wider than long; with three filter cavities, filter plates obliquely arranged, filter mesh more developed than in other species, with main and secondary folds, and tertiary folds especially developed on third filter plate.
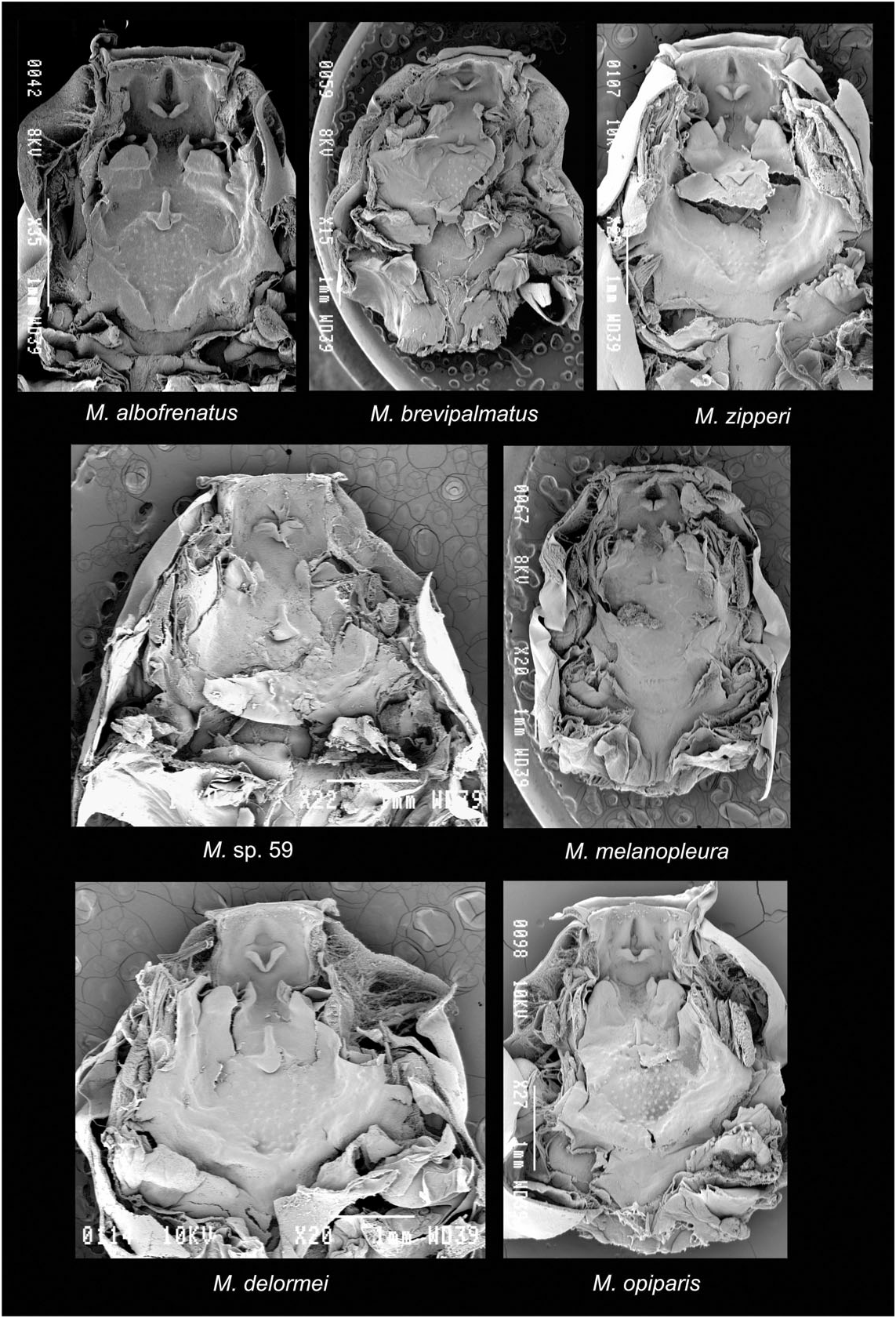
Buccal roof ( Fig. 4 View Figure 4 ): Prenarial arena round; one pair of flat and triangular prenarial papillae on the floor of arena, vertically orientated. Choanae moderately sized, transverse; anterior wall slightly elevated, smooth, bearing a triangular papilla halfway; narial valve slightly elevated, forming a triangular prominence wrapping medial extremity of choana whose tip orientated anteriorly. A large, flat, and rounded flap behind each choana on a prominence, probably homologous to postnarial papilla. Postnarial arena without ornamentation. Median ridge arrow-like, with tip directed posteriorly. No lateral ridge papillae. Buccal roof arena roughly triangular; a pair of tiny buccal roof arena papillae posterolaterally; interior of arena with about 50 faint pustules. Posterolateral ridge present, prominent but not well defined, shortly interrupted medially. Glandular zone present, interrupted medially, larger laterally than medially, with relatively large secretory pits. Dorsal velum massive, interrupted medially, elevated laterally, without papillae; secretory pits present on ventral surface of velum. A pressure cushion apparently present laterally on ventral surface of velum.
Variation of buccal structures: Shape of tongue anlage more or less stretched transversely and lingual papillae more or less elongate.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |