Theopea, Baly, 1864
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4508.3.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:4C0CAE39-B5C3-419C-9A4D-493806280141 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5957157 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03928782-A84A-FFC0-1E89-7350FA72FCFE |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi (2019-03-26 07:40:26, last updated 2024-11-26 23:34:07) |
|
scientific name |
Theopea |
| status |
|
Key to the species of Theopea in East Asia, excluding species with modified clypeus in males
1 Longitudinal ridges on elytra distinct...................................................................... 2
- Longitudinal ridges on elytra indistinct or reduced........................................................... 9
2 Elytra with extremely coarse punctures, space between punctures narrower than diameters of punctures; head and prothorax yellow except vertex and pronotum; Taiwan ( Figs 2 View FIGURES 2 D–2H)......................................... collaris Kimoto
- Elytra with coarse punctures, space between punctures broader than diameters of punctures; head and prothorax metallic blue or green except mouth parts............................................................................. 3
3 General color metallic green; longitudinal ridges on elytra apically abbreviated from apical 1/3 ( Figs 4 View FIGURES 4 A–4C); antennomeres III–VII straight in males ( Fig. 5A View FIGURES 5 ); Taiwan..................................................... T. cheni sp. nov.
- General color metallic blue; longitudinal ridges on elytra not apically abbreviated; antennomeres III–VII more or less curved................................................................................4. ( T. sauteri species group)
4 Males with longitudinal ridges on the elytra more or less reduced................................................ 5
- Males with longitudinal ridges on the elytra prominent...................................................... w8
5 Penis asymmetric, bent to the right ( Figs 14 View FIGURES 14 C–14E, 20C–20E)................................................. 6
- Penis symmetrical ( Figs 15 View FIGURES 15 C–15E, 18C–18F)............................................................... 7
6 Penis relatively slender, 10.0x longer than wide; dorsal sclerite of endophallus extremely elongate, 3.6x longer than basal piece; Laos ( Figs 20 View FIGURES 20 C–20E)............................................................... T. sekerkai sp. nov.
- Penis relatively broad, 9.0x longer than wide; dorsal sclerite of endophallus less elongate, 1.6x longer than basal piece; China ( Figs 14 View FIGURES 14 C–14E)............................................................... T. coerulea Gressitt & Kimoto
7 Triangular sclerites of endophallus elongate; ventral sclerites absent; basal piece longer than apical piece, with longitudinal row of tiny teeth along lateral margin; India ( Figs 15 View FIGURES 15 C–15E)...................................... T. geiseri sp. nov.
- Triangular sclerites of endophallus small; ventral sclerites present; basal piece shorter than apical piece, without tiny teeth; China, Laos, Vietnam ( Figs 18 View FIGURES 18 C–18F)...................................................... .. laosensis sp. nov.
8 Males with antennomeres III–X moderately curved ( Fig. 19A View FIGURES 19 ); swollen tarsomeres I of front legs not apically narrowed ( Fig. 19I View FIGURES 19 ); Taiwan............................................................................. T. sauteri Chûjô
- Males with antennomeres III–X straight ( Fig. 16A View FIGURES 16 ); swollen tarsomeres I of front legs apically narrowed ( Fig. 16E View FIGURES 16 ); Taiwan................................................................................... T. hainanensis . sp. nov.
9 Elytra with extremely coarse punctures, space between punctures narrower than diameters of punctures ( Figs 2 View FIGURES 2 A–2C); Japan..................................................................................... T. aureoviridis Chûjô
- Elytra with moderately coarse punctures, space between punctures broader than diameters of punctures ( Figs 8 View FIGURES 8 , 11 View FIGURES 11 )....... 10
10 General color sexually dimorphic, elytra yellowish brown with metallic green sides, pronotum and vertex metallic green in males; elytra entirely metallic green, prothorax and head yellow in females; hypomeron yellowish brown ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 11 ); antenna in males relatively shorter, antennomeres V–IX less than six times longer than wide ( Fig. 12A View FIGURES 12 ); Taiwan........................................................................................................ T. kanmiyai (Kimoto)
- General color not sexually dimorphic, elytra, pronotum, and vertex metallic green or blue in both sexes; hypomeron dark or blackish brown ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 8 ); antenna in males more slender, antennomeres V–IX more than six times longer than wide ( Figs. 9A, 9B View FIGURES 9 ); Taiwan........................................................................ T. irregularis Takizawa
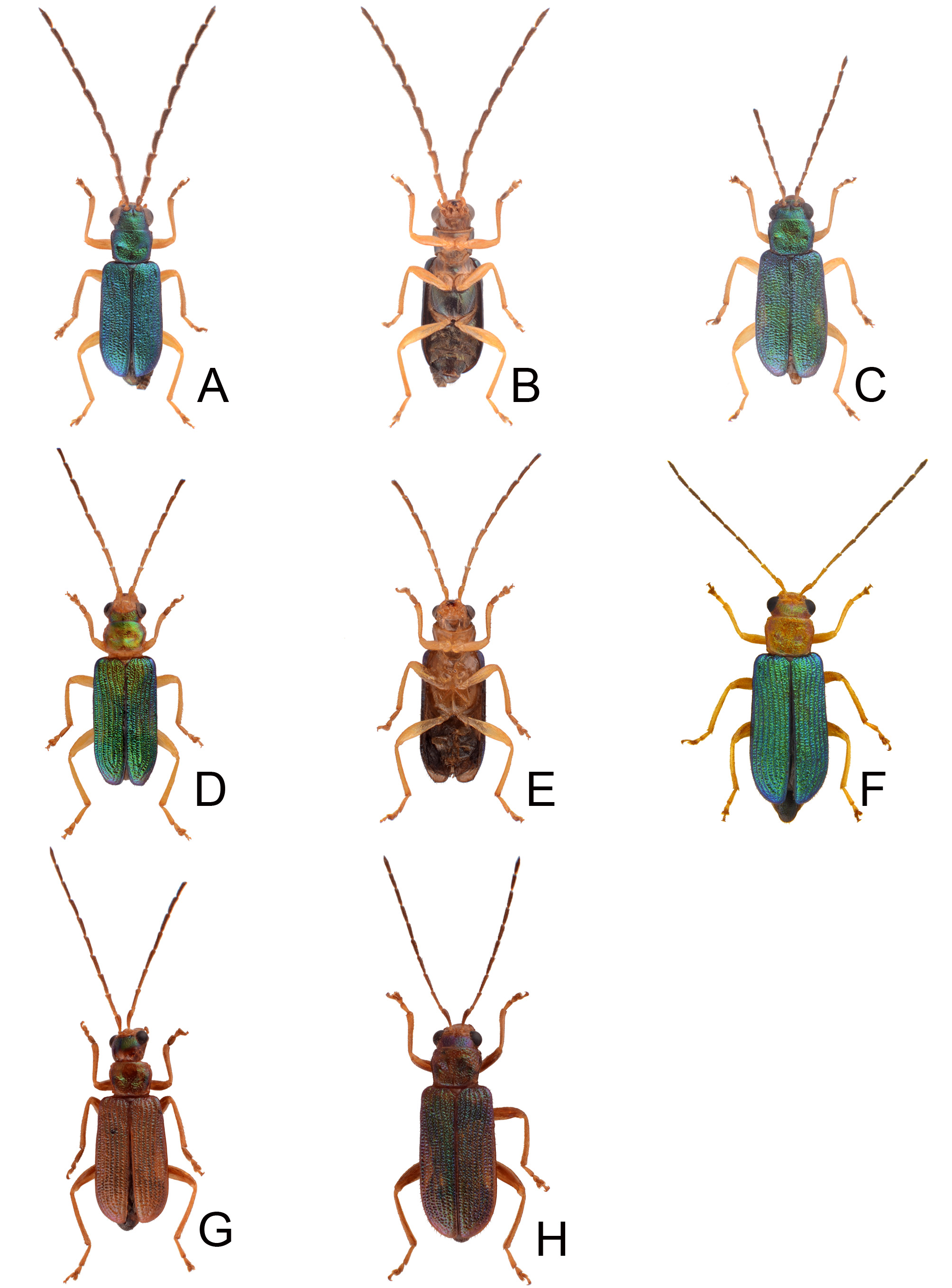
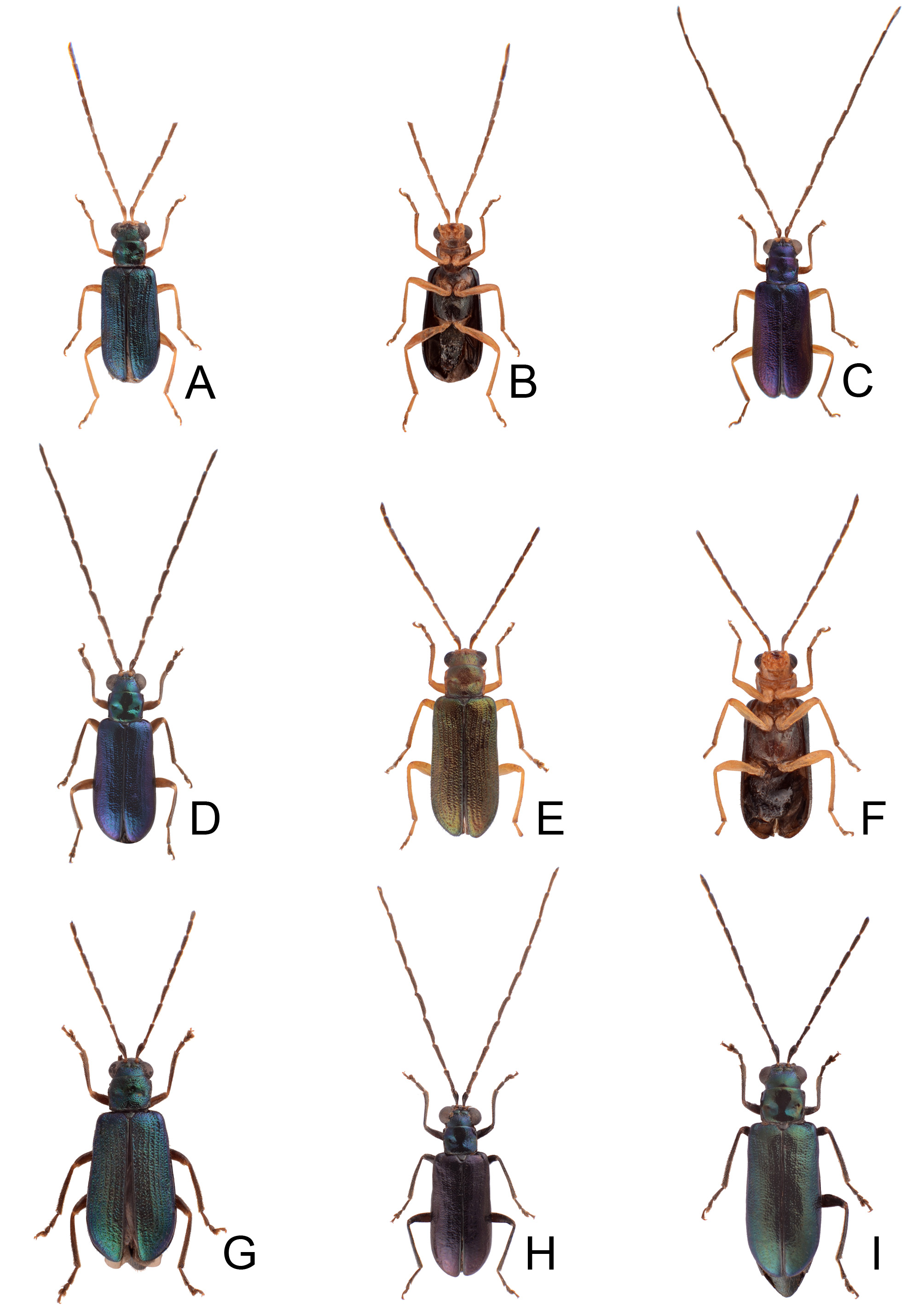
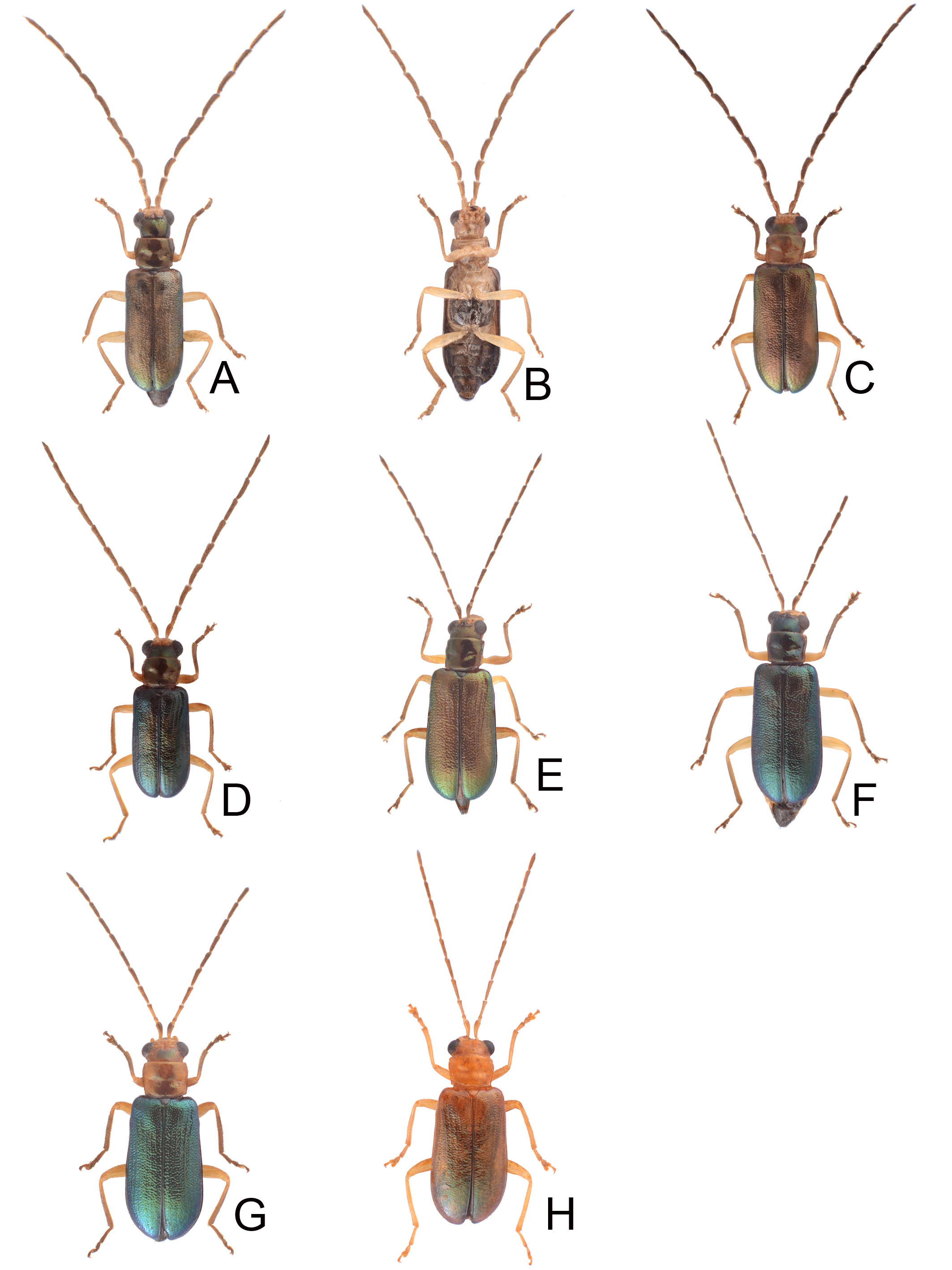
FIGURES 2. Habitus of Theopea aureoviridis Chûjô and T. collaris Kimoto. 2A. T. aureoviridis, male, dorsal view; 2B. Same, ventral view; 2C. T. aureoviridis, female, dorsal view; 2D. T. collaris, male, Tahanshan (大漢山), dorsal view; 2E. Same, ventral view; 2F. T. collaris, female, Tahanshan (大漢山), dorsal view; 2G. T. collaris, male, Kenting (墾丁), dorsal view; 2H. T. collaris, female, Nanjenshan (南仁山), dorsal view.
FIGURES 4. Habitus of Theopea cheni sp. nov. and T. sauteri Chûjô. 4A. T. cheni sp. nov., male, dorsal view; 4B. Same, ventral view; 4C. T. cheni sp. nov., female, dorsal view; 4D. T. sauteri, male, Mutanchihshan (ËṚḾƜ), dorsal view; 4E. Same, ventral view; 4F. T. sauteri, male, Liyuan (Mȁ), dorsal view; 4G. T. sauteri, female, Liyuan (Mȁ), dorsal view; 4H. T. sauteri, male, Lilungshan (BÊƜ), dorsal view; 4I. Same, ventral view.
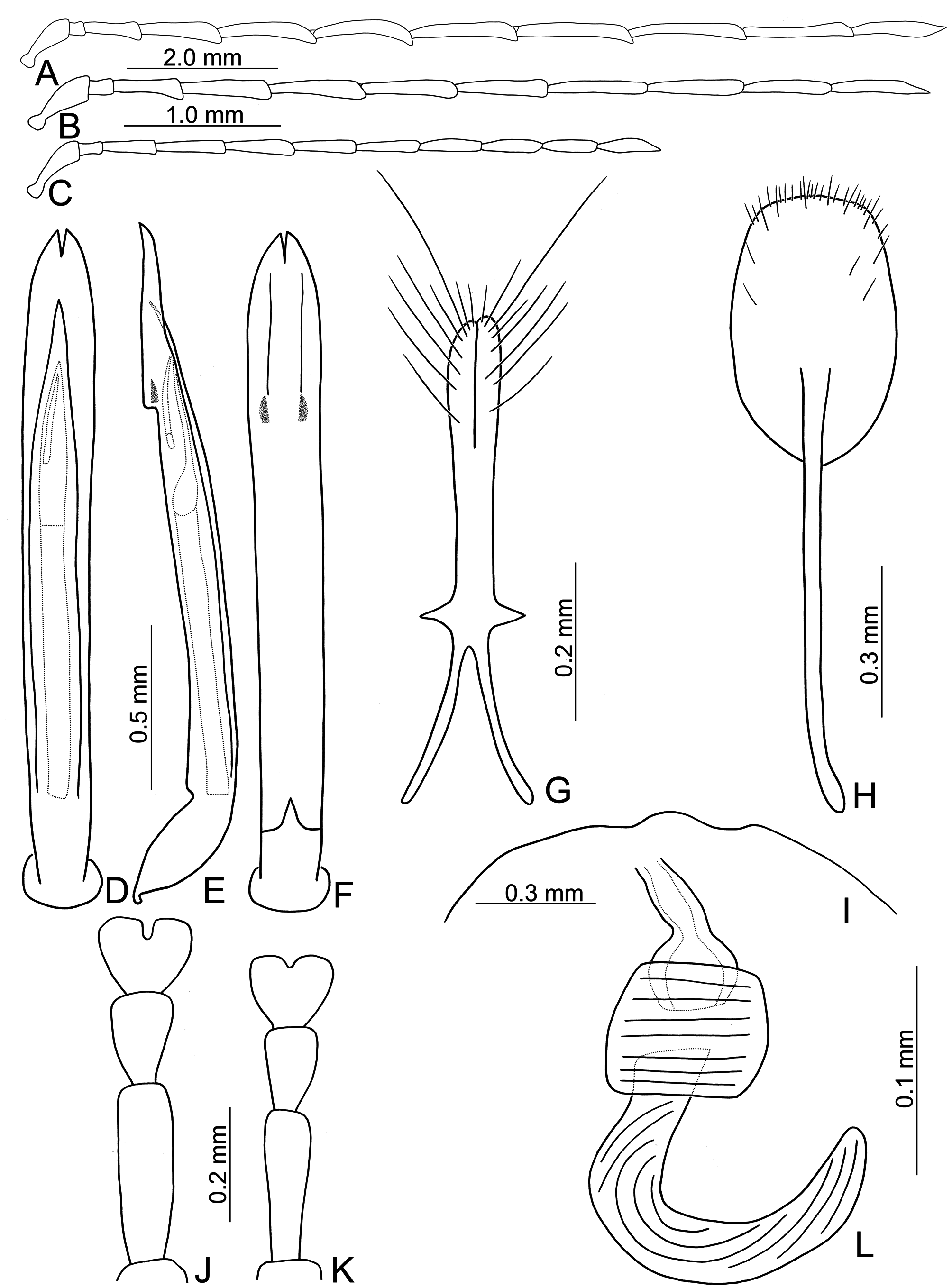
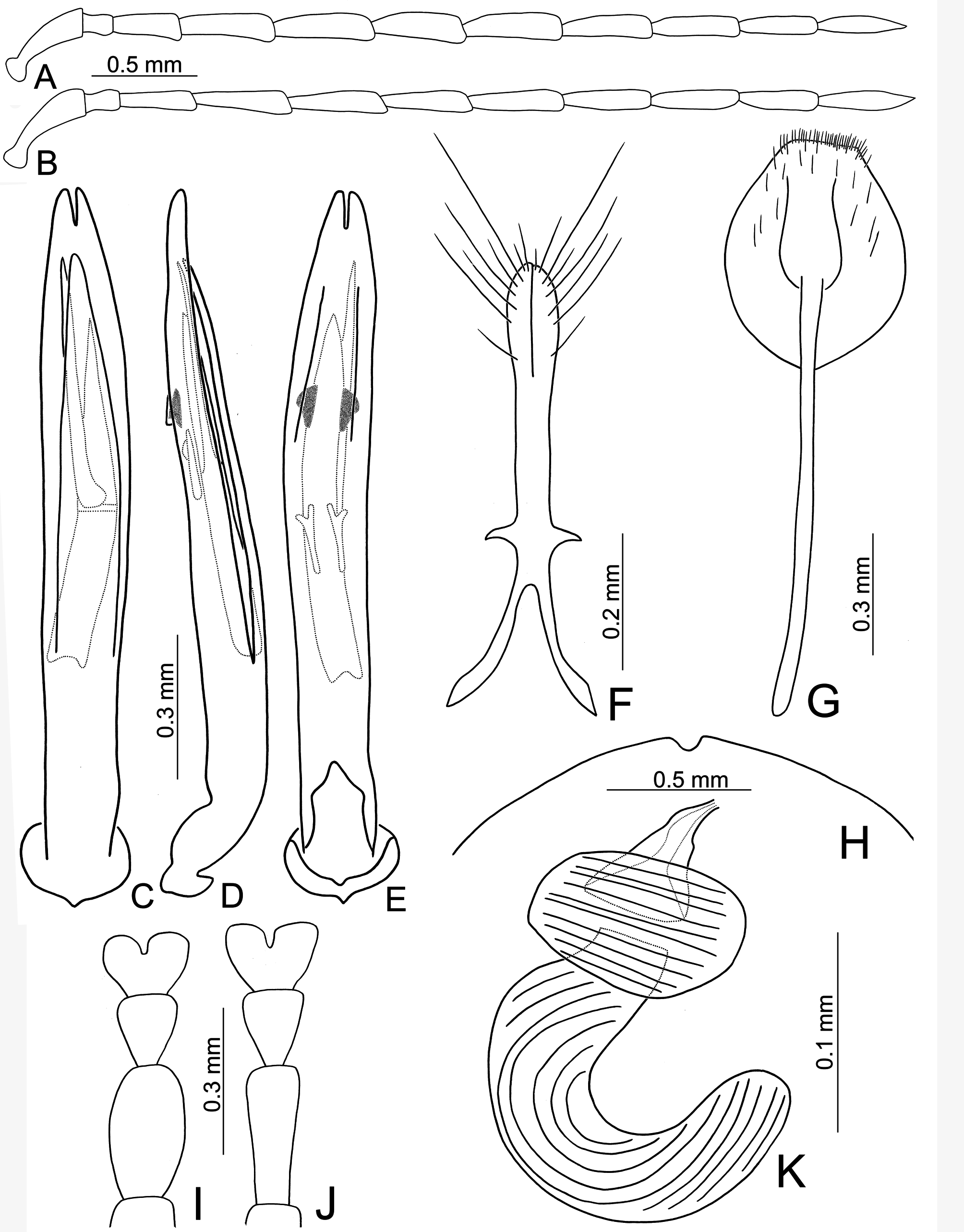
FIGURES 5. Diagnostic characters of Theopea cheni sp. nov. 5A. Antenna, male; 5B. Antenna, female; 5C. Penis, dorsal view; 5D. Penis, lateral view; 5E. Penis, ventral view; 5F. Gonocoxae; 5G. Abdominal ventrite VIII; 5H. Apical margin of abdominal ventrite V, female; 5I. Tarsi of front leg, male; 5J. Tarsi of front leg, female; 5K. Spermatheca.
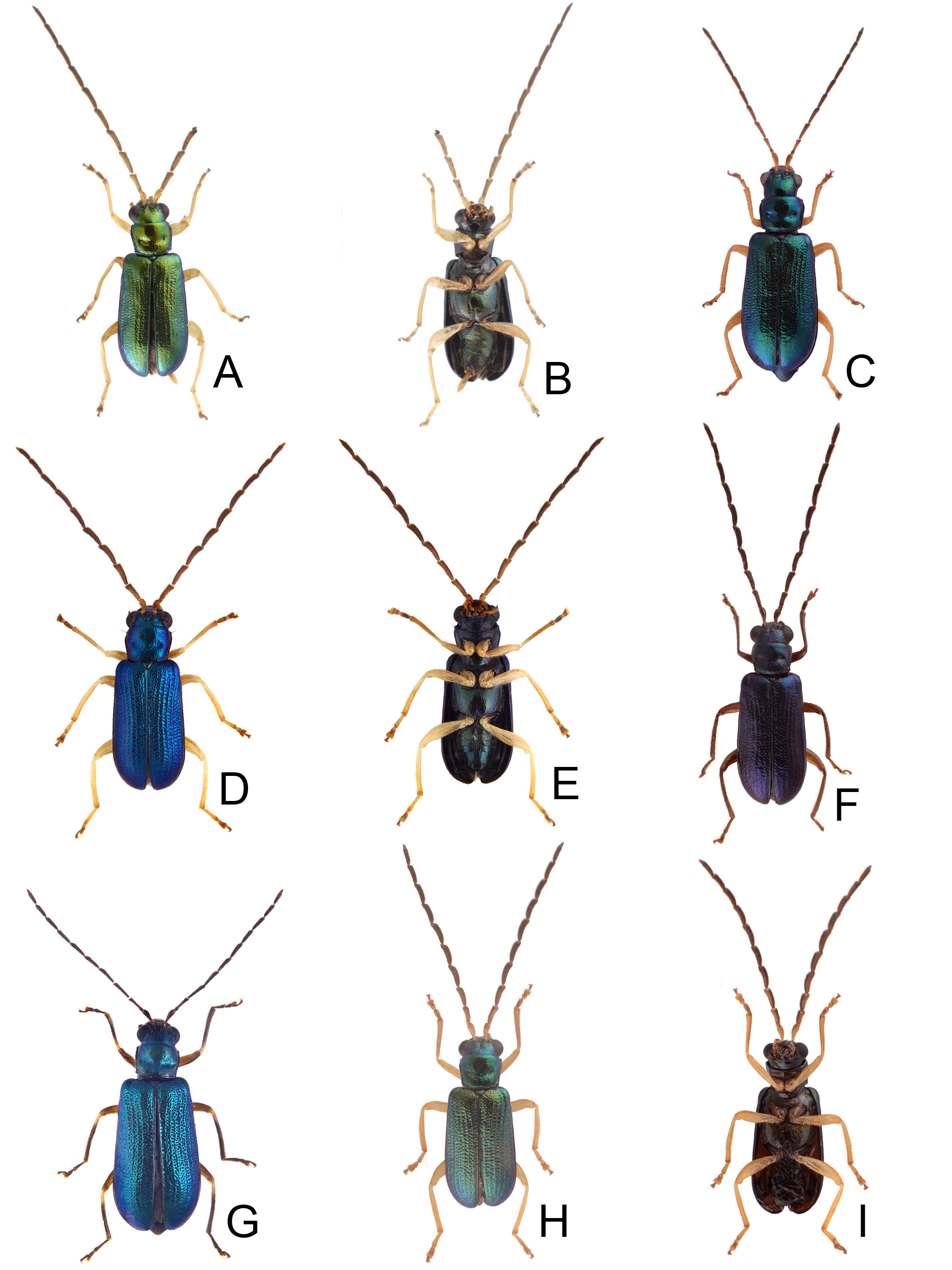
FIGURES 8. Habitus of Theopea irregularis Takizawa. 8A. Male, Taipeingshan (‡ ṬƜ), dorsal view; 8B. Same, ventral view; 8C. Male, Motien (±), dorsal view; 8D. Male, Tsuifeng (Ṝẘ), dorsal view; 8E. Female, Anmashan (ḎḄƜ), dorsal view; 8F. Same, ventral view; 8G. Female, Mingchi (ŖḾ), dorsal view; 8H. Male, Tatachia (ḆḆffi), dorsal view; 8I. Female, Tatachia (ḆḆffi), dorsal view.
FIGURES 9. Diagnostic characters of Theopea irregularis Takizawa. 9A. Antenna, male; 9B. Antenna, male; 9C. Antenna, female; 9E. Penis, dorsal view; 9E. Penis, lateral view; 9F. Penis, ventral view; 9G. Gonocoxae; 9H. Abdominal ventrite VIII; 9I. Apical margin of abdominal ventrite V, female; 9J. Tarsi of front leg, male; 9K. Tarsi of front leg, female; 9L. Spermatheca.
FIGURES 11. Habitus of Theopea kanmiyai (Kimoto). 11A. Male, Alishan (ȐBƜ), dorsal view; 11B. Same, ventral view; 11C. Male, Motien (±), dorsal view; 11D. Male, Tahanshan (XÃƜ), dorsal view; 11E. Female, Paling (ƂD), dorsal view; 11F. Female, Chungchihkuan (¢ŽṞ), dorsal view; 11G. Female, Tahanshan (XÃƜ), dorsal view; 11H. Female, Tahanshan (XÃƜ), dorsal view.
FIGURES 12. Diagnostic characters of Theopea kanmiyai (Kimoto). 11A. Antenna, male; 11B. Antenna, female; 11C. Penis, dorsal view; 11D. Penis, lateral view; 11E. Penis, ventral view; 11F. Gonocoxae; 11G. Abdominal ventrite VIII; 11H. Apical margin of abdominal ventrite V, female; 11I. Tarsi of front leg, male; 11J. Tarsi of front leg, female; 11K. Spermatheca.
FIGURES 14. Diagnostic characters of Theopea coerulea Gressitt & Kimoto. 14A. Antenna, male; 14B. Antenna, female; 14C. Penis, dorsal view; 14D. Penis, lateral view; 14E. Penis, ventral view; 14F. Gonocoxae; 14G. Abdominal ventrite VIII; 14H. Apical margin of abdominal ventrite V, female; 14I. Tarsi of front leg, male; 14J. Tarsi of front leg, female; 14K. Spermatheca.
FIGURES 15. Diagnostic characters of Theopea geiseri sp. nov. 15A. Antenna, male; 15B. Antenna, female; 15C. Penis, dorsal view; 15D. Penis, lateral view; 15E. Penis, ventral view; 15F. Gonocoxae; 15G. Abdominal ventrite VIII; 15H. Apical margin of abdominal ventrite V, female; 15I. Tarsi of front leg, male; 15J. Tarsi of front leg, female; 15K. Spermatheca.
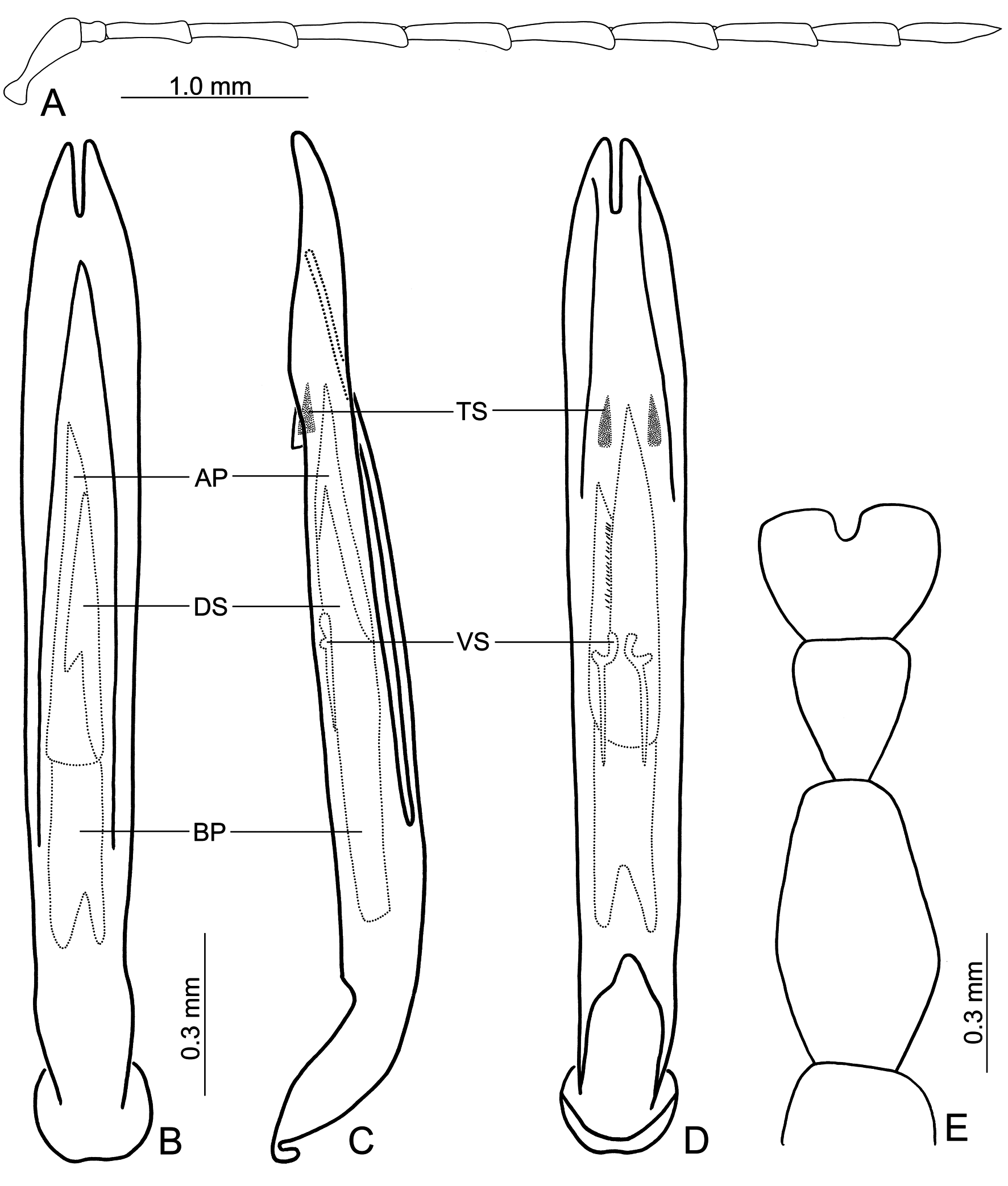
FIGURES 16. Diagnostic characters of Theopea hainanensis sp. nov. 16A. Antenna, male; 16B. Penis, dorsal view; 16C. Penis, lateral view; 16D. Penis, ventral view; 16E. Tarsi of front leg, male; AP: apical piece, BP: basal piece, DS: dorsal sclerite, TS: triangular sclerite, VS: ventral sclerite.
FIGURES 18. Diagnostic characters of Theopea laosensis sp. nov. 18A. Antenna, male; 18B. Antenna, female; 18C. Penis, dorsal view; 18D. Endophallic sclerites, Vietnam; 18E. Penis, lateral view; 18F. Penis, ventral view; 18G. Gonocoxae; 18H. Abdominal ventrite VIII; 18I. Apical margin of abdominal ventrite V, female; 18J. Tarsi of front leg, male; 18K. Tarsi of front leg, female; 18L. Spermatheca.
FIGURES 19. Diagnostic characters of Theopea sauteri Chûjô. 19A. Antenna, male; 19B. Antenna, female; 19C. Penis, dorsal view; 19D. Penis, lateral view; 19E. Penis, ventral view; 19F. Gonocoxae; 19G. Abdominal ventrite VIII; 19H. Apical margin of abdominal ventrite V, female; 19I. Tarsi of front leg, male; 19J. Tarsi of front leg, female; 19K. Spermatheca.
FIGURES 20. Diagnostic characters of Theopea sekerkai sp. nov. 20A. Antenna, male; 20B. Antenna, female; 20C. Penis, dorsal view; 20D. Penis, lateral view; 20E. Penis, ventral view; 20F. Gonocoxae; 20G. Abdominal ventrite VIII; 20H. Apical margin of abdominal ventrite V, female; 20I. Tarsi of front leg, male; 20J. Tarsi of front leg, female; 20K. Spermatheca.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Galerucinae |
1 (by plazi, 2019-03-26 07:40:26)
2 (by ImsDioSync, 2019-03-26 09:51:42)
3 (by ImsDioSync, 2019-03-28 01:46:51)
4 (by ExternalLinkService, 2019-09-25 23:33:37)
5 (by ExternalLinkService, 2022-01-29 14:29:09)
6 (by ExternalLinkService, 2022-02-03 09:48:42)
7 (by GgImagineBatch, 2022-04-30 04:47:36)
8 (by plazi, 2023-10-30 11:43:21)