Elattoma cerambycidum Rahiminejad & Hajiqanbar
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.204757 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5677139 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/056E879D-DA69-C241-5AD3-A3A8A5E3FC11 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Elattoma cerambycidum Rahiminejad & Hajiqanbar |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Elattoma cerambycidum Rahiminejad & Hajiqanbar sp. nov.
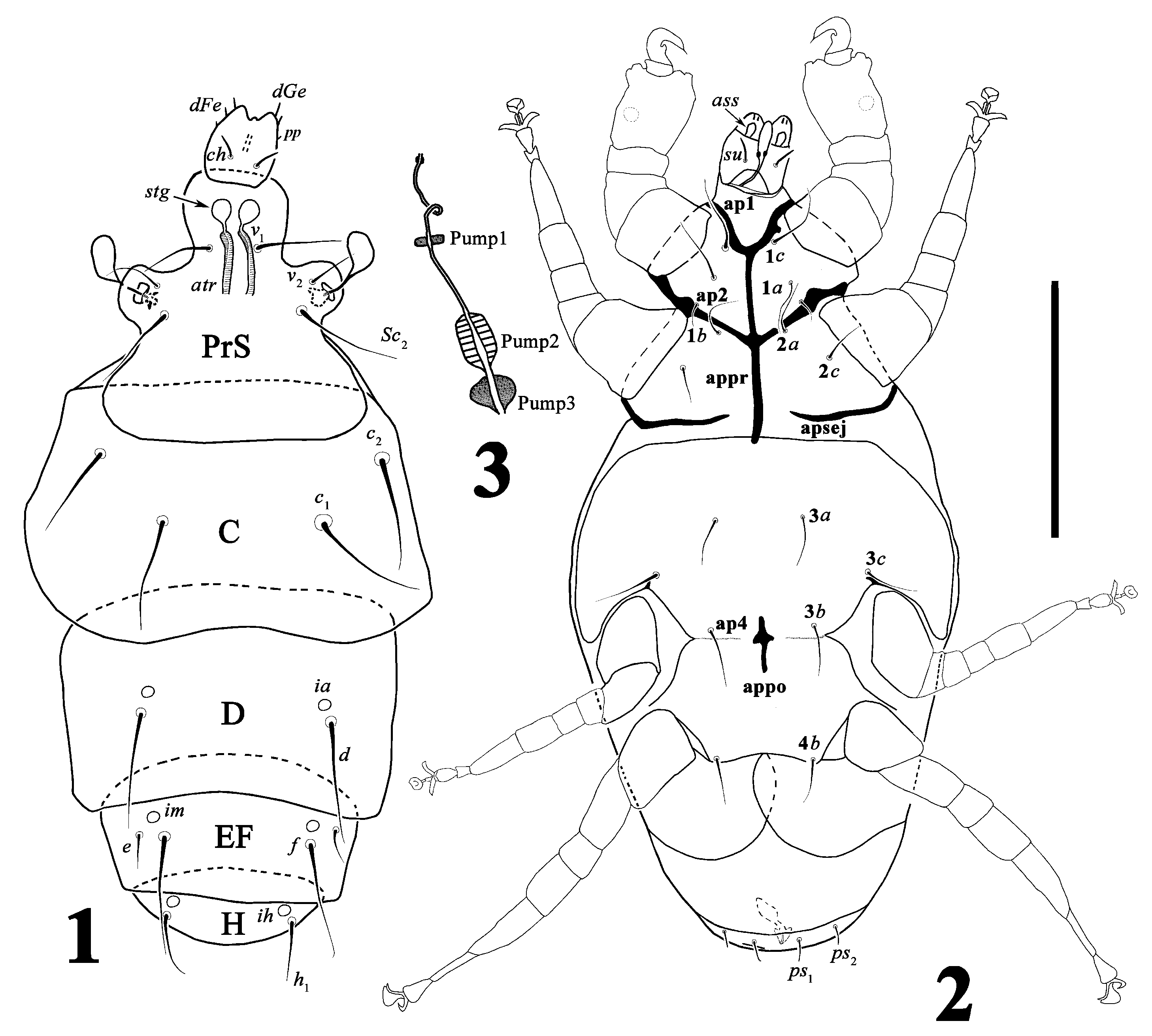
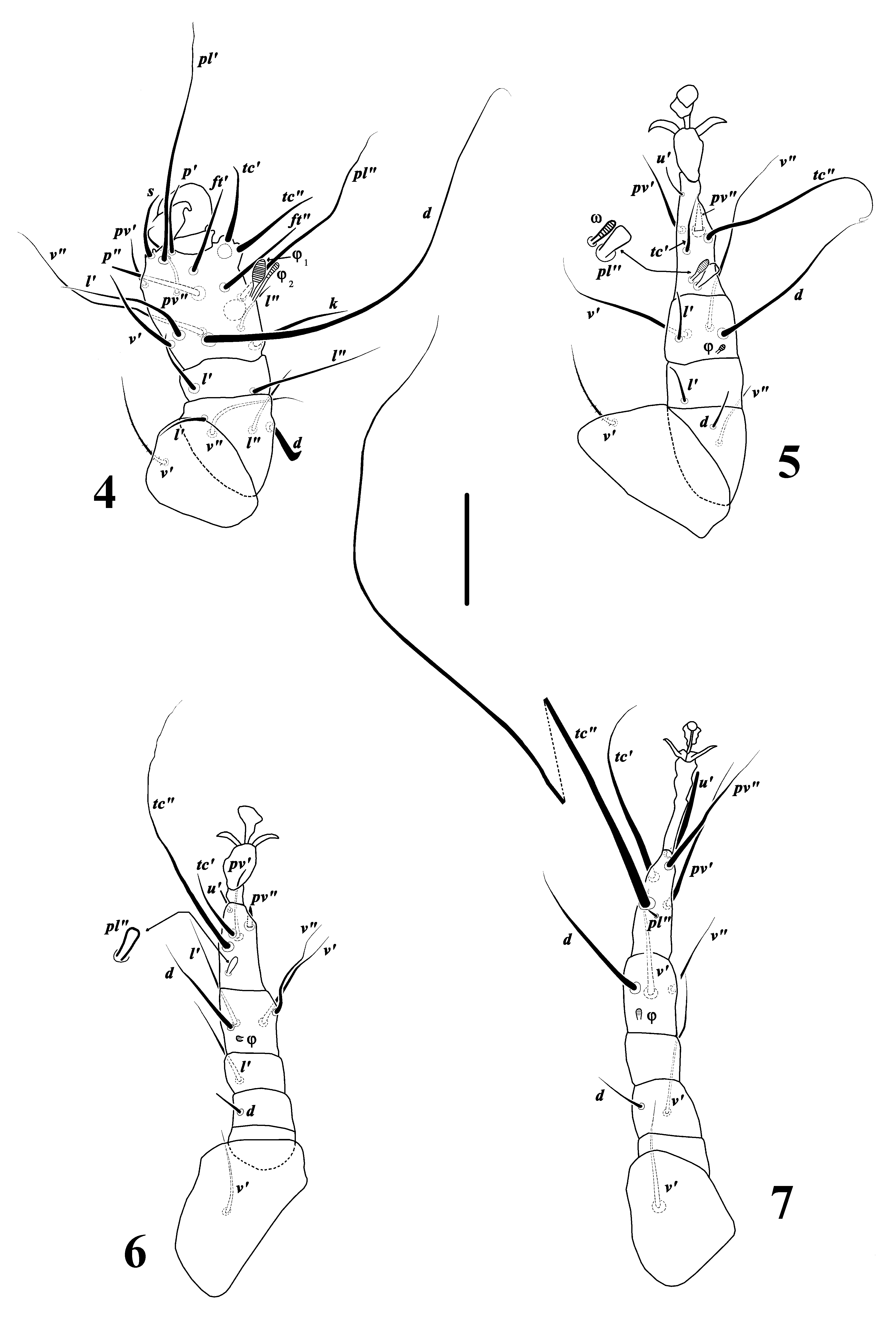
( Figures 1–7 View FIGURES 1 – 3 View FIGURES 4 – 7 )
Differential diagnosis. The new species is close to E. kornilovi Khaustov, 2000 but differs from it by seta f more than three times longer than seta e (seta f two times longer than seta e in E. kornilovi ) and seta c 1 longer than seta c 2 (seta c 1 shorter than seta c 2 in E. kornilovi ). The new species is also resembles E. abeskoun sp. nov. but differs from it by solenidion φ2 longer than φ1 (solenidion φ2 shorter than φ 1 in E. abeskoun ), seta e shorter than h 1 (seta e longer than h 1 in E. abeskoun ), seta f more than three times longer than e (seta f less than two times longer than e in E. abeskoun ) and setae h 1 pointed (setae h 1 blunt-ended in E. abeskoun ).
Phoretic female. Length of idiosoma 172 (169–179), width 89 (83–91).
Gnathosoma ( Figs. 1, 2 View FIGURES 1 – 3 ). Gnathosomal capsule subquadrangular, dorsally with a median small apodeme, one pair of cheliceral setae ch 2 (2–3) needlelike and one pair of small postpalpal setae pp located anterolaterally to setae ch; ventrally with one pair of subcapitular setae su 4 (4–5) needlelike; each palp dorsally with two needlelike setae dFe 2 (2–3) and dGe 3 (3–4), dGe longer than dFe, ventrally with accessory setigenous structure (ass), two solenidia and one tiny rod-shape structure; chelicerae indiscernible; pharyngeal system ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1 – 3 ) with three pumps, pump 1 smallest, pump 2 the largest and striated, pump 3 oval-shaped.
Idiosomal dorsum ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 3 ). Rounded stigmata visible in anterior part of prodorsal shield with conspicuous atria; all dorsal setae smooth and pointed; prodorsal shield with one pair of capitate trichobothria and three pairs of setae v 1 20 (18–20), v 2 12 (11–12) and sc 2 22 (22–23), seta v 1 longer than seta v 2, both shorter than seta sc 2; all tergites smooth, tergite C with two pairs of setae c 1 25 (24–26) and c 2 22 (22–23), seta c 1 longer than c 2, posterior border of tergite C slightly concave medially; tergite D with setae d 25 (24–27) and one pair of cupuli ia; tergite EF with two pairs of setae e 8 (7–8) and f 27 (26–27) and one pair of cupuli im, seta f more than 3 times longer than seta e; tergite H with only one pair of setae h 1 14 (13–15) and one pair of cupuli ih; Distances between dorsal idiosomal setae: v 1– v 1 11 (11–13), v 2– v 2 35 (35–37), sc 2– sc 2 32 (30–34), c 1– c 1 37 (36–37), c 2– c 2 61 (58–62), d–d 44 (43–47), e– e 44 (44–47), f–f 33 (31–34), h 1– h 1 29 (26–31).
Idiosomal venter ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1 – 3 ). Ventral plates smooth; all ventral setae smooth and pointed except setae ps 1 and ps 2 which are needlelike; apodemes 1 and 2 reaching to presternal apodeme (appr), sejugal apodeme (apsej) not reaching to appr, no apodemes III and V, apodeme IV vestigial, poststernal apodeme (appo) very short; posterior border of poststernal plate bi-parties; epimeres I with three pairs of setae 1 a 11 (10–12), 1 b 4 (4–5) and 1 c 12 (11–12), 1 b shortest, 1 a and 1 c subequal; epimeres II with two pairs of setae 2 a 9 (8–10) and 2 c 10 (8–11), 2 a and 2 c subequal; epimeres III with three pairs of setae 3 a 13 (13–15), 3 b 13 (10–13) and 3 c 12 (11–13), all subequal; epimeres IV with only one pair of seta 4 b 11 (10–11); tergite PS with two pairs of setae ps 1 6 (6-6) and ps 2 5 (4–5).
Legs. Leg I ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 4 – 7 ) thicker and shorter than other legs; setal formula: Tr1-Fe4-Ge2-TiTa17(2) (number of solenidia in parenthesis). Tibiotarsus with one large claw; solenidion φ1 5 (5–6) prominent and finger shaped; solenidion φ2 7 (7–8) uniformly thin, φ2 longer than φ1, with six eupathidial setae (p’, p”, ft’, ft”, tc’ and tc”) bluntly ended, tc’ and tc” on pinnaculum, setae pl’ and pl” whip-like, setae d whip-like and longest on leg I and almost two times longer than pl’, seta v” more than two times longer than v’, seta l’ twice as long as l”; genu with seta l” longer than l’; femur with seta d hook-like, seta l” longer than l’, seta v” sparsely barbed and longer than l’ and l”; trochanter with seta v’ sparsely barbed.
Leg II ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 4 – 7 ). Setal formula: Tr1-Fe2-Ge1-Ti4(1)-Ta6(1). Solenidion ω 4 (4-4) finger shaped, anterior to modified and spatulate seta pl”, seta pv” spine like, seta tc” whip-like and approximately three times longer than tc’, seta u’ needlelike, sometimes indiscernible in some species; tibia with a small finger shaped solenidion φ 2(2– 3), setae d and v” subequal, seta l’ needlelike and shorter than length of its segment; genu with only one seta l’ needlelike; femur with seta d needlelike, shorter than v”; trochanter with seta v’ weakly barbed.
Leg III ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 4 – 7 ). Setal formula: Tr1-Fe1-Ge1-Ti4(1)-Ta6. Tarsus with seta pl” spatulate, setae pv” spine like, seta u’ needlelike, seta tc” whip-like and longest; tibia with a small solenidion φ 1 (1–2) and four subequal setae; genu with seta l’ almost three times longer than seta d on femur; femur divided into basifemur and telofemur, seta d needlelike and inserted on telofemur; seta v’ on trochanter smooth.
Leg IV ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 4 – 7 ). Ambulacrum stalked; setal formula: Tr1-Fe2-Ge0-Ti3(1)-Ta6. Tarsus with seta pl” short, behind wipe-like and ultralong seta tc”; seta u’ blunt-ended; setae pv’ and pv” subequal, both shorter than tc’; tibia with small solenidion φ 1 (1–2), seta d longer than setae v’ and v”; genu with no seta; femur divided into basifemur and telofemur, setae d and v’ inserted on telofemur, seta v’ more than two times longer than d; trochanter with seta v’ smooth.
Male and larva unknown.
Type material. Holotype female (15/1) phoretic on Morimus verecundus ( Coleoptera : Cerambycidae ) clinging to ventral surface, around coxae I–III, collected from Oak trees in Naharkhoran forest, Golestan province, northern Iran, 36.46°N, 54.27°E, altitude 450 m., coll. V. Rahiminejad, 26 June 2009.
Paratypes: more than 150 females, same collection data as holotype.
Etymology. The name of the new species refers to its host family name, Cerambycidae .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |