Marma baeri Simon, 1902
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4899.1.16 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:27E67BBB-DFD0-4A96-8269-9E1CB6153B83 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4456839 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03403F11-FF9B-FF87-538B-FBDB08C6F86D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Marma baeri Simon, 1902 |
| status |
|
Marma baeri Simon, 1902 View in CoL
Figures 2–11 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 View FIGURE 7 View FIGURE 8 View FIGURE 9 View FIGURE 10 View FIGURE 11 , 57A View FIGURE 57 , 58A View FIGURE 58
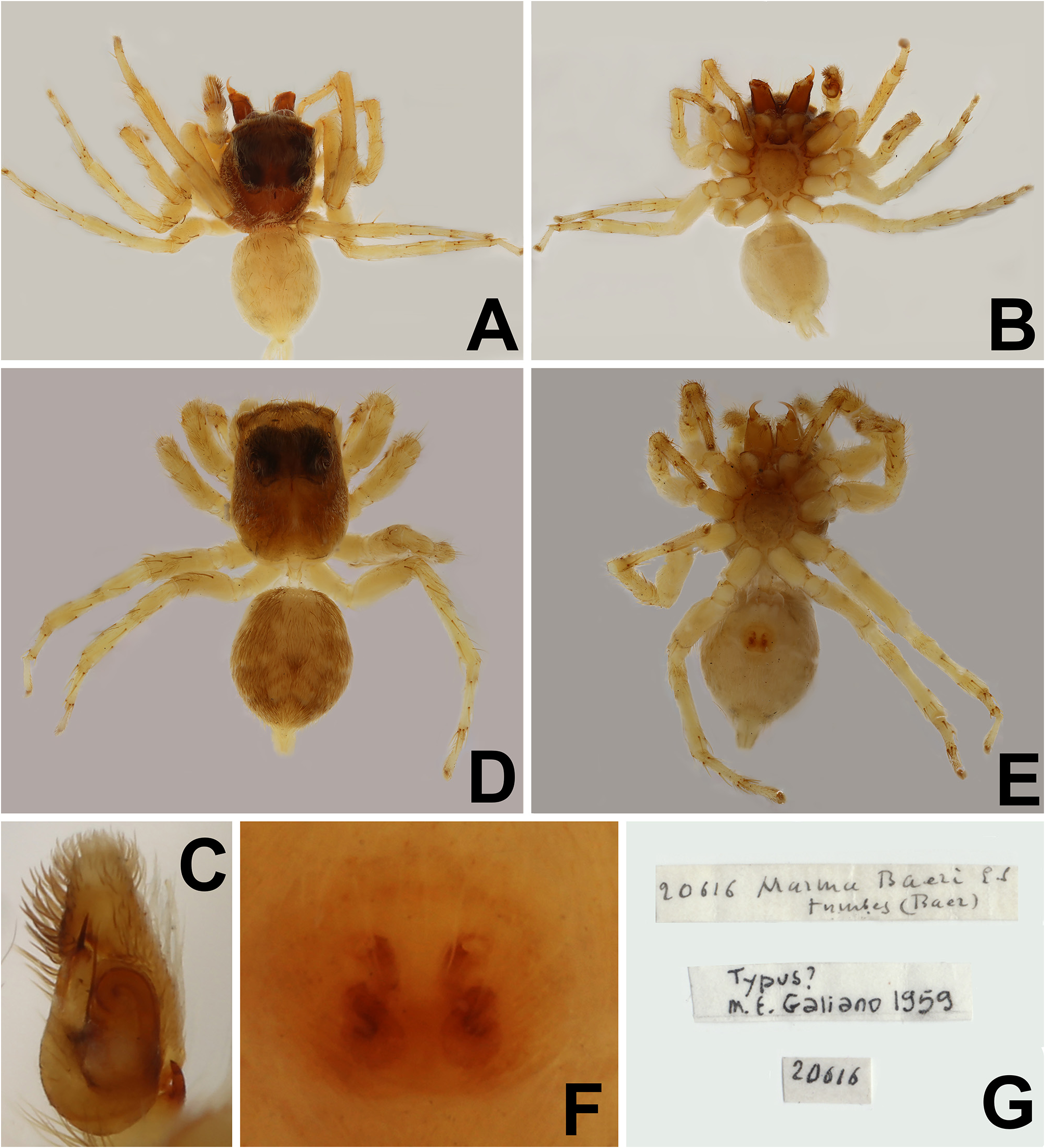
Marma baeri Simon, 1902: 376 View in CoL (Holotype ♁: ECUADOR: Túmbez [00°49’01.2”N, 78°21’00.2”W], leg. G.A. Baer, deposited in MNHN, collection of E. Simon; allotype ♀, same data as holotype, both examined by photographs); Galiano, 1962: 36, pl. I, figs 1–5; Galiano, 1963: 395, pl. XXVIII, figs 7–10.
Note. Both sexes are redescribed based on newly collected specimens. Photographs of the type specimens were provided by MNHN ( Figs 4 View FIGURE 4 A–G).
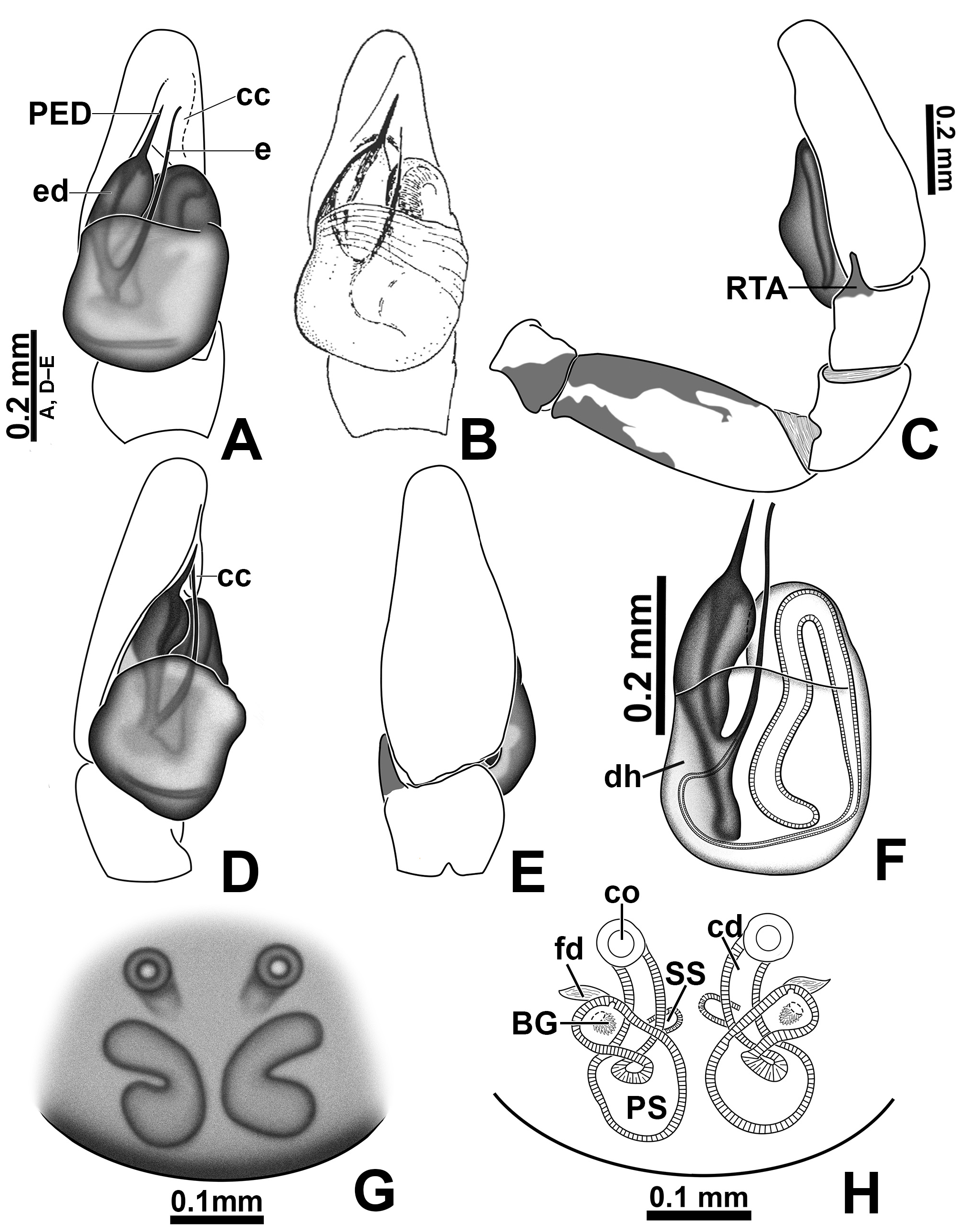
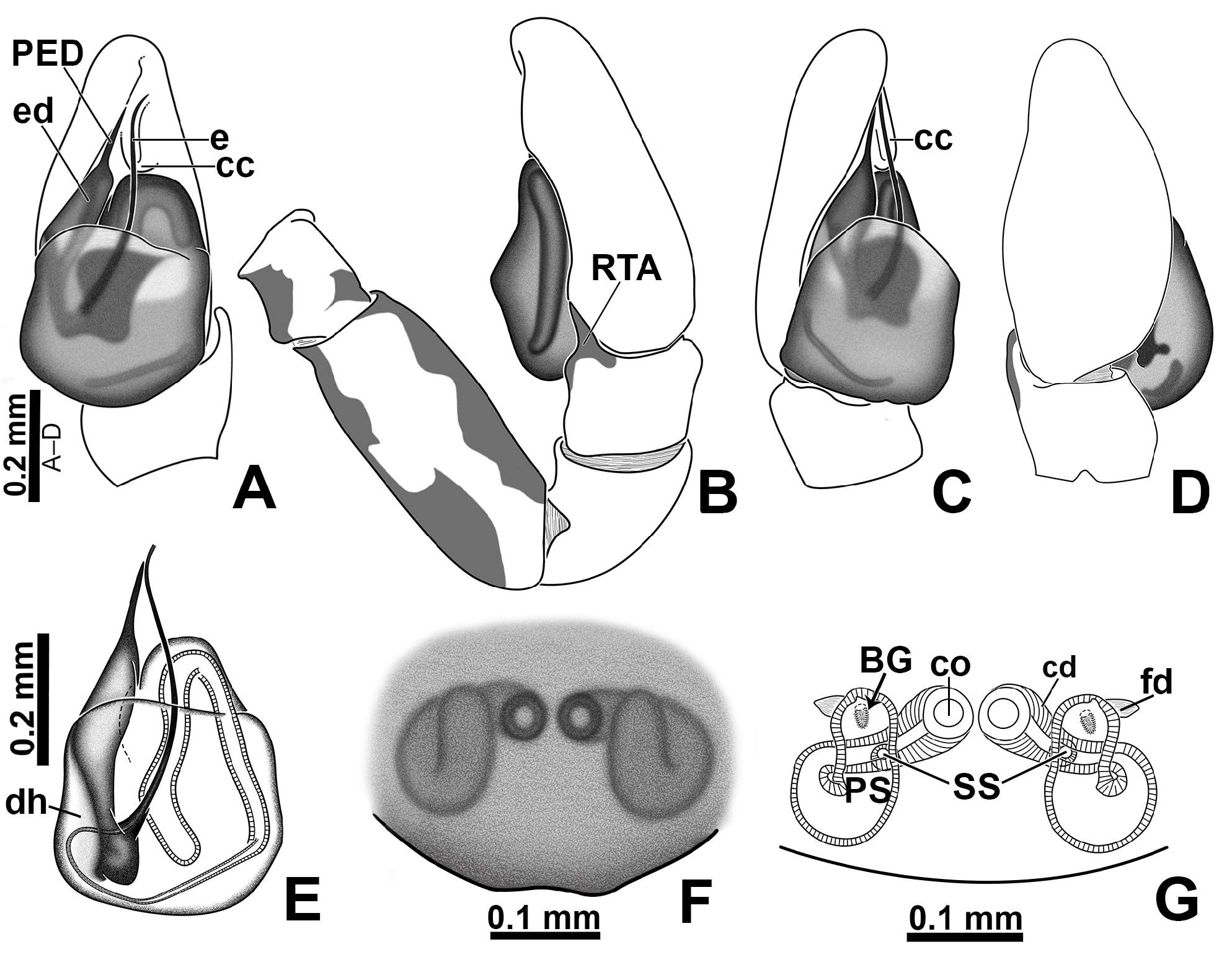
Diagnosis. The males of M. baeri are most similar to those of M. linae sp. nov. by having a short process on the embolic disc (PED; 5C, 7A, 13C, 15A), but differ by having a thicker embolic disc ( Figs 57 View FIGURE 57 A–B). Besides, the embolus shaft (e) in M. baeri emerges from a less proximal portion of embolic disc and is consequently shorter than the embolus of M. linae sp. nov. (best visualized cleared in clove oil; Figs 7F View FIGURE 7 , 9C View FIGURE 9 , 15E View FIGURE 15 , 16A View FIGURE 16 ). The females of M. baeri differ from those of M. linae sp. nov. by having the copulatory openings separated by approximately three times the girth of the copulatory duct and by its placement anterior to the primary spermathecae ( Figs 6C View FIGURE 6 , 7 View FIGURE 7 G–H, 58A), whereas they are very close (separated by less than 1/2 their diameter) and placed at the same level of the primary spermathecae in M. linae sp. nov. ( Figs 14C View FIGURE 14 , 15 View FIGURE 15 F–G, 58B). Also, females of M. baeri have the distal portion of the primary spermathecae projecting laterally ( Figs 6C View FIGURE 6 , 7H View FIGURE 7 , 58A View FIGURE 58 ), whereas they project anteriorly in M. linae sp. nov. ( Figs 14C View FIGURE 14 , 15G View FIGURE 15 , 58B View FIGURE 58 ). Females of M. baeri are also very similar to those of M. femella , both with copulatory openings far from each other and the distal portion of primary spermathecae projecting laterally ( Figs 58A, D View FIGURE 58 ). However, in M. baeri the initial portion of spermathecae is dilated, whereas the spermathecae of M. femella have an elliptical shape ( Figs 58A, D View FIGURE 58 ).
Description. Male (QCAZ). Total length: 3.12. Carapace 1.64 long, 1.27 wide, 0.97 high. Ocular quadrangle 0.90 long. Anterior eye row 1.11 wide, posterior 0.96 wide. Legs 1432. Length of legs: I 4.30 (1.29 + 1.75 + 1.26); II 2.95 (0.99 + 1.04 + 0.92); III 3.55 (1.20 + 1.16 + 1.19); IV 3.66 (1.10 + 1.22 + 1.34).
Leg macrosetae: femur I d1-1-1, p1di, r0; II d1-1-1, p1di, r1di; III d1-1-1, p1di, r0; IV d1-1-1, p0 (or p1di), r1di; patella I–II 0, III–IV p0, r1; tibia I p0-1-0, r0, v1r-2-2; II p0-1-0, r0, v1r-2-1p; III p0-1-1-0, r0-1-1-0, v1p-0- 0-2 (v2di); IV p0-1-1-0, r1-1-1-0, v2di; metatarsus I p1di, r0, v2-2; II p1-1, r1di, v2-2; III d1p-0-0, p1-0-2, r1-0-2, v2-0-2; IV p1-1-2, r1-1-2, v1p-0-2.
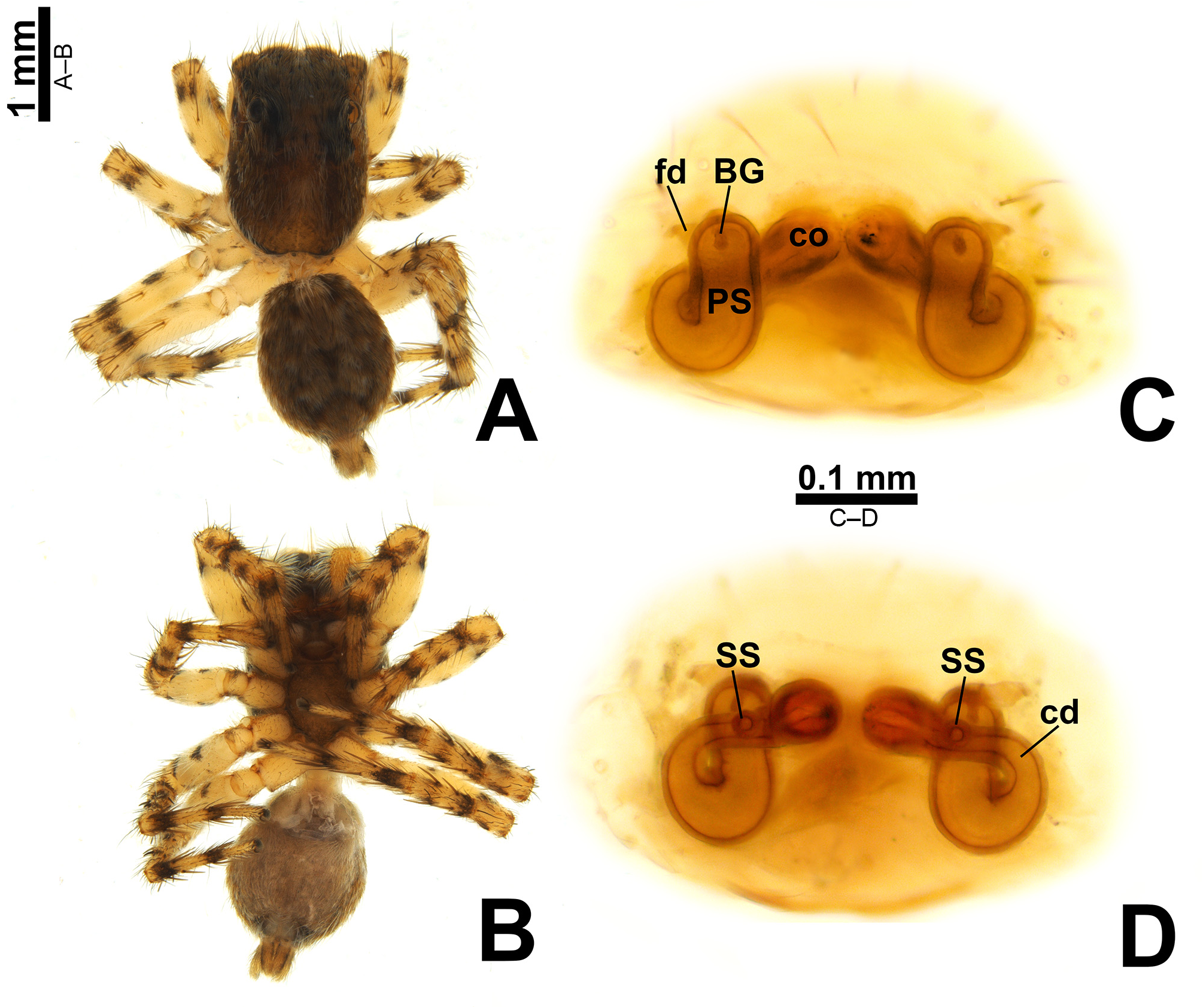
Color in alcohol ( Figs 5 View FIGURE 5 A–B): carapace with triangle of scales pointing backwards; regions beside the triangle with less concentrated scales; abdomen pale ventrally, with three dark brown longitudinal stripes; legs: femur I with dark distal ring and proximal region with dark prolateral spot, II with dark distal ring and proximal region with prolateral and retrolateral dark spot, III–IV with dark distal ring and proximal region with dark proventral spot; tibia I with dark proximal ring and distal region with dark retrolateral spot, II–IV with proximal and distal dark ring; tarsus I almost black, II with dark tip, III–IV with dark proximal ring.
Palp: RTA finger-shaped ( Figs 5D View FIGURE 5 , 6C View FIGURE 6 ); embolic disc with both edges curved ( Figs 5C View FIGURE 5 , 7A View FIGURE 7 ); PED with approximately same length of exposed portion of embolic disc and emerging from the middle-distal part of embolic disc ( Figs 5C View FIGURE 5 , 7A View FIGURE 7 ); tip of embolus aligned with tip of PED ( Figs 5C View FIGURE 5 , 7F View FIGURE 7 ).
Female (QCAZ). Total length: 3.51. Carapace 1.70 long, 1.20 wide, 0.81 high. Ocular quadrangle 0.73 long. Anterior eye row 1.13 wide, posterior 0.94 wide. Legs 4312. Length of legs: I 2.71 (0.86 + 1.03 + 0.82); II 2.57 (0.86 + 0.92 + 0.79); III 3.39 (1.13 + 1.16 + 1.10); IV 3.65 (1.11 + 1.23 + 1.31).
Leg macrosetae: Femur I d1-1-1, p1di, r0; II d1-1-1, p1di, r1di; III d1-1-1, p1di, r0; IV d1-1-1, p1di (or p0), r0 (or r1di). Patella I–II 0, III–IV p0, r1. Tibia I–II p0-1-0, r0, v1r-2-2; III p0-1-1-0, r0-1-1-0, v1p-0-0-1; IV d0-1p-0-0, p0-1-1-1 (p1-0-1-0), r1-1-1-0, v1p-0-0-2 (or 2di). Metatarsus I p1di, r0, v2-2; II p1-1, r1di, v2-2; III d1p-0-0, p1-0- 2, r1-0-2, v2-0-2; IV d1p-0-0 (or d0), p1-0-2 (or p1-1-2), r1-0-2 (or r1-1-2), v2-0-2 (or v1p-0-2).
Color in alcohol ( Figs 6 View FIGURE 6 A–B): carapace as in male, abdomen ventrally with three dark longitudinal stripes and with dark brown edge with pale circles; legs: femur I with dark distal ring and proximal region with dark retroventral spot, II–III with dark distal ring and proximal region with incomplete dark ring (dorsal portion not totally colored), IV with dark distal ring and proximal region with dark proventral spot; tibia I–IV with proximal and distal dark ring; tarsus I–II without dark marks, III–IV with dark proximal ring.
Epigyne ( Figs 6 View FIGURE 6 C–D, 7G–H, 10A–D): copulatory openings separated by approximately three times the girth of copulatory ducts, placed anteriorly to primary spermathecae; copulatory ducts short; proximal copulatory duct with approximately same length as distal section; primary spermathecae with initial portion dilated, tapering towards fertilization ducts; primary spermathecae laterally projected.
Other material examined. ECUADOR: Santa Elena : Montañita, 01°49’01.8”S, 80°45’29.1”W, 2019, 1♁ 1♀ ( QCAZ) GoogleMaps .
Distribution. Known from the provinces of Imbabura and Santa Elena ( Ecuador) ( Fig. 59A View FIGURE 59 ).
| QCAZ |
Museo de Zoologia, Pontificia Universidad Catolica del Ecuador |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Salticinae |
|
Tribe |
Euophryini |
|
Genus |
Marma baeri Simon, 1902
| Salgado, Alexandre & Ruiz, Gustavo R. S. 2020 |
Marma baeri
| Galiano, M. E. 1963: 395 |
| Galiano, M. E. 1962: 36 |
| Simon, E. 1902: 376 |