Ceratodoris plebeia ( Bergh, 1902 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5443.4.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:F4D19D80-3772-4F85-ACB2-6140D2F3BABB |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11074256 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B587E3-FFC6-EE1C-00F9-4DCEFCBAF8C0 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Ceratodoris plebeia ( Bergh, 1902 ) |
| status |
|
Ceratodoris plebeia ( Bergh, 1902) View in CoL
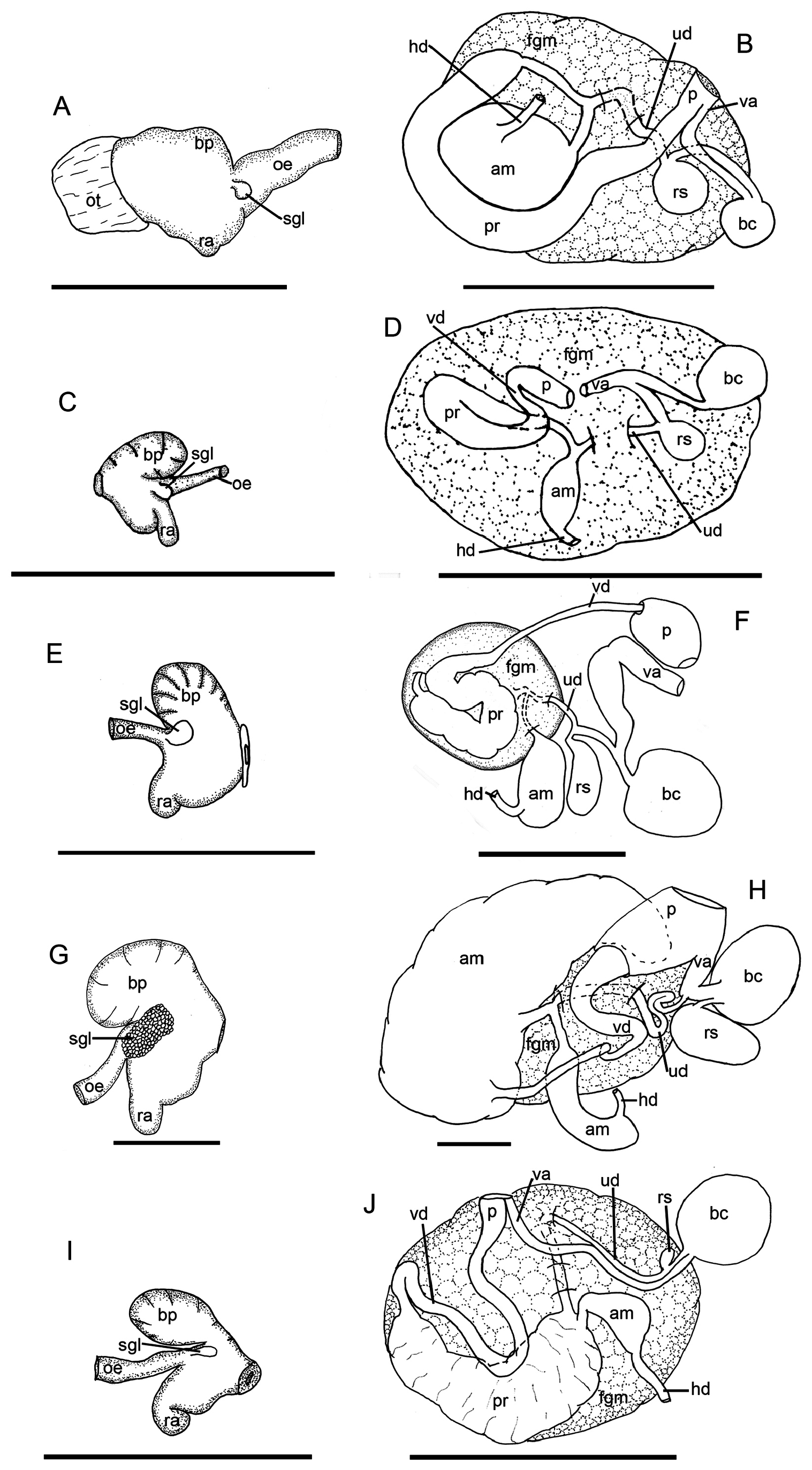
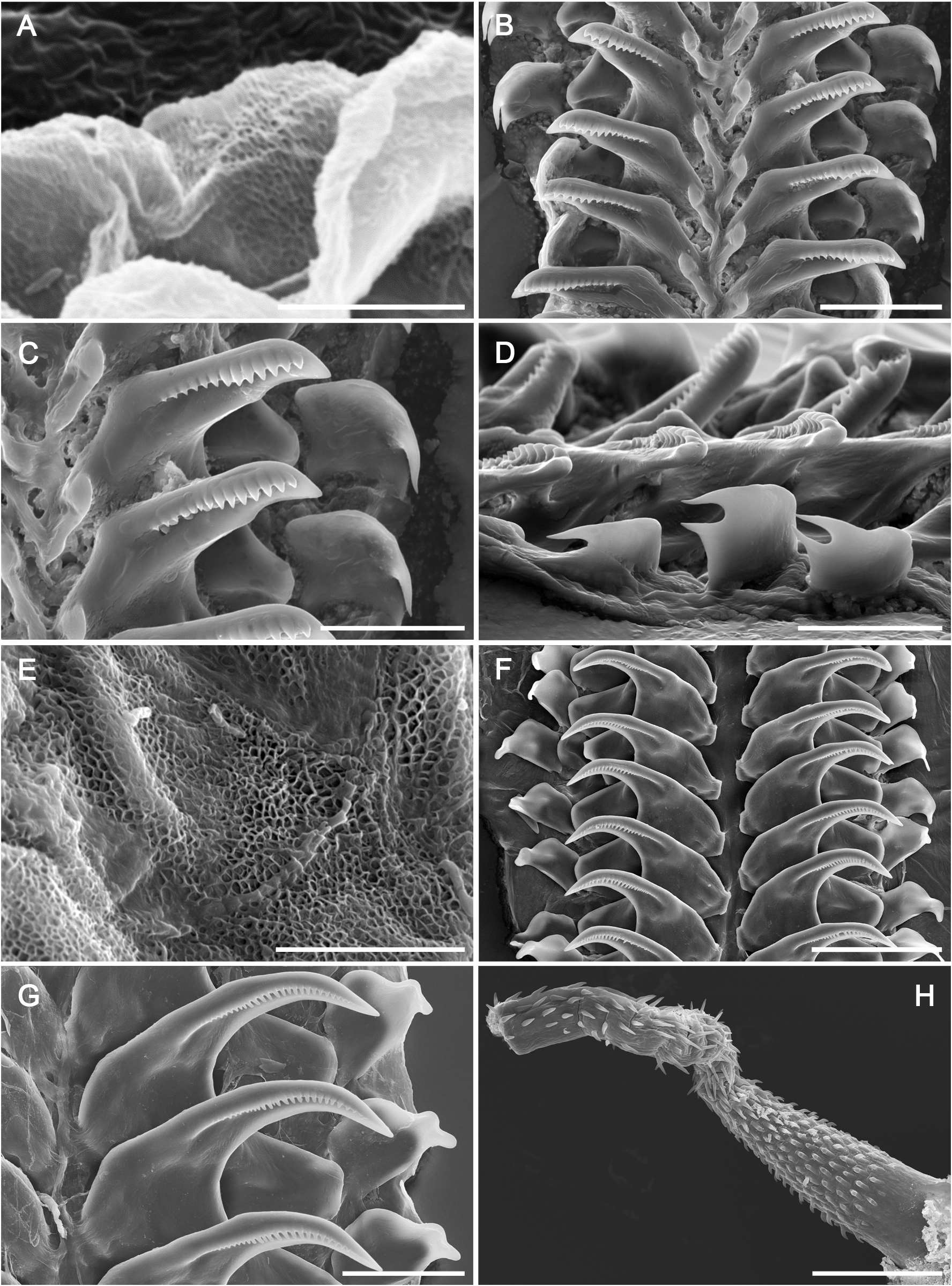
( Figs 1E View FIGURE 1 , 2G‒H View FIGURE 2 , 4E‒H View FIGURE 4 )
Idalia plebeia Bergh (1902): 186 View in CoL ; plate III; Figs. 15‒19.
Okenia cf. plebeia View in CoL — Hung & Huang (2021): 111, text-figs.
Material examined. MNCN 15.05 About MNCN /94477, Kinmen, Taiwan, intertidal, 28 November 2019, col. by S . T. Huang , 96% EtOH, dissected ( SEM: Radula, labial cuticle, penis) ; MNCN 15.05 About MNCN /94478, Kinmen, Taiwan, intertidal, 28 November 2019, col. by S . T. Huang , 96% EtOH, dissected ( SEM: Radula, labial cuticle, penis) ; MNCN 15.05 About MNCN /94479, Kinmen, Taiwan, intertidal, 28 November 2019, col. by S . T. Huang , 96% EtOH .
External morphology and color pattern ( Figs. 2C‒D View FIGURE 2 ). Preserved specimens 10–20 mm length. The species was described in detail by Bergh (1902) in its original description.
Foregut anatomy ( Figs. 2G View FIGURE 2 , 4E‒G View FIGURE 4 ). Buccal bulb thick and muscular ( Fig. 2G View FIGURE 2 ). Rounded, wide, dorsal buccal pump expanding posteriorly. Radular sac located ventrally, expanding backwards. Esophagus begins from buccal bulb behind buccal pump. Salivary glands elongated and granulated, formed by several small, rounded glands. Salivary glands located at junction of esophagus with buccal bulb. Nervous system covers this junction. Esophagus continues posteriorly and inserts into digestive-hermaphroditic gland. Labial cuticle surrounds lips and expands within buccal pump. Part of labial cuticle located within buccal pump with honey-comb elements ( Fig. 4E View FIGURE 4 ). Radular formula 25‒26 × 1.1.0.1.1. Inner lateral tooth with single large and thin cusp, and wide, rectangular base ( Figs. 4F– G View FIGURE 4 ). Cusp large and pointed, with a masticatory margin bearing 22–25 small, pointed denticles ( Fig. 4G View FIGURE 4 ). Denticles with rounded tips. Denticles located in middle part of masticatory margin larger than lateral ones. Outer base ends in somewhat prominent wing, with rounded external edge. Outer lateral tooth much smaller ( Figs. 4F–G View FIGURE 4 ). Base of outer lateral tooth rectangular, top with an extension, with a rounded base from which an oval peak emerges ( Fig. 4G View FIGURE 4 ).
Reproductive system ( Figs. 2H View FIGURE 2 , 4H View FIGURE 4 ).Reproductive system located in anterior third of body.Thin hermaphroditic duct begins at ovotestis, located inside digestive-hermaphroditic gland. Hermaphroditic duct expands into elongate, sausage-shape ampulla. Postampullary duct emerges from ampulla and divides into two, thin ducts. Short oviduct enters inside female gland mass, other connects with prostate. Prostate very big, with fluffy texture, covers almost half size of reproductive system. It continues as a very thin vas deferens. End of vas deferens widens and expands to ejaculatory duct. Penis with penial spines ( Fig. 4H View FIGURE 4 ). Penial spines at base short and hooked, arranged in longitudinal rows. Spines become larger, straight in middle, and more spread out, slight shorter and hooked towards opening area. Vagina small, wider than vas deferens, connects with large, oval bursa copulatrix. From base of bursa copulatrix arises a very thin duct that connects with an elongated receptaculum seminis. Approximately in middle part of vagina, a very thin uterine duct arises and enters female gland mass. Uterine duct wider at part that enters female gland mass.
Distribution. Thailand ( Bergh 1902; Gosliner et al. 2018), India ( Gosliner et al. 2018) and Taiwan ( Hung & Huang 2021; present study).
Natural history. The species lives on rocks, inhabiting shallow reefs and gravel areas. Ceratodoris plebeia feeds on bryozoan. Its egg mass is yellowish white and is a simple spiral consisting of 4-5 whorls ( Hung & Huang 2021).
Remarks. Since its original description, C. plebeia has hardly been found ( Gosliner et al. 2018; Hung & Huang 2021). The external morphology of this species was described in detail by Bergh (1902) and our specimens agree with it. Bergh (1902) also described and drawn the radular teeth, which are shown for first time by scanning electron microscope in the present study. Moreover, Bergh (1902) described some details of the reproductive system, mainly focused on the male part. Here we provide a complete description.
| T |
Tavera, Department of Geology and Geophysics |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Goniodoridinae |
|
Genus |
Ceratodoris plebeia ( Bergh, 1902 )
| Paz-Sedano, Sofia, Cobb, Gary, Gosliner, Terrence M. & Pola, Marta 2024 |
Okenia cf. plebeia
| Hung, C. C. & Huang, S. T. 2021: 111 |
Idalia plebeia
| Bergh, R. 1902: 186 |