Eiphosoma Cresson, 1865
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5330.4.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:8D26337E-7A73-47A7-A221-B6A1BB84398F |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8257540 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03BD87CF-B94C-F425-FF5E-F964FA11F9E7 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Eiphosoma Cresson, 1865 |
| status |
|
Key to Colombian species of Eiphosoma Cresson, 1865 View in CoL View at ENA
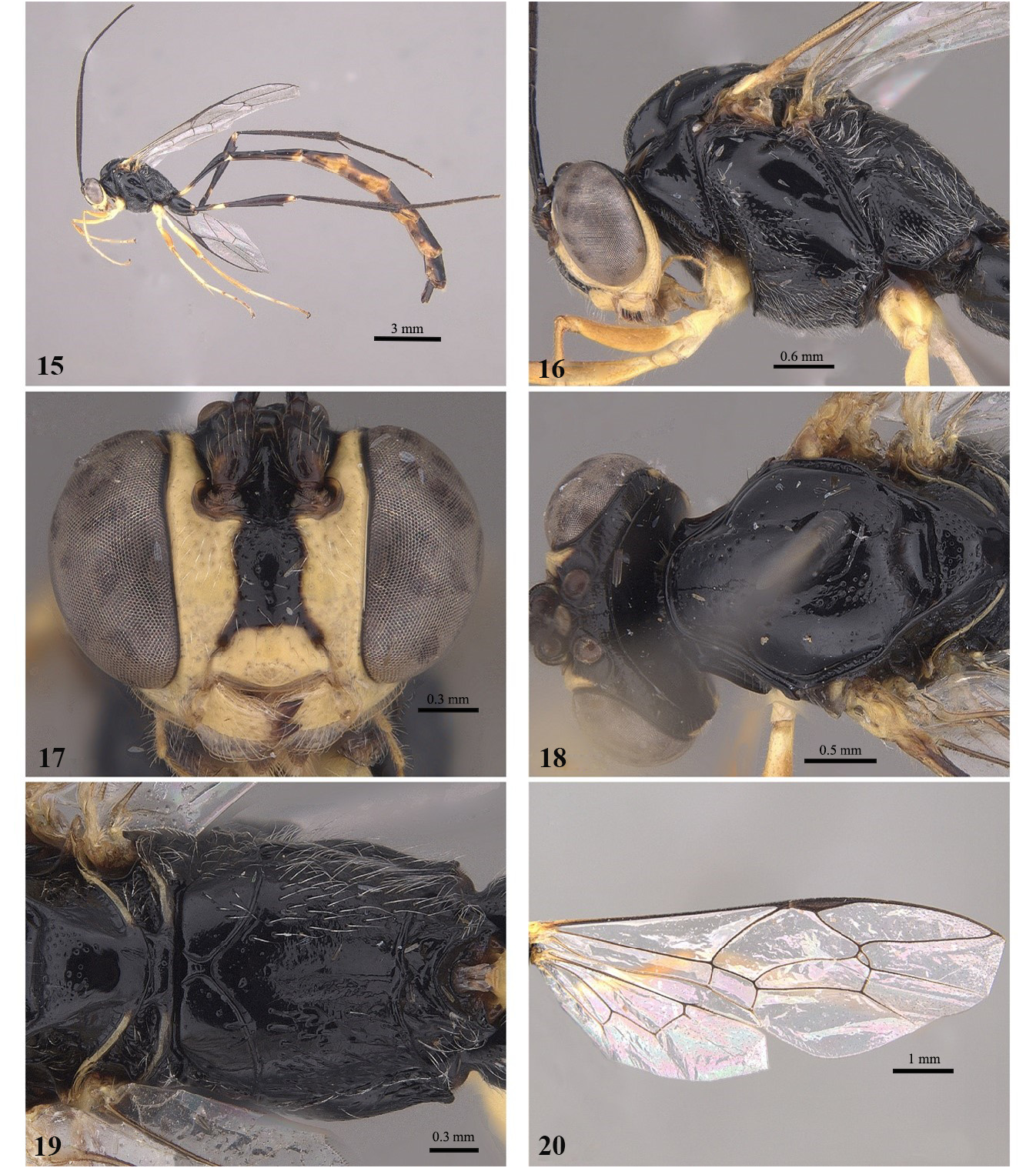
1 Mesosoma predominantly or entirely black ( Figs 16 View FIGURES 15–20 , 23 View FIGURES 22–27 , 58 View FIGURES57–62 )................................................... 2
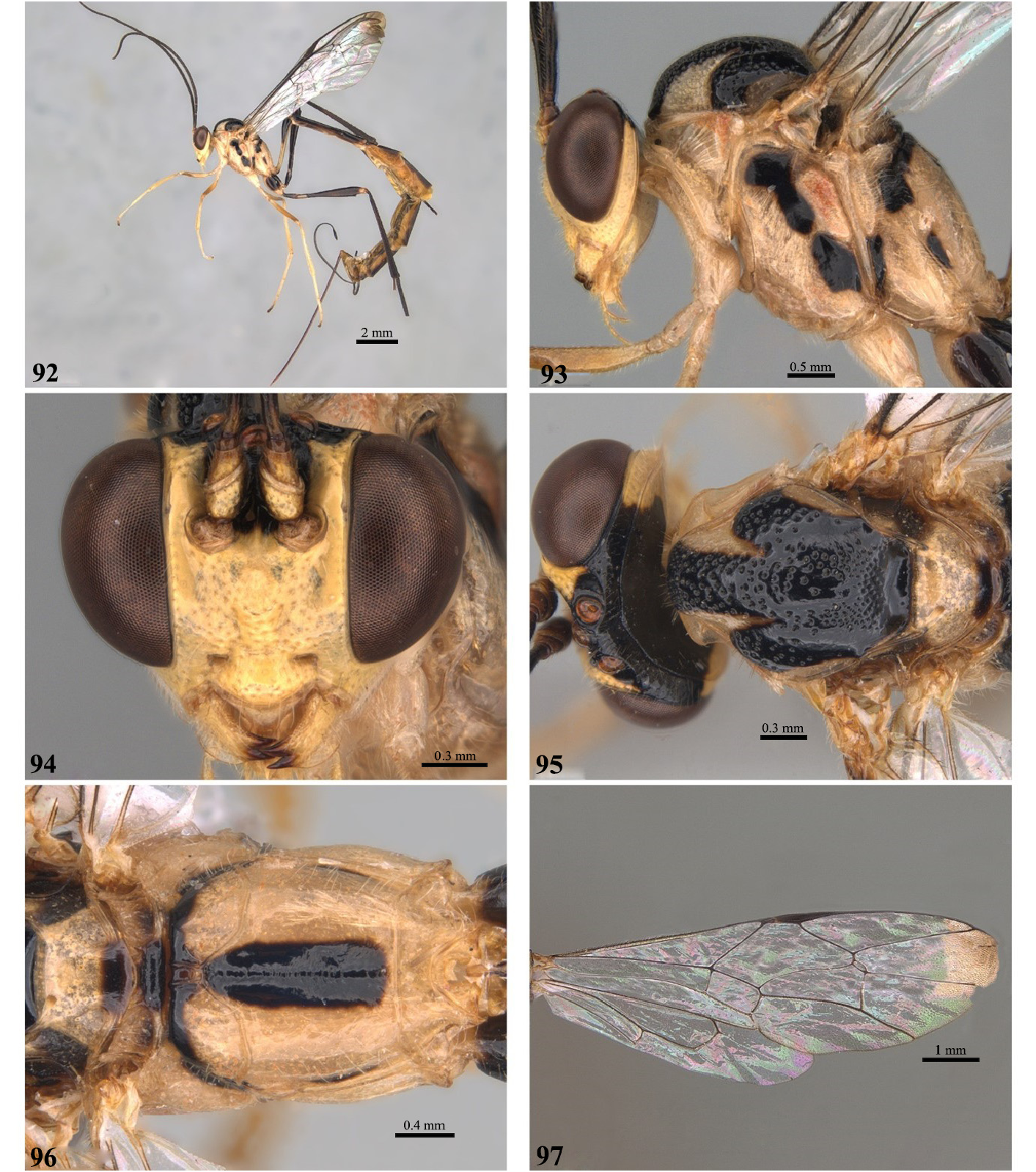
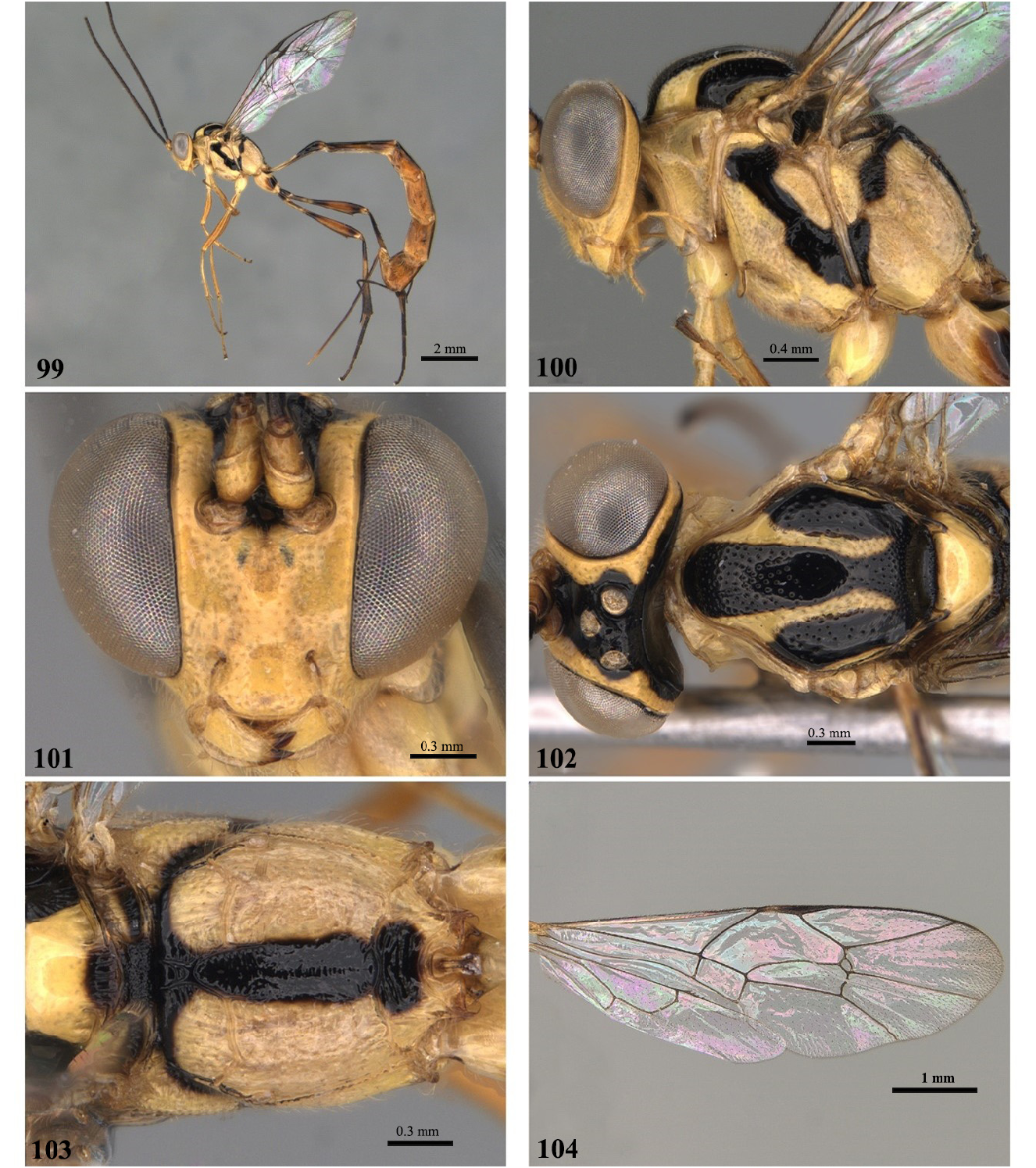
- Mesosoma predominantly yellow ( Figs 2 View FIGURES 1–6 , 9 View FIGURES 8–13 , 30 View FIGURES 29–34 , 37 View FIGURES 36–41 , 44 View FIGURES 43–48 , 51 View FIGURES 50–55 , 65 View FIGURES64–69 , 72 View FIGURES 71–76 , 79 View FIGURES 78–83 , 86 View FIGURES 85–90 , 93 View FIGURES 92–97 , 100 View FIGURES 99–104 )................................. 4
2 Mesosoma entirely black ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 15–20 ); scutellum and metapleuron entirely punctate; propodeum centrally smooth ( Figs 18–19 View FIGURES 15–20 ).............................................................................. E. nigrum ( Szépligeti, 1906) View in CoL
- Mesosoma with at least pronotum and propodeum with yellow marks, scutellum smooth and metapleuron punctate only on upper part; propodeum striate............................................................................ 3
3 Anterior transverse carina of the propodeum without angulations ( Fig. 26 View FIGURES 22–27 ); scutellum and mesoscutellum completely black, without raised lateral longitudinal scutellar carina ( Fig. 25 View FIGURES 22–27 ); fore wing with apex darkened......... E. bogan Gauld, 2000 View in CoL *
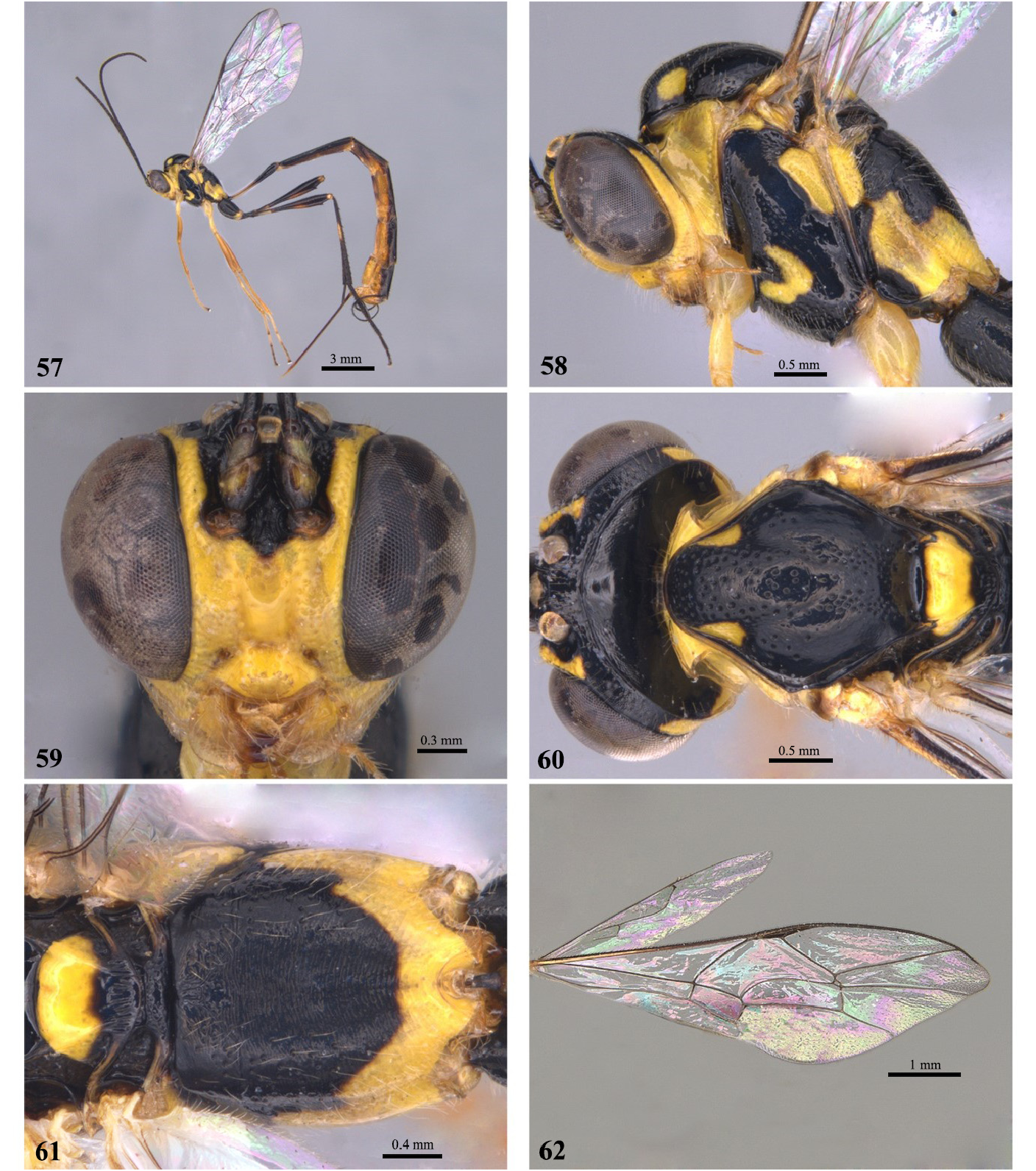
- Anterior transverse carina of the propodeum with angulations ( Fig. 61 View FIGURES57–62 ); scutellum yellow with only a black posterior part, scutellar longitudinal carina laterally elevated; mesoscutellum black with yellow marks at level of notaulus ( Figs 60–61 View FIGURES57–62 ); fore wing completely hyaline.................................................................... E. rumi sp. nov.
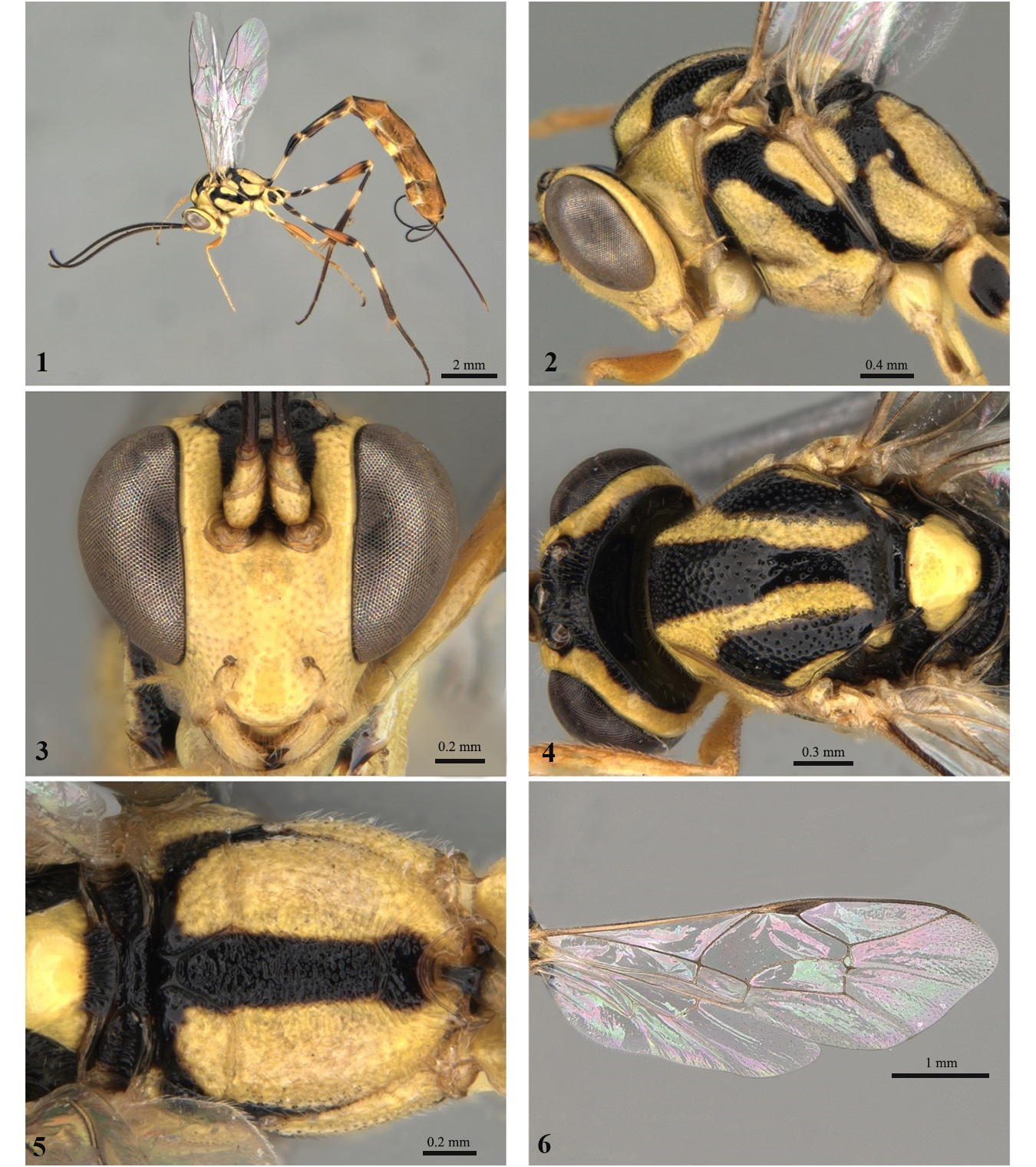
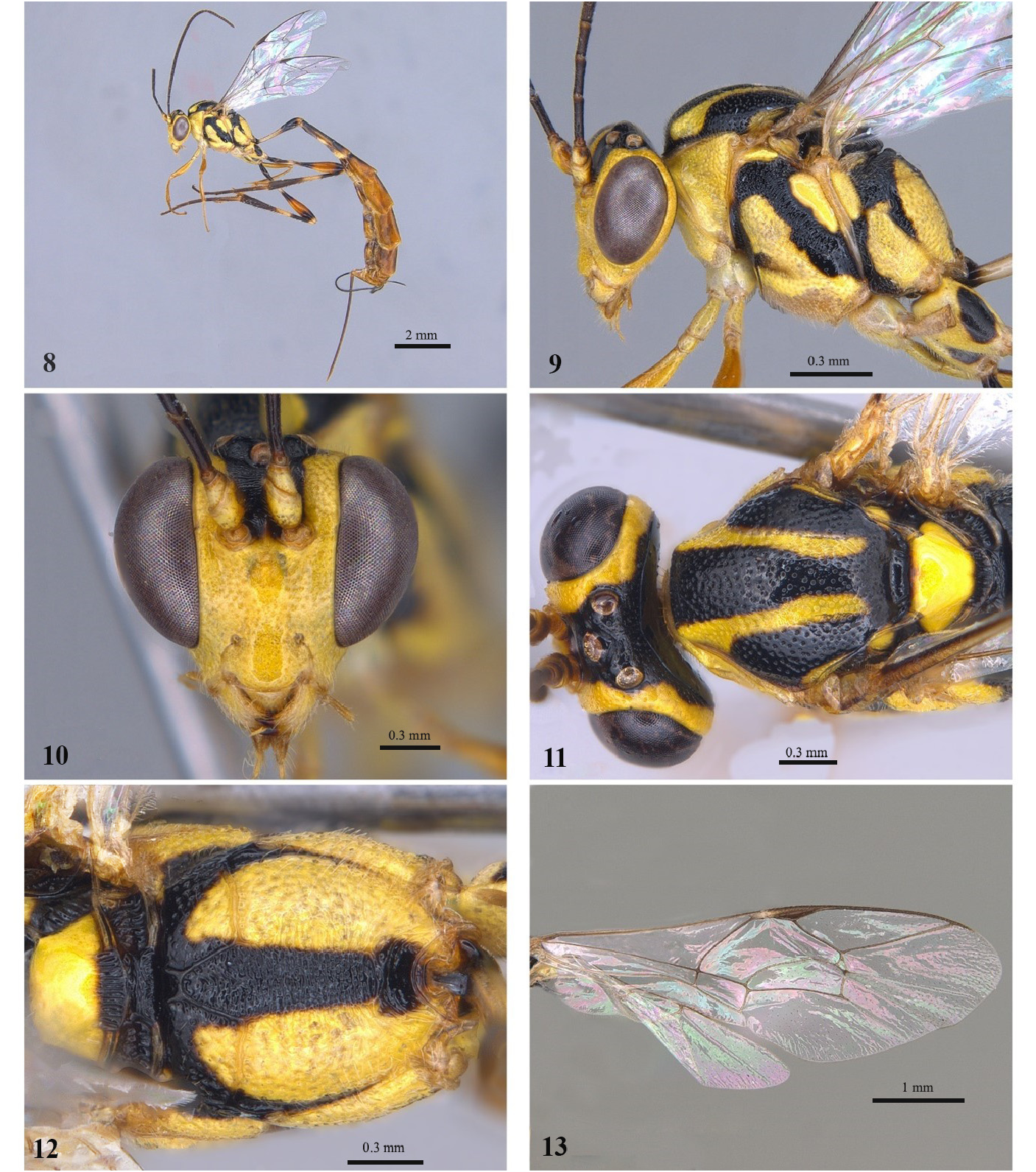
4 Metapleuron entirely punctate ( Figs 2 View FIGURES 1–6 , 9 View FIGURES 8–13 ), fore wing with distal region of M vein absent ( Figs 6 View FIGURES 1–6 , 13 View FIGURES 8–13 ), pleural carina incomplete ( Figs 2 View FIGURES 1–6 , 9 View FIGURES 8–13 )........................................................................................... 5
- Metapleuron with punctate upper part; fore wing with distal region of M vein present; pleural carina complete ( Figs 16 View FIGURES 15–20 , 23 View FIGURES 22–27 , 30 View FIGURES 29–34 , 37 View FIGURES 36–41 , 44 View FIGURES 43–48 , 51 View FIGURES 50–55 , 58 View FIGURES57–62 , 65 View FIGURES64–69 , 72 View FIGURES 71–76 , 79 View FIGURES 78–83 , 86 View FIGURES 85–90 , 93 View FIGURES 92–97 , 100 View FIGURES 99–104 ).................................................................... 6
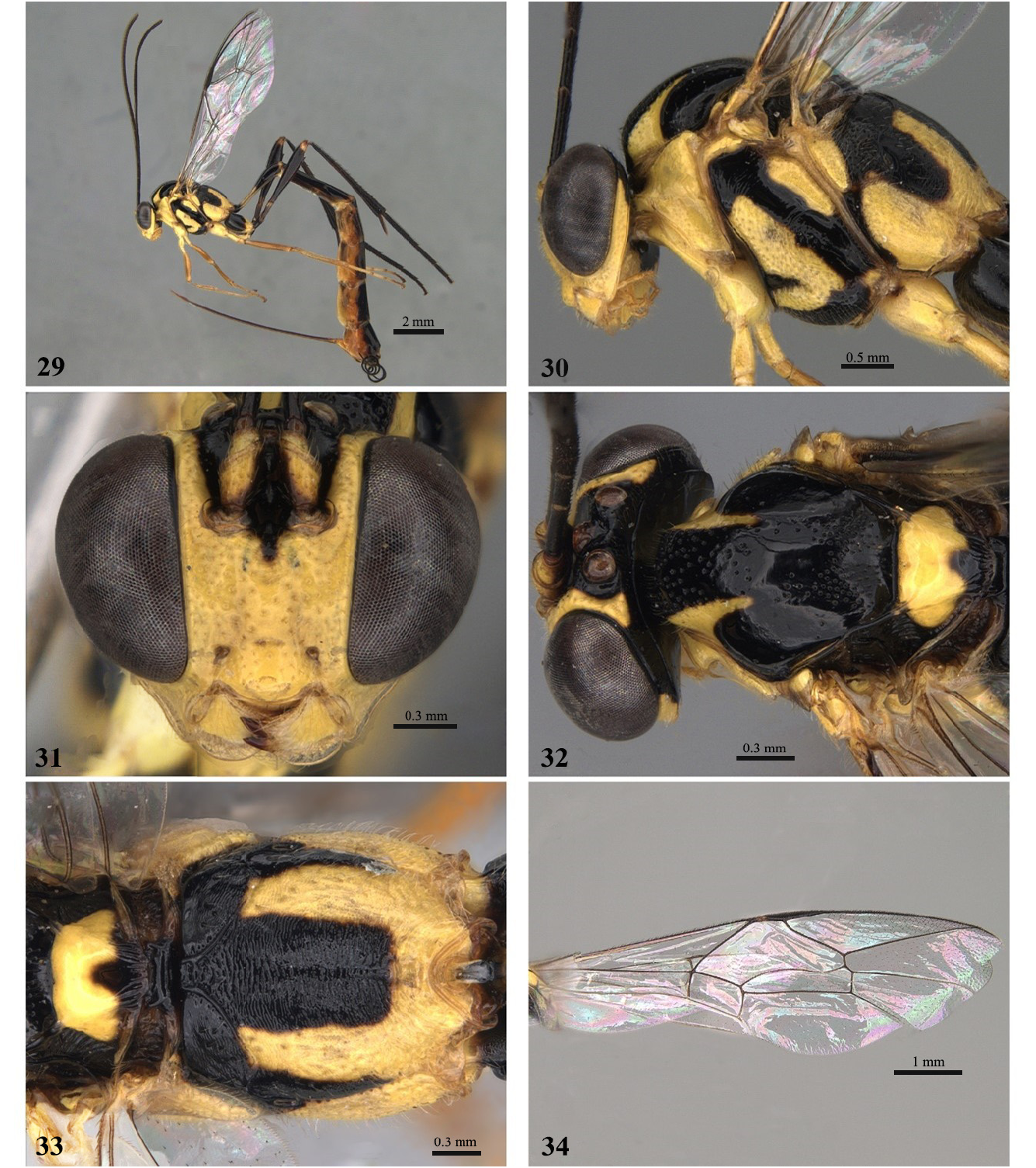
5 Propodeum with posterior transverse carina present ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1–6 ); scutellum without punctures ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 ); pronotum with punctate upper part; mesopleuron with a discontinuously striate central diagonal stripe ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1–6 )........ E. dentator ( Fabricius, 1804) View in CoL
- Propodeum with posterior transverse carina present only centrally ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 8–13 ); scutellum punctate vaguely only in anterior part ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 8–13 ); pronotum completely punctate; mesopleuron with strongly striate central diagonal stripe ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 8–13 )............................................................................................... E. interpunctum sp. nov.
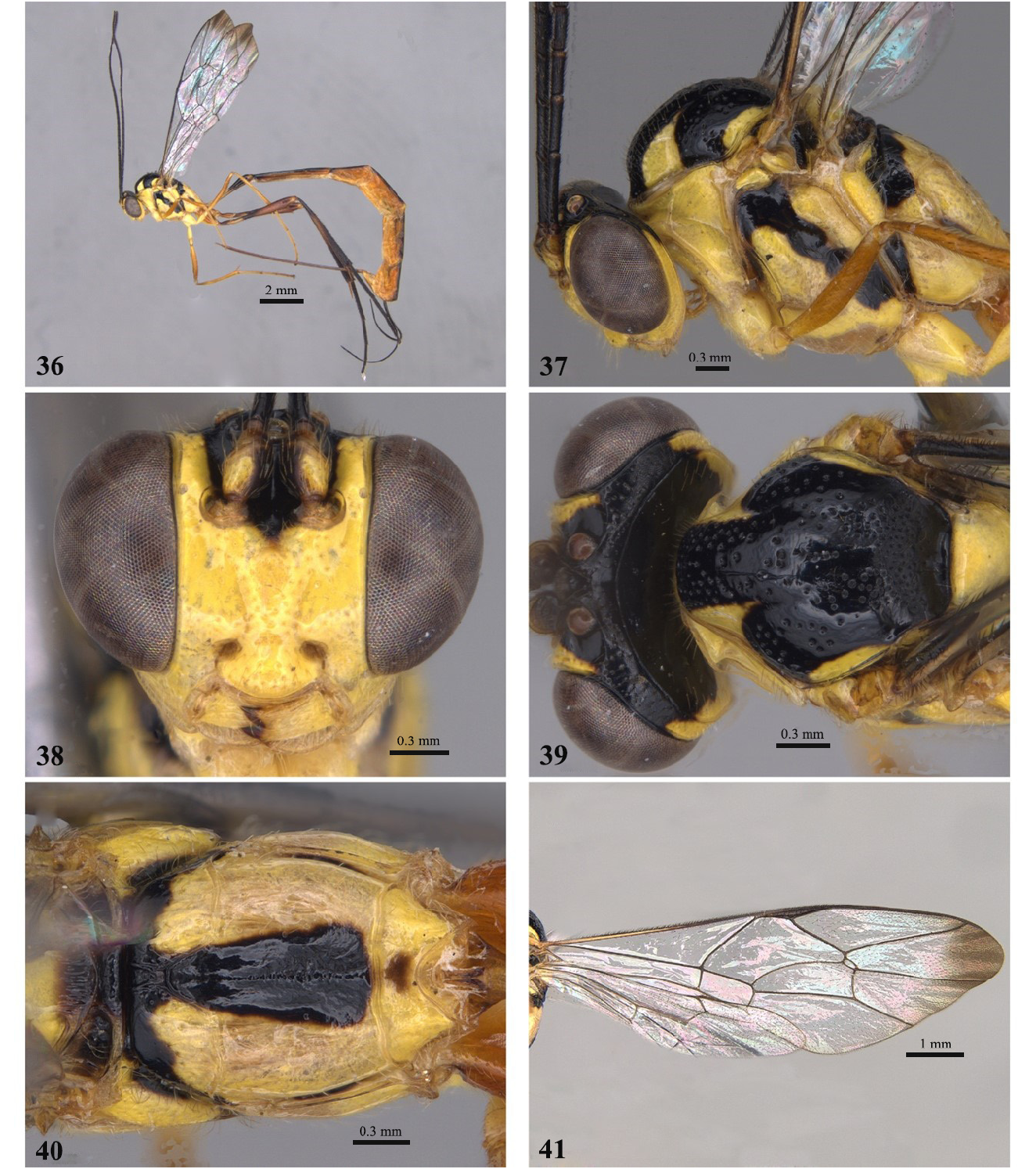
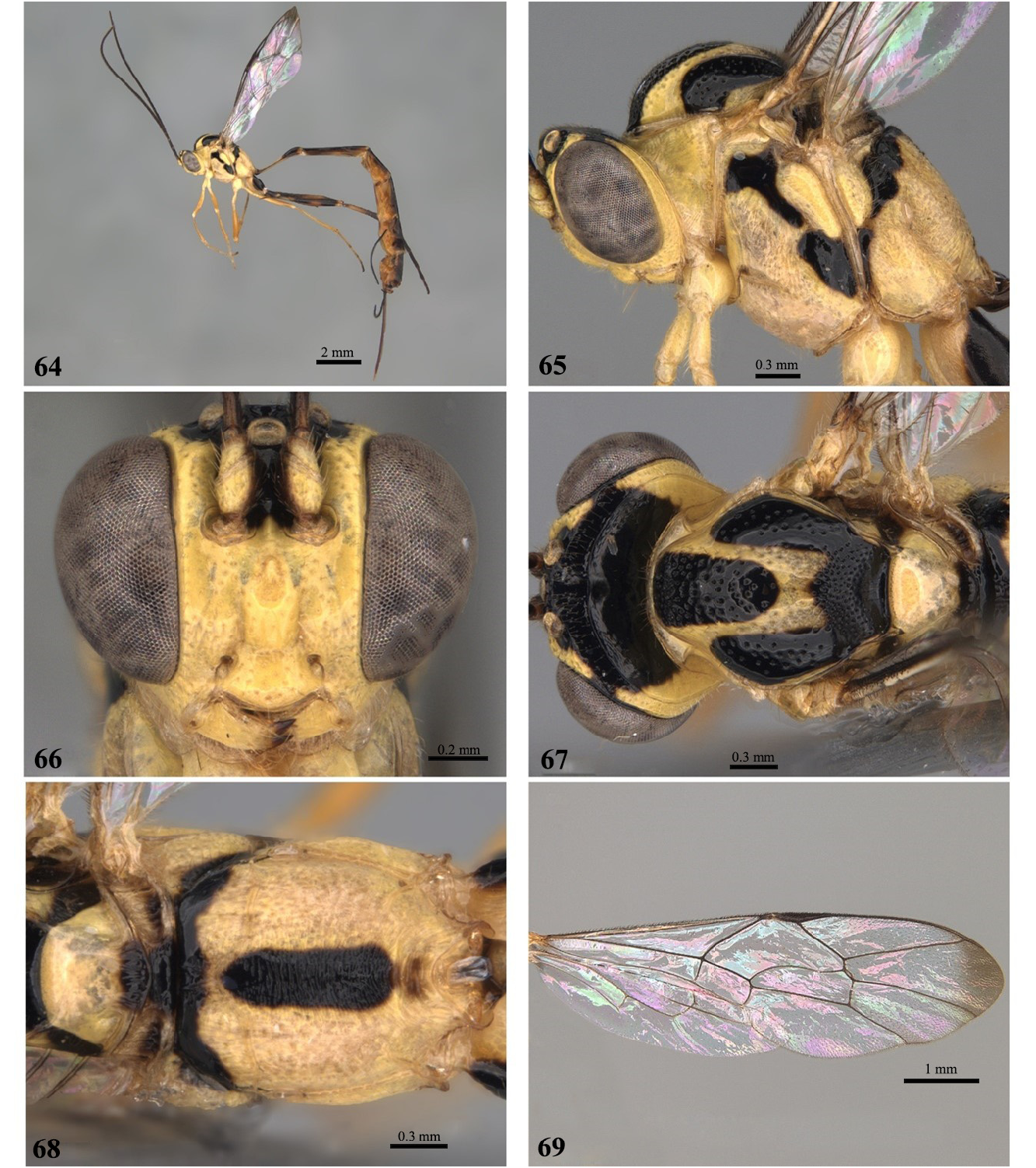
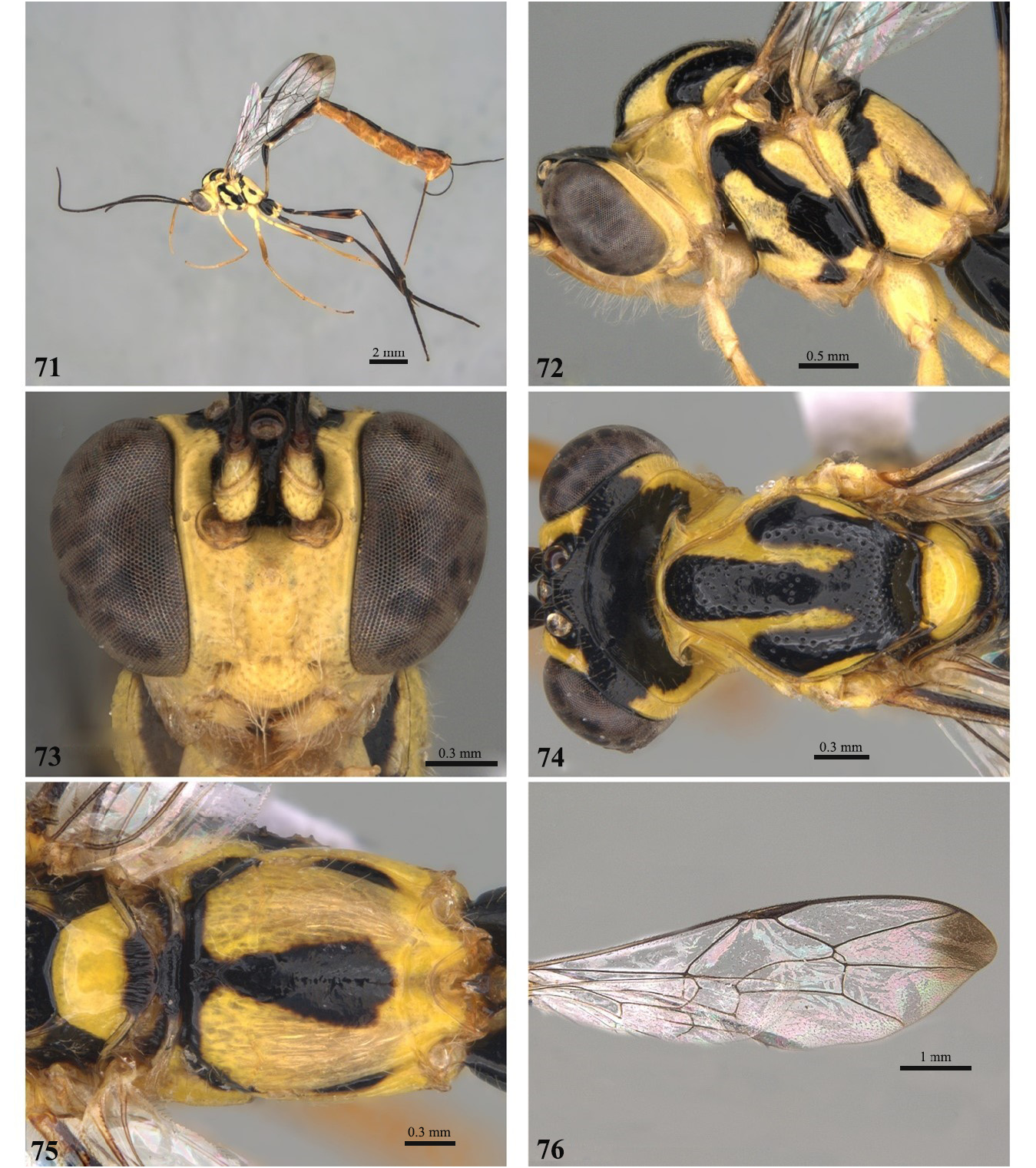
6 Pubescence long and conspicuous on basal flagellomeres and face ( Fig. 72 View FIGURES 71–76 ), mesopleuron and legs; fore wing hyaline with darkened apex ( Figs 27 View FIGURES 22–27 , 41 View FIGURES 36–41 , 69 View FIGURES64–69 , 76 View FIGURES 71–76 , 97 View FIGURES 92–97 ).................................................... E. fuzhi Gauld, 2000 View in CoL
- Pubescence short on basal flagellomeres and face ( Figs 2 View FIGURES 1–6 , 9 View FIGURES 8–13 , 16 View FIGURES 15–20 , 23 View FIGURES 22–27 , 30 View FIGURES 29–34 , 37 View FIGURES 36–41 , 44 View FIGURES 43–48 , 51 View FIGURES 50–55 , 58 View FIGURES57–62 , 65 View FIGURES64–69 , 79 View FIGURES 78–83 , 86 View FIGURES 85–90 , 93 View FIGURES 92–97 , 100 View FIGURES 99–104 ), mesopleuron and legs; fore wing completely hyaline without darkened apex ( Figs 6 View FIGURES 1–6 , 13 View FIGURES 8–13 , 20 View FIGURES 15–20 , 34 View FIGURES 29–34 , 48 View FIGURES 43–48 , 55 View FIGURES 50–55 , 62 View FIGURES57–62 , 83 View FIGURES 78–83 , 90 View FIGURES 85–90 , 104 View FIGURES 99–104 ).................. 7
7 Metapleuron short, submetapleural carina short and deep ( Figs 79 View FIGURES 78–83 , 86 View FIGURES 85–90 )........................................... 8
- Metapleuron moderately long, submetapleural carina shallow ( Figs 30 View FIGURES 29–34 , 37 View FIGURES 36–41 , 44 View FIGURES 43–48 , 51 View FIGURES 50–55 , 65 View FIGURES64–69 , 93 View FIGURES 92–97 , 100 View FIGURES 99–104 )...................... 10
8 Mesopleuron entirely yellow, at most with a black dot near the trailing edge.................. E. vitticolle Cresson, 1865 View in CoL
- Mesopleuron with diagonal black stripe continuous or discontinuous ( Figs 2 View FIGURES 1–6 , 9 View FIGURES 8–13 , 30 View FIGURES 29–34 , 37 View FIGURES 36–41 , 44 View FIGURES 43–48 , 51 View FIGURES 50–55 , 65 View FIGURES64–69 , 72 View FIGURES 71–76 , 79 View FIGURES 78–83 , 86 View FIGURES 85–90 , 93 View FIGURES 92–97 , 100 View FIGURES 99–104 )..... 9
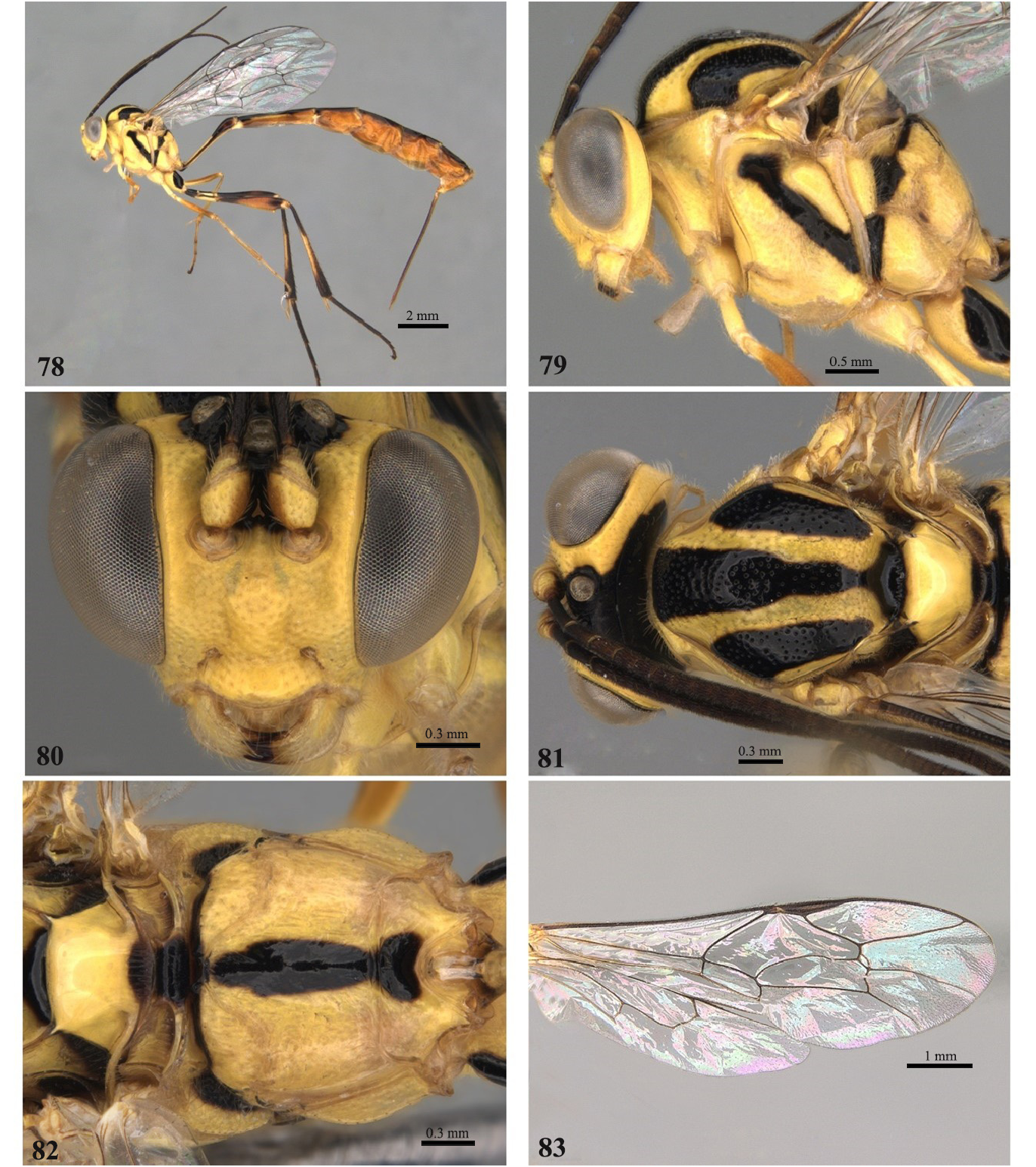
9 Propodeum smooth and polished, with anterior and posterior carina present ( Fig. 82 View FIGURES 78–83 ); mesoscutum yellow, completely punctate with two lateral black stripes and one central stripe extending from anterior to base of scutellum ( Fig. 81 View FIGURES 78–83 )......................................................................................... E. laphygmae View in CoL Costa Lima, 1953
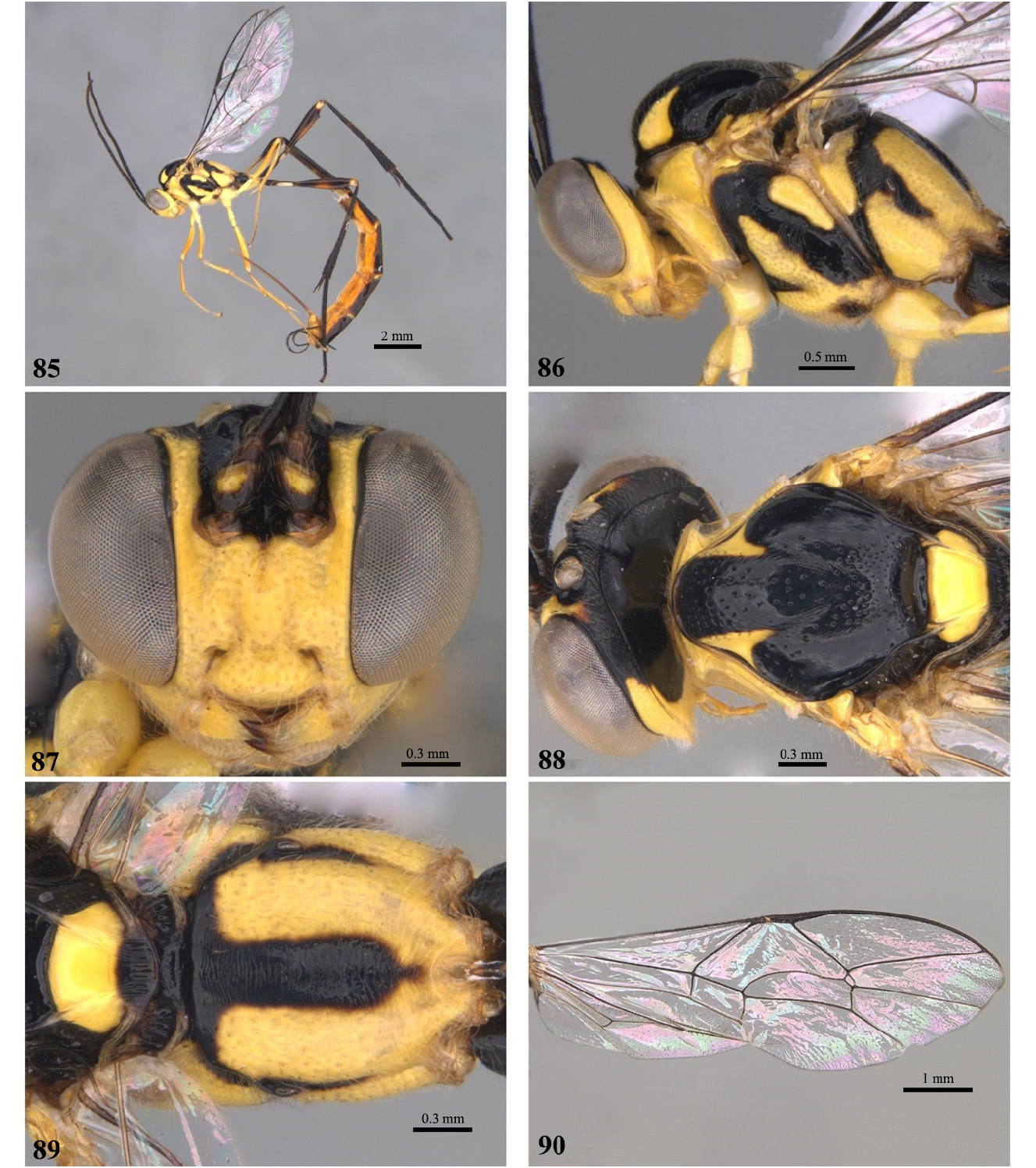
- Propodeum striate to coriaceous, with anterior and posterior transverse carina absent ( Fig. 89 View FIGURES 85–90 ); mesoscutum predominantly black, centrally punctate, lateral lobes only punctate anteriorly, with two small yellow marks anterior to notaulus ( Fig. 88 View FIGURES 85–90 )................................................................................. E. sinecarenatum sp. nov.
10 Fore wing with apex darkened ( Figs 27 View FIGURES 22–27 , 41 View FIGURES 36–41 , 69 View FIGURES64–69 , 76 View FIGURES 71–76 , 97 View FIGURES 92–97 )...................................................... 11
- Fore wing entirely hyaline ( Figs 6 View FIGURES 1–6 , 13 View FIGURES 8–13 , 20 View FIGURES 15–20 , 34 View FIGURES 29–34 , 48 View FIGURES 43–48 , 55 View FIGURES 50–55 , 62 View FIGURES57–62 , 83 View FIGURES 78–83 , 90 View FIGURES 85–90 , 104 View FIGURES 99–104 ).......................................... 12
11 Fore wing without areolet or rarely present in lenticular form, with the vein 1 m -cu touching the upper of vein 3 rs- m ( Fig. 69 View FIGURES64–69 ); propodeum with posterior transverse carina incomplete and delimited petiole area ( Fig. 68 View FIGURES64–69 )...... E. tantalium Gauld, 2000 View in CoL
- Fore wing with areolet quadrangular or triangular with vein 1 m-cu located below the upper part of vein 3 rs-m ( Figs 41 View FIGURES 36–41 , 97 View FIGURES 92–97 ); propodeum with posterior transverse carina complete and without delimited area petiolaris ( Figs 40 View FIGURES 36–41 , 96 View FIGURES 92–97 )............... 15
12 Fore wing with areolet................................................................................ 13
- Fore wing without areolet............................................................................. 14
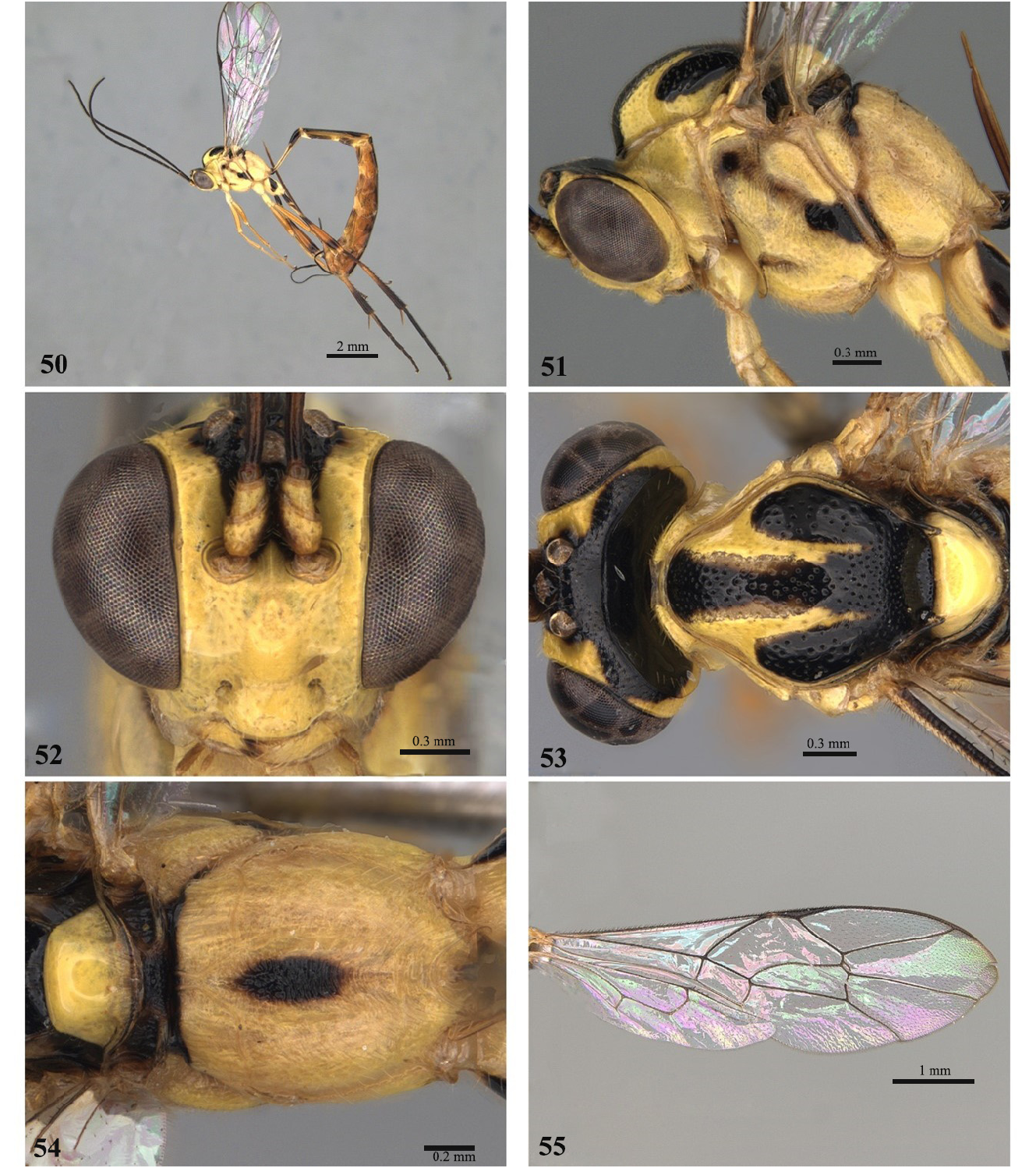
13 Propodeum rugose-punctate, with anterior and posterior transverse carina complete, with a central black band attached to the transverse band, touching the area petiolaris, without lateral bands ( Fig. 103 View FIGURES 99–104 )............... E. minense View in CoL Costa Lima, 1953
- Propodeum centrally rugose, with complete anterior and incomplete posterior transverse carinae, with a central black band separated from the transverse band ( Fig. 54 View FIGURES 50–55 )....................................... E. fluminense View in CoL Costa Lima, 1953
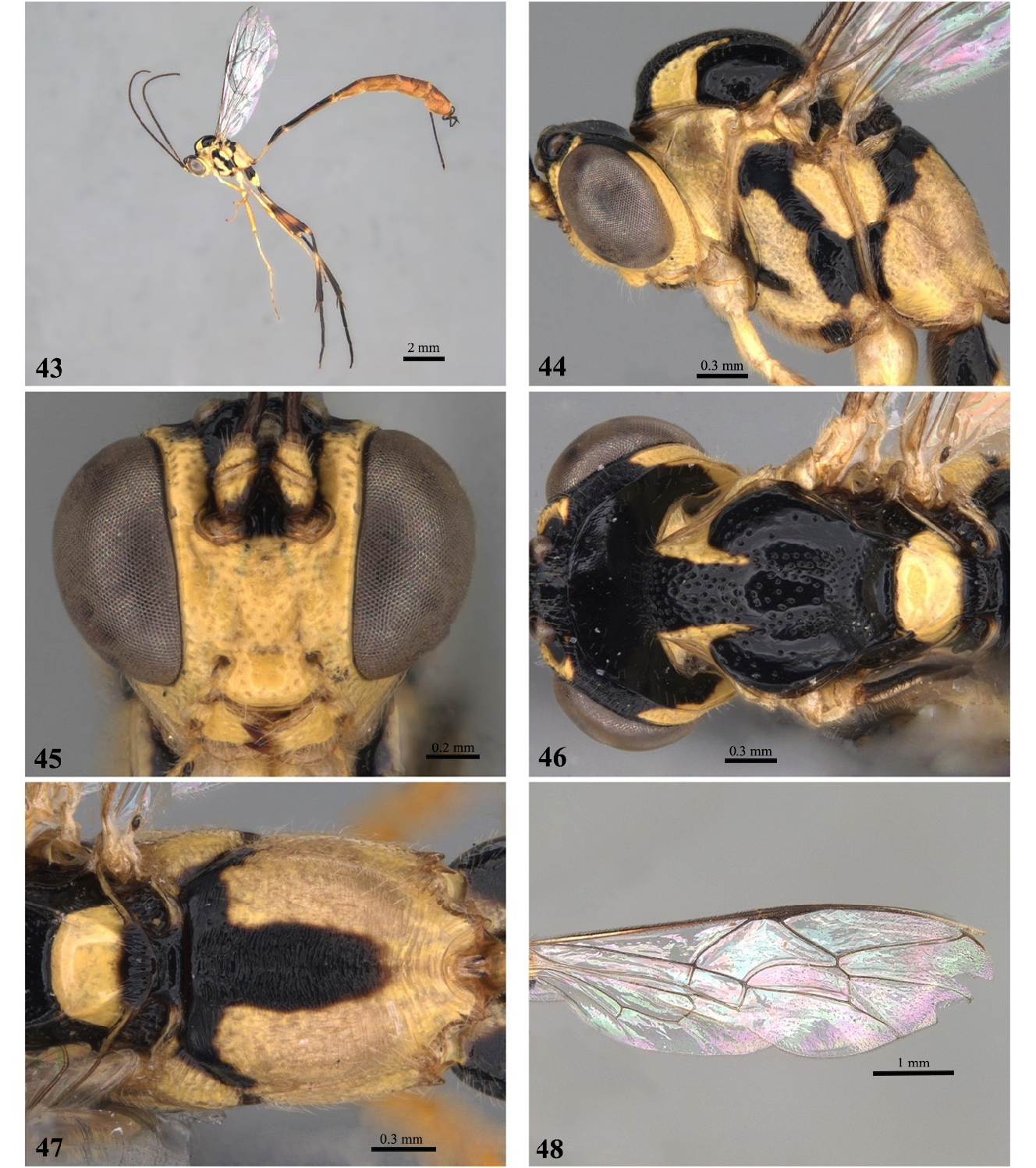
14 Propodeum striate with anterior transverse carina weak and barely present in central area, posterior carina absent ( Fig. 47 View FIGURES 43–48 ); pronotum with the upper extremity of the epomia strongly elevated ( Fig. 44 View FIGURES 43–48 ); ovipositor short, equal to length of hind posterior tibia ( Fig. 43 View FIGURES 43–48 )........................................................................... E. eneke sp. nov.
- Propodeum striate and wrinkled with transverse anterior carina complete and strong, posterior carina present only in the central area ( Fig. 33 View FIGURES 29–34 ); pronotum with the upper extremity of the weakly raised epomia ( Fig. 30 View FIGURES 29–34 ); ovipositor straight, 1.7 × times longer than hind tibia ( Fig. 29 View FIGURES 29–34 )................................................................. E. caqueta sp. nov.
15 Sternaulus strongly marked anteriorly ( Fig. 37 View FIGURES 36–41 ); scutellum without punctures; hind coxa without black mark.............................................................................................. E. dolopon Gauld, 2000 View in CoL
- Sternaulus moderately marked anteriorly ( Fig. 93 View FIGURES 92–97 ); scutellum punctate; hind coxa with black mark.................................................................................................. E. macrum ( Enderlein, 1921) View in CoL
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |