Tropisternus (Pristoternus) latus ( Brullé, 1837 ), Brulle, 1837
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3790.2.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:9CE1C14D-7C9D-4480-BC43-F556259CF118 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5613781 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038987BE-5A33-FFB2-1BCA-707AFCCF5E8E |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Tropisternus (Pristoternus) latus ( Brullé, 1837 ) |
| status |
|
Tropisternus (Pristoternus) latus ( Brullé, 1837) View in CoL
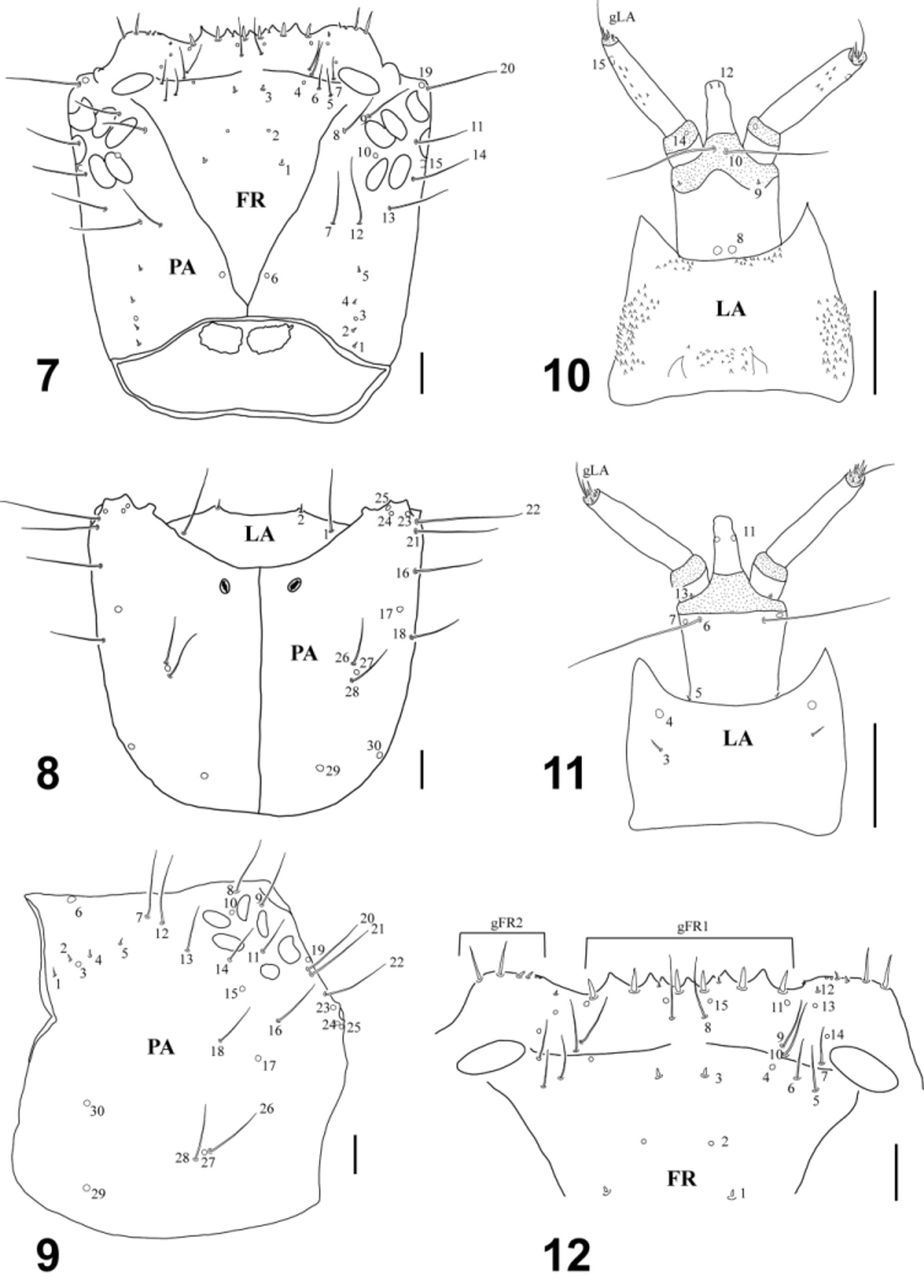
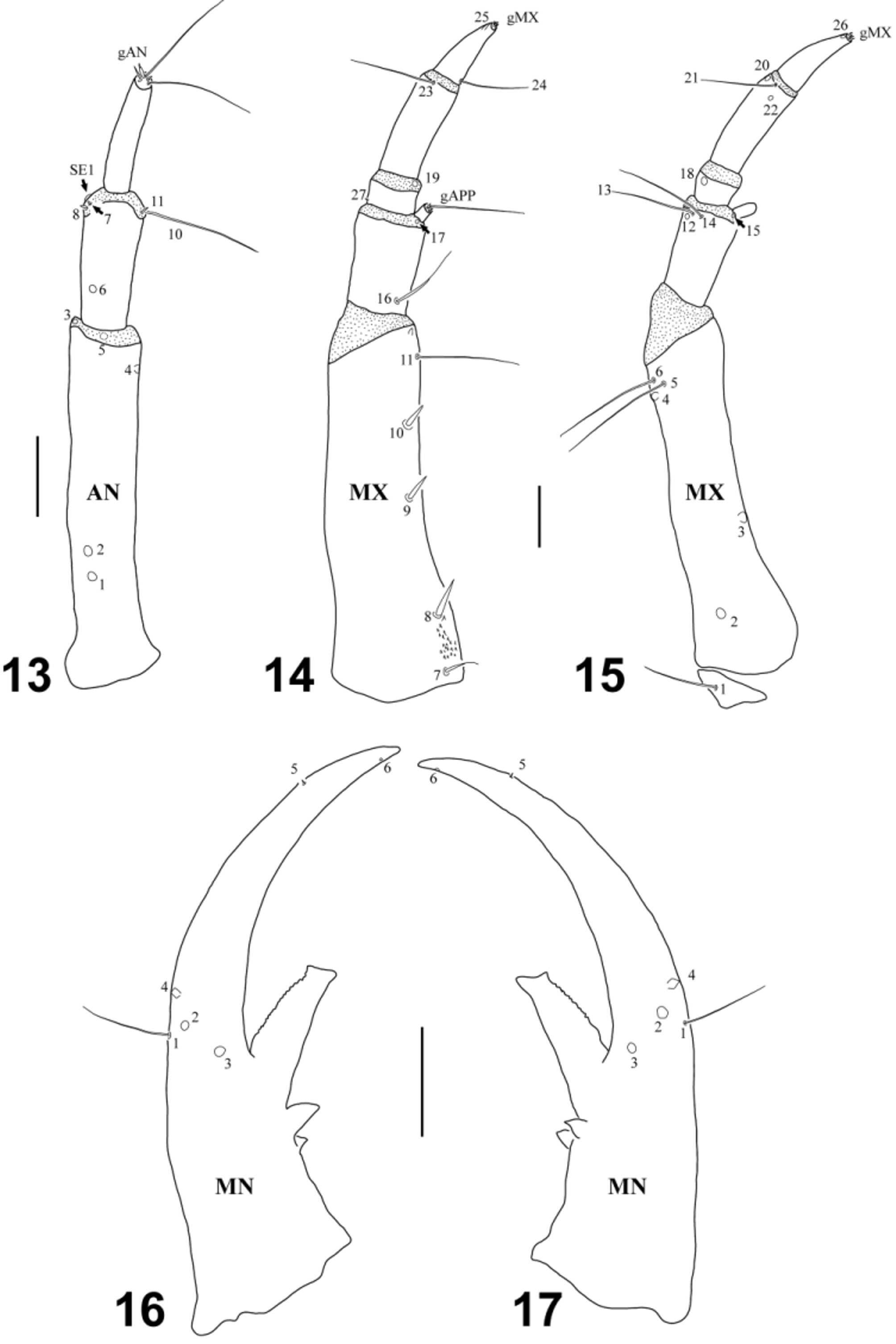
( Figs. 1–2 View FIGURES 1 – 6 , 7–19 View FIGURES 7 – 12 View FIGURES 13 – 17 View FIGURES 18 – 21 )
Material examined. Seven egg cases, 8 larvae of instar I, 6 of instar II, 5 of instar III and 5 pupae were used for the descriptions. Breeding adults were collected at the following locality: Argentina: Buenos Aires Province, Sierra de la Ventana (Ernesto Tornquist Provincial Park), X-2007 (see Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 6 in Fernández et al. 2010).
