Mazama americana (Erxleben, 1777) Clinton, 1822
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.6514377 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6514589 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A087C4-FFE7-FFE7-FA4B-F6B1E50AFC78 |
|
treatment provided by |
Conny |
|
scientific name |
Mazama americana |
| status |
|
Common Red Brocket
French: Mazame roux / German: GrolRmazama / Spanish: Corzuela roja
Other common names: Red Brocket
Taxonomy. Moschus americanus Erxleben, 1777 ,
Cayenne ( French Guiana).
It is possibly a superspecies or a species complex. Although quite uniform morphologically, Common Red Brockets exhibit an extensive karyotype variation. A recent analysis of karyotypes and mtDNA has allowed recognition of at least two clearly separated lineages, a West Amazonian and an East Amazonian one. Monotypic, pending revision.
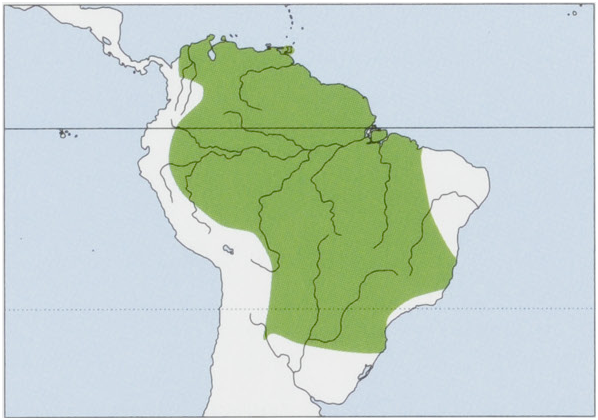
Distribution. From Colombia and Venezuela to S Brazil, Paraguay, and N Argentina;it also occurs on Trinidad I, and previously was found on Tobago I, but has been extirpated from there recently. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body 90-145 cm, tail 12-16 cm, shoulder height 60-80 cm; weight 30-35 kg (up to 65 kg). Males and females are of similar size. It is the largest brocket. The coat is reddish brown; the face and neck are gray. Newborn fawns are spotted. Antlers are about 10 cm long. The diploid number of chromosomes is 42-54.
Habitat. It lives in tropical and subtropical forests, sometimes in savanna close to the forest edge. Dense humid forests are preferred.
Food and Feeding. It feeds mostly on fruits and seeds, but also eats leaves and flowers. In Suriname it is mainly frugivorous during rainy season and it becomes folivorous during dry season.
53 Common Dwarf Brocket (Muamu chunyl
Breeding. Puberty is attained at eleven months of age. Mating occurs between April and June in Venezuela, between April and October in Suriname, in June-August in Peru. After a gestation of 240 days, females give birth to a single fawn weighing around 1-8 kg. There is a postpartum estrus.
Activity patterns. It is mainly crepuscular and nocturnal. It becomes more nocturnal in hunted areas.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. It is a good swimmer. Almost always solitary and home ranges are probably around 50-100 ha. It is territorial and marks the boundaries by defecating in latrines.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Data Deficient on The IUCN Red List. When not hunted it is fairly common. Hunting and the conversion of forest into cropland remain important threats.
Bibliography. Abril, Carnelessi et al. (2010), Branan & Marchinton (1987), Di Bitetti et al. (2008), MacNamara & Eldridge (1987), Rivero et al. (2005), Varela et al. (2010).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.