Macronotops dianensis Qiu, Xu & Chen, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4556.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:7C55D5CB-5A0F-4DCE-A5A7-755339CF45F3 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5934005 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03CA3425-FF98-A424-C2E9-F817173E15EA |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Macronotops dianensis Qiu, Xu & Chen |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Macronotops dianensis Qiu, Xu & Chen View in CoL new species
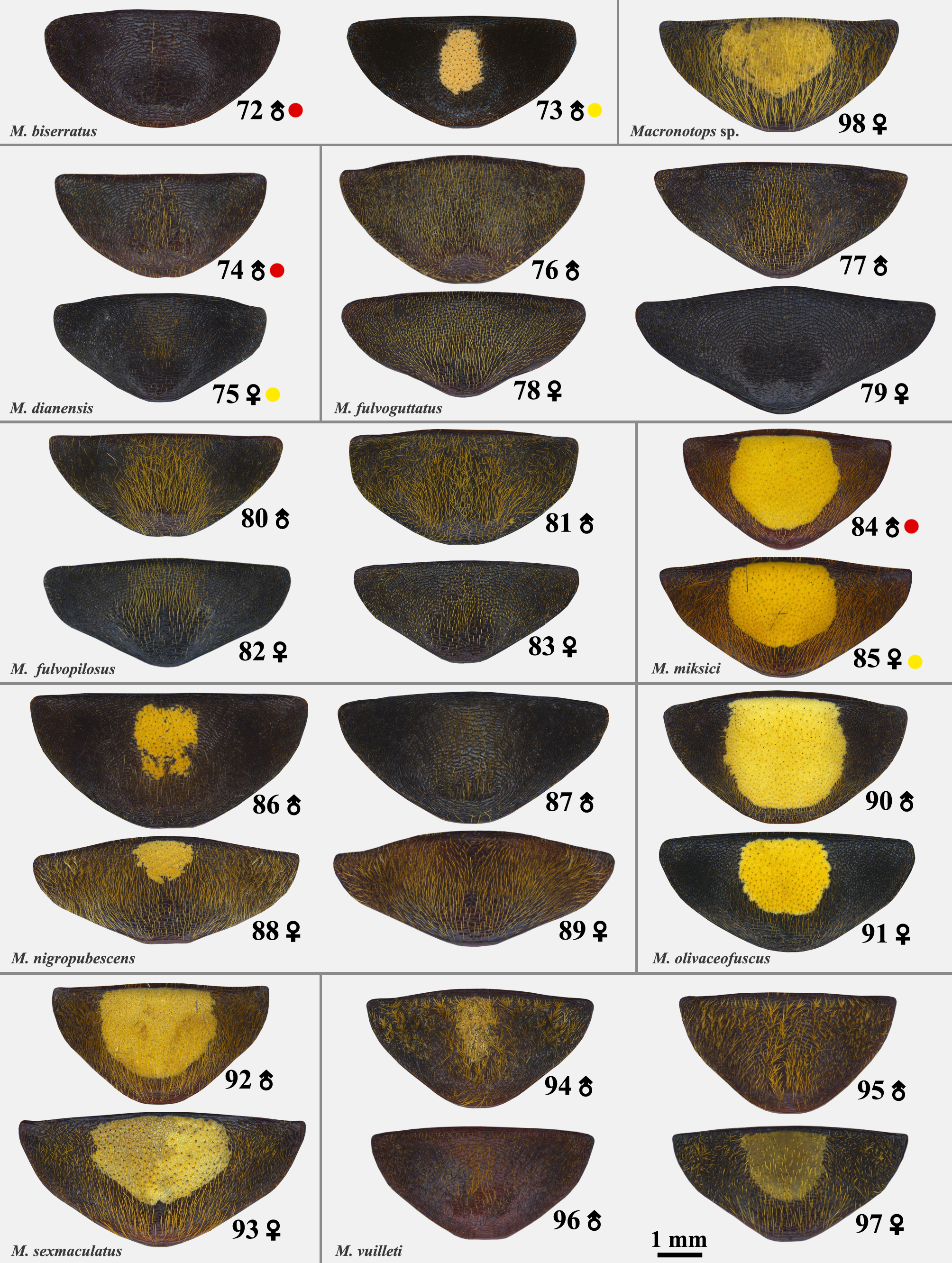
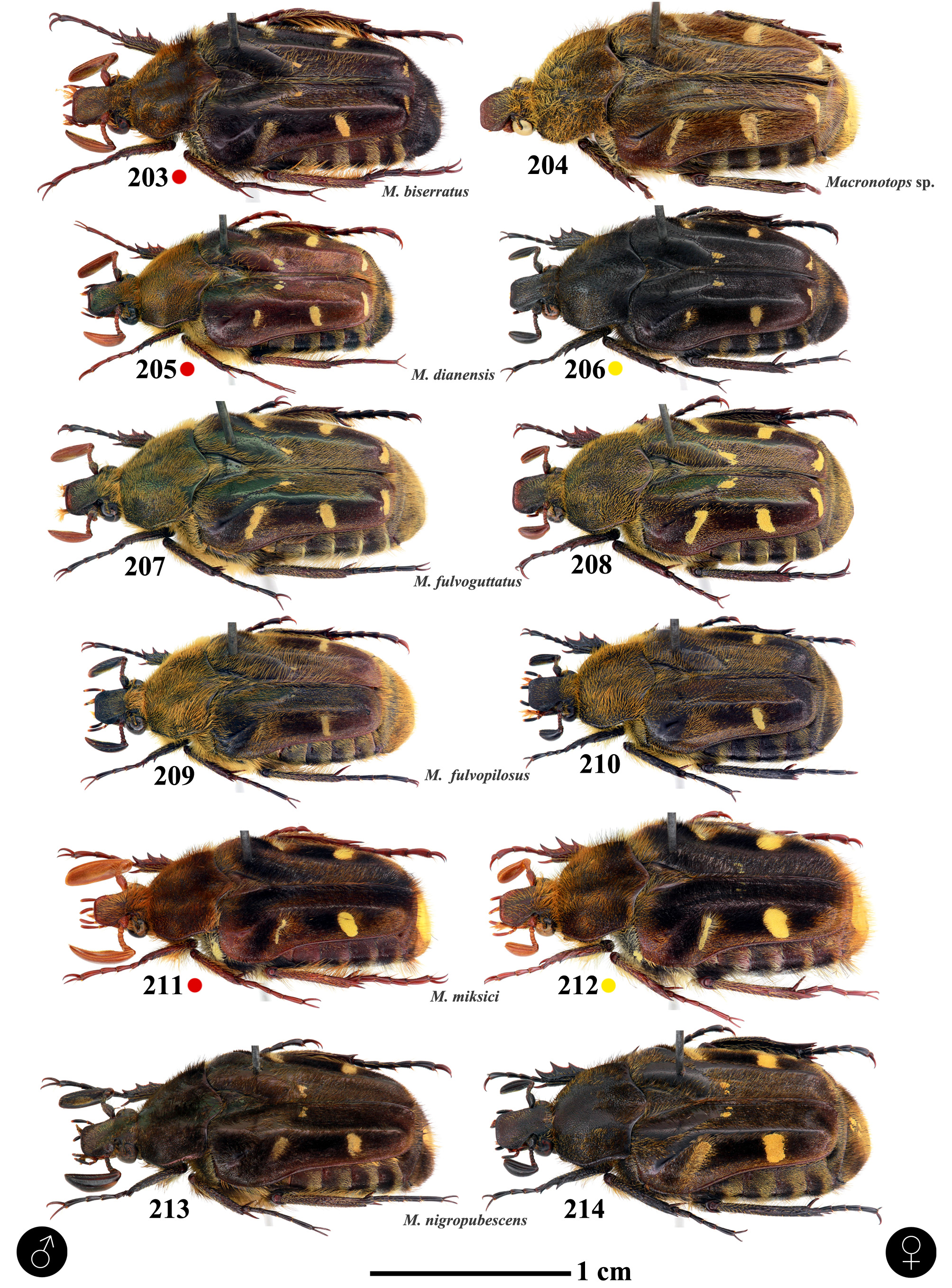
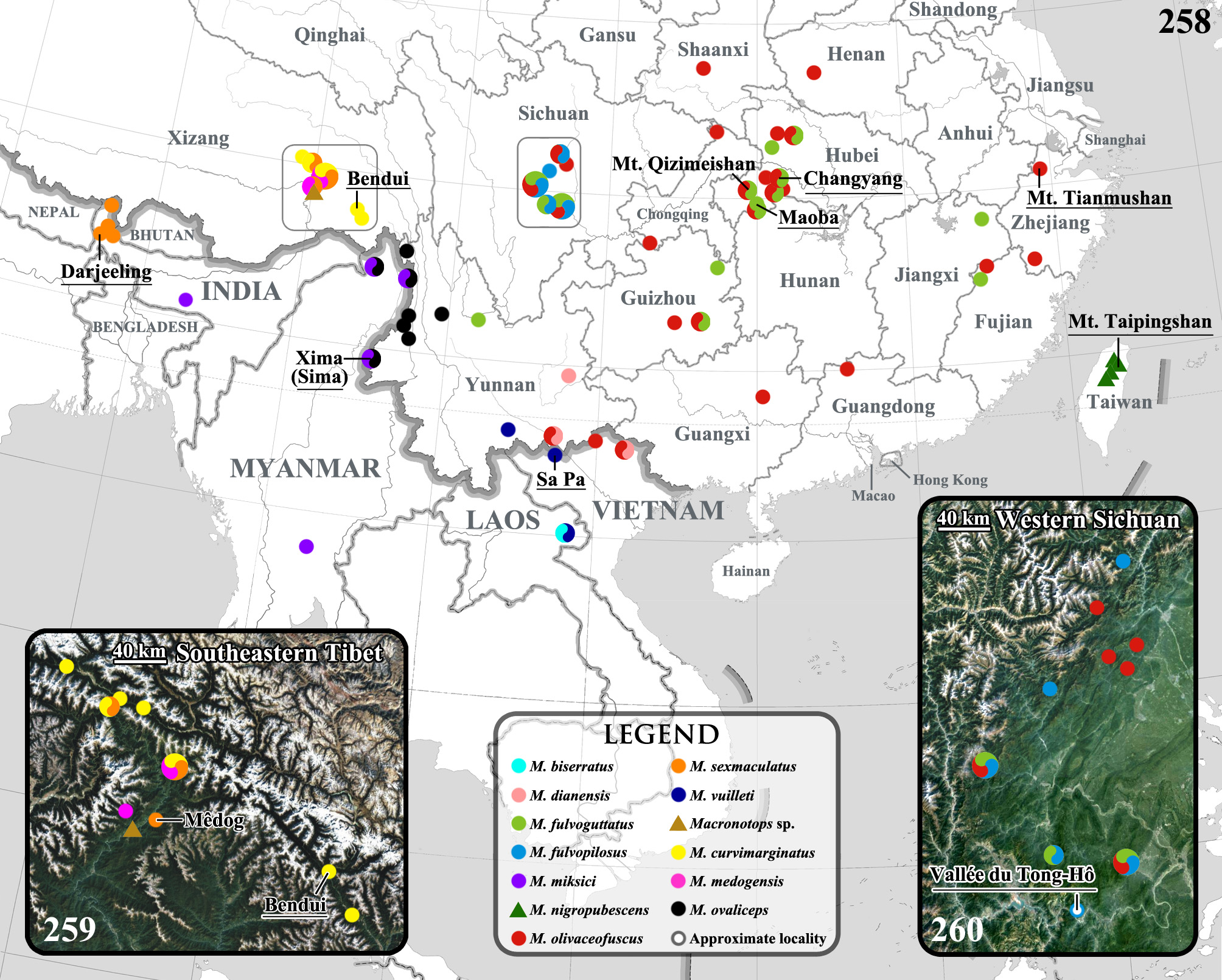
( Figs. 2–3 View FIGURES 1–23 , 25–26 View FIGURES 24–47 , 49–50 View FIGURES 48–65 , 74–75 View FIGURES 72–98 , 112 View FIGURES 111–122 , 124 View FIGURES 122–134 , 137–140 View FIGURES 137–140 , 205–206 View FIGURES 203–214 , 258 View FIGURES 258–260 , 261–262 View FIGURES 261–268 , 295–297 View FIGURES 295–309 )
Macronotops fulvoguttata (Fairmaire) : Krikken 1977: 208 (partim, specimens from Sse-Tsong [=Shizong County, E. Yunnan, China], fig. 21 ♂. (misidentification).
Type material. CHINA: Yunnan: ♂ (Holotype, SWU), Mount Daweishan Nature Reserve , Pingbian County, 2,100 m, Jian-Yue QIU & Hao XU, 3 nd instar in rotten wood 1.III.2015, adult emerged IV.2015. Paratypes (9♂♂, 8♀♀): CHINA: 1♀ (Allotype, SWU), 1♂ ( QCCC), Mount Daweishan Nature Reserve, Pingbian County, 2,100 m, Jian-Yue QIU & Hao XU, 3 nd instar in rotten wood 1.III.2015, adult emerged IV.2015; 1♀ ( QCCC), Mount Daweishan Nature Reserve , Pingbian County , 2,100 m, Gui-Qiang HUANG, 3 nd instar in rotten wood 27– 28.X.2016, adult emerged IV.2017; 2♂♂, 1♀ ( QCCC), Mount Daweishan Nature Reserve , Pingbian County , 2,100 m, Jian-Yue QIU & Hao XU, 3 nd instar in rotten wood 25.II.2018, adult emerged IV.2018; 2♀♀ ( QCCC), Mount Daweishan Nature Reserve , Pingbian County , 2,100 m, Zheng ZHOU, 3 nd instar in rotten wood II.2018, adult emerged V.2018; 1♀ ( IBDU), 14.VII.2015, Mount Daweishan Nature Reserve , Pingbian County , 2,104 m, Kai-Ge XU; 4♂♂, 3♀♀ ( QCCC), Mount Junzishan Nature Reserve , Shizong County , Ke TANG, 3 nd instar in rotten wood II.2018, adult emerged V.2018; 1♂ ( MNHN), Yunnan Kutsingfu [Qujing], R. P. Letourmy 1917 . VIETNAM: 1♂ ( KSCJ), 30.VI.1998, Mt. Pia Oac [E 105°52′, N 22°36′], Cao Bang GoogleMaps .
Holotype (male). General: Body length 14.5 mm; width 6.5 mm, widest at humeral umbone, gradually narrowed backward. Body reddish-brown to brown. Surface with fulvous, brown, light yellow and black setae, and yellow tomentous maculae. Head: Brown. Dorsal surface with dense setiferous punctures; setae fulvous, longer on frons. Clypeus with green metallic reflections; anterior margin nearly straight and slightly raised; clypeolateral ridge distinct. Frons slightly convex ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1–23 ). Maxillary palpus and labial palpus brown. Antenna yellowish-brown; antennal club long, about 1.5 times length of antennomeres 2–7 combined; inner side of the antennomere 8 with long, fulvous setae ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1–23 ). Ventral surface clad with long, fulvous setae ( Fig. 138 View FIGURES 137–140 ). Pronotum: Brown with winered metallic reflections. Widest at base; basomedian area depressed. Lateral margin curved; posterior margin distinctly protruded. Surface evenly clad with dense, setiferous punctures; setae long, fulvous; sparse, brown setae on basolateral area ( Fig. 137 View FIGURES 137–140 ). Scutellum: Reddish-brown with weak wine-red metallic reflections. Surface with sparse, setiferous punctures; setae long, fulvous. Elytron: Reddish-brown with weak wine-red metallic reflections; with posthumeral macula, lateral macula, median macula, and distal macula. Surface densely clad with setae; setae long between sutural and discolateral costae; setae light yellow on maculae; setae black near humeral umbone; setae brown on lateral declivity (between posthumeral macula and lateral macula); setae fulvous on the rest of elytron; humeral umbone glabrous ( Fig. 137 View FIGURES 137–140 ). Mesepimeron, metepisternum and metepimeron: Reddish-brown, evenly clad with yellow setae. Sternum: Preprosternum brown, sides clad with sparse, fulvous setae. Mesosternum brown, clad with sparse, yellow setae. Mesometasternal process, short, glabrous, brown, apex rounded; mesometasternal suture depressed, clad with fulvous, long setae. Metasternum reddish-brown to black from side to midline; evenly clad with long, yellow setae; middle portion glabrous ( Fig. 138 View FIGURES 137–140 ). Pygidium: Black. Surface clad with long, dense, fulvous and black setae; most fulvous setae in median ( Figs. 74 View FIGURES 72–98 , 137 View FIGURES 137–140 ). Abdomen: Brown. Longitudinal groove in median indistinct. Six abdominal sternites visible; sternites II–V evenly clad with fulvous setae on ventral surface, densely clad with black and light yellow setae in dorsal and lateral portion; setae on sternite II long; setae on sternites III–V short, but longer on sides; setae near posterior margin of sternite VI long, dense; sternite VII with sparse, short, fulvous setae on sides ( Fig. 138 View FIGURES 137–140 ). Legs: Slender, simple. Metacoxa black; with long, black setae. Femora and tibia reddish-brown; with long, fulvous and light yellow setae. Tiny teeth between 3 large teeth of protibia indistinct ( Fig. 25 View FIGURES 24–47 ); mesotibia with a sharp spine in middle; metatibia with a blunt spine in middle; metatibia with a row of brushlike, fulvous setae along inner margin ( Figs. 137–138 View FIGURES 137–140 ); dorsal tooth of metatibia as long as basitarsus of metatarsus, outer tooth small and short ( Fig. 49 View FIGURES 48–65 ). Tarsi reddish-brown; basitarsus of metatarsus with a cluster of sparse, long setae ( Fig. 49 View FIGURES 48–65 ). Genitalia: Parameres broad, short; apex rounded, slightly expanded. Apical half of interparameral split constricted; base with membrane, distinctly divided in medial. Median lobe ribbon-like, apical portion of median lobe reversed; nearly twice length of paramere ( Fig. 112 View FIGURES 111–122 ).
Female. Body length 16.5–18.0 mm; width 7.0–7.5 mm. Body color darker. Surface of head with short, sparse, fulvous and brown setae; midline of frons convex, glabrous ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1–23 ). Pronotum clad with sparse, short, fulvous, dark brown, and black setae. Elytra dark brown to black; clad with dark brown and black setae, except the yellow tomentous maculae ( Fig. 139 View FIGURES 137–140 ). Ventral surface black, clad with fulvous setae; abdomen convex, with less setae ( Fig. 140 View FIGURES 137–140 ). Legs dark brown to black; dorsal and outer teeth of metatibia large, as long as basitarsus of metatarsus ( Fig. 50 View FIGURES 48–65 ); setae on mesotibia and metatibia shorter; basitarsus of metatarsus with less setae ( Fig. 50 View FIGURES 48–65 ).
Variability. Male paratypes body length 16.5 mm, width 7.0 mm; some with green metallic reflections on dorsal surface. The length of dorsal tooth of metatibia sometimes slightly longer than basitarsus of metatarsus. Body color of the females from Mount Junzishan appears lighter, and is similar to males from the same location.
Differential diagnosis. Length of clypeus almost equal to width ( Figs. 2–3 View FIGURES 1–23 ). Elytra with posthumeral maculae, median maculae, lateral maculae, and distal maculae ( Figs. 137 View FIGURES 137–140 , 1 39 View FIGURES 1–23 View FIGURES 24–47 ). Pygidium without macula ( Figs. 74–75 View FIGURES 72–98 ). Abdominal sides without yellow macula ( Figs. 138 View FIGURES 137–140 , 1 40 View FIGURES 1–23 View FIGURES 24–47 ). Male: Dorsal surface reddish-brown with fulvous short setae ( Fig. 137 View FIGURES 137–140 ); antenna yellowish-brown ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1–23 ); protibia with tiny teeth ( Fig. 25 View FIGURES 24–47 ) and dorsal tooth of metatibia longer than basitarsus of metatarsus ( Fig. 49 View FIGURES 48–65 ); abdomen without median groove. Female: Dorsal surface dark brown to black with black short setae ( Fig. 139 View FIGURES 137–140 ); head with a longitudinal ridge on frons and antenna black ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1–23 ).
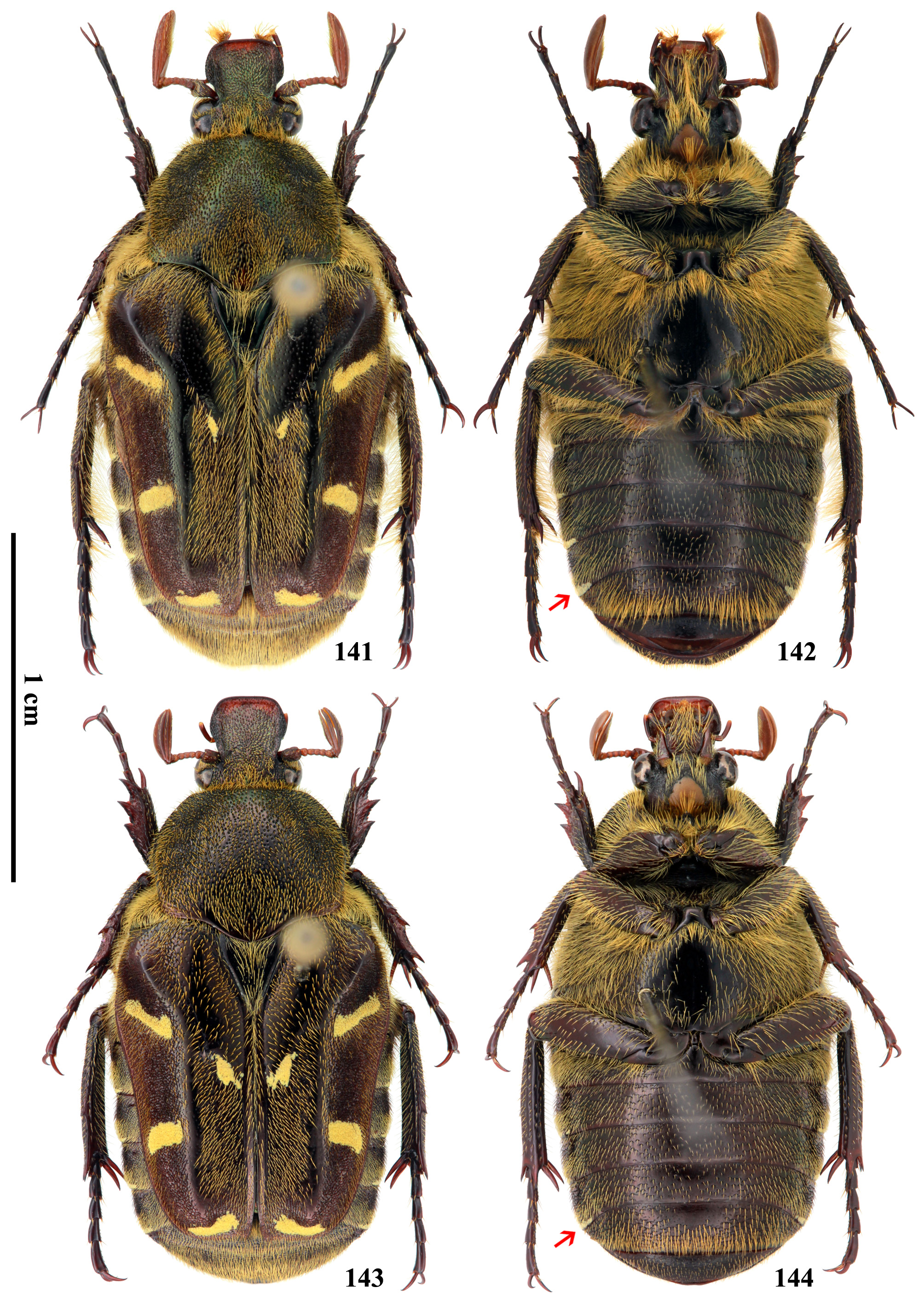
Male of Macronotops dianensis new species is very similar to M. fulvoguttatus , but can be distinguished by tiny teeth of protibia indistinct ( Fig. 25 View FIGURES 24–47 ; distinct in M. fulvoguttatus , Fig. 27 View FIGURES 24–47 ), abdomen without tomentous maculae ( Fig. 138 View FIGURES 137–140 ; abdominal sides with yellow maculae in M. fulvoguttatus , Fig. 142 View FIGURES 141–144 ), dorsal tooth of male metatibia longer than basitarsus of metatarsus ( Fig. 49 View FIGURES 48–65 ; that of M. fulvoguttatus shorter than basitarsus of metatarsus, Fig. 51 View FIGURES 48–65 ), parameres shorter but broader, and apical portion of median lobe reversed ( Fig. 112 View FIGURES 111–122 ).
Etymology. It is named for the alias name of Yunnan (Dian) where the type locality is located.
Distribution. China: Yunnan; Vietnam.
Natural history. This new species occurs sympatrically with M. olivaceofuscus ( Bourgoin, 1916) at Mount Daweishan, and the mature larvae in rotten wood were found near the mountain top (elevation approximately 2,100 m, Figs. 261–262 View FIGURES 261–268 ), but larvae of the latter species were collected from the mountainside at an elevation of around 1,600 m.
Remarks. All type series of this new species were obtained in recent years, except the old specimen in MNHN collected by Letourmy. Since 1910, Father Omer Letourmy (1884–1963) visited several places in Qujing (Eastern Yunnan, China) for missionary work, and he stayed at “San-pe-fou” in 1914–1928 ( Moussay & Appavou 2004). San-pe-fou, i.e. Sanbaihu, is a village now called Wulian (E 103°50'14.05", N 25°24'51.00", alt. 1,860 m) and located in Sanbao Town not far from the south of Qujing City. The male labeled “ Yunnan Kutsingfu, R. P. Letourmy 1917” perhaps was captured in the mountains around the village.
A couple of specimens identified by Krikken (1977) as M. fulvoguttatus appear to be M. dianensis new species. These two specimens originated from Sse-Tsong in eastern Yunnan, i.e. Shizong County, where seven paratypes of M. dianensis new species were collected. The characters for separation of these two species are provided in the differential diagnosis section and in the key.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Macronotops dianensis Qiu, Xu & Chen
| Qiu, Jian-Yue, Xu, Hao & Chen, Li 2019 |
Macronotops fulvoguttata (Fairmaire)
| Krikken, J. 1977: 208 |