Pseudosinella orba Christiansen, 1961
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.275457 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6208556 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0B21878A-637F-FD11-F7EF-CCCAFED88FFD |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Pseudosinella orba Christiansen, 1961 |
| status |
|
Pseudosinella orba Christiansen, 1961
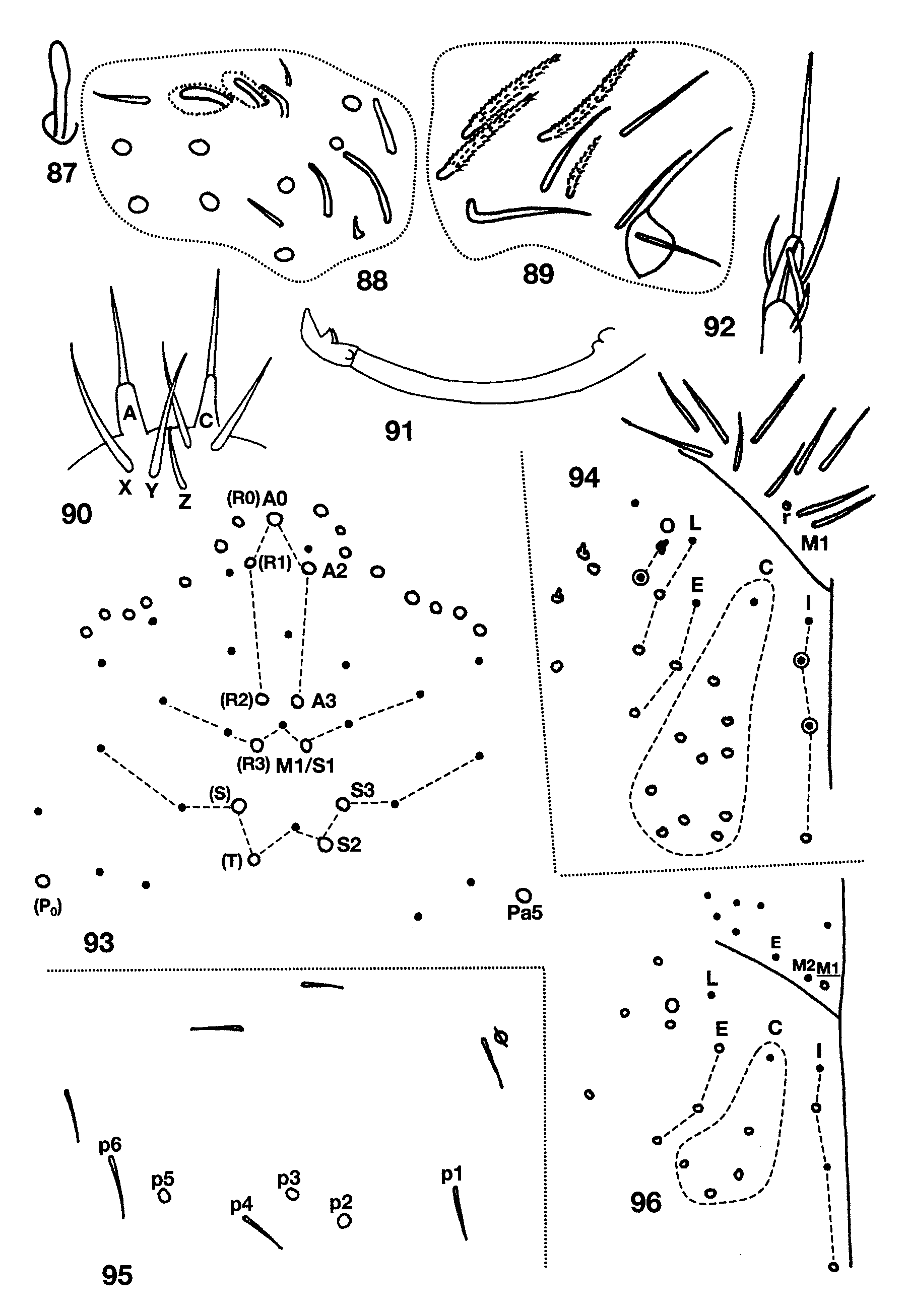
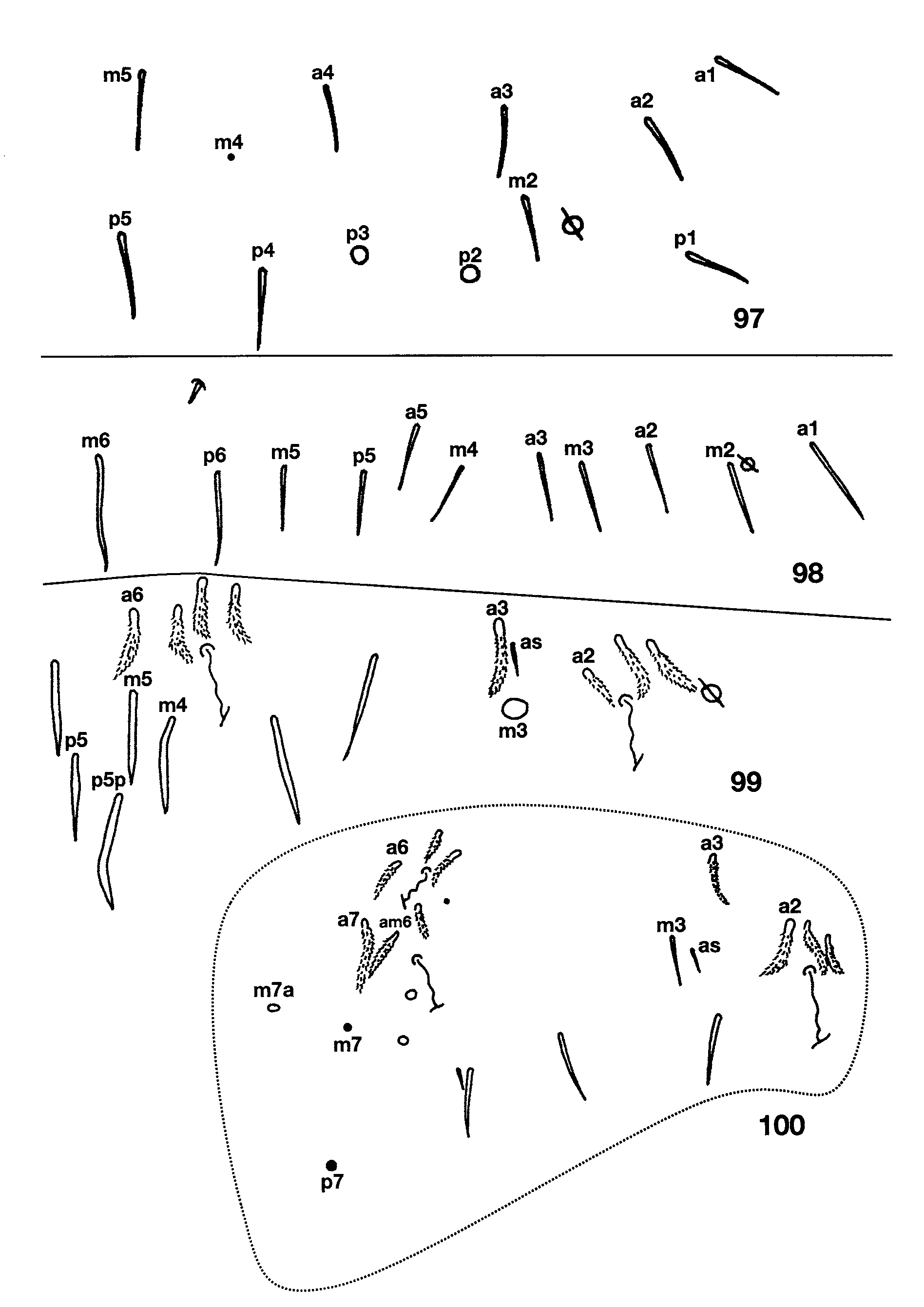
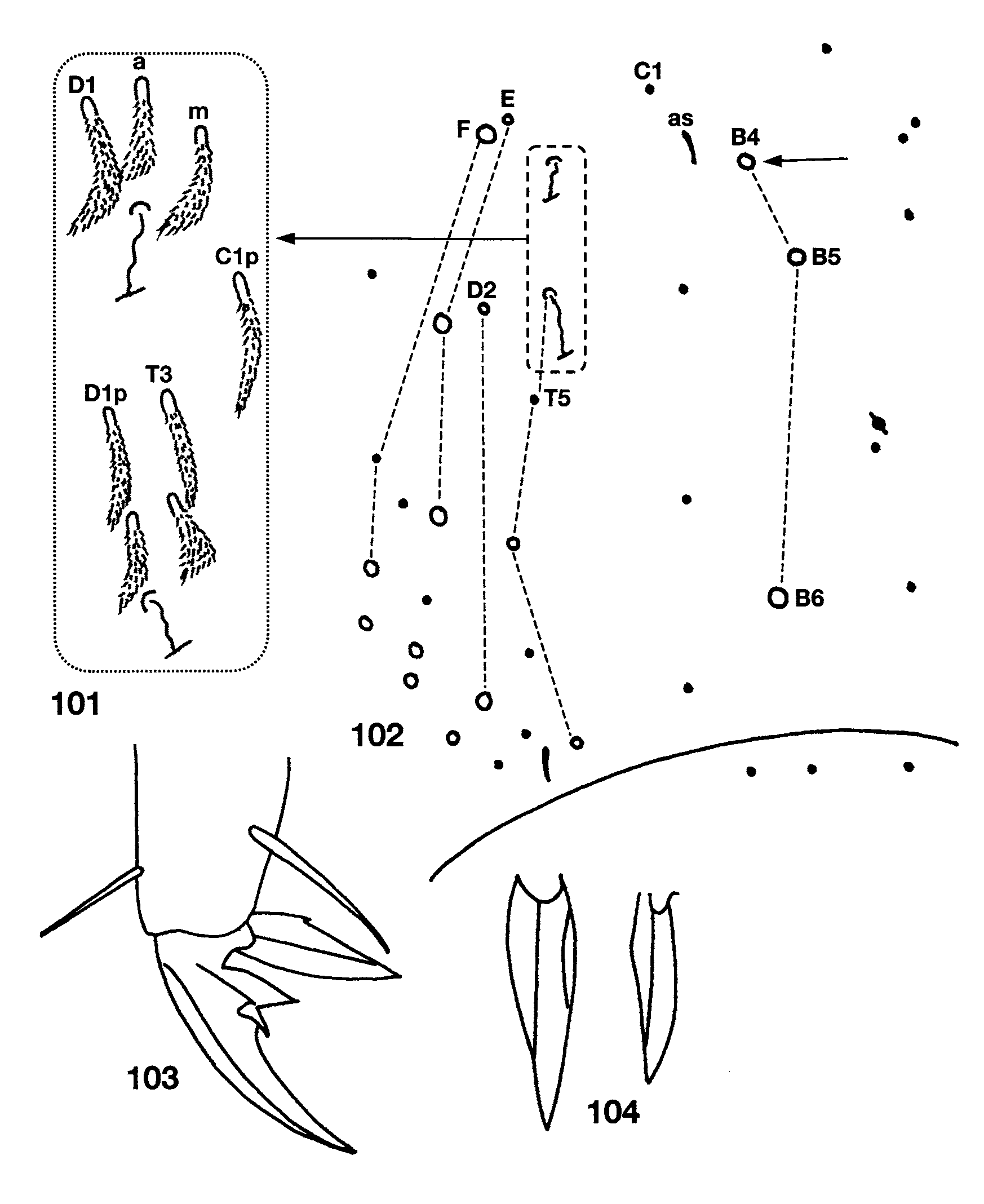
Figs 88–104 View FIGURES 87 – 96 View FIGURES 97 – 100 View FIGURES 101 – 104 , Table 6 View TABLE 6
Material Examined. West Virginia, MERCER Co., Honacker Cave, 2 individual on one slide and 2 others in alcohol; Chris’s Last Look, 2 individual on one slide and 2 others in alcohol. Virginia, SMYTHE Co., Dead Air Cave, water pool, 16 March 2000, 3 individuals on one slide.
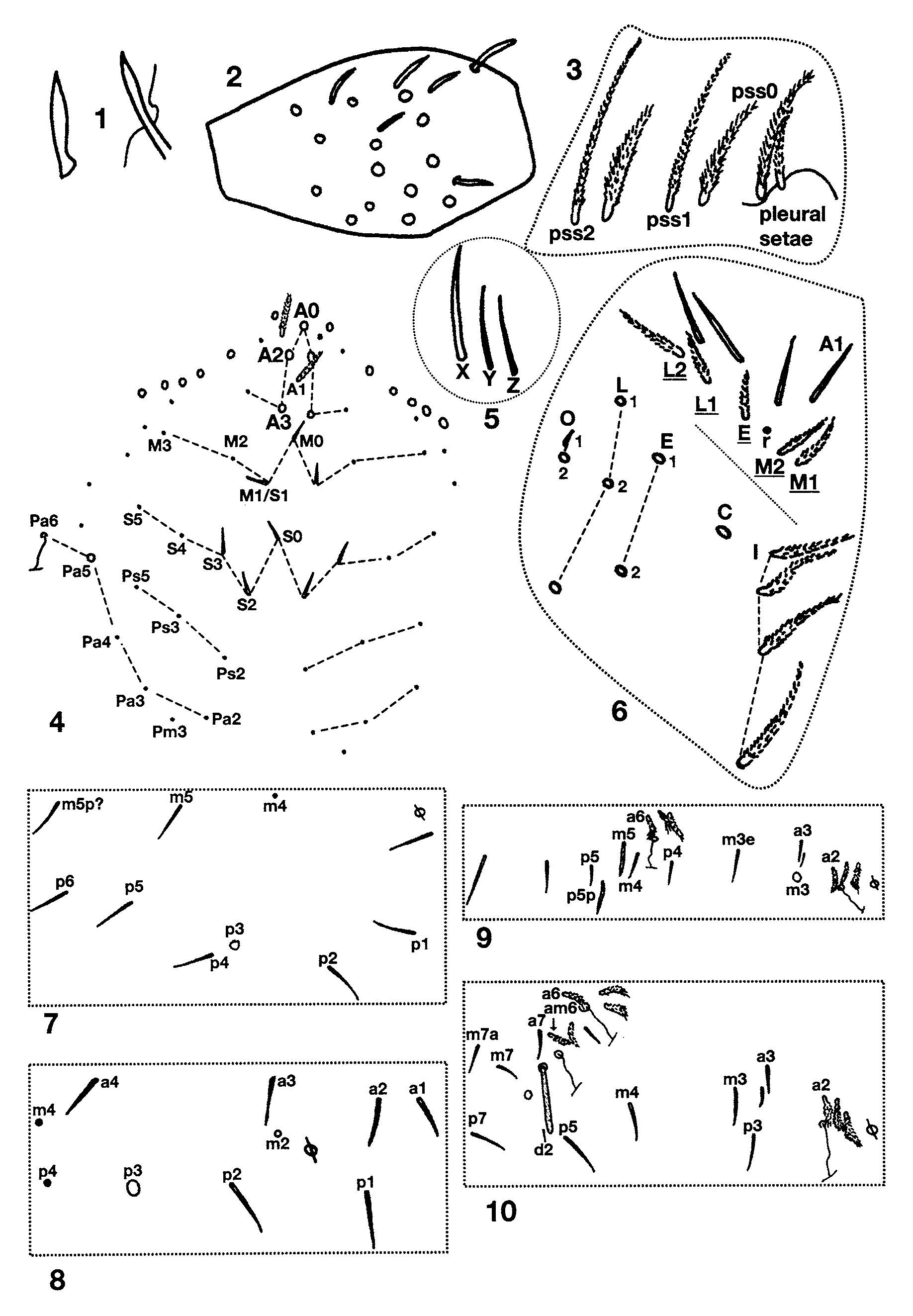
Descriptive notes. Length to 2.4mm; color in alcohol white, without trace of pigment. Subapical sense organ weakly clavate ( Fig. 87 View FIGURES 87 – 96 ). Ant. 3 sense organ formed by two thin walled rods in shallow pits ( Fig. 88 View FIGURES 87 – 96 ); the segment has additional basally-swollen, thin walled setae and conic sensilla near the usual sense organ. Dorsal head chaetotaxy ( Fig. 93 View FIGURES 87 – 96 ) includes 6–7 macrosetae along antennal base, and macrosetae A0, A2, A3, M1/S1, S2, S3 and Pa5; A1 ciliate, all other dorsal microsetae smooth; seta S0 closer to S2 than S3; M1/S1 just posterior to M2. Eyes absent. Prelabral and all labral setae smooth. Labral papillae obscured. Peristomal setae ( Fig. 89 View FIGURES 87 – 96 ) pss0 ciliate, pss1–2 smooth, pleural fold setae smooth. Ungulum of maxilla with 3 teeth. Labial papilla E ( Fig. 92 View FIGURES 87 – 96 ) with lateral process curved inwards and not reaching tip of papilla. Labial palp with proximal seta Z distinctly shorter than seta Y ( Fig. 90 View FIGURES 87 – 96 ). Labial chaetotaxy M1M2oEL1L2A1–5; in some individuals r visible as a translucent conic sensilla barely protruding beyond socket. Postlabial chaetotaxy ( Fig. 90 View FIGURES 87 – 96 ) with 4+4 setae along ventral groove, seta I1 always smooth, I4 always ciliate, I2–3 variable, either ciliate or smooth; C1 smooth, and 5–8 posterior ciliate setae not organized into a column; E1 smooth, E2 ciliate; L1 smooth, L2 ciliate but not modified; O1 modified into a conic microsetae similar to but longer than labial r, O2 smooth or ciliate. Inner macrochaetotaxy of body as 32/0100+3. Mesothoracic macrosetae p2, p3 and p5 present ( Fig. 95 View FIGURES 87 – 96 ). Metathorax ( Fig. 97 View FIGURES 97 – 100 ) with macroseta p2 and p3. Abd. 1 seta a6 absent, a3 and/or a5, displaced anteriorly out of the row ( Fig. 98 View FIGURES 97 – 100 ). Chaetotaxy of Abd. 2 ( Fig. 99 View FIGURES 97 – 100 ) with a6 and all supplementary setae fan-shaped; a2 ciliate, a2p absent; a3 fan-shaped, external to as, and surpassing tip of as; as not reaching socket of macroseta m3; m3e not reaching socket of as; socket of m5 modified as a normal macroseta, but seta itself subequal or shorter than seta p5p; p5p a short, ciliate mesoseta. Abd. 3 ( Fig. 100 View FIGURES 97 – 100 ) with a2, a6, am6, a7 and all supplementary setae fan-shaped or ciliate; mi shorter than ml; a3 ciliate, anterior to and far from as; as reaching m3, nearly half the length of m3; d2 reaching p5; a7 inserted close to, longer than, and reaching am6; m7 a normal microseta inserted anterior to p6; p7 a long microseta; m7a macroseta; 1–2 additional acuminate macrosetae present posterior to p7. Abd. 4 bothriotrichal complex as in Fig. 101 View FIGURES 101 – 104 : s absent; a, m, D1, Pi and Pe fan-shaped; C1p, T3 and D1p ciliate; T3 and D1p almost forming a row, T3 and D1p reaching Pi and Pe respectively. General chaetotaxy of Abd. 4 ( Fig. 102 View FIGURES 101 – 104 ) with macrosetae B4, B5, B6, T6, T7, D2, E1, D3, E2, E3, F1 and F3; microseta posterior to E3 present; macroseta B5 anterior to a line drawn between A5 and C2. Posterior setae on Abd. 4 usually 3+3. Trochanteral organ with 17–18 setae. Metathoracic femora with three blunt macrosetae inserted near the middle of the segment. Tenet hair ( Fig. 103 View FIGURES 101 – 104 ) acuminate, slightly shorter than unguiculus; unguiculus lanceolate with a small basal swelling and weakly truncate on third pair of legs; posterior lamella of all legs with small, clear tooth in the two largest individuals, but smooth on smaller specimens, all other lamellae smooth ( Fig. 104 View FIGURES 101 – 104 ). Unguis with three teeth ( Fig.103 View FIGURES 101 – 104 ): basal pair clearly unequal in size, shortest member of the pair smaller than distal unpaired tooth; unpaired tooth prominent; outer teeth short, not nearly attaining basal inner teeth, clearly seen only on pro- and mesothoracic legs, metathoracic claws apparently lacking outer teeth. Collophore with up to 11 distolateral setae; anterior face with 7–8 setae; posterior face with 3+3 distal setae. Dens with distal uncrenulate section at least 4x length of mucro ( Fig. 91 View FIGURES 87 – 96 ). Manubrial plate with 2 outer and 2 inner setae separated by 2 pseudopores. Apical mucronal tooth longer and narrower than basal tooth ( Fig. 91 View FIGURES 87 – 96 ).
Remarks. I have examined three individuals from Dead Air Cave in Smythe Co. Virginia kindly sent to me by Kenneth Christiansen and they differ from the material from West Virginia ( Table 6 View TABLE 6 ) in the structure of labial seta m1, number and structure of setae in postlabial row O ( Fig. 96 View FIGURES 87 – 96 ) and in that Abd. 4 B4 is a micro-, instead of a macroseta ( Fig. 102 View FIGURES 101 – 104 , arrow). Some of this variation (e. g., number of setae on postlabium, Th. 2 and Abd. 4) may be attributed to differences in body size between locations given that the smallest specimen from Mercer Co. is 1.8mm long whereas the largest specimen seen from Smythe Co. is just 1.3mm long.
However, populations considered by Christiansen and Bellinger (1998) as con-specific with P. o r b a also vary in details of the chaetotaxy of the head (dorsal), labium, postlabium, Th. 2, Th. 3 and Abd. 4 as shown in Table 6 View TABLE 6 . These different ‘populations’ may in fact represent isolated species in a species complex, but a detailed analysis of the geographic distribution of the variation must be completed before reaching a conclusion. In addition, the chaetotaxy of the types from Tennessee needs description.
Head Labium m1 Postlabium Th. 2 Macrosetae Th. 3 Abd. 4 Abd. 4
Macroseta S2 Column O Macrosetae Macroseta C1 Medial ‘Population’ Macrosetae Material Examined. GREENBRIER Co., Water Trough Cave, 3 on slides, 7 in alcohol; Tin Cave, 9 June 2004, 1 on slide.
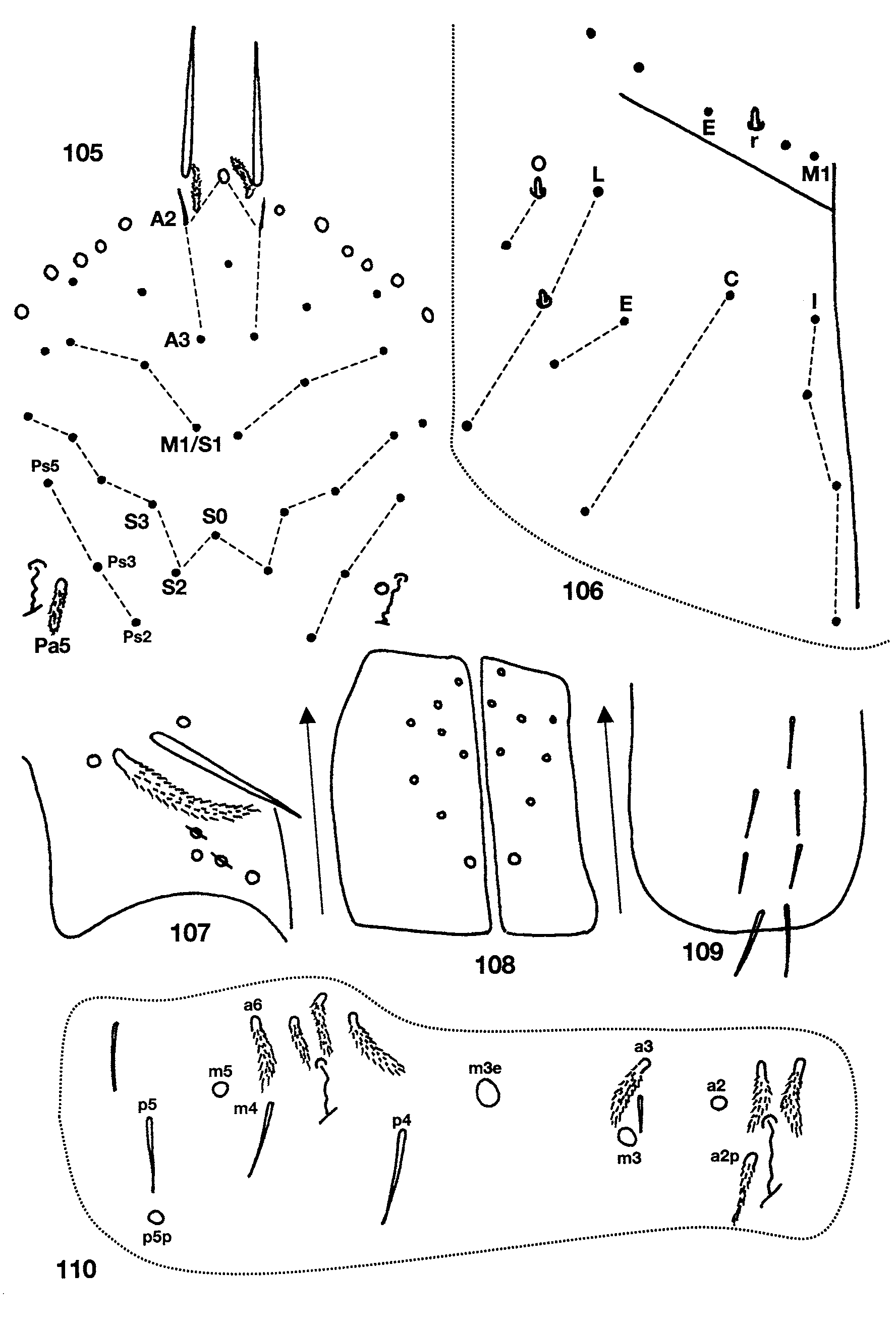
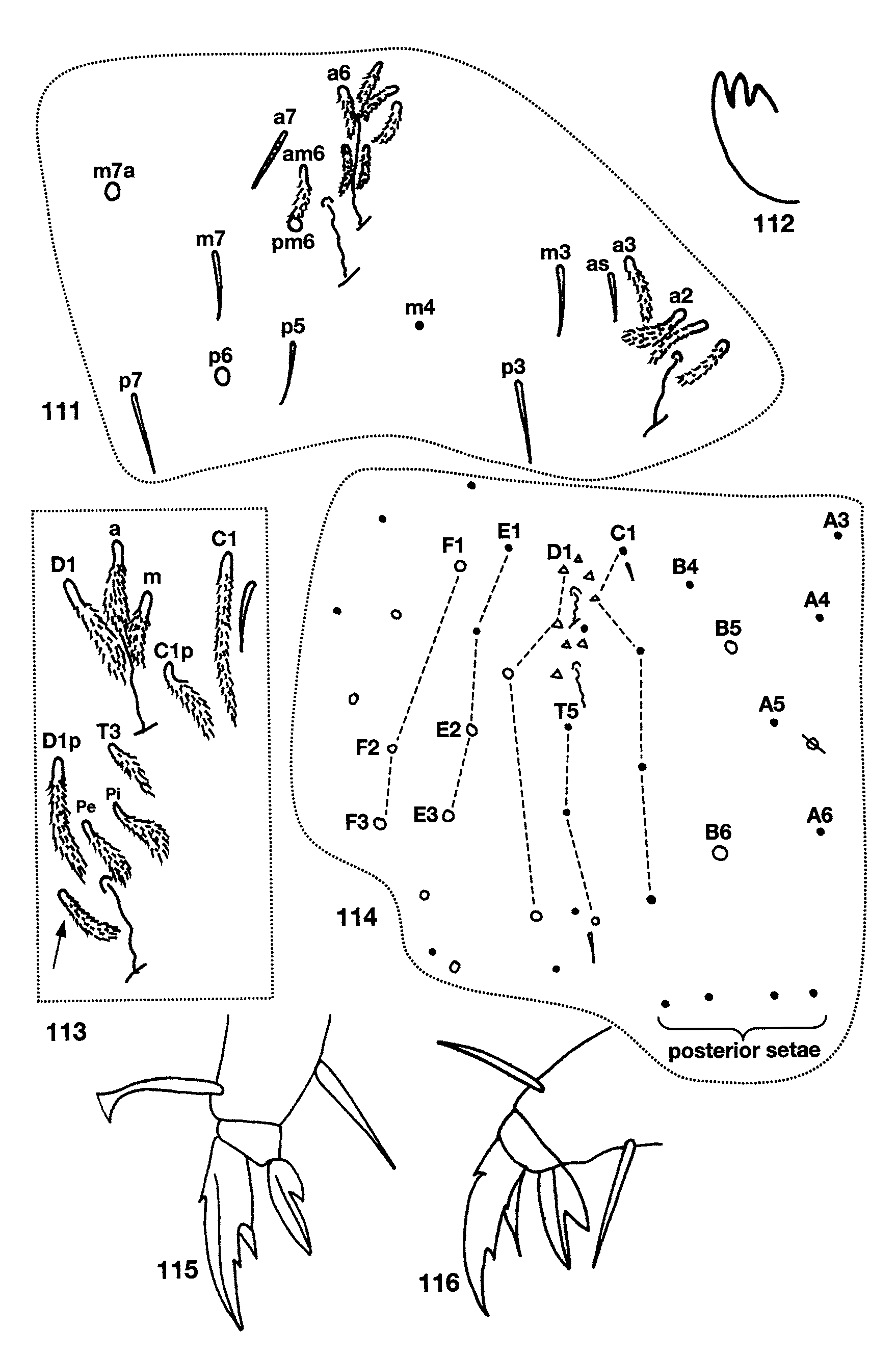
Descriptive notes. The dorsal chaetotaxy of the head includes 5–6 macrosetae along the base of the antenna and posterior to needle-shaped smooth setae ( Fig. 105 View FIGURES 105 – 110 ); A0 and Pa5 are the only macrosetae present, all other setae in series A (except A1, which is ciliate), M, S and Ps are short and smooth; anterior to A0 there is a conic sensilla (not shown in Fig. 105 View FIGURES 105 – 110 ); M0 absent. Macroseta Pa5 and postocular bothriotricha (Pa6) distinctly displaced medially and inserted closer to seta Ps3 than Ps5 (cf. Figs. 105 View FIGURES 105 – 110 and 4 View FIGURES 1 – 10 ). Pleural and peristomal setae smooth and undifferentiated. Lateral appendage of labial palp papilla E curved internally and surpassing tip of papilla. Three of the four individuals examined have labial chaetotaxy as M1M2rEL1L2 ( Fig. 106 View FIGURES 105 – 110 ), one individual with m1 shorter than M2. All postlabial setae smooth in three of the four individuals examined, in one individual from Water Through Cave most setae are very weakly, but noticeably ciliate: columns I, C, E, L and O with 4, 2, 2, 3, 2 setae; L2 and O1 are conic to weakly blunt sensilla ( Fig. 106 View FIGURES 105 – 110 ). Ungulum of maxilla with three teeth ( Fig. 112 View FIGURES 111 – 116 ). Formula for inner macrochaetotaxy of body as 00/ 0300+2. Seta a6 on Abd. 1 present. Abd. 2 ( Fig. 110 View FIGURES 105 – 110 ) with a6, a3 and all supplementary setae around bothriotricha fan-shaped; a2p ciliate or smooth; macrosetae a2, m3, m3e, m5 and p5p present. Abd. 3 ( Fig. 111 View FIGURES 111 – 116 ) with a2, a6 and all supplementary setae around bothriotricha fan-shaped; a3 ciliate, displaced posteriorly as to almost form a row with m3 and as; a7 ciliate, anterior to and reaching am6; d2 absent; p6 posterior to p5 and m7; m7a a macroseta. Bothriotrichal complex of Abd. 4 ( Fig. 113 View FIGURES 111 – 116 ) with T3 ciliate, all other setae fanshaped; s absent; T3 and D1p almost aligned into a row; D1p reaching Pe; a supplementary fan-shaped seta present between Pe and T5 (arrow, Fig. 113 View FIGURES 111 – 116 ). General chaetotaxy of Abd. 4 ( Fig. 114 View FIGURES 111 – 116 ) with macrosetae B5, B6, T7, F2, D2, D3, E2, E3, F1, F3, and two others probably belonging to series Fe present, B5 anterior to a line drawn between A5 and C2; C1 a ciliate microseta; a supplementary microseta present between E1 and E2. Abd. 4 Posterior setae 4+4. All individuals have claws with three inner teeth, with one of the basal teeth clearly larger than the other, unguiculus with a large posterior tooth. In the individuals from Water Trough Cave the difference in size between the basal paired teeth is less marked than in the specimen from Tin cave (cf. Figs 115, 116 View FIGURES 111 – 116 ). In addition, the posterior unguicular tooth is longer in the individual from Tin cave than in those from Water Trough Cave. Anterior face of ventral tube with 1+1 distal macrosetae and seven other basal setae ( Fig. 108 View FIGURES 105 – 110 ); posterior face with 1+1 distal and 5 basal setae ( Fig. 109 View FIGURES 105 – 110 ); lateral vesicles view obstructed in all specimens examined. The three individuals from Water Trough Cave have one smooth seta on the dorsodistal row of the manubrium ( Fig. 107 View FIGURES 105 – 110 ), 1 internal and 1 external setae on the manubrial plate and short spatulate tenet hairs on all feet (fig. 115), whereas in the individual from Tin Cave all manubrial setae are ciliate, the manubrial plate has two external setae and all tenent hairs are acuminate (fig. 116).
Remarks. Christiansen and Culver (1969) dealt with the extensive variation seen in this species across North America. The descriptive notes presented above are provided to place the West Virginian collections in the context of the geographic variation of the species and to add some characters not considered by previous authors.
Pseudosinella violenta is distinguished from other blind North American Pseudosinella by a combination of characters which include having the postocular bothriotricha and macroseta Pa5 displaced dorsomedially on the head, having a large posterior unguicular tooth, all posterior setae on labial triangle, and the anterior row of postlabial setae smooth, Abd. 2 with five macrosetae, Abd. 3 with setae a3, as and m3 forming an irregular row and macroseta p6 displaced posteriorly as to be inserted between p5 and p7, Abd. 4 with macroseta B5 displaced interiorly, closer to C1 than B6, and supplementary setae between Pe–T5 and E1–E2.
absent
1Enlarged and roughly ciliate, but not a macroseta in the sense used here for Abd. 4 setae in series B.
The characteristic displacement of the cephalic bothriotricha and macrosetae Pa5 is rare among Pseudosinella species, were it has been reported (to my knowledge) only in P. rolfsi Mills, 1932 , P. folsomi ( Mills, 1931) , P. ashmoleorum Gama, 1988 , P. gamae Gisin, 1967 , and P. halophila Bagnall, 1939 (sensu Fjellberg 2008). These six species, plus P. bellingeri Wang, Chen & Christiansen, 2002 (relative position of the postocular bothriotricha unknown) have been considered as part of an informally defined species group (e.g., Wang et al. 2004). Of the seven species, P. bellingeri and to some extent P. folsomi and P. rolfsi can be unambiguously distinguished, but the separation between the European forms ( ashmoleorum , gamae and halophila ) from P. v i o l e n t a as circumscribed by Christiansen & Bellinger (1998) is not clear. Table 7 View TABLE 7 presents a list of characters used to separate species in this group. According to Christiansen and Culver (1969) P. violenta from Central Texas and south through Mexico and South America have Abd. 4 seta s, whereas in North American populations north of Texas, seta s is absent. Christiansen and Culver (1969) also report great variation in claw complex structure, with some individuals having three inner teeth while others only having two teeth. This circumscription of P. v i o l e n t a, leads me to concluded that P. gamae is a junior synonym of P. violenta (Central and South American populations), P. ashmoleorum is a junior synonym of P. halophila (sensu Fjellberg 2007), which in turn differs from some North American populations of P. v i o l e n t a only in the absence of one inner ungual tooth. I refrain from proposing a formal synonymization of these names until I have the opportunity to study types or topotypical material of each species. In any case, it is possible that the great interpopulation variation reported for P. violenta in the Americas masks a species complex, and that some of the names applied to European populations may be available to identify particular lineages within the complex.
TABLE 6. Differences between populations identified as Pseudosinella orba in Christiansen and Bellinger (1998) (C & B) and individuals described here from new collections from Mercer Co., WV and Smythe Co, VA. macroseta C 1 + = present or – = absent.
| WV, Mercer Co. present smooth 2–3 setae; O1 (New) modified | 3 | 2 | – | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WV, Mercer Co present smooth? (C&B, 1998) | 3 | 3 | + | 2 |
| VA, Smythe Co. present ciliate 1 seta; O1 (New) normal | 2 | 2 | – | 2 |
| VA, not Smythe present ciliate? Co. (C&B, 1998) | 3 | 3 | – | 2 |
| NC, Macdowell absent smooth? Co. (C&B, 1998) | 2 | 2 | + | 2 |
| Pseudosinella violenta (Folsom), 1924 Figs 105–116, Table 7 |
TABLE 7. Characteristics of members of the P. violenta species group. M = macroseta; µ = microseta; + = present; – =
| P o st oc u l a r Abd. bothriotricha 4 s m ed i a l l y Species displaced | Abd. 2 a2p | Abd. 2 a2 | Abd. 2 m3 | Abd. 2 m3e | I n ne r C l a w Teeth | Tenet Hair | Abd. 4 C1 | P o s t er i o r U n gu i c u l a r Tooth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| violenta + + – | + | M | M | M | 2–3 | clavate acuminate | µ 1 | + |
| halophila + – | + | M | M | M | 2 | acuminate | µ | + |
| ashmoleorum + – | + | M | M | M | 2 | acuminate | µ | + |
| gama + + | + | M | M | M | 3 | clavate | µ | + |
| bellingeri ? – | – | M | M | µ | 4 | clavate | M | + |
| folsomi + + | + | M | M | M | 3 | clavate | M | – |
| rolfsi + – | + | µ | µ | M | 3 | clavate | µ 1 | + |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |