Leptopholcus Simon, 1893
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2014.81 |
|
publication LSID |
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:AC69F89F-C11B-49B1-8EEE-183286EDA755 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6139594 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038C87B3-FF93-FF84-845A-1428FBB9FEBE |
|
treatment provided by |
Jeremy |
|
scientific name |
Leptopholcus Simon, 1893 |
| status |
|
Leptopholcus Simon, 1893 View in CoL View at ENA
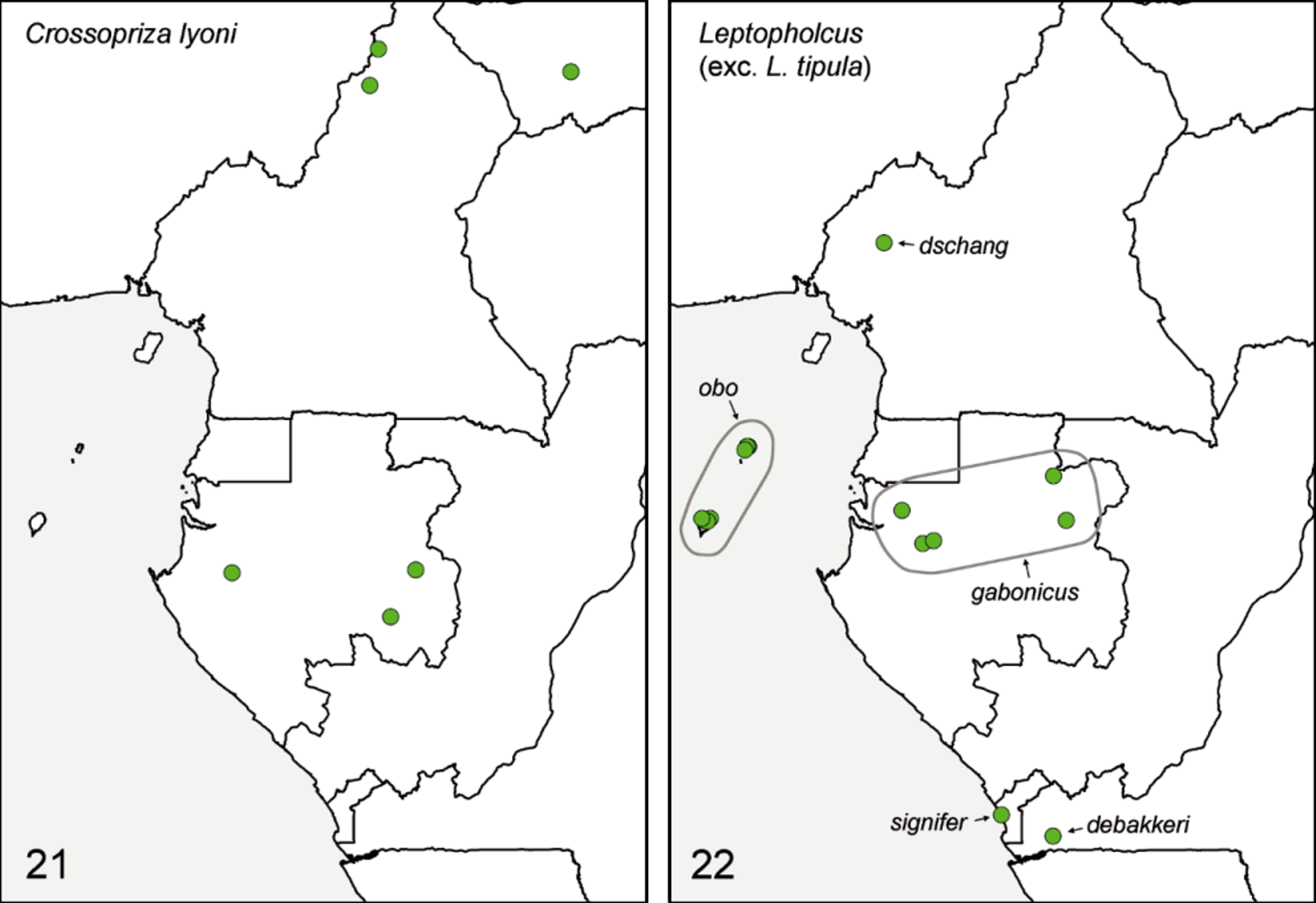
Of the ten species of Leptopholcus currently known from mainland Africa ( Huber 2011b; Huber & Kwapong 2013), six occur in Central Africa ( Figs 22-23 View Figs 21 - 22 View Figs 23 - 24 ). Of these, four are endemic to Central Africa ( L. dschang Huber, 2011 ; L. obo Huber, 2011 ; L. debakkeri Huber, 2011 ; L. gabonicus sp. nov.); the fifth [ L. tipula ( Simon, 1907) ] occurs throughout the entire Guineo-Congolian rainforest ( Huber 2011b). The type species L. signifer Simon, 1893 was described from Central Africa (Cabinda, Angola) but its actual range is dubious ( Huber 2011b).
4. Leptopholcus debakkeri Huber, 2011 . Congo D.R. ( Huber 2011b).
5. Leptopholcus dschang Huber, 2011 . Cameroon ( Huber 2011b).
6. Leptopholcus gabonicus sp. nov. (see below). Gabon.
7. Leptopholcus obo Huber, 2011 . São Tomé and Príncipe ( Huber 2011b) .
8. Leptopholcus signifer Simon, 1893 . Angola (Cabinda) ( Simon 1893).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.