Description, egg case ( Figs. 1–2 View FIGURES 1 – 6 ). Whitish, saccular, subtriangular in cross-section. Mast present (n = 4) ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 6 ) or absent (n = 3) ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1 – 6 ). Length = 10.7–12.4 mm, width = 8.3–8.7 mm, height = 5.3–5.8 mm; cap length = 5.2–5.7 mm; mast length= 11.5–12.8 mm. Mast length/cap length = 2.21–2.24.
Description, instar I ( Figs. 7–17 View FIGURES 7 – 12 View FIGURES 13 – 17 ). Color: head capsule testaceous, with pale brown areas around frontal sulci and on dorsolateral surface of parietale. Cephalic and thoracic appendages yellowish. Thoracic tergites testaceous, with some pale brown scattered maculae; thoracic sternites testaceous. Body: for morphometric measurements and ratios see Table 1 View TABLE 1 . Head capsule ( Figs. 7–9, 12 View FIGURES 7 – 12 ): nasale with 7 teeth on anterior margin, without anteroventral denticles ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 7 – 12 ). Mandibles ( Figs. 16–17 View FIGURES 13 – 17 ): distal tooth of retinaculum bifid apically, outer lateral surface slightly serrate. Labium ( Figs. 10–11 View FIGURES 7 – 12 ): anterolateral angles of mentum strongly projected forward. Dorsolateral surface of mentum with strong spinulae. Dorsal surface of second labial palpomere with some spinulae. Chaetotaxy. Antenna ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 13 – 17 ): seta AN8 present.
Description, instar II. As instar I except for the following features. Color: head capsule testaceous with brown areas around frontal sulci, maculae of parietale more notorious. Thoracic tergites with dark brown maculae. Body: for morphometric measurements and ratios see Table 1 View TABLE 1 . Head capsule: nasale with two anteroventral denticles. Chaetotaxy. Head capsule: with 68–84 secondary setae distributed in the area delimited by the intersection of PA6, PA7 and FR1, between PA7 and PA10, between PA21 and PA26, and in the stemmatal area. Outer gFR2 setae blunt or pointed. Mandibles: with 2 short secondary setae at the base and 18–21 secondary minute sensilla distributed mainly along dorsolateral surface. Antenna: A1 with numerous secondary setae arranged as follows: 12–14 short setae on ventral surface, 19–32 stout spiniform setae on inner lateral surface, 3–4 setae on outer lateral surface, and two distal rings of long setae, apical one with 4–5 setae, the other with 10–11 setae. Maxilla: outer lateral surface of stipes with 7–8 hair-like secondary setae at the base, and 32–36 secondary setae unevenly distributed. Outer lateral surface of MP1 with 1 distal secondary seta. Labium: Mt with 1 stout secondary seta on each anterolateral angle, 4–6 secondary setae on laterobasal surfaces, 18–21 stout secondary setae on dorsal surface,and 8–11 thin secondary setae on ventral surface.
Description, instar III. As instar II except for the following features. Body: for morphometric measurements and ratios see Table 1 View TABLE 1 . Chaetotaxy. Head capsule: 78–99 secondary setae with similar distribution as in instar II. Mandibles: with 2 short secondary setae at the base and 48–57 secondary minute sensilla distributed mainly along dorsolateral surface. Antenna: A1 with numerous secondary setae arranged as follows: 15–20 short setae on ventral surface, 33–36 stout spiniform setae on inner lateral surface, 6–7 setae on outer lateral surface, and two distal rings of long setae, apical one with 5 setae, the other with 9–12 setae. Maxilla: outer lateral surface of stipes with 5–6 hair-like secondary setae at the base, and 35–37 secondary setae unevenly distributed. Labium: Mt with 1 stout secondary seta on each anterolateral angle, 5–8 secondary setae on laterobasal surfaces, 21–23 stout secondary setae on dorsal surface, and 15–20 thin secondary setae on ventral surface.
Description, pupa ( Figs. 18–19 View FIGURES 18 – 21 ). Color: Whitish (young pupae) to pale brown (mature pupae). Body: TL (excluding pronotal styli and cerci) = 11.3–12.6 mm; MW = 4.9–5.8 mm. Head: posterior surface with two oval sclerites close to midline, without supraorbital styli. Antennae partially hidden by pronotum. Maxillary palpi extending beyond base of mesocoxae. Thorax: pronotum with 22 styli distributed as follows: 2 on pronotal disc and 20 on lateral surfaces (10 large styli anteriorly, 2 on each postero-lateral angle, and 6 styli posteriorly). Meso- and metanotum with 2 styli close to midline. Metasternal spine long. Metathoracic legs partially covered by wingpads. Tibiae with two apical spines. Abdomen: segment I with 4 styli; segments II–VI with 8 styli (6 in a transverse row on each tergum and 1 about two thirds shorter on each pleural area); segment VII with 6 styli (4 tergal and 1 on each pleural area); segment VIII with a pair of minute styli posteriorly; all styli with irregular surface and bearing a terminal seta; segment IX with 2 long bifid cerci, each bearing 2 spines at mid-length; segments II–VI without tubercles or horn-like projections.
TABLE 1. Measurements (in mm) and ratios for the three larval instars of Tropisternus latus.
| Measure | Instar I | Instar II | Instar III |
|---|---|---|---|
| TL | 2.58–4.30 | 9.00–11.50 | 15.00–16.50 |
| MW | 0.83–1.00 | 2.00–2.50 | 3.50–4.00 |
| HL | 0.72–0.73 | 1.20–1.25 | 1.70–1.73 |
| HW | 0.96–0.99 | 1.55–1.73 | 2.23–2.25 |
| HL/HW | 0.74–0.75 | 0.72–0.77 | 0.76–0.77 |
| AL | 0.74–0.76 | 1.25–1.28 | 1.62–1.71 |
| A1L | 0.42–0.44 | 0.80–0.82 | 1.10–1.20 |
| A2L | 0.18 | 0.24 | 0.28 |
| A3L | 0.15 | 0.21–0.22 | 0.24 |
| A1L/(A2L+A3L) | 1.27–1.33 | 1.80 | 2.10–2.33 |
| HL/AL | 0.96–0.97 | 0.96–0.98 | 0.99–1.06 |
| HW/AL | 1.29–1.30 | 1.24–1.35 | 1.30–1.38 |
| SL | 0.54–0.55 | 0.97–0.99 | 1.38–1.40 |
| MPL | 0.46–0.47 | 0.67 | 0.83–0.85 |
| SL/MPL | 1.18 | 1.44–1.47 | 1.61–1.68 |
| MP1L | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.29–0.31 |
| MP2L | 0.05 | 0.08–0.09 | 0.12–0.13 |
| MP2W | 0.06 | 0.08–0.09 | 0.08–0.09 |
| MP3L | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.26 |
| MP4L | 0.11–0.12 | 0.15 | 0.16 |
| MP2L/MP2W | 0.85–0.92 | 0.94–1.13 | 1.39–1.53 |
| ML | 1.00–1.02 | 1.64–1.66 | 2.23 |
| LPL | 0.18–0.19 | 0.26–0.27 | 0.25–0.30 |
| LP1L | 0.04 | 0.05–0.06 | 0.05–0.07 |
| LP2L | 0.14–0.15 | 0.21 | 0.20–0.23 |
| LP2L/LP1L | 3.33–3.50 | 3.50–3.82 | 3.29–4.00 |
| LigL/LPL | 0.41–0.44 | 0.41–0.42 | 0.45–0.52 |
| MtW | 0.25 | 0.47–0.48 | 0.68–0.69 |
| PrmtW/PrmtL | 0.93–1.00 | 0.86–0.90 | 0.74–0.78 |
| PrmtW/MtW | 0.52 | 0.40 | 0.33–0.34 |
| LEG 1 L | 1.84–1.89 | 2.71–2.72 | 3.76–3.81 |
| LEG 2 L | 1.94–1.98 | 2.87–2.89 | 4.00–4.08 |
| LEG 3 L | 1.99–2.03 | 3.10–3.13 | 4.39–4.41 |
| LEG 3/LEG 1 | 1.05–1.10 | 1.14–1.15 | 1.16–1.17 |
| LEG 3/LEG 2 | 1.01–1.05 | 1.08 | 1.08–1.10 |
| LEG 1 (TITA/FE) | 0.74–0.80 | 0.74–0.77 | 0.72–0.73 |
| LEG 2 (TITA/FE) | 0.78–0.80 | 0.73 | 0.67–0.71 |
| LEG 3 (TITA/FE) | 0.81–0.89 | 0.78–0.79 | 0.73–0.76 |
| LEG 1 (CL/TITA) | 0.65 | 0.50–0.51 | 0.43–0.46 |
| LEG 2 (CL/TITA) | 0.64 | 0.50 | 0.44–0.47 |
| LEG 3 (CL/TITA) | 0.56–0.64 | 0.45–0.48 | 0.38–0.41 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
|
SubGenus |
Pristoternus |