Xiphinema simile Lamberti, Choleva et Agostinelli, 1983
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.3897/zookeys.3.26 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3792762 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03DB8789-DC30-0209-4E83-875AFBDB6C5B |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Xiphinema simile Lamberti, Choleva et Agostinelli, 1983 |
| status |
|
Xiphinema simile Lamberti, Choleva et Agostinelli, 1983
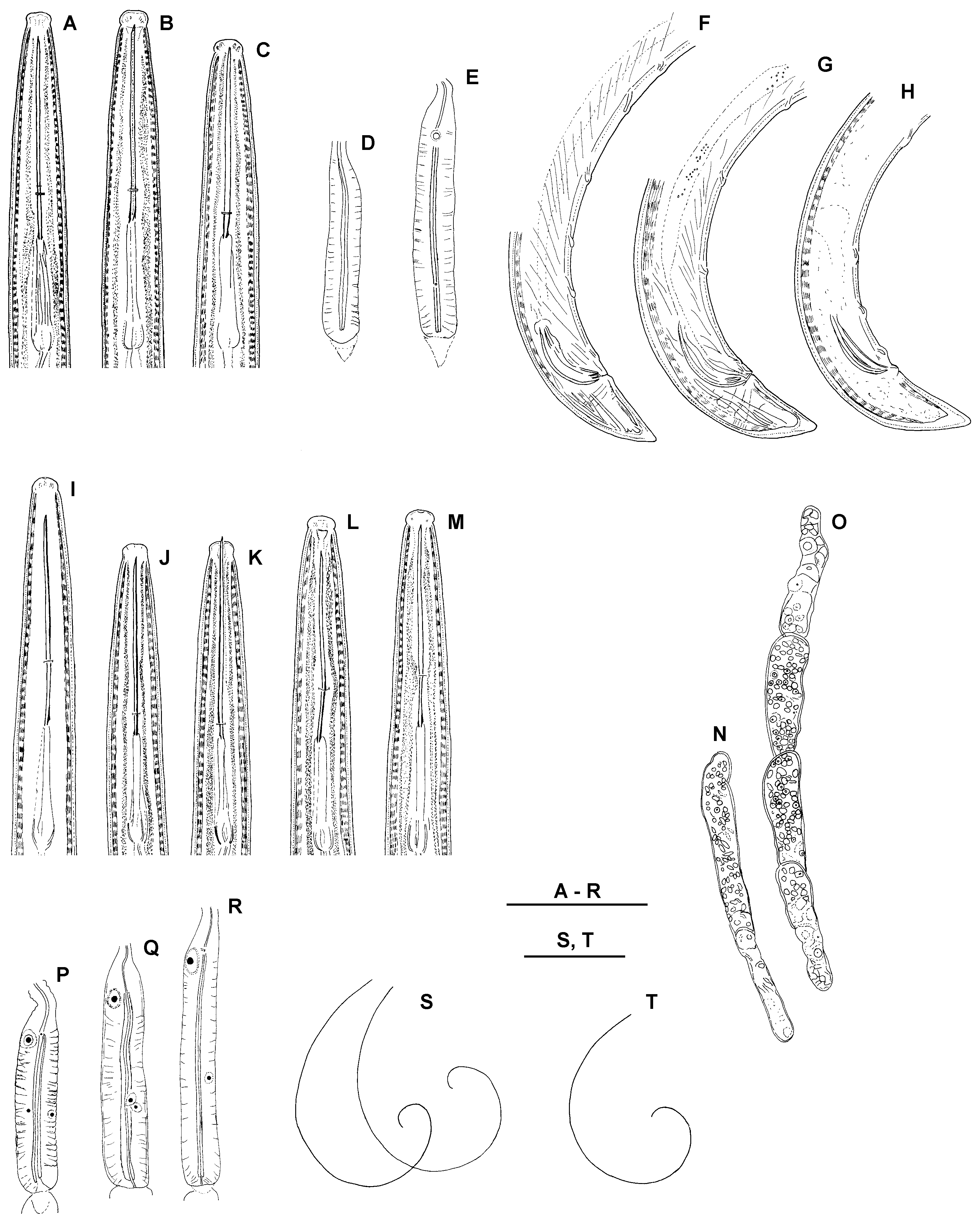
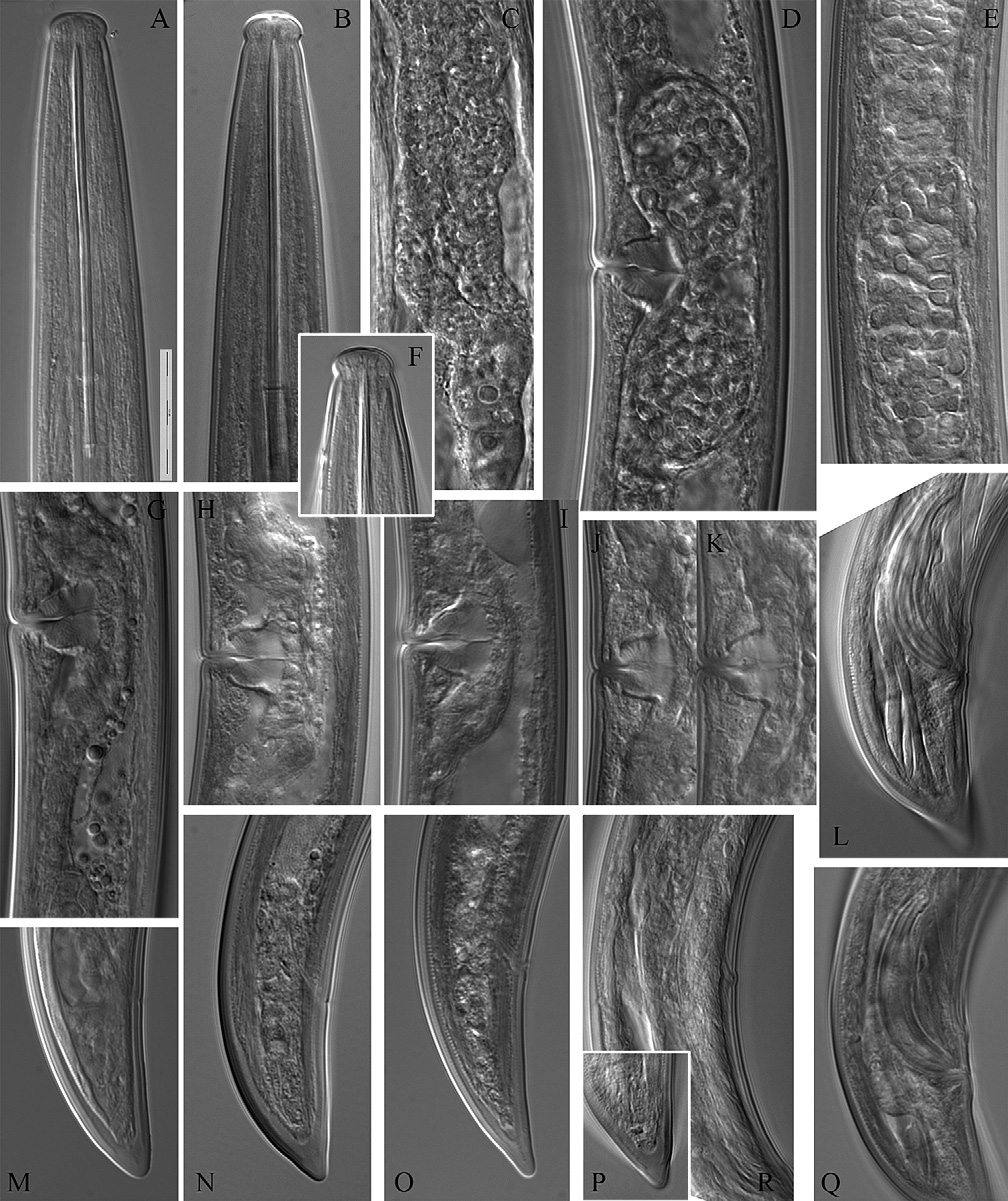
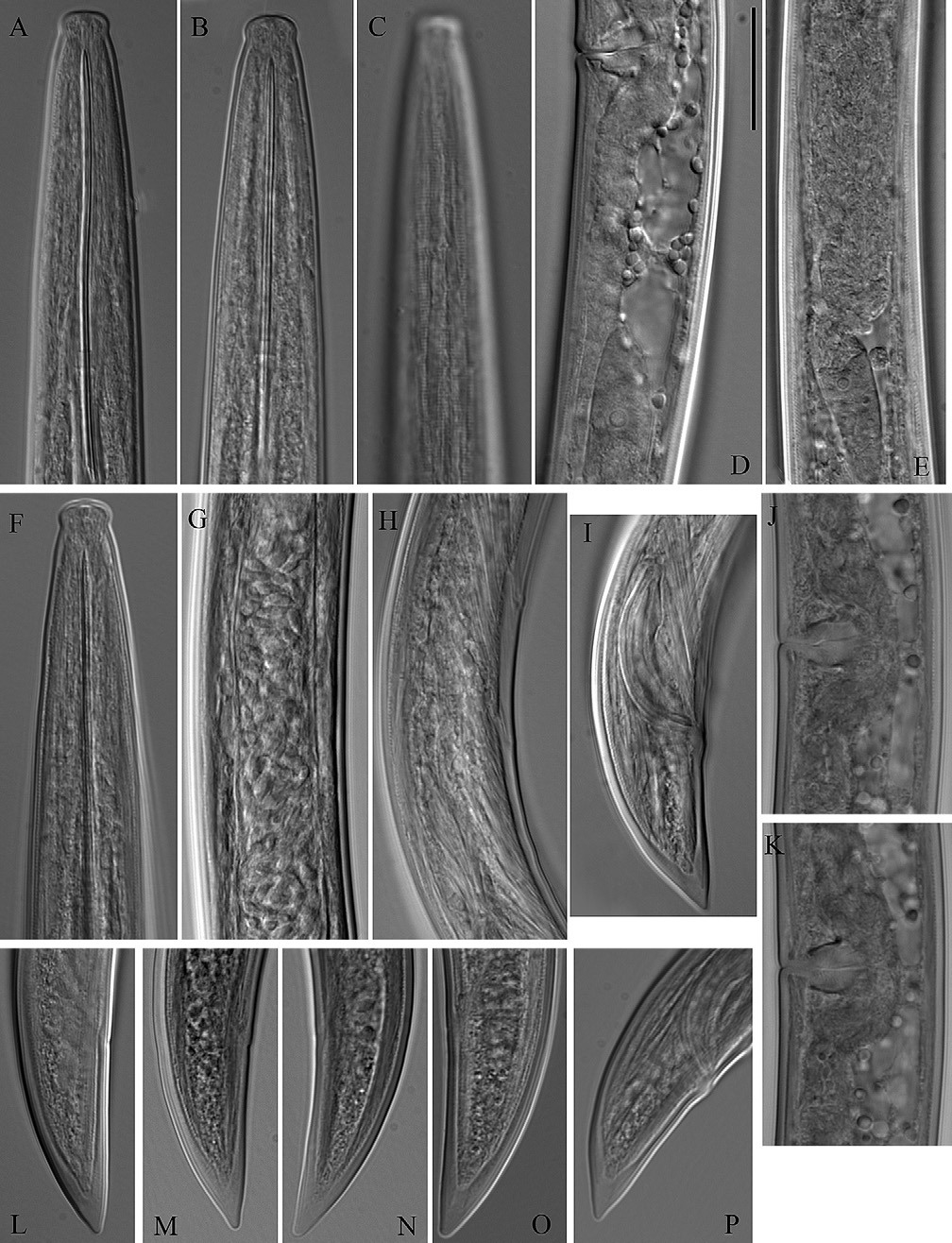
( Figs 2B, C, E, G, H, L, M, O View Fig , Q-S; 3 View Fig D-H; 4 View Fig F-K; 5 View Fig D-H; 9-11 View Fig View Fig )
Measurements. See Tables 2 View Table 2 -4
Description. Females. Body slender, slightly tapering towards both ends; C- to spiral-shaped. Th ickness of the cuticle at postlabial region 1 µm; at dorsal side of the tail cuticle thickness increases gradually from 2 to 3.6 (3-4) µm towards tail end. Lip region expanded, flatly rounded, 4 (4-5) µm high. Amphidial opening 4-5 µm wide, occupying 44-50% of the corresponding body width (n=4), located just below the demarcation line. Odontostyle with moderately developed basal collar, guiding ring not appearing single. Pharyngeal characters presented at Table 2 View Table 2 . Genital system with two almost equally developed branches, uteri short ( Table 3 View Table 3 ); vagina 13–16 µm long or 46–56 % of the corresponding body diameter. Sperm cells observed in females from Kalimok and Orlyane populations. Ovaries contain symbiotic bacteria. Rectum 20.1 (18-22) µm long. Tail conoid, dorsally convex, terminus rounded, in some specimens pointed; presence of slight dorsal constriction at the level of hyaline part.
Males. Similar to female apart from body more curved at the posterior end and higher lip region (5-5.5 µm). Spicules slightly curved, one adanal pair and 3 ventromedian supplements present, lateral guiding piece 6 µm long Th e spicules of the specimen from Srebarna Reserve were not well developed and the testes were not observed while the specimen from Kalimok-Brashlen locality was apperantly functional with well developed testes filled with sperm. Tail longer than in female, especially in the specimen from Srebarna, conoid, dorsally convex with rounded terminus.
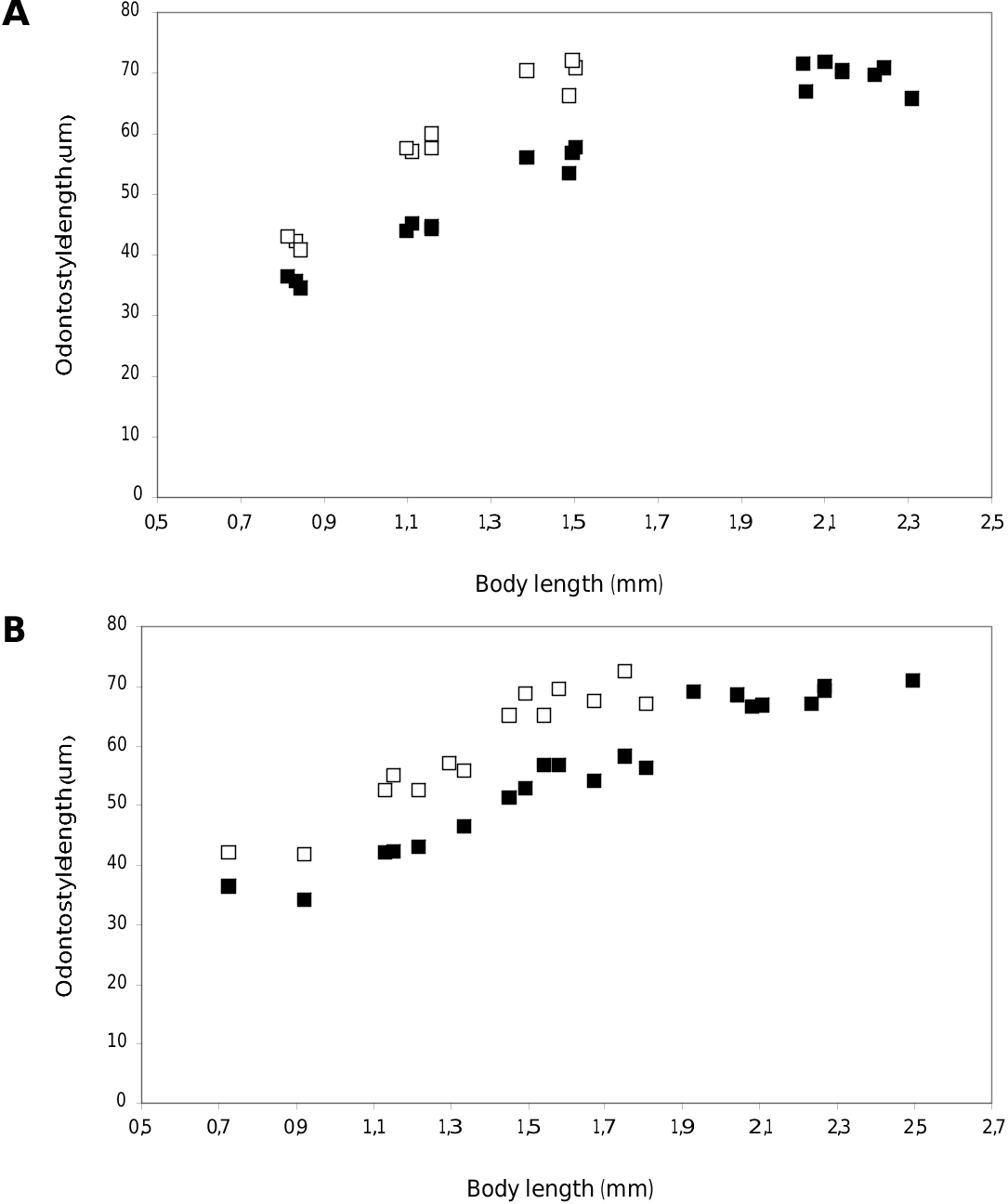
Juveniles. Th e scatter diagram based on functional and replacement odontostyle, and body length reveal presence of three juvenile stages ( Figs 11A & B View Fig ).
Remarks. According to Barsi and Lamberti (2002) the populations of X. simile found in different localities have shown a broad range of variability in body length with populations with more southern distribution being shorter. This study revealed one population of X. simile from Kamen brayg area with lower mean values for body and tail length, a - and c’ -ratios and higher c -ratio, as compared to other three populations. The comparisons with populations from different localities, showed that this population has similar body length with other Bulgarian ( Lamberti et al. 1983, Peneva and Choleva 1992) and the Kenyan populations ( Coomans and Heyns 1997), but still nematodes of this population had shorter tail length, higher c -ratios, and smaller c’ -ratios. The other populations studied were within the range of those reported from northern localities of the range ( Barsi 1994, Lišková and Brown 1996, Lamberti et al. 1999, Barsi and Lamberti 2002, Barsi and Lamberti 2004, Kumari 2006, Repasi et al. 2008).
Measurements of juvenile stages and male specimens are presented for the first time for Bulgarian populations. Th e obtained values were equal or close to those reported by Barsi and Lamberti (2002) and Barsi and De Luca (2008). The frequency distribution graphs of functional and replacement odontostyle lengths represent four
groups, corresponding to three juvenile stages and an adult stage and confirm the findings of other authors ( Coomans and Heyns 1997, Barsi and Lamberti 2002, Barsi and Lamberti 2004, Kumari 2006) for the developmental pattern of X. simile .
Xiphinema simile was found to occur together with X. parasimile (Orlyane locality) and X. pachtaicum (Tulaganov, 1938) Kirjanova, 1951 (Kalimok-Brashlen protected area).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |