Ctenophora fumosa Men
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3841.4.8 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:FCD30A2B-22B7-4818-95B5-5D2DB7645F70 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6125131 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C98790-FFAC-1737-FF75-ECEE48AA4C4E |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Ctenophora fumosa Men |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Ctenophora fumosa Men View in CoL , sp. nov.
( Figs 1–19 View FIGURES 1 – 8 View FIGURES 9 – 17 View FIGURES 18, 19 )
Description. Body length: male. 17.5 mm (n=2). Wing: male. 14.4 mm (n=2). Female unknown.
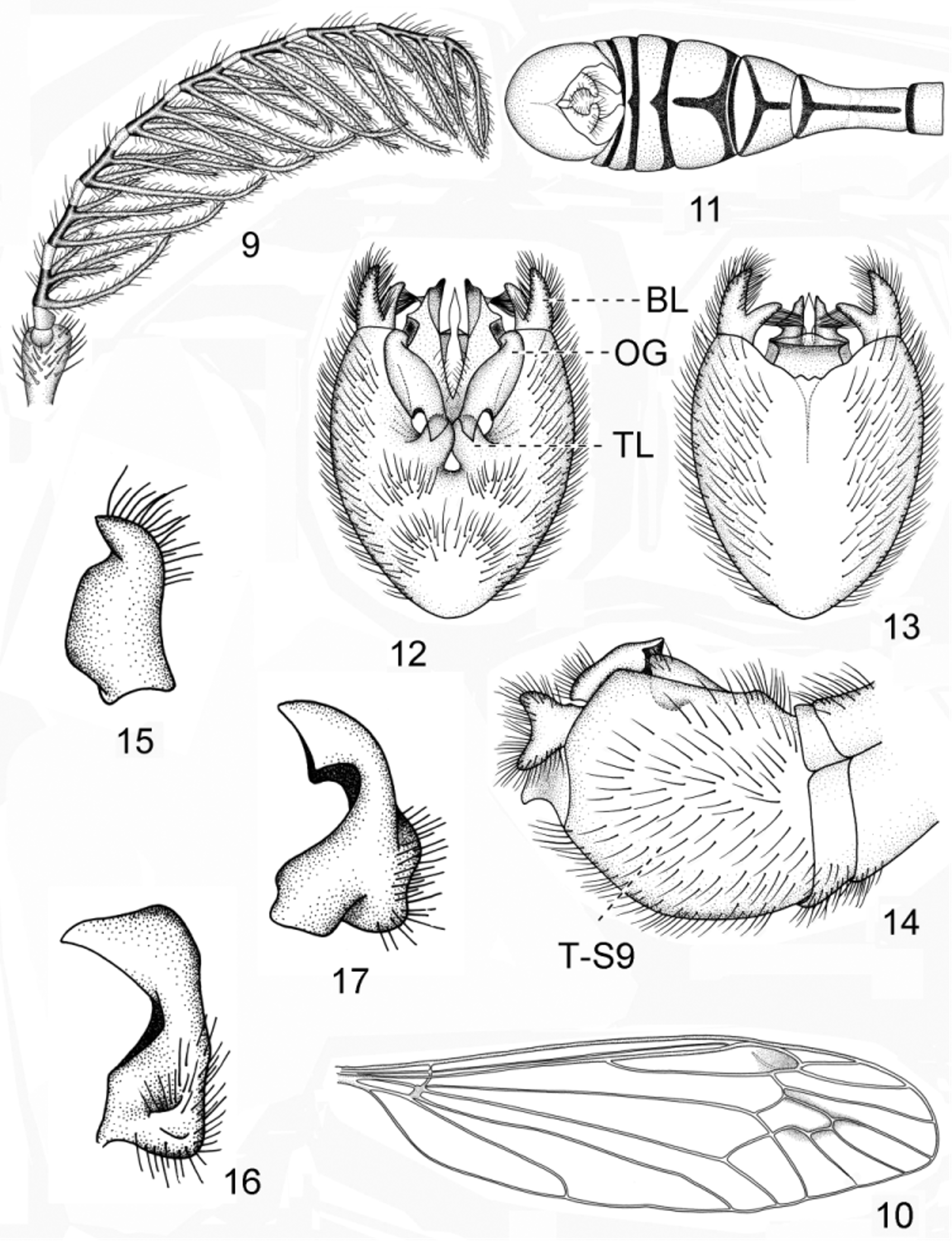
Head. Rostrum reddish with yellowish-brown nasus ( Figs 1, 4 View FIGURES 1 – 8 ). Vertex yellow ( Figs 1, 3, 4 View FIGURES 1 – 8 ). Occiput with a broad black transverse band connecting the eyes behind the antennal fossae ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1 – 8 ). Orbit yellow. Setae on head yellow except that of occiput, which is dark brown. Antenna with scape yellow, pedicel tawny; axis of basal eight flagellomeres black on basal two thirds, tawny on distal one third, axis of flagellomere nine entirely black; all branches black ( Figs 1, 3 View FIGURES 1 – 8 , 9 View FIGURES 9 – 17 ). First and second segment of palpi brown, the rest segments of palpi black, setae on palpi relatively elongate and same color as the segment where they are found.
Thorax. Pronotum yellow, changing to yellowish-brown laterally ( Figs 3, 4 View FIGURES 1 – 8 ). Prescutum yellow with three dark brown stripes, median one percurrent and expanded at apex, two lateral stripes rounded apically, extending to middle of prescutum ( Figs 1–4 View FIGURES 1 – 8 ). Scutum yellow with two dark brown spots on each side ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1 – 8 ). Scutellum tawny. Mediotergite yellow with one brown triangular spot at the middle, the point directed cephalad. Pleura yellow ( Figs 1, 4 View FIGURES 1 – 8 ). Anepisternum and katepisternum yellow, with a brown mark on the ventral border ( Figs 1, 4 View FIGURES 1 – 8 ). Setae on thorax mainly distributed on the lateral side of the prescutum and the whole surface of the katepisternum ( Figs 3, 4 View FIGURES 1 – 8 ). Coxae yellow; trochanters tawny; fore and middle femora tawny, hind femora tawny with light brown belt near apex; fore and middle tibiae tawny, darker in coloration at apex, basal half of hind tibiae tawny except for the most basal part, with a broad whitish band before the darkened apex; tarsi dark tawny ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 8 ). Setae on coxae and trochanters long, the rest setae relatively short. Wings with a faint and light brown tinge, more yellow in cells C and Sc; stigma inconspicuous, light brown, the posterior border darker; the base of cells R5, M1, M2 and M3 tinged with a smokey mark, surrounding the distal margins of dm cell, the mark connecting with the stigma; Rs long, approximately 4.5 times as long as m-cu, m-cu curved at an obtuse angle, cell M1 broadly sessile; veins dark brown ( Figs 5, 6 View FIGURES 1 – 8 , 10 View FIGURES 9 – 17 ). Halteres with stem yellow, knob weakly darkened ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1 – 8 ).
Abdomen. General color yellow ( Figs 1, 2 View FIGURES 1 – 8 ). First tergite narrowly ringed with dark brown, extending to sternite; second and third tergite also have a dark brown ring near the posterior margin and extending to the sternite, with a dark brown stripe at middle; tergite four with a dark brown stripe at anterior margin, median stripe distinct but not extending to posterior margin; tergite five to eight with a dark brown stripe at anterior margin, without a middle stripe ( Figs 1, 2 View FIGURES 1 – 8 , 11 View FIGURES 9 – 17 ).
Hypopygium. General color dark brown to black, deepened in coloration at the base in ventral view, densely covered with yellow or brown setae ( Figs 7, 8 View FIGURES 1 – 8 , 12–14 View FIGURES 9 – 17 ). The ninth tergite and ninth sternite fused forming an entire genital ring, with a pair of tergal lobes, black and strongly sclerotized, rounded apically and divided medially by a deep notch ( Figs 12–14 View FIGURES 9 – 17 ). Inner gonostylus black, very densely covered with black setae, terminating into a curved spine ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 9 – 17 ). Outer gonostylus black, strongly sclerotized, broadened in middle and narrowed at both ends in dorsal view, fluted in ventral view, dorsally terminating into truncated end and jutting into the tergal lobes ( Figs 12, 16, 17 View FIGURES 9 – 17 ). A pair of yellowish-brown lobes arising from the apex of the basistylus, caudad directed, very densely covered with long and yellowish-brown setae; the lobes bilobed, the ventral one with a wisp of yellow hairs very long and pointed inward ( Figs 12–14 View FIGURES 9 – 17 ). Aedeagus and semen pump as shown in Figs 18, 19 View FIGURES 18, 19 .
Material examined. Holotype male, China: Anhui Province, Yuexi County, Yaoluoping National Nature Reserve, 1000 m, 15 Aug. 2013, coll. Qiulei Men. Paratype. China: 1 male, Anhui Province, Yuexi County, Yaoluoping National Nature Reserve, 1000 m, 16 Aug. 2013, coll. Zhengkui Liu.
Distribution. China (Anhui).
Remarks. This new species is similar to another Chinese species C. pselliophoroides Alexander, 1938 in the colors of antenna and thorax, and in the shape of the flagellum segments and morphological structure of hypopygium. It can be easily distinguished from the latter by the first to eighth tergite narrowly ringed with dark brown, the second to fourth tergite also with median stripesas illustrated in Fig. 11 View FIGURES 9 – 17 (only the first segment narrowly ringed with blackish in C. pselliophoroides as described by Alexander, 1938: 338), the hind femora tawny with light brown belt near apex, the hind tibiae tawny with a broad whitish band as shown in Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 8 (hind legs reddishyellow without such patterns as described by Alexander, 1938: 338), the outer gonostylus dorsally terminating into truncated end as illustrated in Figs 12, 16, 17 View FIGURES 9 – 17 (terminating into a curve spine as described by Alexander, 1938: 338).
Etymology. The specific epithet is a noun derived from the Latin ‘ fumos ’ with the feminine termination ‘- a ’, referring to the presence of smoky mark on the wing.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |