Belzebub, Vereshchaka & Olesen & Lunina, 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1111/zoj.12398 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5459372 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A33A12-FFA7-7548-FC32-FC84FD978528 |
|
treatment provided by |
Marcus (2021-08-29 16:49:35, last updated by Plazi 2023-11-05 15:43:25) |
|
scientific name |
Belzebub |
| status |
gen. nov. |
KEY TO SPECIES OF BELZEBUB View in CoL GEN. NOV.
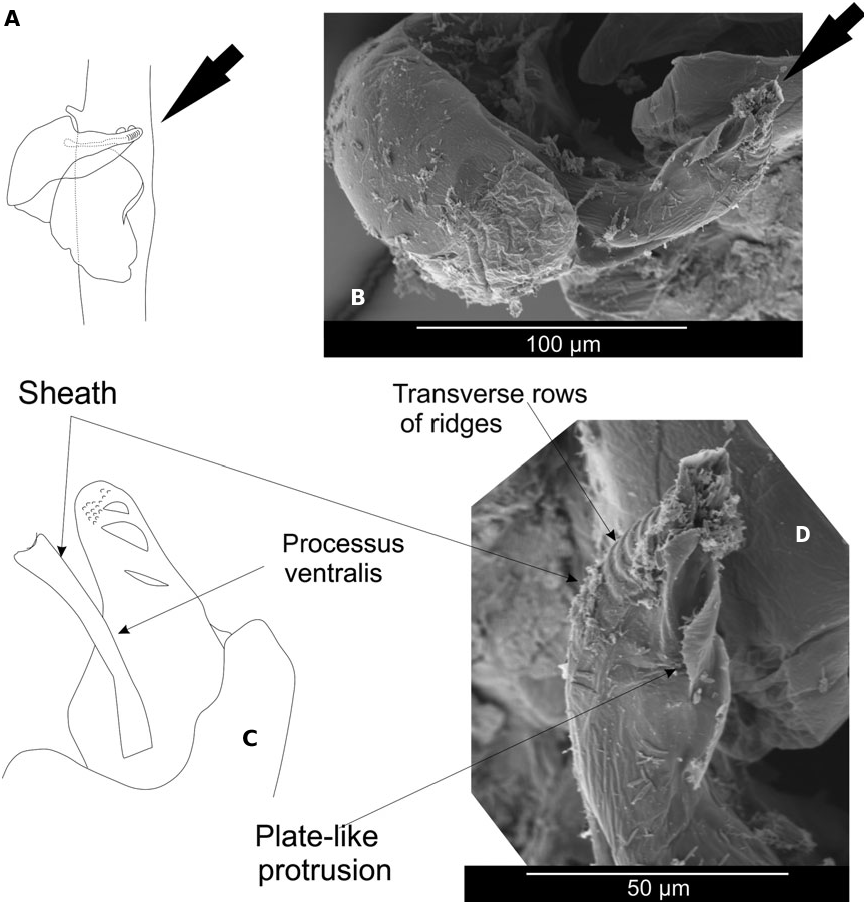
1. Petasma: sheath bottle-shaped, with distal transverse rows of ridges, plate-like structures large and fringed ( Fig. 5C, D View Figure 5 ) ……. B. intermedius ( Hansen, 1919) View in CoL comb. nov.
– Petasma: sheath subconical, with distal longitudinal rows of fine scales, plate-like structures small, with entire margins ( Fig. 7F View Figure 7 ) ……… 2
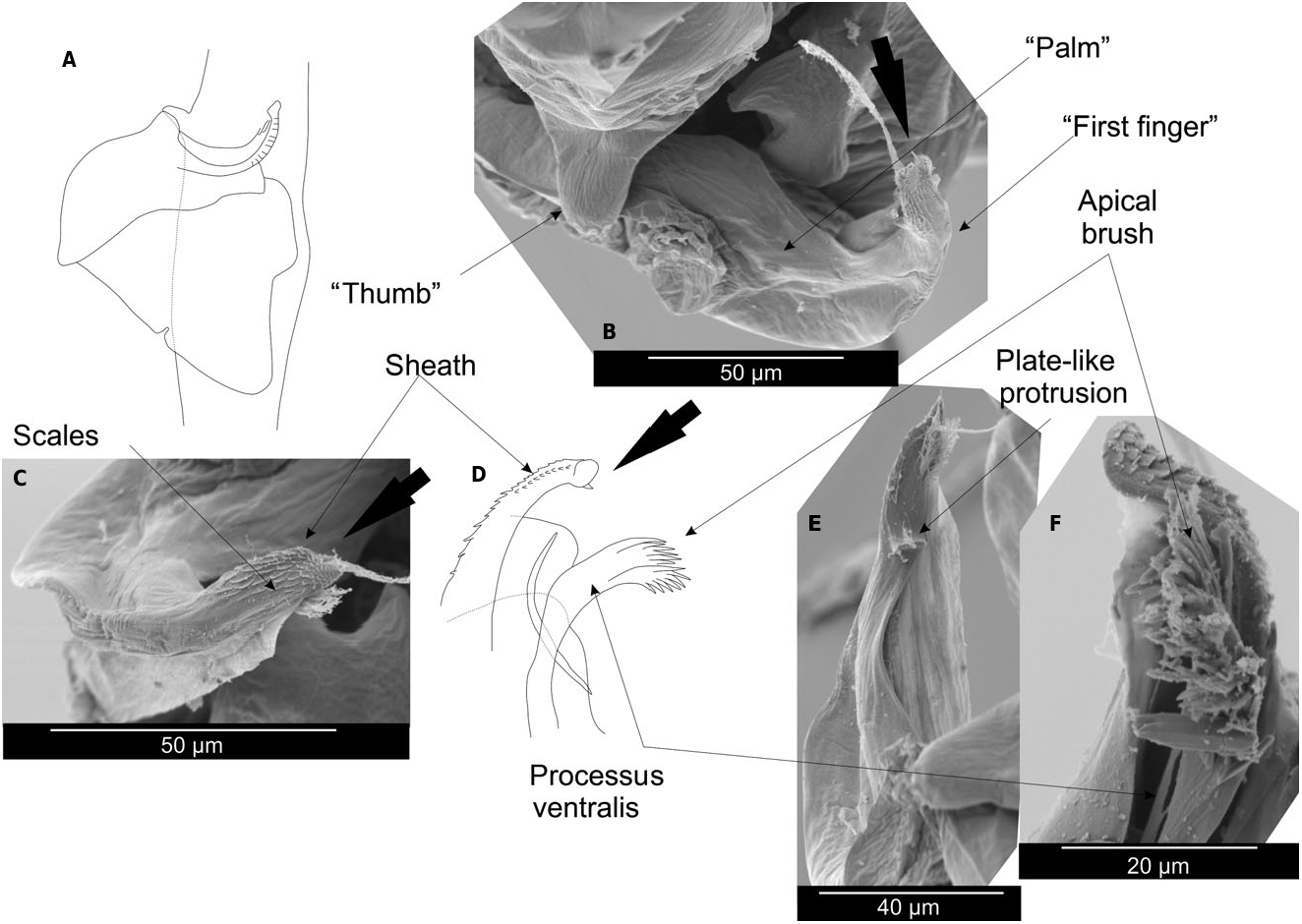
2. Petasma: processus ventralis bearing a dense brush of long terminal setae ( Fig. 6D – F View Figure 6 ) ………. B. penicillifer ( Hansen, 1919) View in CoL comb. nov.
– Petasma: processus ventralis with short, scattered lateral setae only, without dense brush of terminal setae ( Figs 7F View Figure 7 , 8D View Figure 8 ) …….. 3
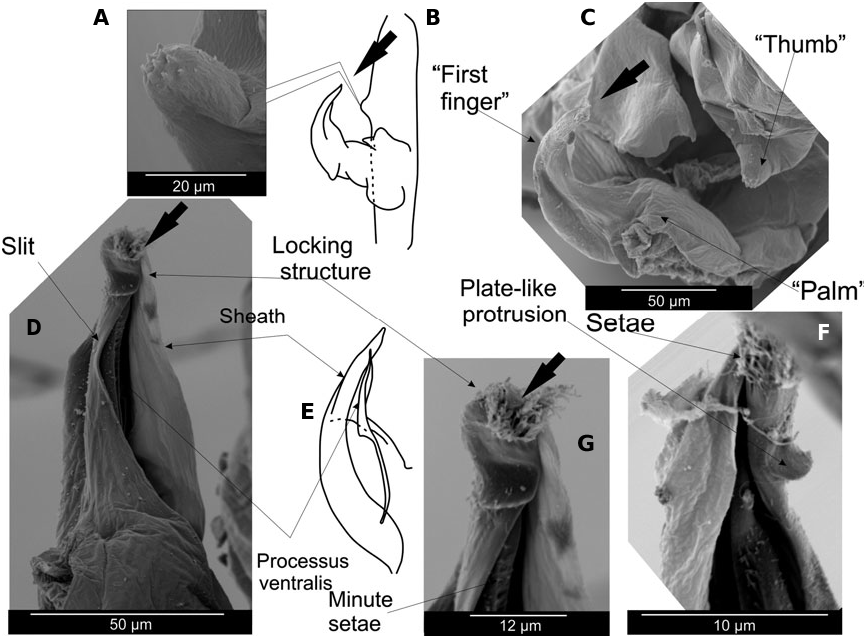
3. Outer tooth of uropodal exopod far from reaching distal end of exopod; petasma: processus ventralis setose along medial part ( Fig. 7G, F View Figure 7 ) …… B. hanseni ( Nobili, 1905) View in CoL comb. nov.
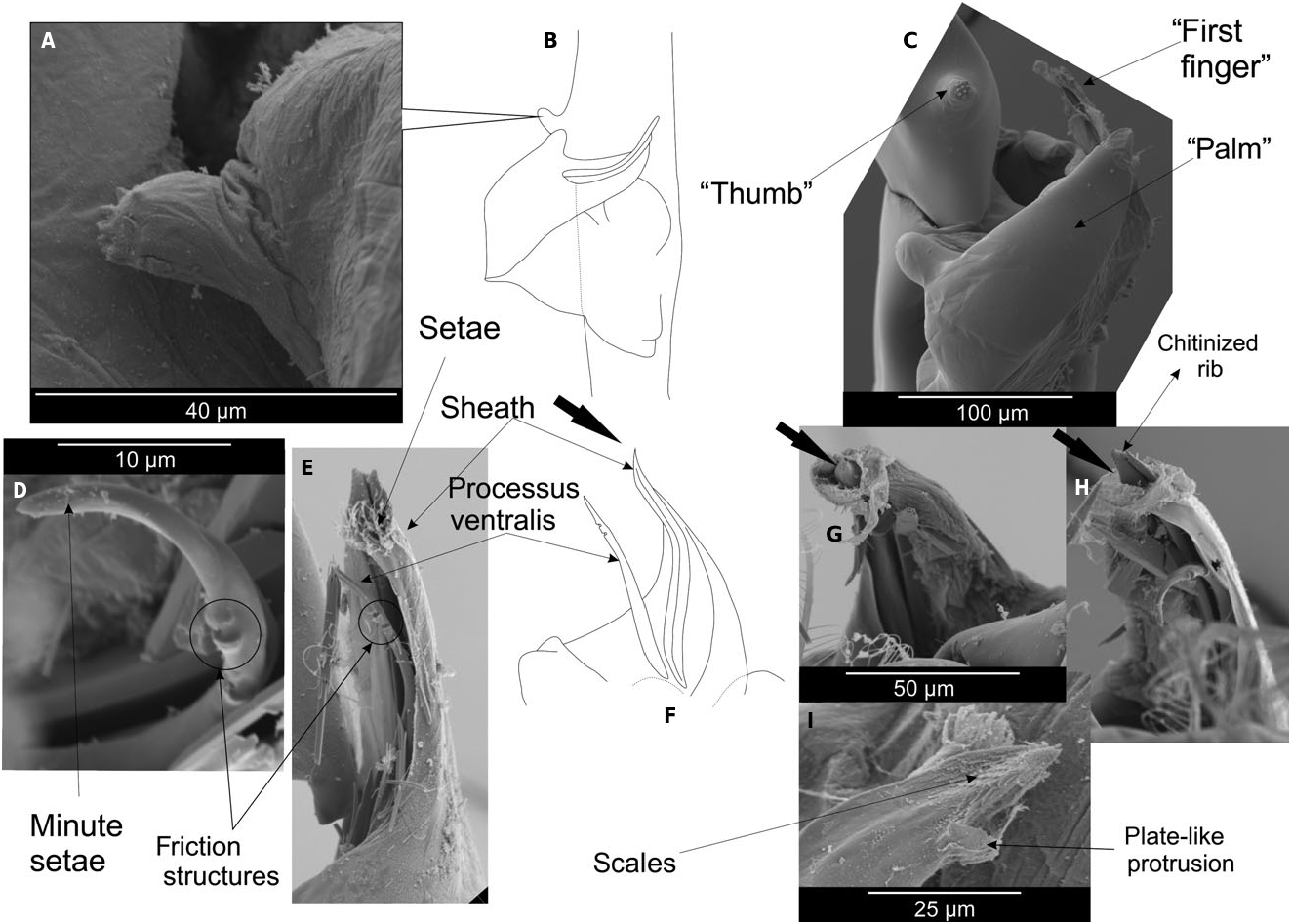
– Outer tooth of uropodal exopod nearly reaching distal end of exopod; petasma: processus ventralis setose along distal part ( Fig. 8D View Figure 8 ) …….. 4
4. Atlantic species …… B. faxoni ( Borradaile, 1915) View in CoL comb. nov.
– Indo-Pacific species ………. B. chacei ( Bowman & McCain, 1967) View in CoL comb. nov.
Antony G. 2005. Occurrence and distribution of the planktonic shrimps of the genus Lucifer in the EEZ of India. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of India 47: 20 - 30.
Bate CS. 1881. On the Penaeidea. Annals and Magazine of Natural History 5: 169 - 196.
Borradaile LA. 1915. Notes on Carides. Annals and Magazine of Natural History 15: 205 - 213.
Bowman TE, McCain JC. 1967. Distribution of the planktonic shrimp, Lucifer, in the Western North Atlantic. Bulletin of Marine Science 17: 660 - 671.
Fabricius JC. 1798. Entomologia systematica emendata et aucta: supplementum. Hafniae: Proft et Storch, 1 - 572.
Hansen HJ. (1919). The Sergestidae of the Siboga expedition. 1 - 65.
Lee WY, Omori M, Peck RW. 1992. Growth, reproduction and feeding behavior of the planktonic shrimp, Lucifer faxoni Borradaile, off the Texas coast. Journal of Plankton Research 14: 61 - 69.
Ma Z, Xu Z, Zhou J. 2009. Effect of global warming on the distribution of Lucifer intermedius and L. hanseni (Decapoda) in the Changjiang estuary. Progress in Natural Science 19: 1389 - 1395.
Nobili G. 1905. Diagnoses preliminaires de 34 especes et varietes nouvelles, et de 2 genres nouveaux de Decapodes de la Mer Rouge. Bulletin du Museum d'Histoire Naturelle 6: 393 - 411.
Omori M. 1977. Distribution of warm water epiplanktonic shrimps of the genera Lucijier and Acetes (Macrura, Penaeidea, Sergestidae). Proc. Symp. Warm Water Zooplankton. Spl. Publ., Goa: NIO, 1 - 12.
Perez-Farfante I, Kensley B. 1997. Penaeoid and sergestoid shrimps and prawns of the world. Keys and diagnoses for the families and genera. Editions du Museum national d'Histoire naturelle 1997: 233.
Teodoro SDSA, Negreiros-Fransozo ML, Sim oes ~ SM, Lopes M, Costa RCD. 2012. Population ecology of the planktonic shrimp Lucifer faxoni Borradaile, 1915 (Crustacea, Sergestoidea, Luciferidae) of the southeastern coast of Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Oceanography 60: 245 - 253.
Xu ZL. 2010. Determining optimal temperature and salinity of Lucifer (Dendrobranchiata: Sergestoidea: Luciferidae) based on field data from the East China Sea. Plankton and Benthos Research 5: 136 - 143.
Figure 5. Petasma of Belzebub intermedius (Hansen, 1919) comb. nov.: general structure (A), apical view of the sheath (B, scanning electron micrograph), lateral view of the sheath and the processus ventralis (C, D, scanning electron micrographs). Arrows point at same morphological structures.
Figure 6. Petasma of Belzebub peпicillifer (Hansen, 1919) comb. nov.: general structure (A), apical view of the petasma (B, scanning electron micrograph), apical view of the sheath (C, scanning electron micrograph), lateral view of the sheath and the processus ventralis (D, E, scanning electron micrographs), apex of the processus ventralis (F, scanning electron micrograph). Arrows point at same morphological structures.
Figure 7. Petasma of Belzebub hanseni (Nobili, 1905) comb. nov.: ‘thumb’ (A, scanning electron micrograph), general structure (B), apical view of the petasma (C, scanning micrograph), lateral view of the sheath and the processus ventralis (D, scanning electron micrograph, E), apex of processus ventralis and the sheath (F, G, scanning electron micrographs). Arrows point at same morphological structures.
Figure 8. Petasma of Belzebub faxoni (Borradaile, 1915) comb. nov.: ‘thumb’ (A, scanning electron micrograph), general structure (B), apical view of the petasma (C, scanning electron micrograph), lateral view of the sheath and the processus ventralis (D, scanning electron micrograph, E, scanning electron micrograph, F), distal part of the sheath with apical scales (G–I, scanning electron micrographs). Arrows point at same morphological structures.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |