Thrichomys laurentius
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.277069 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6189810 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039A87FE-FFCF-FFD9-7C8F-7101FF0DFD4A |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Thrichomys laurentius |
| status |
|
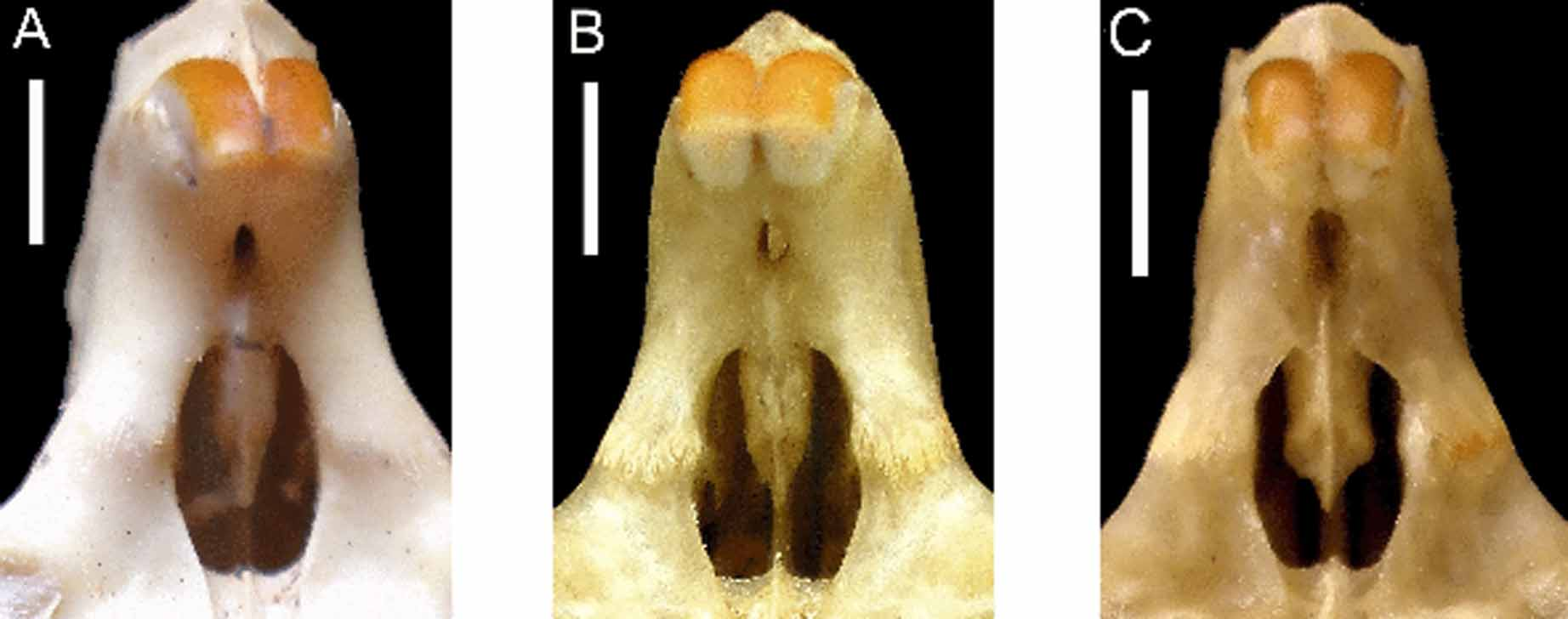
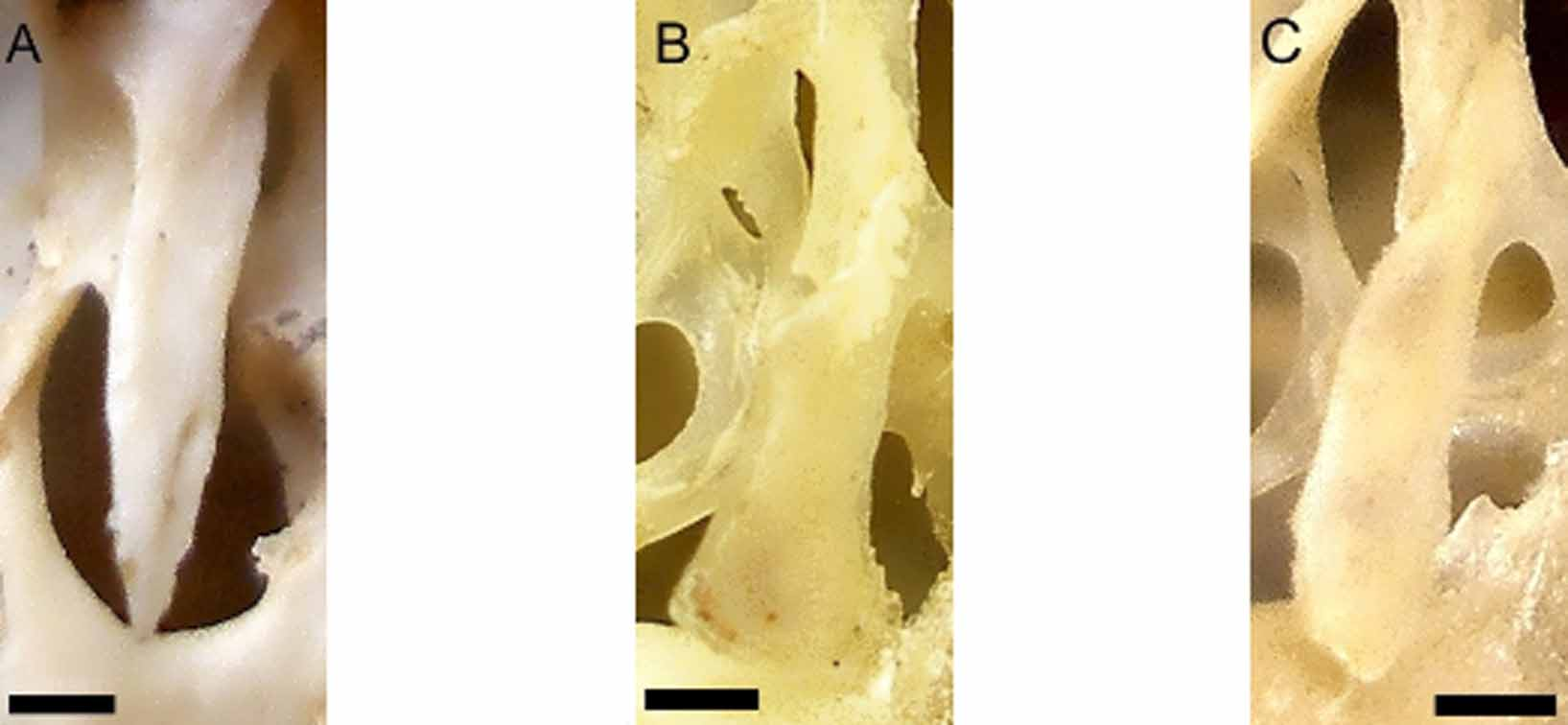
Nine age groups were described for the sample from Caruaru, identified as T. laurentius ( Fig 1 View FIGURE 1 .A–I). As expected, the wear of occlusal surface of cheekteeth varied considerably during ontogeny. Age 1 shows pre-molar and first molar erupted ( Fig 1 View FIGURE 1 .A), while the second molar begins to erupt at age 2, but its occlusal surface is completely formed only in age 3 ( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 .B and 1.C). These three ages, before the eruption of third molar, are grouped in Juvenile category. The third molar is erupted at age 4 ( Fig 1 View FIGURE 1 .D) and its occlusal surface is completely formed at age 5 ( Fig 1 View FIGURE 1 .E). These ages are grouped in Sub-adult category. All specimens have basisphenoid-basiocciptal suture obliterated at age 6, marking the Adult. The first signal of wear appears at age 6 in pre-molar, and at age 7, both flexi of pre-molar and first molar leaves the impression of an enamel island, even as the first flexus of second molar ( Fig 1 View FIGURE 1 .G). Senile specimens show severe wear of cheek teeth’s occlusal surface. All flexi looks like an enamel island ( Fig 1 View FIGURE 1 .H) even as the hypoflexi of pre-molar and first molar ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 .I). Most cranial characters observed and the wear of cheekteeth varied during ontogeny. However, some aspects of the skull did not vary, as the extension of the supra-orbital ridge, which always reaches the suture between frontal and squamosal. The anterior palatal foramens are always anterior to the anterior margin of the pre-molars. The mesopterygoid fossa is "V"-shaped; the interpremaxilar foramen is oval, narrow and short; and the incisive foramen is rounded, and does not show a constriction at the suture between pre-maxila and maxilla ( Fig 4 View FIGURE 4 .A). The shape of the hamular process of the pterygoid bones is has a pointed shape. ( Fig 5 View FIGURE 5 .A). Finally, the pre-maxillary portion of the septum of the incisive foramen exceeds half of the length of the foramen ( Fig 4 View FIGURE 4 .A). The nasal bones reach posterior limit of pre-maxilla only at ages 1 to 3. The ventral crest of the infra-orbital foramen develops through ontogeny. The position of ventral crest at age 1 is after the edge of infra-orbital foramen. However, from sub-adult the ventral crest is anterior to the edge of infra-orbital foramen. The post-orbital process of zygomatic arch can be formed by only squamosal, only jugal or a combination of these two bones. The posterior palatal foramens are located at posterior limit of palate. At age 1, the mesopterigoid fossa reaches posterior margin of first molar and at age 9 it extends up to half of the third molar.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |