Compsaraia iara, Maxwell J. Bernt & James S. Albert, 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1643/CI-16-529 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:ED8EB131-6D29-4664-B4AF-00A7BD2C247A |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5681256 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/089E738D-0D2D-4C35-B3B2-6518CB675C26 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:089E738D-0D2D-4C35-B3B2-6518CB675C26 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Compsaraia iara |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Compsaraia iara View in CoL , new species
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:089E738D-0D2D-4C35-B3B2- 6518CB675C26
Figures 1 View Fig. 1 , 3, 4, 5B; Table 1 View Table 1
Porotergus gymnotus Cox Fernandes, 1995:30 View in CoL –31, 93–95. Porotergus View in CoL sp. Cox Fernandes, 1995:31–32, 102–104. Porotergus View in CoL sp. 2. Cox Fernandes et al., 2004 (supplementary
material):4.
Porotergus View in CoL sp. Crampton and Cella-Ribeiro, 2013:272–273.
Holotype.— MZUSP 121514 , 203 mm TL, Brazil, Pará, Rio Amazonas, between Rio Mojui and Furo do Tajapuru, between towns Gurupá and Serraria , 01°12 "26 " "S, 51°19"09" "W, A. Zanata et al., 15 November 1994. GoogleMaps
Paratypes.— Brazil: Amazonas: ANSP 192781, 1, 220 mm TL, Rio Juruá, upriver of Pauapixuna, downriver of Humaitá, 0 2°441"14.1" "S, 65°46"37.4" "W; FMNH 128428, 1, 235 mm TL, Rio Solimões near Manaus, immediately upstream of the confluence with Rio Negro; MZUSP 56074, 15, Rio Solimões, 1 5 km downstream or Paraná Iranduba, 3°1 4"2 2 " "S, 59°53"53" "W. Pará: ANSP 195554, 9, 137–181 mm TL, Rio Amazonas above mouth of Rio Tapajós, 6.5 km downriver of Astréia; FMNH 115028, 14, 3 CS, 133–216 mm TL, Rio Amazonas, between Furo de Urucuricaia and Paraná dos Arraiolos, between towns Almeirim and Gurupá, 0 1°29"11" "S, 0 52°0 9"46" "W; FMNH 115029, 1, 198 mm TL, Rio Amazonas, between Rio Mojui and Furo do Tajapuru, between towns Gurupá and Serraria, 0 1°12"26" "S, 51°19"0 9 " "W.
Non-type material.— FMNH 115 0 33, 1, 185 mm TL, Rio Amazonas, between tributaries Trombetas and Paraná Mirim de Óbidos, between Juruti and Óbidos, 0 1°5 4"1 5 " "S, 0 55°34"44" "W; FMNH 115037, 1, 204 mm TL, Rio Amazonas, between tributaries Trombetas and Paraná do Amador, between Óbidos and Santarém, 0 2°0 2"55" "S, 0 55°20"56" "W. Roraima: ANSP 192777, 3, 196–230 mm TL, Rio Branco, 12 km upriver of Rio Negro, between Ataúba and Caruna, 0 1°17"45.6" "S, 0 61°51"21.9" "W; ANSP 192778, 2, 199–219 mm TL, Rio Branco, between Ataúba and Caruna.
Diagnosis.— Compsaraia iara can be unambiguously distinguished from all congeners by the following characters: forehead strongly rounded with dorsal margin of frontals and parasphenoid convex (vs. straight or concave in adult C. compsa and C. samueli; Figs. 2 View Fig. 2 , 3A View Fig. 3 , 5A View Fig. 5 ). Mouth small, gape not reaching vertical with eye in adults ( Fig. 3C View Fig. 3 ), vs. reaching or exceeding vertical with eye in adult C. compsa and C. samueli. Teeth absent from premaxilla, vs. 8–16 teeth on the premaxilla in C. compsa and 4–10 in C. samueli.
Description.— Body elongate and laterally compressed ( Figs. 1 View Fig. 1 , 3). Morphometric and meristic data summarized in Table 1 View Table 1 . Largest recorded size 235 mm TL. Body strongly compressed laterally. Scales absent from nape (above lateral line to about
fifth lateral-line pore) and along entire dorsal midline. Scales ovoid, oriented in 6–8 rows above lateral line at midbody. Eyes small and subdermal. Head short, dorsal profile convex, snout rounded. Mouth small and subterminal. Gape extending to vertical with posterior nares. Ventrally rounded lips covering most of lower jaw. Electroreceptive dorsal organ originating at about midbody. Nasal capsule elongate. Posterior nares about equidistant from eye and anterior nares. Premaxillae crescent-shaped in ventral view and lacking teeth ( Fig. 4B View Fig. 4 ). Maxillae with anteroventral shelf and anterior hook. Descending blade evenly tapered with slight dorsal curve.
Mesethmoid strongly decurved ( Fig. 4A View Fig. 4 ). Ventral ethmoid robust with short, posteriorly angled lateral processes contacting lateral ethmoid cartilage. Width of lateral process at base roughly equal to width at distal end. Lateral ethmoid robust in adults with dorsal articulating surface expanded, roughly twice width of ventral end. Frontal convex in lateral profile. Orbitosphenoid broadened dorsally and ventrally. Junction of orbitosphenoid and pterosphenoid protruding ventrally. Pterosphenoid without descending ventral process (seen extending toward or contacting the parasphenoid in some adult specimens of C. compsa and C. samueli, see Fig. 5A View Fig. 5 ). Supratemporal laterosensory canal forming elongated C or L shape on posterolateral surface of parietal, extending posteriorly onto nape, visible externally ( Fig. 3B View Fig. 3 ; Albert, 2001:fig. 19C). Parietal branch of postotic canal with short, posteriorly angled tubule.
Lower jaw triangular, slightly longer than deep ( Fig. 4B View Fig. 4 ). Ten to 14 conical teeth arranged in single, uneven row on anterior half of dentary. Anterior process of retroarticular overlapping with descending process of dentary. Mandibular canal bones ossified as five short, broad ossicles. Three ossicles below dentary, two below preopercle. Endopterygoid edentulous with robust, anteriorly angled ascending process slightly anterior to midlength of bone. Metapterygoid triangular with all sides roughly equal in length. Hyomandibula angled posteriorly, oriented at roughly 1 2 0° to horizontal cranium axis, broad articulating head roughly twice diameter of distal end. Preopercle oriented vertically, rounded ventrally with narrow anterior process articulating with quadrate. Opercle with slightly concave dorsal margin and rounded posterior margin.
Gill rakers ossified, not contacting gill arch. Basihyal with weakly developed ridge on posterior dorsal surface. Basibranchial 2 approximately hourglass-shaped with slightly broader anterior half. Basibranchials 3–5 unossified. Hypobranchials 1 and 3 triangular in dorsal view, hypobranchials 2 joined by medial processes (Albert, 2001:fig. 32B), hypobranchials 4 and 6 unossified. Pharyngobranchials 2–4 ossified, epibranchials 3 and 4 shallowly forked. Ceratobranchial 5 with 13– 16 long teeth arranged in two irregular rows. Dentigerous plate of epibranchial 4 with 13 tightly grouped conical teeth.
Posttemporal broad and flat dorsal to region of overlapping contact with supracleithrum, then tapering to sharp point. Broadened region bears short, wide, anteriorly angled canal. Supracleithrum elongate with long overlapping articulation with cleithrum and dorsolateral hook. Anteroventral process of coracoid thin and elongate, reaching ventral cleithral margin. Mesocoracoid not ossified. Four independently ossified proximal radials. First radial articulated with first pectoral-fin ray. Sixteen pectoral-fin rays, first ray, about one fourth length of remaining rays.
Body cavity short with 14 (n ¼ 5) precaudal vertebrae. First rib broadened proximally with concave anterior surface. Two displaced hemal spines. Anterior displaced hemal spine long and sickle-shaped, following posterior and ventral margin of body cavity to about third rib. One posterior displaced hemal spine, roughly same length of other hemal spines, angled anteriorly. Anal-fin pterygiophores slightly longer than hemal spines, and broadened near distal tip. Median number of anal-fin rays 167 (n ¼ 16, range: 155–174). Caudal fin small and lanceolate with 14 rays.
Color.— White to pale pink ground color in living specimens, with brighter pink over anal-fin pterygiophores. Dense grayish brown chromatophores over dorsum and nape, becoming diffuse at lateral line. Pigment limited to posterior scale margins, giving lightly mottled pattern in regions with large scales. Anterior dorsum and head speckled with pale tuberous electroreceptors. Faint vertical lines of chromatophores often present between anal-fin pterygiophores. Dorsal surface of head and cheeks pigmented. Underside of head and lower jaws pale, with white in areas overlying mandibular canal bones. Upper lip with narrow depigmented patch extending dorsally over nares, anterior to eye. Subdermal laterosensory canals visible as pale C- or L-shaped lines on nape (see Fig. 3B View Fig. 3 ). Midsaggital dorsal organ lighter graybrown than anterior dorsum. Pectoral, anal, and caudal fins hyaline. In alcohol-preserved specimens, coloration much as in life, but ground color becomes pale cream-yellow.
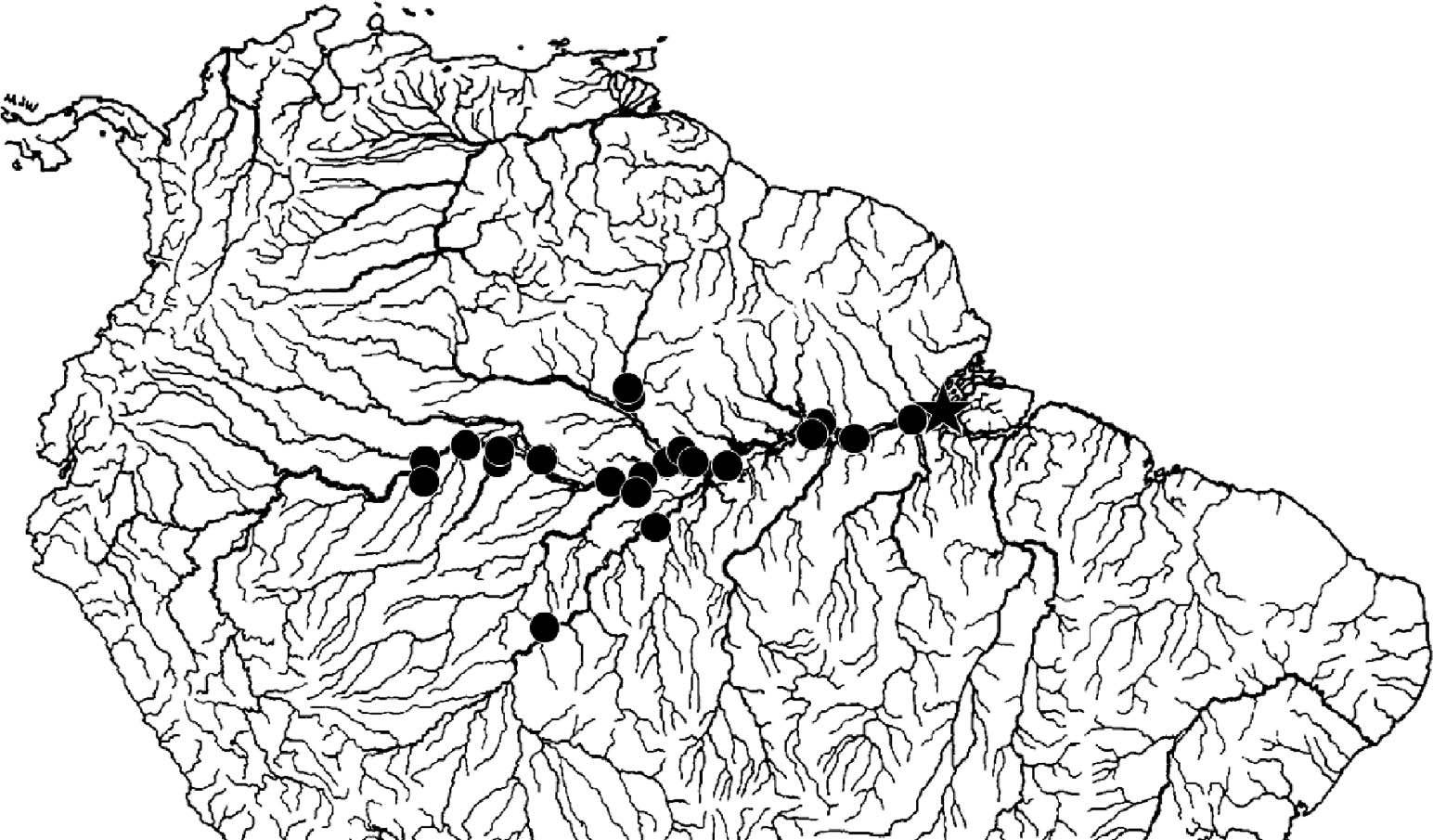
Distribution.— Widespread in the Brazilian Amazon River and near the mouths of its larger tributaries. The furthest upstream that this species has been reported is near the mouth of the Rio Içá. Trawl sampling by the authors and colleagues in the Peruvian Amazon has not resulted in any additional specimens. Two lots (n ¼ 2 specimens each) were collected near the mouth of the Rio Branco, Roraima, Brazil, but none are reported from the Rio Negro or other blackwater rivers. In addition to those specimens listed under materials examined, 17 collection localities were reported by Cox Fernandes (1995) and are shown on the distribution map in Figure 6 View Fig. 6 . There is an additional report of this species from the vicinity of Teotônio and at Novo Aripuanã on the Rio Madeira ( Crampton and Cella-Ribeiro, 2013). Geographic ranges of congeners C. compsa and C. samueli are summarized in Figure 7 View Fig. 7 .
Ecology.— Specimens of C. iara examined in this study were collected from white waters at depths ranging from two to 30 meters. Gut contents of several specimens collected in the Amazon River near the mouth of the Rio Xingu were exclusively composed of dipteran ( Ceratopogonidae ) larvae mixed with very fine sand, suggesting this species is a benthic forager. No secondary sexual dimorphism has been observed in this species, although the closely related C. samueli is known to have pronounced sexual dimorphism of the snout and jaws ( Albert and Crampton, 2009). Considering that mature male specimens of C. samueli are rarely captured using conventional sampling methods, a more extensive examination of the gonads of C. iara or collection of reproductive specimens during high water will be needed to confirm the absence of dimorphism.
Etymology.— This species is named for the Iara, a water nymph from Tupi-Brazilian folklore said to reside in the rivers of the Brazilian Amazon and often blamed for the disappearance of fishermen. A noun in apposition.
Table 1. Summary of morphometric and meristic measurements for Compsaraia iara.
| Character | C. iara | C. samueli | C. compsa |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 34 | 60 | 51 |
| Total length (TL) | 133–235 | 68–241 | 75–326 |
| Length to end of anal fin (LEA) | 100–199 | 63–212 | 62–235 |
| Anal-fin base (AFB) | 86–168 | 54–176 | 53–203 |
| Caudal appendage length (CL) | 11–51 (n ¼ 32) | 1–65 (n ¼ 56) | 10–91 (n ¼ 49) |
| Tail depth (TD) | 0.7–5.4 | 0.5–5.0 | 0.4–3.5 |
| Head length (HL) | 14.2–27 | 10.3–37.5 | 8.6–38.5 |
| Length to origin of dorsal organ (LOD) | 64–134 | 31–148 | 43–152 |
| Body depth/LOD | 0.22 (0.19–0.25) | 0.22 (0.17–0.31) | 0.18 (0.14–0.22) |
| Prepectoral length/LOD | 0.24 (0.21–0.28) | 0.28 (0.22–0.40) | 0.24 (0.21–0.30) |
| Preanal length/LOD | 0.22 (0.14–0.27) | 0.26 (0.18–0.33) | 0.23 (0.2–0.29) |
| Snout-anus length/HL | 0.57 (0.34–0.72) | 0.67 (0.43–0.94) | 0.68 (0.40–1.0) |
| Pectoral fin length/HL | 0.77 (0.62–0.90) | 0.72 (0.57–0.93) | 0.71 (0.55–0.91) |
| Head depth at opercle/HL | 0.76 (0.67–0.86) | 0.67 (0.52–0.77) | 0.65 (0.53–0.74) |
| Head depth at eye/HL | 0.50 (0.42–0.55) | 0.43 (0.36–0.51) | 0.43 (0.36–0.57) |
| Head width/HL | 0.48 (0.37–0.53) | 0.40 (0.31–0.47) | 0.40 (0.33–0.51) |
| Snout length/HL | 0.35 (0.31–0.39) | 0.38 (0.32–0.44) | 0.38 (0.30–0.45) |
| Postorbital/HL | 0.65 (0.59–0.74) | 0.58 (0.51–0.63) | 0.58 (0.53–0.63) |
| Gape length/HL | 0.23 (0.16–0.31) | 0.33 (0.23–0.50) | 0.28 (0.15–0.43) |
| Eye diameter/Postorbital length (PO) | 0.13 (0.10–0.23) | 0.14 (0.09–0.20) | 0.14 (0.09–0.19) |
| Posterior naris-snout/PO | 0.37 (0.31–0.43) | 0.40 (0.22–0.49) | 0.42 (0.27–0.49) |
| Posterior naris-eye/PO | 0.18 (0.11–0.24) | 0.25 (0.14–0.45 | 0.22 (0.10–0.42) |
| Internarial distance/PO | 0.23 (0.17–0.28) | 0.25 (0.20–0.32) | 0.25 (0.15–0.30) |
| Interocular width/PO | 0.30 (0.20–0.37) | 0.27 (0.17–0.37) | 0.26 (0.17–0.31) |
| Branchial opening/PO | 0.34 (0.27–0.40) | 0.31 (0.21–0.40) | 0.28 (0.17–0.39) |
| Body width/PO | 0.52 (0.40–0.71) | 0.48 (0.35–0.60) | 0.47 (0.29–0.63) |
| Anal-fin rays | 167 (155–174) (n ¼ 16) | 170 (152–185) (n ¼10) | 195 (164–210) (n ¼ 24) |
| Pectoral-fin rays | 16 (n ¼ 5) | 16 (n ¼ 10) | 16 (n ¼ 6) |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Compsaraia iara
| Maxwell J. Bernt & James S. Albert 2017 |
Porotergus gymnotus
| Cox Fernandes 1995: 30 |