Byblisoides monicae, Peart, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4441.2.9 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:2122E9A6-8ABB-428B-8FBD-DE5CC41ED67C |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5946783 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/02AAC5B7-3DD9-41D9-9167-58695AB1D263 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:02AAC5B7-3DD9-41D9-9167-58695AB1D263 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Byblisoides monicae |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Byblisoides monicae View in CoL n. sp.
( Figs. 1–5 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 )
Type material. Holotype: NIWA 18651 View Materials , ovigerous female (many eggs), 29 mm, Ross Sea , Antarctica, 75.6333°S 168.5333°E, 407 m, 17/01/1959 GoogleMaps , NZOI stn A460.
Paratype: NIWA 126934 View Materials , male, 25 mm, collected with holotype. No other ampeliscids were recorded from this station. GoogleMaps
Other material examined. NIWA 42763, 1 specimen, Ross Sea Antarctica, 75.6217°S 169.8045°E, 520–522 m, 14/02/2008, TAN0802/61, shelf, mud; NIWA 42765, 1 specimen, Ross Sea, Antarctica, 75.6205°S 169.8113°E, 520–522 m, 14/02/2008, TAN0802/61, shelf, mud. Ampelisca barnardi Nicholls, 1938 and an undescribed species of Ampelisca were also recorded from this station.
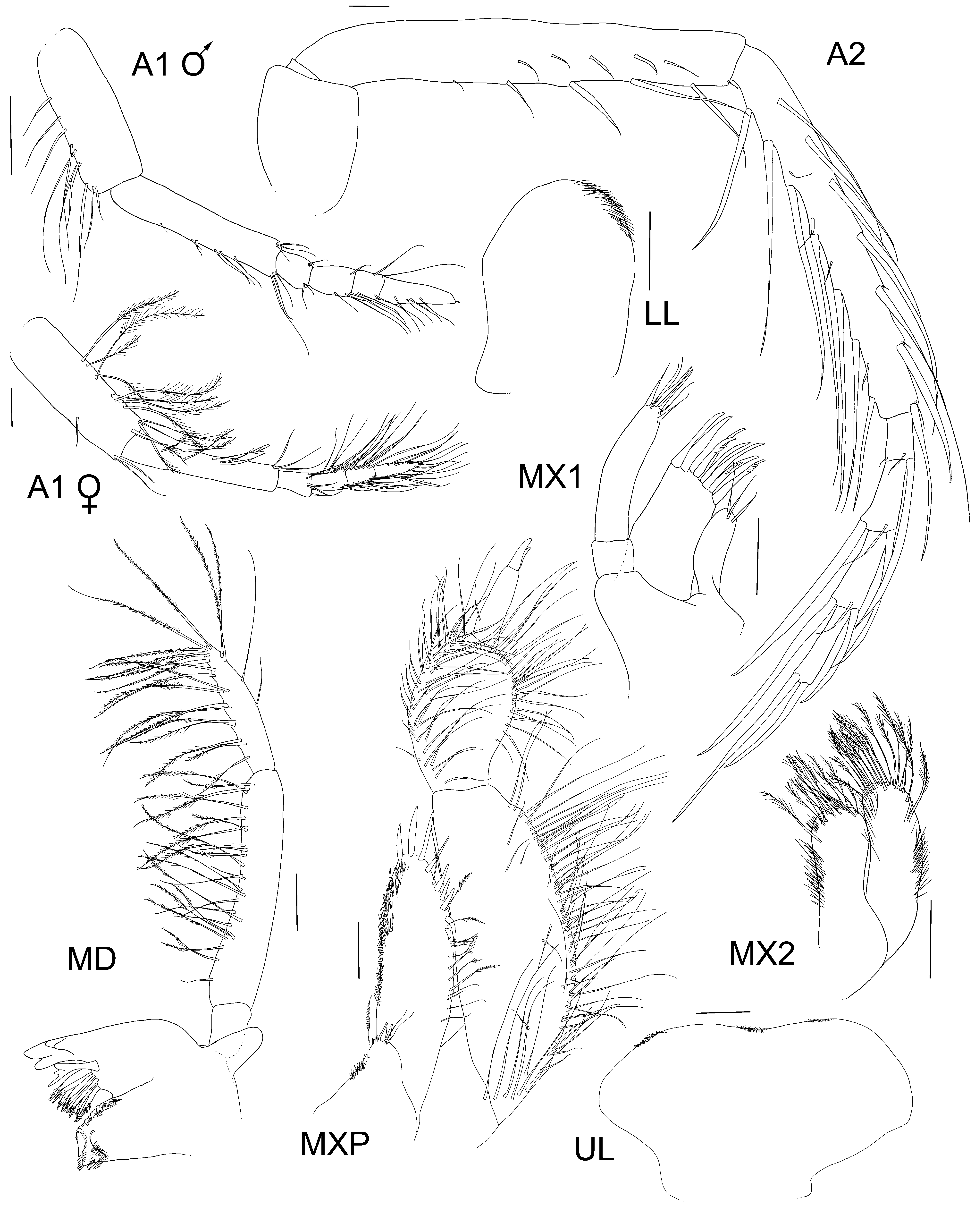
Diagnosis. Anteroventral corner of head acute, produced to length of anterior margin of head. Antenna 1 short, reaching to three-fourths of antenna 2 peduncle article 4, flagellum with 3 articles. Coxa 1 ventral margin angled anteriorly, uneven. Pereopod 5 basis posterior margin uneven, sinuous. Pereopod 7 carpus anterior margin without plumose setae. Pereopod 7 basis posteroventral corner rounded. Uropod 2 inner ramus bearing marginal robust setae.
Description. Based on holotype female, 29 mm length. Head anteroventral corner produced forward, reaching almost level with anterodorsal corner, anterior margin, excavate at antenna 2 insertion, antennal lobe concave, with 2 acute points, rostrum absent, head longer than deep, ventral margin straight. Antenna 1 short, reaching to just past half length of antenna 2 peduncle article 4; peduncle article 1 subequal in length to article 2 (1.1 ×), article 2 longer than article 3 (> 4 ×), article 3 shorter than article 1 (0.2 ×); flagellum shorter than peduncle, comprising of 3 articles (article 3 longest), ventral margin of peduncle article 1 and both margins of flagellum with long plumose, slender setae. Antenna 2 comparatively stout, reaching to just under half of body length; 1.8 × length of head; peduncular article 4 subequal in length to article 5, article 5 ventral and dorsal margin slightly serrate, with long slender setae; flagellum shorter than peduncle, with 4 articles.
Mandible molar well-developed, triturating, 10 plumose robust setae in accessory setal row; incisor toothed; lacinia mobilis with many teeth of different sizes; palp long, article 1 very short, article 2 longer than article 3 (1.7 ×) and straight with many setae on the inner margin, article 3 longer than article 1 (2.8 ×), inner margin weakly serrate and strongly setose. Lower lip bilobed (half illustrated as it is symmetrical), inner plate half height of outer. Maxilla 1 inner plate rounded and medium sized, with 3 long slender plumose setae; outer plate topped with toothed robust setae; palp with 2 articles, article 2 longer than toothed robust setae on outer plate, tipped with 7 long plumose setae and no facial slender setae. Maxilla 2 inner plate slightly shorter than outer plate, both tipped with long plumose setae. Maxilliped inner plate very short, rounded, tipped with 3 long robust setae and three slender setae; outer plate not twisted around palp, inner lateral margin lined with smooth robust setae becoming slender plumose setae proximally. Maxilliped palp broad, simple; article 2 narrow, long bearing many strong slender plumose setae; article 3 ovoid, not folded over article 2, reaching only one-third length, strongly setose; article 4 straight, acutely tipped, reaching two-thirds length of article 3.
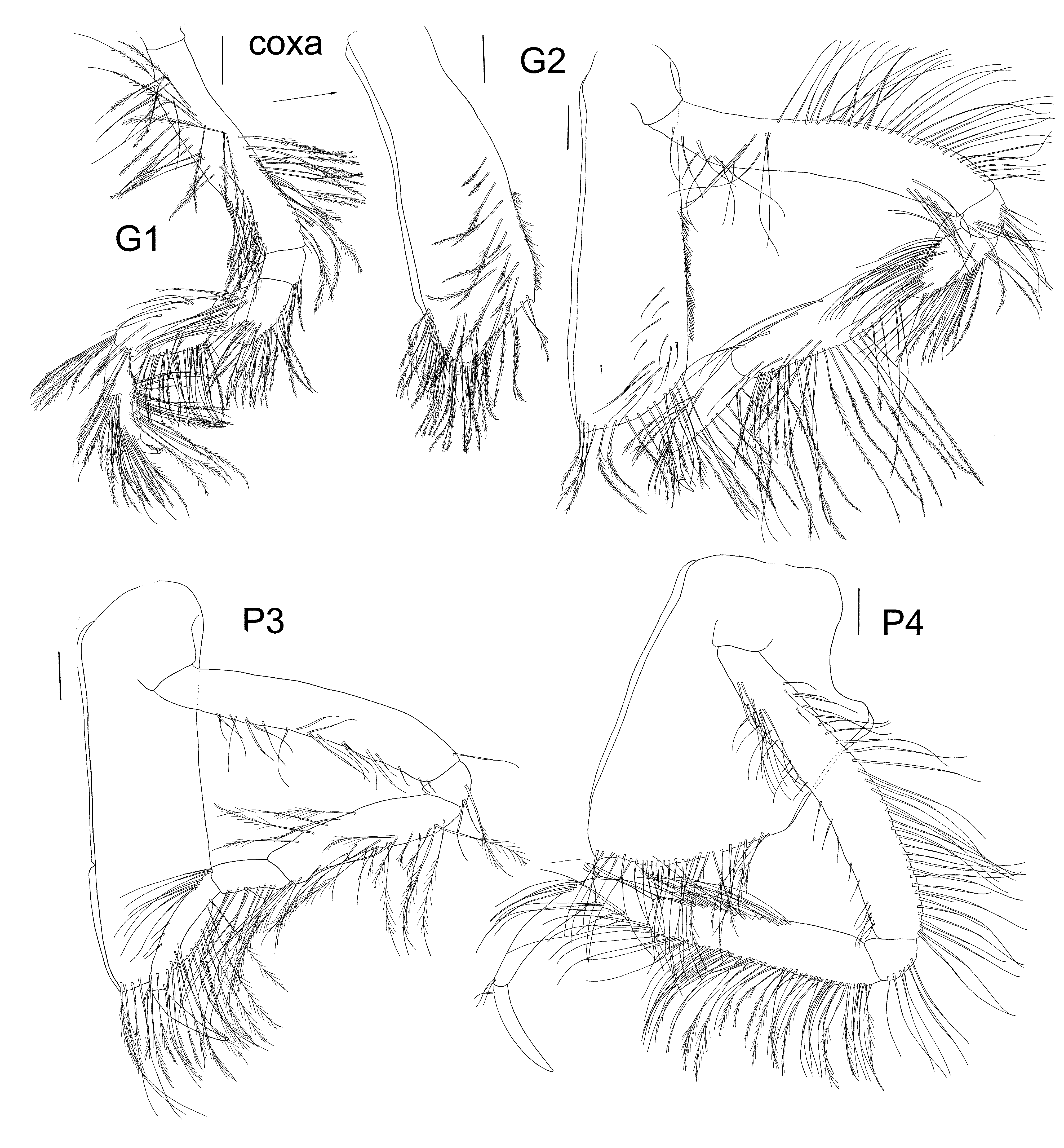
Gnathopod 1 coxa reaching well past head anterior margin, coxa straight sided, not expanded distally, ventral margin strongly produced forward, curved angularly, lined with long plumose slender setae, and few medial plumose setae; basis narrow, lateral margins lined with long plumose, slender setae, medial setae long and plumose; merus lobate and strongly setose particularly medially and posteriorly; carpus longer than merus and subequal in length to the propodus, strongly setose, particularly medially and posteriorly with long plumose setae, slightly lobate; propodus subrectangular, subchelate, palm not well defined, anterior and posterior margins and medially lined with long plumose slender setae, slight anterodistal lobe; dactylus short and curved, one-third length of propodus, inner margin lined several teeth. Gnathopod 2 coxa similar length to coxa 1 (slightly shorter), ventral margin angled forward, but not as strongly as coxa 1, curved (unevenly), fringed with many medial and marginal long plumose setae; basis long and narrow, posterior margin with fringe of long slender plumose setae, merus with rounded posterior lobe, long plumose setae on both anterior and posterior margins and medially; carpus considerably longer than merus (2.6 ×) and longer than propodus (2 ×), narrow and not lobate, covered in long, plumose setae (mainly on posterior margin); propodus narrow, ovoid, covered in long plumose setae (mainly on posterior margin); dactylus short, about one-third length of propodus and slightly curved, inner margin serrate.
Pereopod 3 coxa resembling coxa 2; basis long and narrow, anterior margin with short setal fringe, posterior margin without setae; merus narrow, shorter than basis, subequal to carpus and propodus together, both margins with sparse long plumose setae; carpus with long plumose setae on posterior margin; propodus longer than carpus, short sparse setae on posterior margin, posterior margin slightly concave; dactylus long and narrow, slightly curved, shorter than propodus.
Pereopod 4 coxa trapezoid, posterior margin with extended truncated lobe, posterior margin below lobe straight, ventral margin sinusoidal and strongly setose, anteroventral corner acute; basis longer than coxa, posterior margin slightly serrate with fringe of long plumose setae along the whole length, anterior margin with short slender setae along length; ischium setose along posterior margin; merus long and narrow, shorter than basis, longer than carpus and propodus together, setose with plumose setae along complete length of posterior margin and distal half of anterior margin; carpus shorter than propodus, setose along posterior margin; propodus long and narrow, setose on proximal anterior margin; dactylus long, narrow and straight, shorter than propodus.
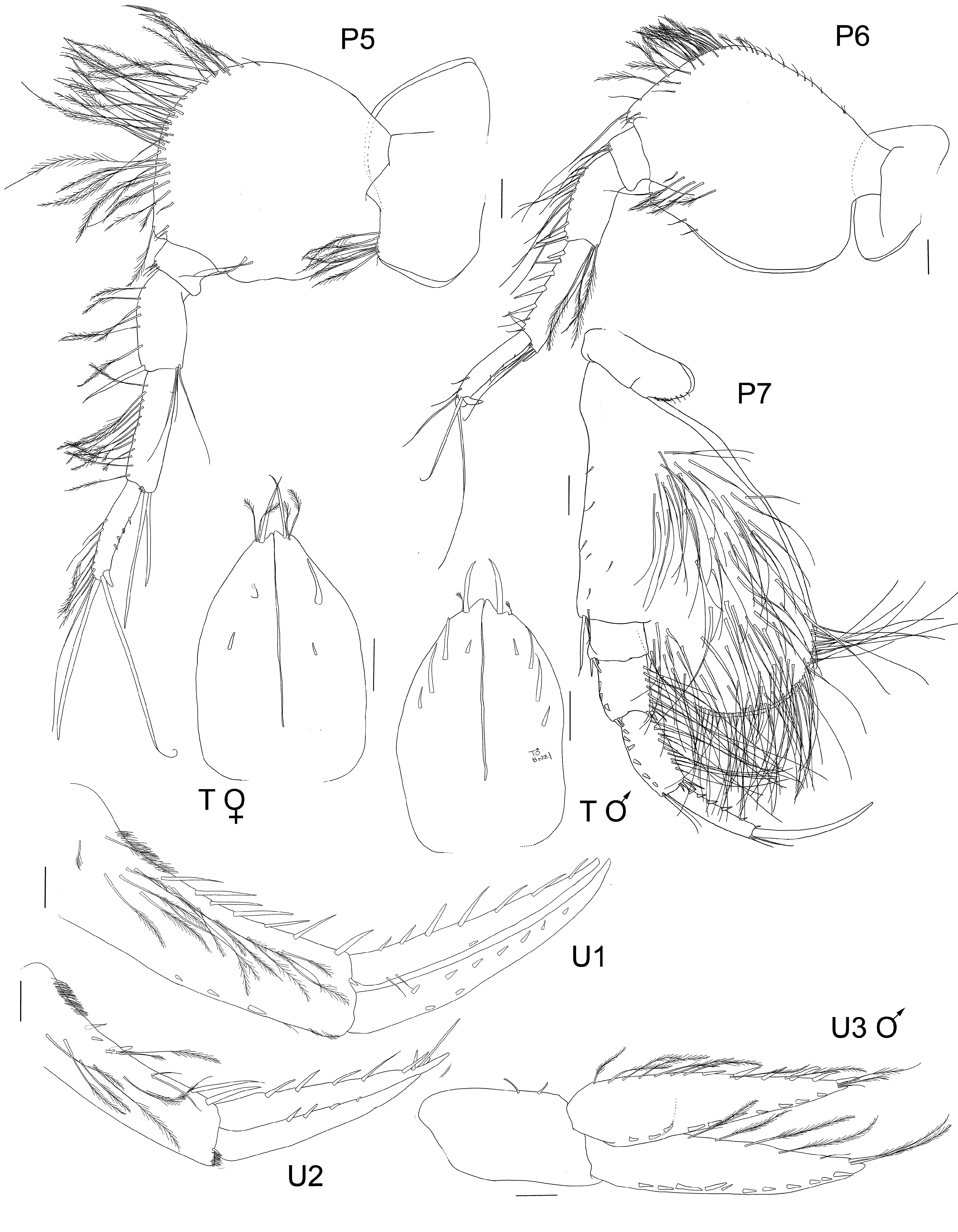
Pereopod 5 coxa with patch of long plumose setae on posterior corner; basis ovoid, narrow distally, anterior margin broadly rounded evenly, lined with long plumose setae, anterior margin uneven, bisinusoidal, with medium proximal distal lobe; ischium with acute posterior lobe; merus longer than ischium, fringed with long plumose setae on anterior margin, no setae on posterior margin; carpus longer than merus, longer than propodus, only setose along anterior margin (all plumose), slight posterodistal lobe, bearing two long strong, slender setae and 2 short robust setae; propodus narrow, plumose setose along distal half of anterior margin, posterior margin with row of small robust setae, anterodistal lobe present and tipped with 2 very long, strong, slender setae; dactylus short, weakly curved and smooth.
Pereopod 6 basis nearly ovoid, but with skewed angle, anterior margin unevenly bulged, lined with short slender setae proximally and many long plumose setae distally, posterior margin rounded proximally and narrow distally, without setae, basis with small anterodistal and posterodistal lobe; ischium with acute posterior lobe; merus longer than ischium, not lobate, anterior margin fringed with many long slender setae but no robust setae, posterior margin without setae; carpus longer than merus and longer than propodus, anterior margin lined with 6 long robust setae, anterior margin no setae, distal corner produced distally with 4 long robust setae; propodus long and narrow, produced to form distal lobe bearing 2 very long, strong, slender setae, anterior and posterior margins lined with short sparse setae; dactylus short, curved and smooth. Pereopod 7 coxa with ventral fringe of short slender setae; basis widest distally, posteroventral margin broadly rounded, lobe reaching just past merus, medial surface densely setose, anterior margin not setose, ventral and part of posterior margin lined with long plumose setae extending to junction with ischium, posterior corner smooth; ischium short and not setose, except for anterodistal corner; merus longer than ischium, not lobate, anterior margin with 3 short robust setae, posterior with 7 long plumose setae and distally with 2 robust setae; carpus narrow, longer than merus, subequal to propodus, anterior margin with 6 short robust setae and 2 distal slender setae, posterior margin with eleven long plumose slender setae, with 4 short distal robust setae; propodus long and narrow, anterior margin without setae, posterior margin with 5 robust setae; dactylus long, straight, narrow, as long as propodus.
Pleon. Epimeron 1 posteroventrally broadly rounded, ventral margin with plumose setae. Epimeron 2 posteroventrally broadly rounded, ventral margin with plumose setae. Epimeron 3 posteroventrally produced to form strong subacute tooth, posterior margin straight, ventral margin with 4 small proximal robust setae. Urosomite 1 produced weakly to form slightly bilobed (in dorsal view) hood over urosomite 2. Uropod 1, in situ, reaching to tip of uropod 2 rami; peduncle longer than rami, outer margin lined with 3 short robust setae, inner margin lined with 8 long robust setae, medial with 14 slender, plumose setae; rami subequal in length, outer ramus lined with 9 robust setae; inner ramus with 7 robust marginal setae. Uropod 2 peduncle same length rami, inner margin with 4 robust lateral setae and 2 medial robust setae; with medial fringe of long, plumose, slender setae; inner ramus equal in length to outer ramus; outer ramus with 5 short marginal robust setae, and long subterminal robust seta; inner ramus with 6 long marginal robust setae. Uropod 3 peduncle shorter than rami, with 2 marginal short robust setae; inner ramus same length to outer ramus, both rami leaf-shaped (broadest proximally); inner ramus lined with long slender plumose setae and 3 robust setae laterally (both margins); outer rami inner margin with long slender, plumose setae, outer margin with 13 short robust setae laterally. Telson longer than wide (1.5 ×), 77% cleft; each lobe subacute distally, each lobe with 2 dorsal robust setae, 1 robust apical and 2 slender apical setae.
Male variations. Based on paratype, male, 25 mm. Epimeron 3 posteroventral corner tooth more acute. Urosomite 1 hood more defined laterally. Telson with 4 dorsal robust setae per lobe, 1 robust seta and 1 slender plumose seta apically per lobe.
Etymology. This species is named for Dr Monica Handler whose project, along with Dr Richard Wysoczanski, brought about the discovery of this species. Used as a noun in the genitive.
Remarks. Byblisoides monicae n. sp. is a large, distinctive ampeliscid only found (so far) in the Ross Sea, Antarctica. As mentioned before and by other researchers, Byblisoides has relatively conservative morphology across the genus with only small, subtle variations present ( Barnard 1961, 1964; Mills 1971).
Morphologically, Byblisoides monicae n. sp. shows greatest similarities to B. juxtacornis , the type species of the genus recorded from a relatively similar locality (Palmer Archipelago, Antarctica), B. esferis from the Tasman Sea and B. richardi n. sp. The similarities between these four species include an acutely produced anteroventral corner of the head, antenna 2 flagellum with four articles, coxa 1 having the same length as coxae 2 and 3, the pereopod 7 basis being pear-shaped with many plumose setae on the medial surface, and urosomite 1 being dorsally unilobed. Byblisoides juxtacornis differs from B. monicae in the presence of three long slender plumose setae on the posterior margin of the pereopod 7 merus, and four long, slender plumose setae on the anterior margin of pereopod 7 carpus. This character is used in identification keys for this genus ( J.L. Barnard 1964; Peart 2018), but B. juxtacornis has seven long, slender plumose setae on pereopod 7 posterior margin, and no slender plumose setae on the anterior margin of pereopod 7 carpus. Other differences include the number of articles in the antenna 1 flagellum (3 in B. monicae and 2 in B. juxtacornis ), coxa 1 reaches well beyond the anterior margin of the head (reaching only halfway along the head in B. juxtacornis ), the pereopod 4 coxa ventral margin is sinusoidal with an acute anterior corner in the new species, posterior margin lobe is truncated (ventral margin straight, anterior corner rounded, posterior margin lobe acute in B. juxtacornis ), pereopod 7 basis posteroventral lobe reaching past the merus, basis medial surface covered in dense long plumose setae ( B. juxtacornis pereopod 7 basis posteroventral lobe reaching only halfway along merus, basis medial surface partly covered with small slender setae), pereopod 7 merus and carpus anterior margins lined with small robust setae (pereopod 7 merus and carpus without robust setae in B. juxtacornis ).
The differences between B. monicae and B. esferis include the relative lengths of antenna 1 to antenna 2 article 4 (reaching all the way to end in B. esferis , and only halfway along in B. monicae ); the shape of the coxa 1 posteroventral corner (smooth in B. esferis and with a small tooth in B. monicae ). The other major differences include the shape of the pereopod 4 coxa (ventral margin sinusoidal and produced to form an acute anteroventral corner in B. monicae , ventral margin convex and the anteroventral corner rounded in B. esferis ). The other differences are in pereopod 7: the merus posterior margin has many plumose setae in B. monicae but none in B. esferis , and the carpus is lined with robust setae in B. monicae but none in B. esferis .
The differences between B. monicae and B. richardi are subtle but warrant specific separation. These differences include the shape of the coxa ventral margin (angled and produced in B. monicae versus evenly rounded in B. richardi ), the setation along the margins of pereopods 5–7 are also significantly different. Byblisoides monicae has significantly more robust setae and long plumose setae on all margins of pereopods 5–7. The other significant difference is in the setation of epimera 2 and 3 (small, plumose setae along the ventral margins of B. monicae and only small robust setae on the ventral margins of B. richardi ). See updated key below, for the significant differences between all the species in this genus.
Distribution. Ross Sea, Antarctica; 407–522 m depth.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |