Letheobia gracilis (Sternfeld)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.177278 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6237830 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B587D9-FF80-3805-90A8-FA5AF0D8FC77 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Letheobia gracilis (Sternfeld) |
| status |
|
Letheobia gracilis (Sternfeld)
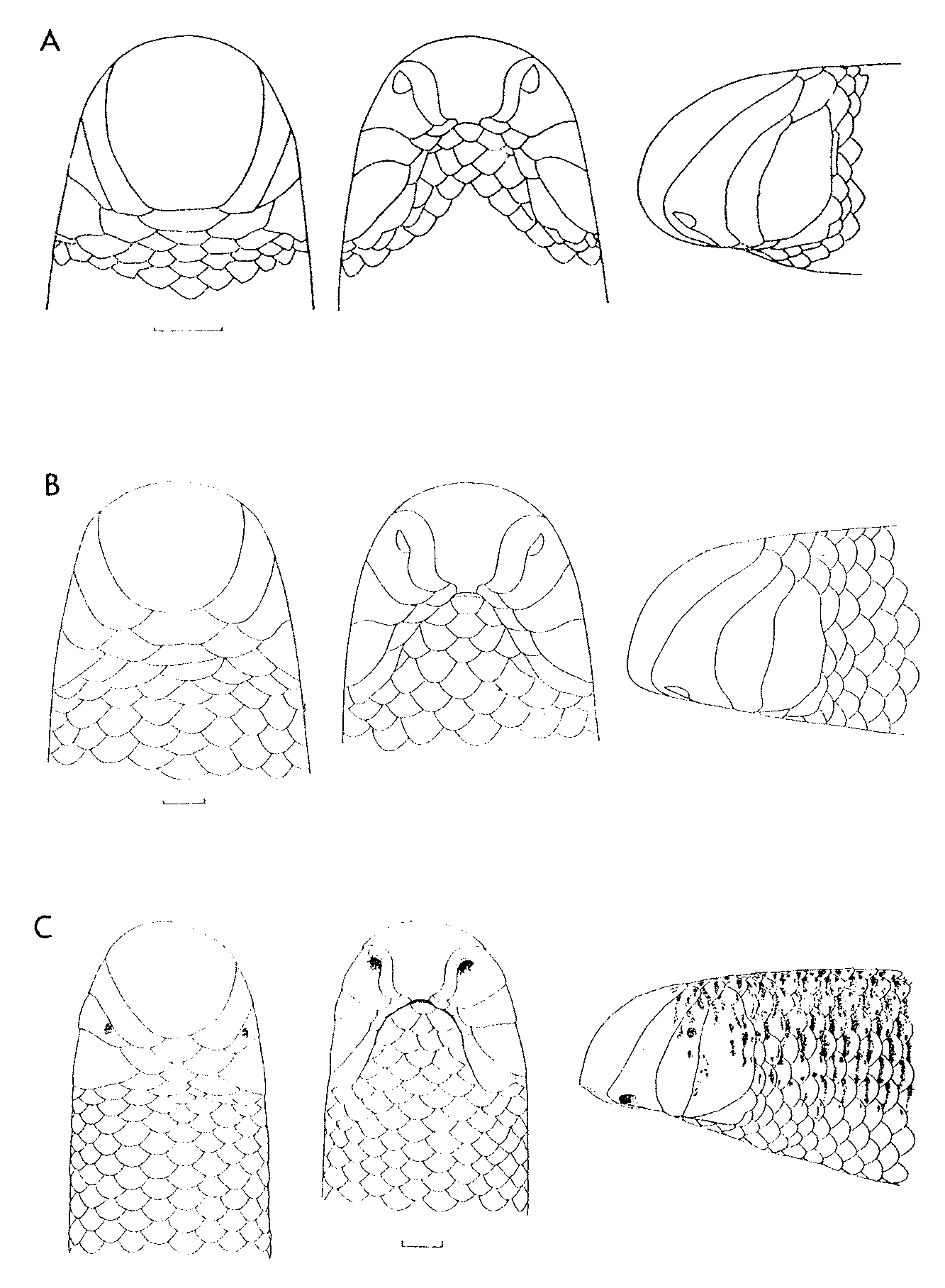
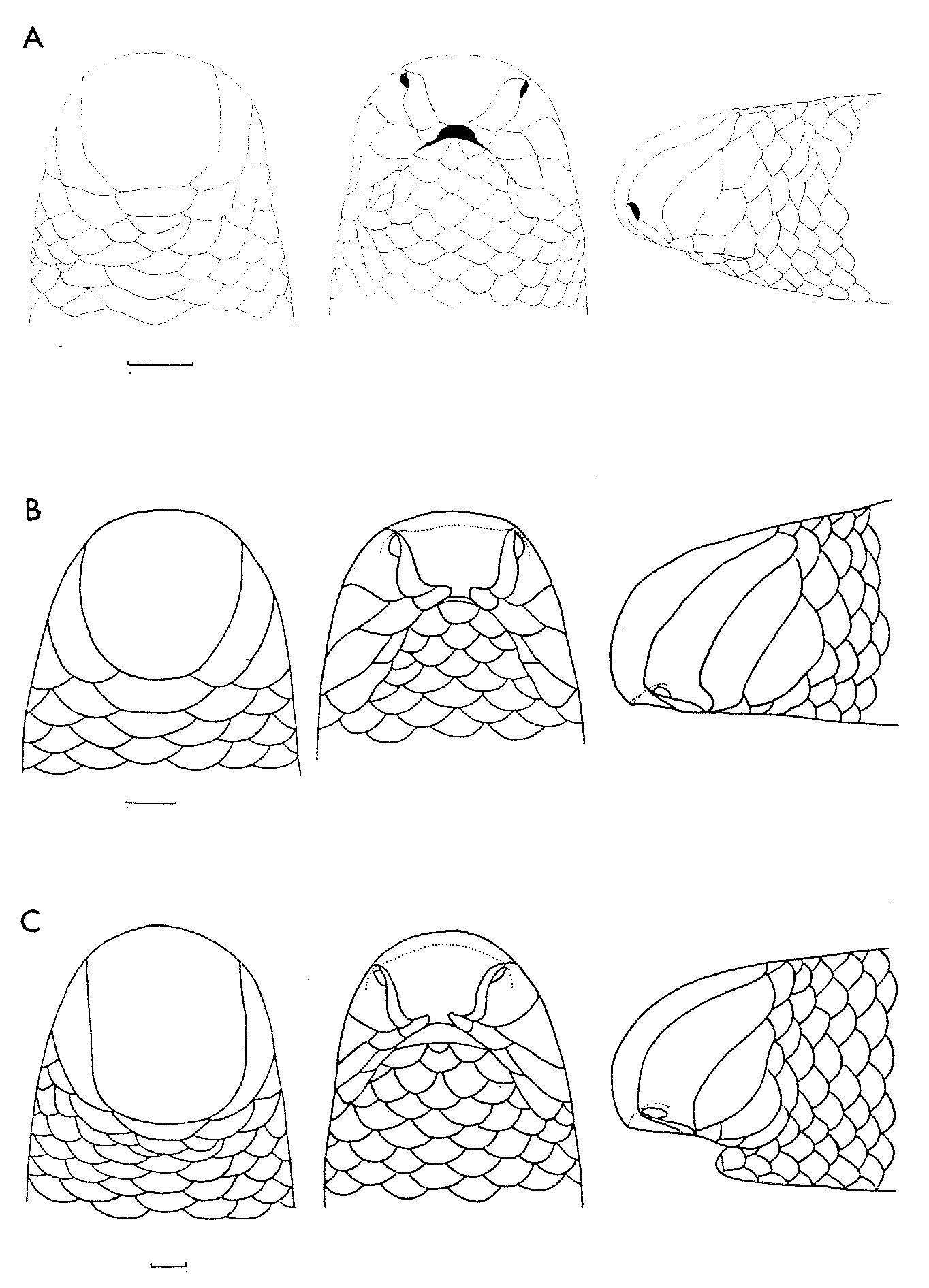
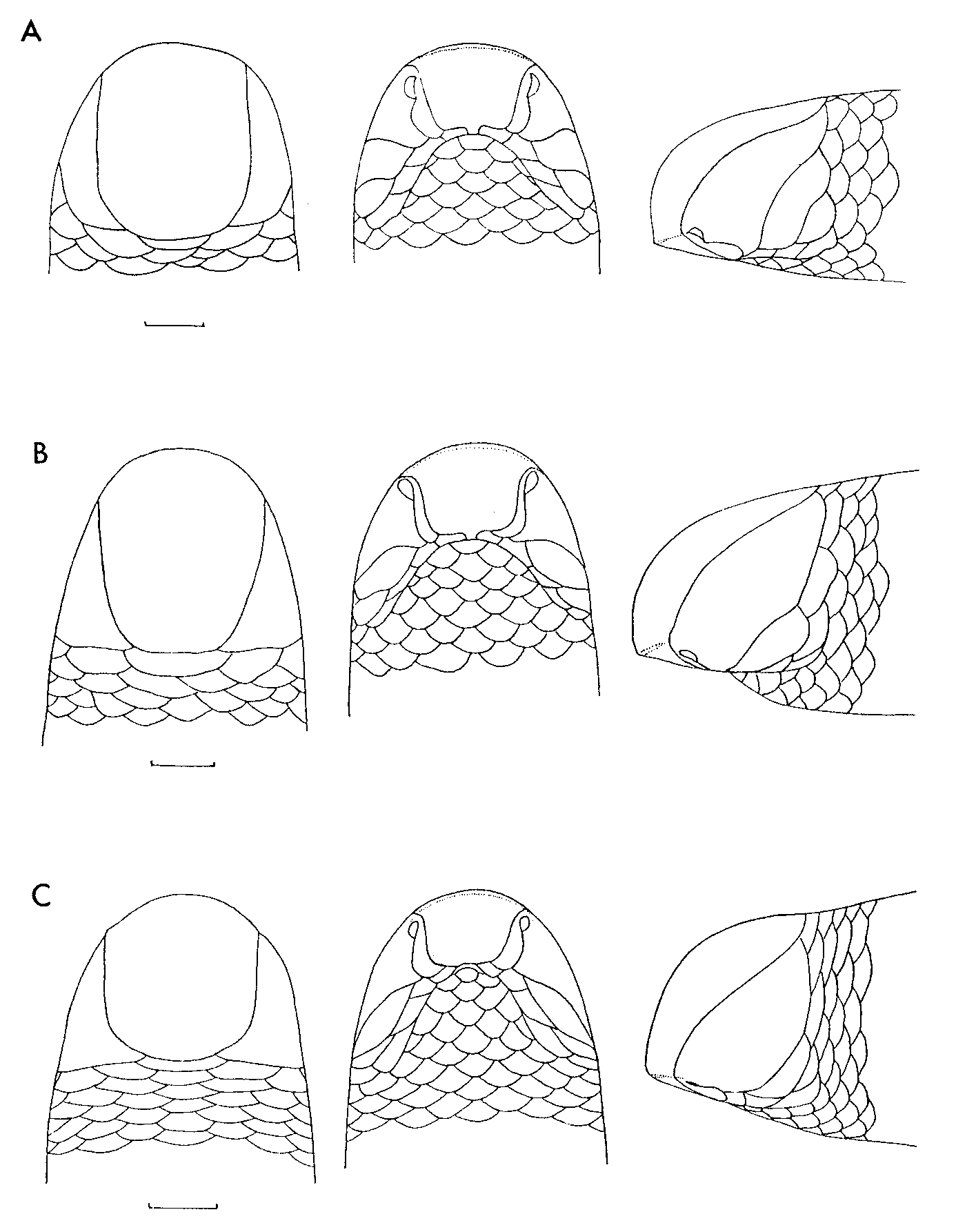
( Fig 7 View FIGURE 7 A)
Gracile blind-snake
Typhlops lumbriciformis – (not Peters) Boulenger 1896: 590 (Fwambo).
Typhlops gracilis Sternfeld 1910 , Mitt. Zool. Mus. Berlin 5: 70. Type locality: Kitungulu in Urungu, Deutsch-Ostafrika [= Sumbawanga District, Tanzania], (ca. 04°32’S, 34°13’E, elevation 1370 m), collected by H. Fromm in 1910, holotype ZMB 22030; Sternfeld 1910b: 10; Boulenger 1915b: 614; Werner 1921: 289; Barbour & Loveridge 1928: 104; Vesey-FitzGerald 1958: 34, Photo 3; Broadley & Pitman 1960: 438; Witte 1962: 43, 1966: 47, Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 ; Broadley 1971: 69; Broadley & Howell 1991: 21.
Typhlops leptosoma Witte 1933 , Rev. Zool. Bot. Afr. 23: 189 & Ann. Mus. Roy. Congo Belge, Zool. (1) 3: 82, Figs. 1–3 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 . Type locality: Lukafu, Haut-Katanga, Congo Belge [= Democratic Republic of Congo] (10°28’S, 27°32’E, elevation 1115 m), holotype MRAC 7251; Witte 1953: 148, Figs. 33–34.
Typhlops katangensis Witte 1933 , Rev. Zool. Bot. Afr. 23: 190, Ann. Mus. Roy. Congo Belge, Zool. (1) 3: 84, Figs. 1–3 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 . Type locality: Lukonzolwa, Haut-Katanga, Congo Belge [= Democratic Republic of Congo] (08°45’S, 28°40’E, elevation 1200 m), holotype MRAC 7375.
Typhlops kibarae – (part) Witte 1953: 150 (Kaswabilenga).
Typhlops gracilis leptosoma – Laurent 1960: 20.
Rhinotyphlops gracilis – Roux-Estève 1974: 224, Fig. 159, 1975: 445; Hahn 1980: 30; Meirte 1992: 21; McDiarmid et al. 1999: 80; Spawls et al. 2002: 296; Spawls et al. 2006: 92.
Letheobia gracilis – Broadley et al. 2003: 43.
Description. Snout with an angular horizontal edge. Rostral very broad, truncated posteriorly; frontal trapezoid, usually separated from nasals by supraoculars, which are oblique, with lateral apex wedged between nasal and ocular, which is separated from the subocular by one temporal (two in types of Typhlops leptosoma Witte ); eye not visible; nasal suture rising from second labial; SIP X (N1, P, S, S); scale rows 22-22-22; MD 629–726; vertebrae 377–465; MD/V ratio 1.54–1.77; L/D ratio 70–107. Colourless.
Size. Largest specimen (NMZB-UM 2542— Chilongowelo, Zambia) 540 mm in total length.
Habitat. Savanna - Miombo woodland and Sumbu thicket. Found crawling upon red earth and dug up in a potato patch in Abercorn ( Vesey-FitzGerald 1958). The Tatanda specimen was ploughed up by oxen.
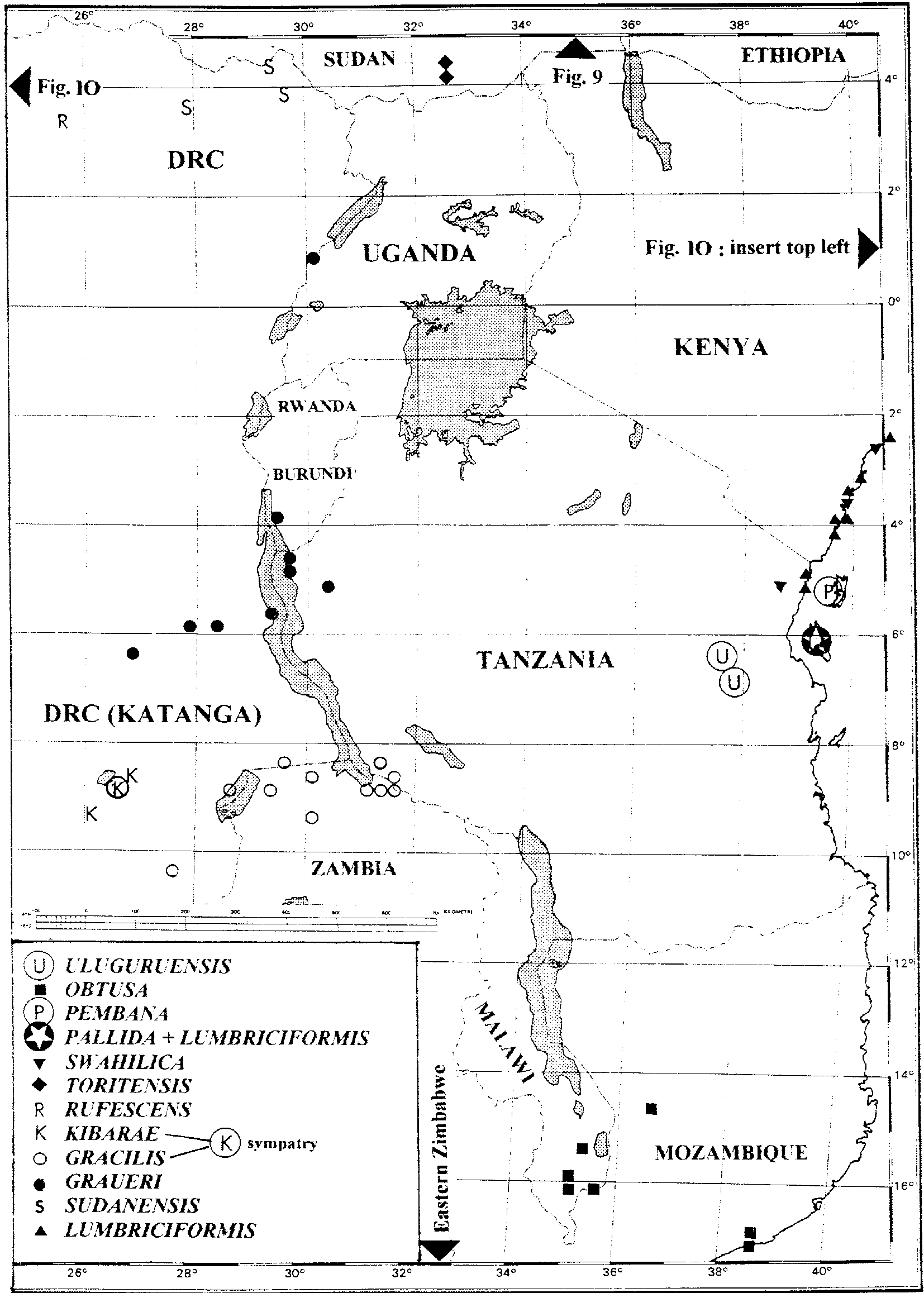
Distribution. Southeastern Democratic Republic of Congo, northeastern Zambia and southwestern Tanzania, 700–1400 m ( Fig. 10 View FIGURE 10 ).
Localities. DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF CONGO. Kaswabilenga IRSNB 2203; Lukafu MCZ 42896; MRAC 7251 (holotype of T. leptosoma ), 7252; Lukonzolwa IRSNB 4972; MRAC 7375 (holotype of T. katangensis ). ZAMBIA. Buleya ( Broadley & Pitman 1960); Chilongowelo NMZB-UM 2542; Fwambo ( Boulenger 1896) BMNH 94.12.20.8; Kaputa IRSNB 8628; Mbala IRSNB 2826, 2827 (4); 9038; MCZ 54051-52, 54054, 183654; NMZB 2540-41; PEM 713; Mporokoso IRSNB 8625; Mukupa IRSNB 8629. TANZANIA. Kitungulu ( Sternfeld 1910) ZMB 44090 (holotype); Tatanda NMZB 6665.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Letheobia gracilis (Sternfeld)
| Wallach, Van 2007 |
Letheobia gracilis
| Broadley 2003: 43 |
Rhinotyphlops gracilis
| Spawls 2006: 92 |
| Spawls 2002: 296 |
| Meirte 1992: 21 |
| Hahn 1980: 30 |
| Roux-Esteve 1974: 224 |
Typhlops gracilis leptosoma
| Laurent 1960: 20 |
Typhlops kibarae
| Witte 1953: 150 |
Typhlops gracilis
| Broadley 1991: 21 |
| Broadley 1971: 69 |
| Witte 1962: 43 |
| Broadley 1960: 438 |
| Vesey-FitzGerald 1958: 34 |
| Barbour 1928: 104 |
| Werner 1921: 289 |
| Boulenger 1915: 614 |
| Sternfeld 1910: 10 |
Typhlops lumbriciformis
| Boulenger 1896: 590 |