Elaphodus cephalophus, Milne-Edwards, 1872
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.6514377 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6514389 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A087C4-FFC7-FFC6-FF43-FDF0E76DF804 |
|
treatment provided by |
Conny |
|
scientific name |
Elaphodus cephalophus |
| status |
|
Tufted Deer
Elaphodus cephalophus View in CoL
French: Elaphode / German: Schopfhirsch / Spanish: Elafodo
Taxonomy. Elaphodus cephalophus Milne-Edwards, 1872 View in CoL ,
Moupin, Sichuan ( China).
Distinct genus closely related to Muntiacus . Three subspecies are generally recognized.
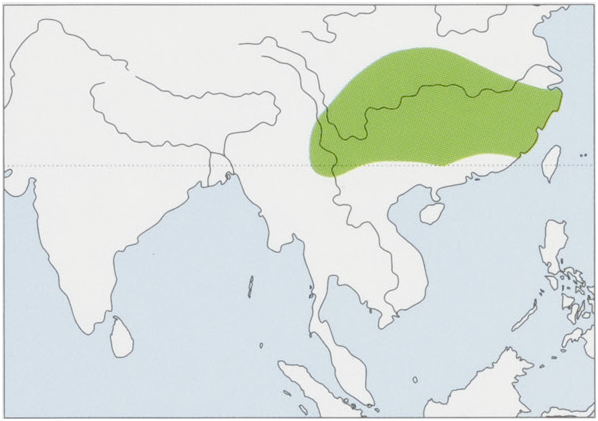
Subspecies and Distribution.
E.c.cephalophusMilne-Edwards,1872—SWChina;oldrecordsfromNMyanmar.
E.c.ichangensisLydekker,1904—SChina.
E. c. michianus Swinhoe, 1874 — SE China. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body 100-120 cm, tail 7-13 cm, shoulder height 50-70 cm; weight 17-30 kg. Relatively largesized muntiacine, with shortened head, short and thin pedicles, and diminutive unbranched antlers hidden by a distinct tuft of tall hair on the top of the head. Ears and tail are small. The coat is mainly dark brown, legs are black. White marks at the base and the tip of the ear. The underside of the tail is white. The fur is coarse. Frontal ridges are weak, large upper canines are present in both sexes. Frontal glands are absent, preorbital gland very large, metatarsal glands present but small. Newborn fawns have one or two rows of faint white spots. Antlers are not shed.
Habitat. Compared to the members of genus Muntiacus , it is adapted to cooler climates. It lives in high damp forests up to the tree line and close to water, up to 4750 m above sea level.
Food and Feeding. Eats bamboo, forbs, fruit, and grass.
Breeding. Females sexually mature at about 10-12 months of age. Mating season is September-December. After about 180 days of pregnancy, in April-July, females give birth to one or two fawns.
Activity patterns. Active mainly at dawn and dusk.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. Observed alone or in pairs. When disturbed it flees with cat-like jumps with tail held up and wagging. It barks like a muntjac when alarmed.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Near Threatened on The IUCN Red List and it is decreasing. Overhunting is a major threat.
Bibliography. Groves & Grubb (1990), Harris (2008a), Ohtaishi & Gao (1990), Smith & Xie Yan (2008), Zhang Zejun et al. (2004).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.