ERIOCOCCIDAE
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4765.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C442D94C-0EB4-4509-B762-913707214819 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3796768 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B2EA64-0A4A-4637-2CFC-F985FD9ED02D |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
ERIOCOCCIDAE |
| status |
|
Group C. BSE ERIOCOCCIDAE View in CoL View at ENA
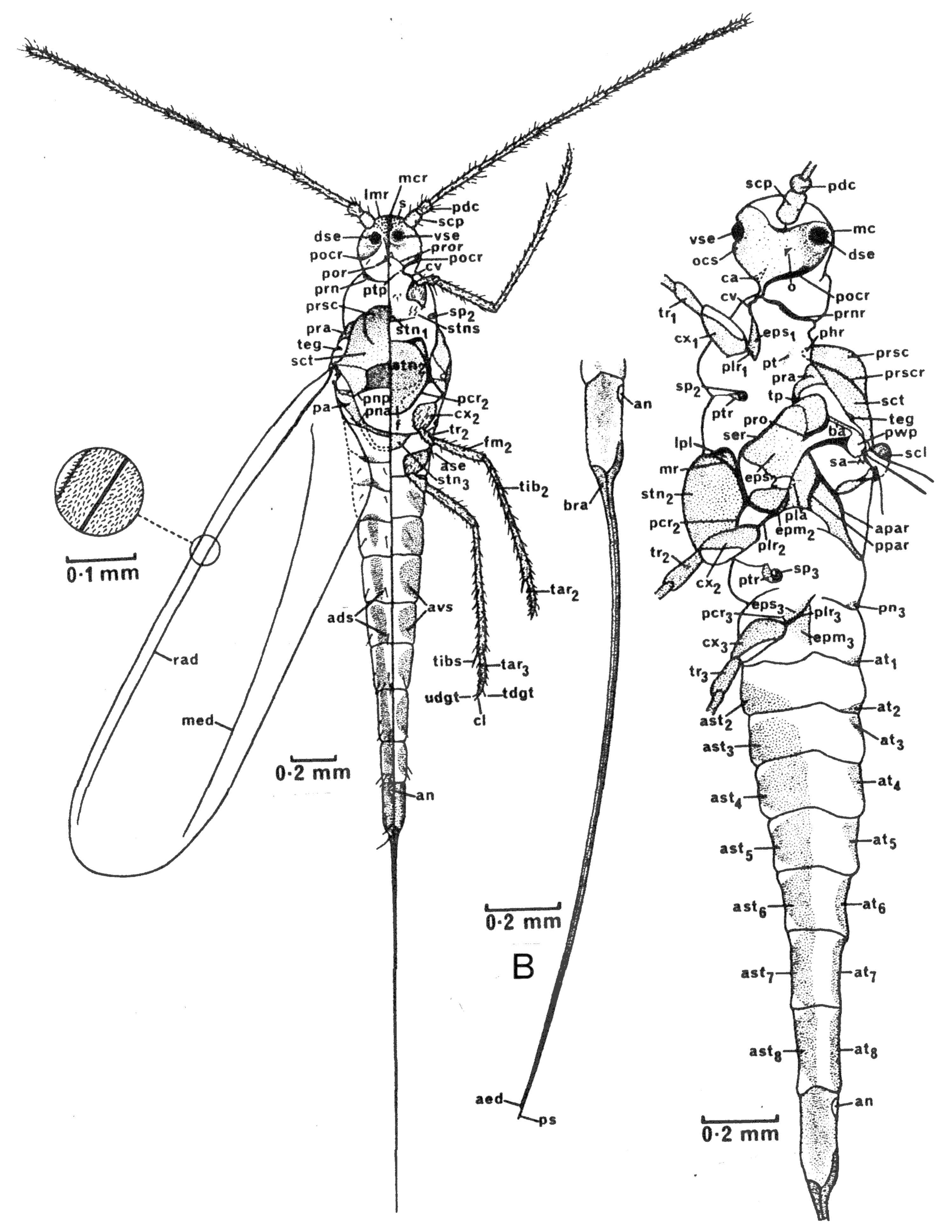
Introduction. The molecular studies of Cook and Gullan ( Cook & Gullan 2004; Gullan & Cook 2007; Kondo et al. 2016) found that there was a clade within the Eriococcidae that included E. buxi , the Australian eriococcid genus Cylindrococcus Maskell (1892) ( Fig. 43 View FIGURE 43 ) and the families Beesoniidae and Stictococcidae . In the analysis of Hodgson and Hardy (2013), E. buxi fell within a polytomy which included the acanthococcine eriococcids, possibly because the sensoria on each trochanter are roundish and in a triangle. However, the italicized character-states below separate it quickly from the acanthococcid group, whilst the possession of halteres separates it from the Gondwanan group and from the Stictococcidae and Beesoniidae . These four taxa ( E. buxi , Cylindrococcus , Beesoniidae and Stictococcidae are dealt with separately below.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |