Atractides Koch, 1836
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.172007 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5679301 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B187E0-FFD9-575B-CD09-F93D0C82CD19 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Atractides Koch, 1836 |
| status |
|
Genus Atractides Koch, 1836 View in CoL
Diagnosis: Character states as given for the family. Differential characters to separate Records ( Table 2): Benthos samples at nine spring sites in Gutland, 51 individuals ( Gerecke et al. 2005). E1 129, E7 54 larvae, parasitic on chironomids. 10 larvae were bred from a female from the spring site Lux Qu19 (E1). Attribution by rearing.
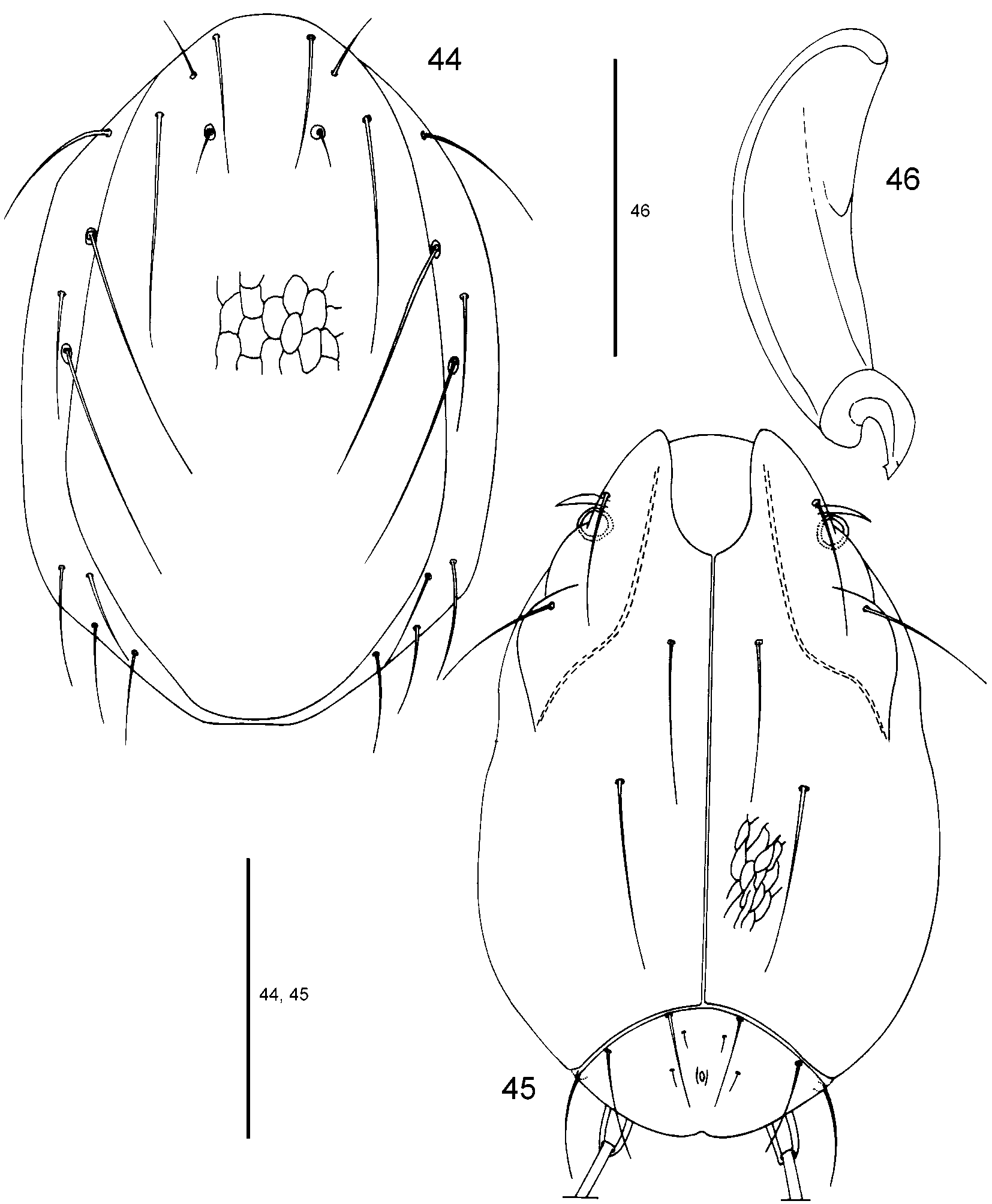
Description (unless otherwise indicated, n = 5): Idiosoma moderately elongated ( Figs. 44, 45 View FIGURES 44 – 46 ). Length/width of idiosoma 225–230 (227)/133–145 (140).
Dorsal idiosoma ( Fig. 44 View FIGURES 44 – 46 ): Dp relatively narrow and slightly tapered posteriorly, largest width in the posterior third of the plate, length/width 243–250 (247)/130–138 (134), Mp2Amdp 38–42 (40), Mp1Mp1 46–50 (48), Mp2Mp2 38–40 (39), Lp1Lp1 34–36 (35), Lp2Lp2 70–73 (72), Mp1Lp 1 12–14 (13), Mp2Lp 2 17–18 (17), Mp1Lp 2 20–23 (22), Lp1Lp2 32–34 (33), Mp 1 18–22 (20), Mp 2 19–22 (21), Lp1 47–65 (54), Lp2 85–91 (89), Hu 57–67 (60), Mh1 95–99 (97), Mh2 88–96 (93), Mh3 43–46 (44), Mh4 37– 42 (40), Lh1 43–52 (47), Lh2 44–48 (46), Lh3 45–48 (46).
Ventral idiosoma ( Fig. 45 View FIGURES 44 – 46 ): Expp relatively large (in contrast to the other Atractides species reported here). Length CXIIII (from the median gnathosomal bay to the posterior end of CXIIII) 180–190 (186), width CXIIII 75–79 (77), common median length of both CXIIII 160–165 (164), maximum length of CXIIII 225–230 (229), C1C2 49–53 (51), C1Mmcp 15–17 (16), C4Pmcp 97–102 (100), C1C4 53–59 (55), C1 55–66 (60), C2 47–52 (49), C3 50–63 (56), C4 95–100 (97), length/width Expp 44–46 (45)/79–87 (81), E1 E 1 12 –16 (13), E2 E 2 22 –23 (22), E1 4 –6 (5), E2 6 –8 (7), V 1 31–35 (32), V2 34 – 37 (36), V3 45 –51 (48), V4 170–180 (176), V1V 1 23–24 (24), V2V2 65 –70 (67), V3V3 79 –82 (80), V4V4 58 –66 (61), V1V 2 25–28 (26), length/width of projecting base of V 4 17–20 (18)/11–11 (11).
Gnathosoma: Base 72–76 (73), chelicera ( Fig. 46 View FIGURES 44 – 46 ) 67–72 (69), chela 18–19 (18), length/width P1+ 2 31–34 (33)/29–33 (31), P 3 19–21 (20)/20–22 (21), length claw 11–13 (12), long seta on P3 76–82 (79).
Legs: Leg I ( Fig. 47 View FIGURES 47 – 49 ): Total length 189–199 (194), length/height IL1 (1se) 30–32 (31)/18–20 (19), IL2 (7se) 37–39 (38)/17–18 (17), IL3 (7se) 32–35 (33)/16–17 (17), IL4 (4se, 1so, 1eu) 40–41 (40)/17–18 (17), IL5 (12se, 1so, 2eu) 50–52 (51)/14–15 (14).
Leg II ( Fig. 48 View FIGURES 47 – 49 ): Total length 205–214 (209), length/height IIL1 (1se) 31–32 (32)/19– 21 (20), IIL2 (7se) 38–39 (38)/18–19 (18), IIL3 (4se, 1 so) 33–35 (34)/16–18 (17), IIL4 (9se, 1 so) 43–45 (44)/16–18 (16), IIL5 (12se, 1so) 60–63 (61)/12–14 (13).
Leg III ( Fig. 49 View FIGURES 47 – 49 ): Total length 241–252 (247), length/height IIIL1 (1se) 38–40 (39)/ 16–18 (17), IIIL2 (6se) 40–43 (42)/16–18 (17), IIIL3 (4se, 1so) 41–42 (41)/15–16 (16), IIIL4 (8se, 1so) 56–58 (57)/16–17 (17), IIIL5 (10se) 66–69 (68)/13–14 (14).
Diagnostic characters of larvae: To date, the larva of Atractides fonticolus has remained undescribed. It differs from the other Atractides larvae here with respect to leg length, length of Dp and width of Expp.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |