Paramacroxiphus maculatus, Ingrisch, 2008
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.1755.1.1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5123670 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0638878C-FFD6-FFFB-19EC-FAEFFB95AA29 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Paramacroxiphus maculatus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Paramacroxiphus maculatus View in CoL sp. n.
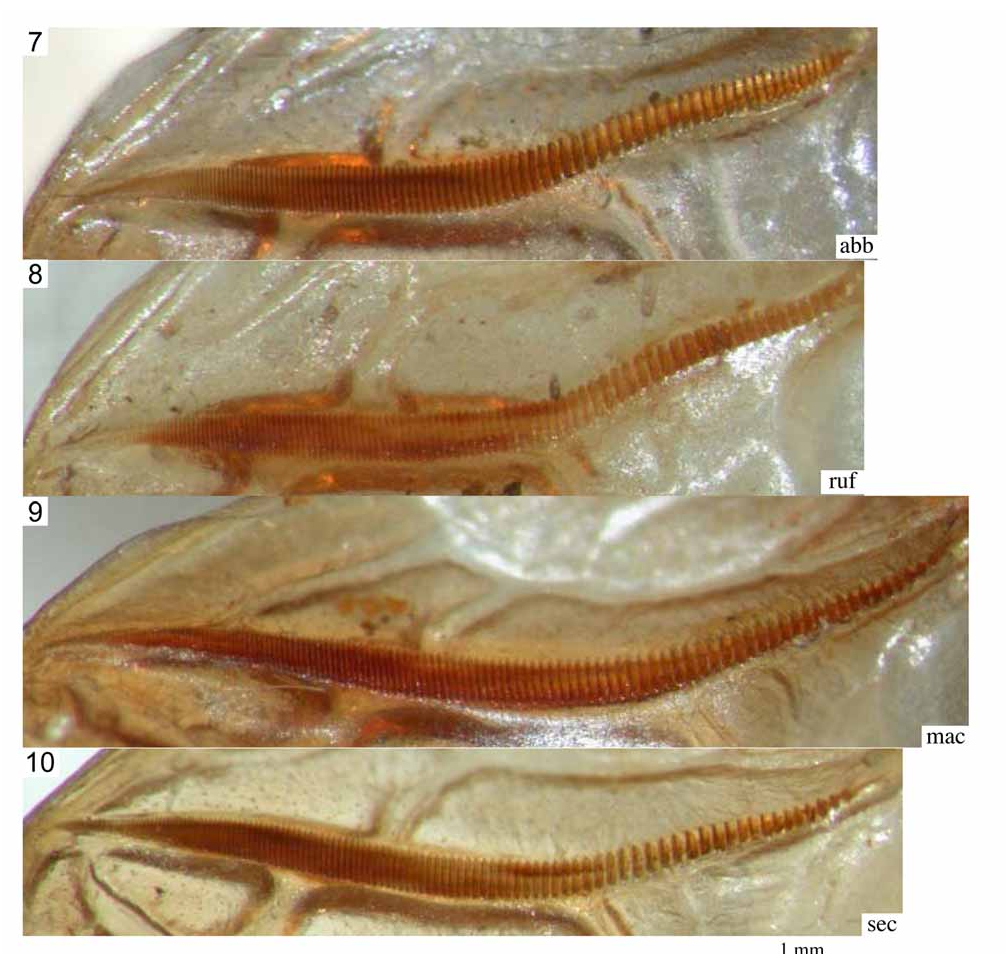
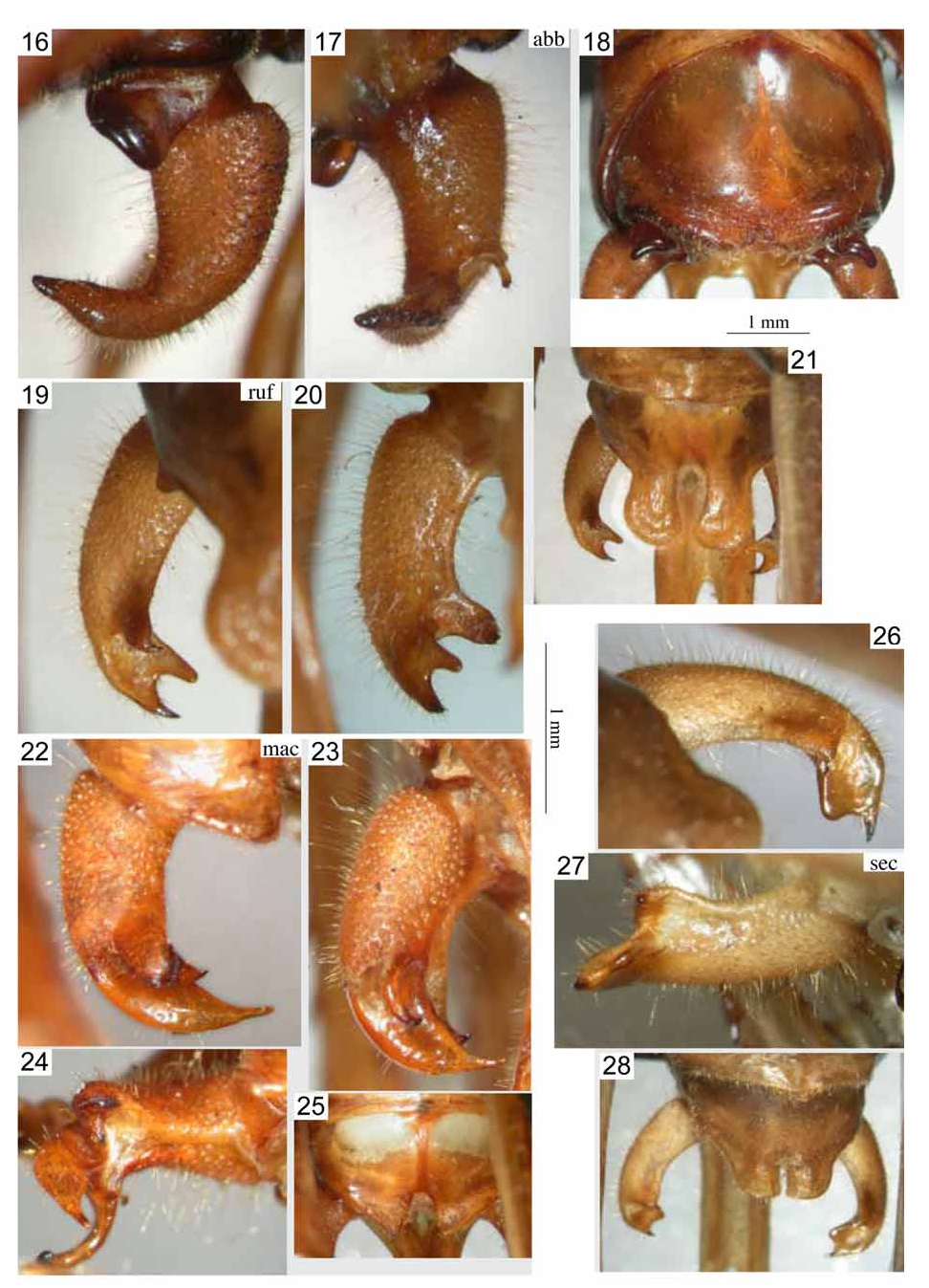
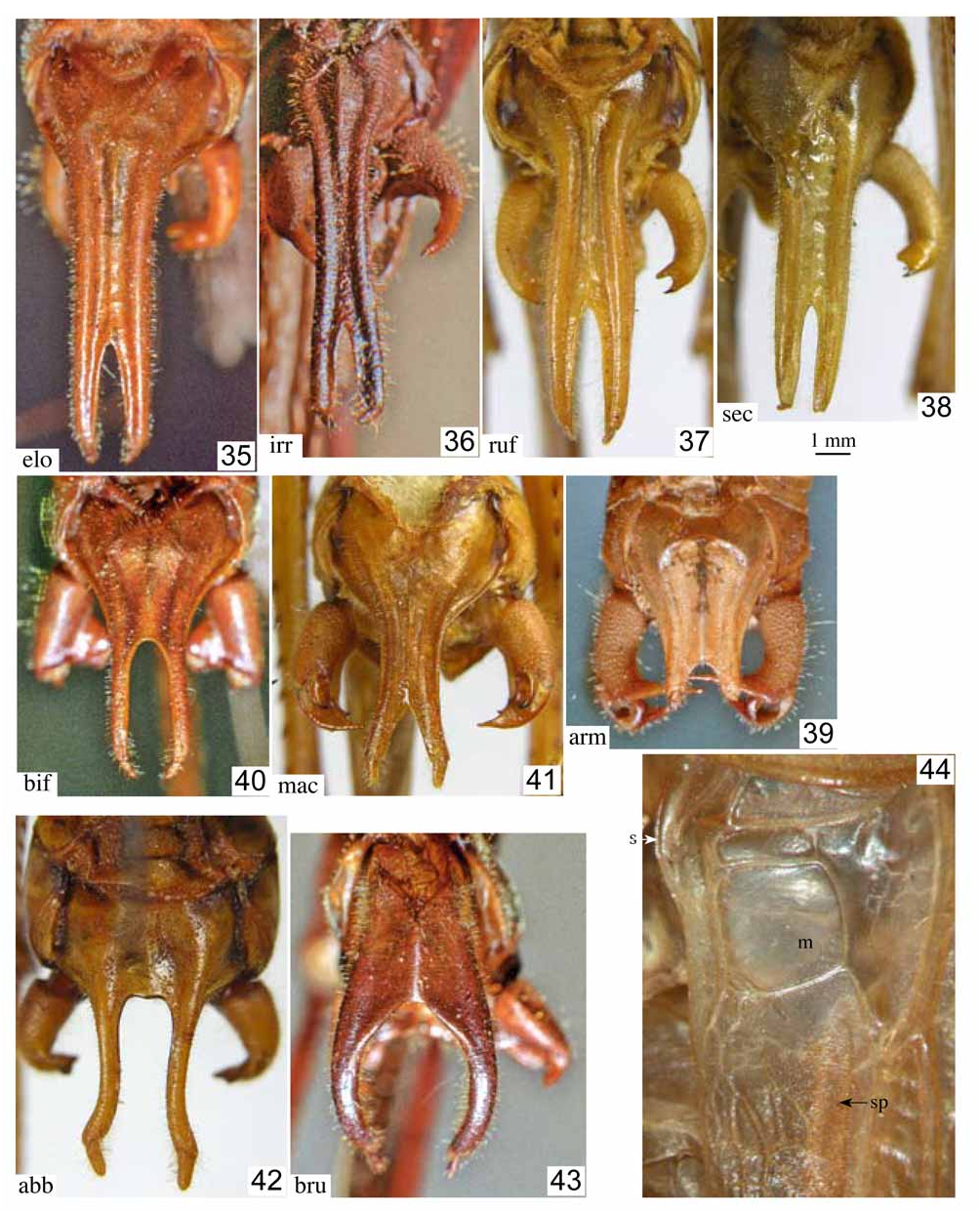
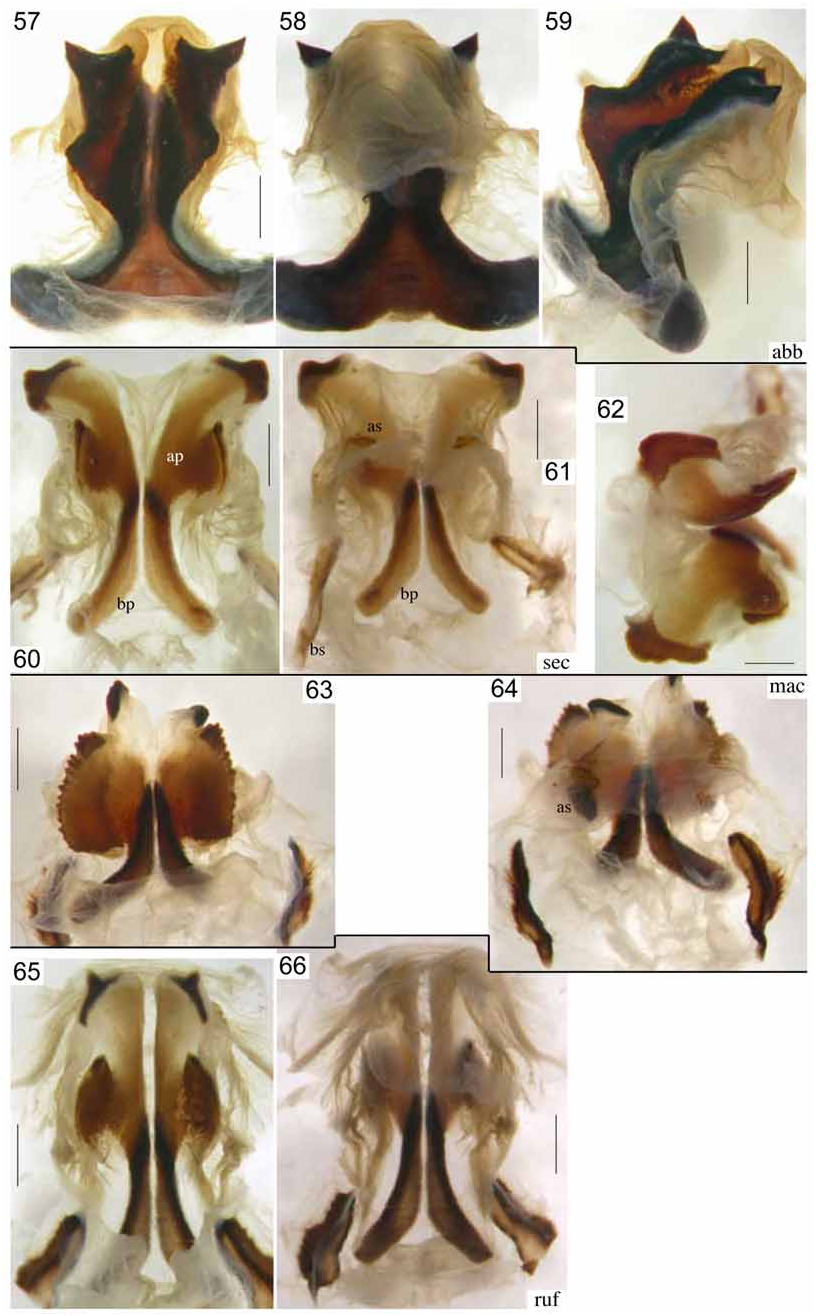
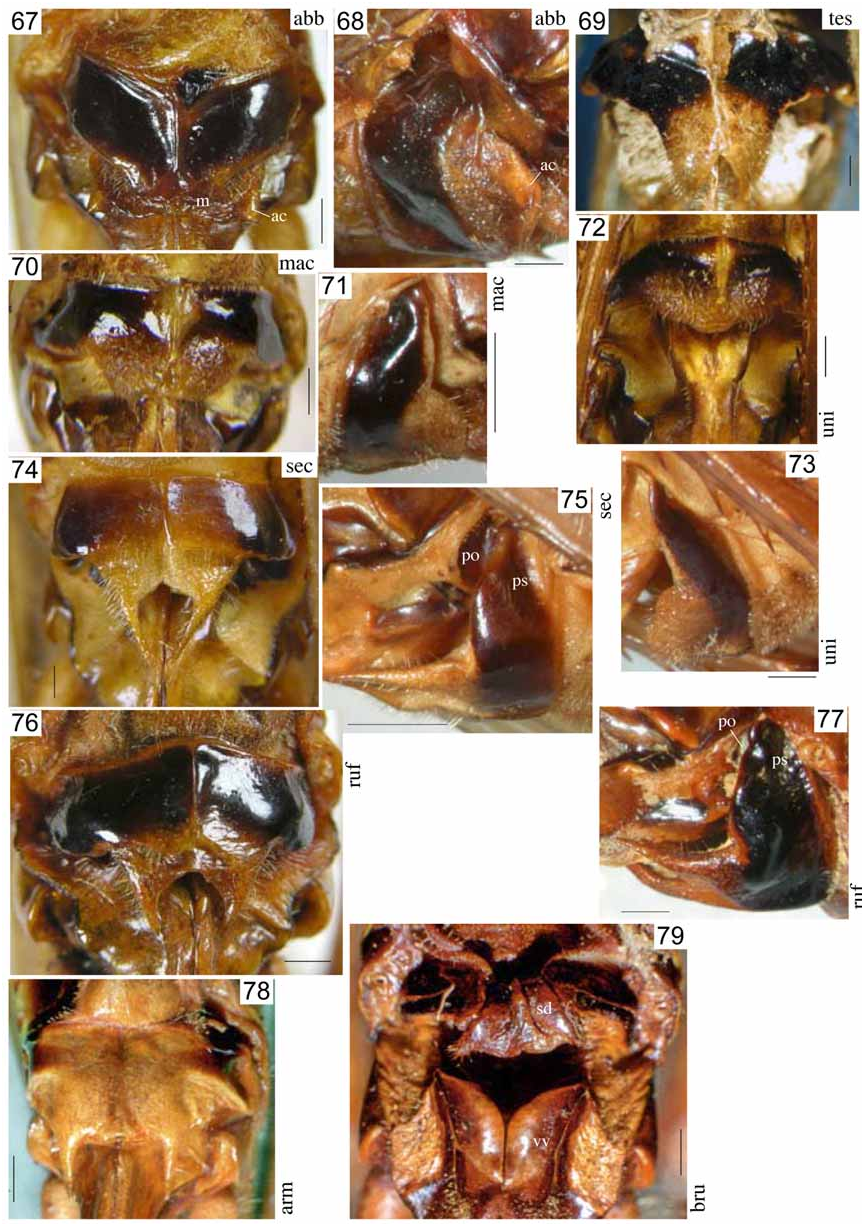
Figs. 9 View FIGURES 7–10 , 22–25 View FIGURES 16–28 , 41 View FIGURES 35–44 , 63–64 View FIGURES 57–66 , 70–71 View FIGURES 67–79 , 95
Holotype (male): Indonesia: Papua, Neth. New Guinea Exp., Star Range, Katem , 200 m, 26.vi.1959 . Holotype in Collection of Fer Willemse , Eygelshoven, Netherlands [later to be deposited in RMNH] .
Specimen examined (Allotype): 1 female, Indonesia: Papua, Star Range, Tiel, 3.ix.1959 (RMNH).
Description. Fastigium verticis: eye diameter 1.3: 2.0 mm; projecting 0.8 mm in front of eyes. Tegmen narrowing in basal half and then slightly widening again towards apex (tegmen width in middle 6.2 mm, near apex 7 mm). Femora with the following number of spines on ventral margins: profemur 7–8 external, 6–7 internal; mesofemur 3–7 external, 3 internal; postfemur 13–15 external, 13–17 internal.
Male.—Stridulatory file 3.39 mm, curved in about middle, with large teeth in basal, narrow teeth in apical half ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 7–10 ); with about 137 teeth or 40.4 teeth per mm; in middle 37.6 teeth per mm, in basal half 20.2 teeth per mm. Mirror quadrate with curved margins, apex convex; 1.86 mm long, 1.80 mm wide. Tenth abdominal tergite globular; apical margin roundly excised in middle and triangularly projecting at both sides of excision ( Fig. 25 View FIGURES 16–28 ). Epiproct circa triangular with a shallow groove in middle. Paraprocts with a dorso-ventrally compressed projection. Cerci with a short, stout, cylindrical but slightly compressed and curved basal trunk and three apical projections: dorsal projection dorso-ventrally compressed, at apex with an acute-triangular ventral tooth; medial projection dorso-ventrally compressed, curved mediad and narrowing to subacute apex; ventral projection strongly curved, hook-shaped, compressed in basal area, otherwise narrow, rounded; apex of cercus blunt but with a minute spinule ( Figs. 22–23 View FIGURES 16–28 ). Subgenital plate semicircular in basal area with central part largely prolonged behind; prolongation with almost parallel lateral margins and a weak medial carinula; apical area split into two narrow deviating branches; styli short, slightly compressed dorso-ventrally ( Fig. 41 View FIGURES 35–44 ).
Titillators separate, basal parts simple; apical parts with two branches: lateral branch large, circa rectangular, with dentate, granular margin; internal surface matt with fine striation; apical branch hyaline with curved, sclerotised, granular margin ( Figs. 63–64 View FIGURES 57–66 ). Baso-lateral sclerites elongate with irregular margins and a longitudinal crest.
Coloration. Head and pronotum dark castaneous brown. Antennal scrobae, part of ventral sides of scapus and pedicellus, mandibles and baso-lateral areas of labrum black. Pronotum with disc paler than paranota but with anterior margin and three spots in midline black; paranota dark brown with pale dots, posterior margin and humeral area black. Tegmen yellowish brown with castaneous spots. Legs yellowish brown; anterior tibia with dark marks in tympanal area; median and posterior femora with black spots on dorsal surface.
Female. Subgenital plate divided in midline by a fine membranous suture; medial area prolonged behind into a membranous lobe with bilobate apex ( Figs. 70–71 View FIGURES 67–79 ).
Coloration. Almost uniformly ochre, somewhat marmorated. Frons yellowish brown, mandibles dark brown. Tegmen light brown with scattered and little conspicuous brown spots. Femora marmorated, mid- and hind femora in apical area medium brown, interrupted by a yellowish ring. Ovipositor medium brown. Subgenital plate dark brown, midline and apical lobe light.
Measurements: body male 33, female 33; pronotum male 9.5, female 10.7; tegmen male 42.5, female 45; postfemur male 25, female 28; ovipositor 46; -height 3.0.
Diagnosis. P. maculatus belongs to the species with globose tenth abdominal tergite in male. From the other three species with that character, P. aberrans , P. securiformis , and P. rufus , it differs by the distinct but short triangular apical projections of the tenth tergite as well as by the shapes of the cerci, subgenital plate and titillators. The male cerci are unique for the apex with a wide, compressed, central projection, a short dorsal projection and a long, narrow ventral projection. The male subgenital plate is intermediate between a rather normal shape as in P.armatus and the shape in the four species with a very long projection. With regard to the latter character, it comes close to P. bifasciatus ; it differs by the subgenital plate being only excised in apical area while it is divided for almost half of its length in P. bifasciatus . The titillators are characteristic for the apical part with a wide lateral branch with zigzag margin and the main branch hyaline with only the apical cap sclerotised. The female subgenital plate has a membranous apical part without projections or spines. In this character it only agrees with P. uniformis . The shapes of the membranous area and of the basal sclerites of the subgenital plate differ between both taxa.
Male and female differ in coloration. It is supposed that this is not of specific value but the specimens represent different colour morphs.
Etymology. The name of the new species refers to the maculated tegmina.
| RMNH |
National Museum of Natural History, Naturalis |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.