Torymus aciculatus Matsuo, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4758.3.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:18E2818F-2248-45A6-AB96-14A41302A727 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3812233 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/E92A87D1-FFDD-FFFC-C98F-F8B36AC6FC4C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Torymus aciculatus Matsuo |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Torymus aciculatus Matsuo n. sp.
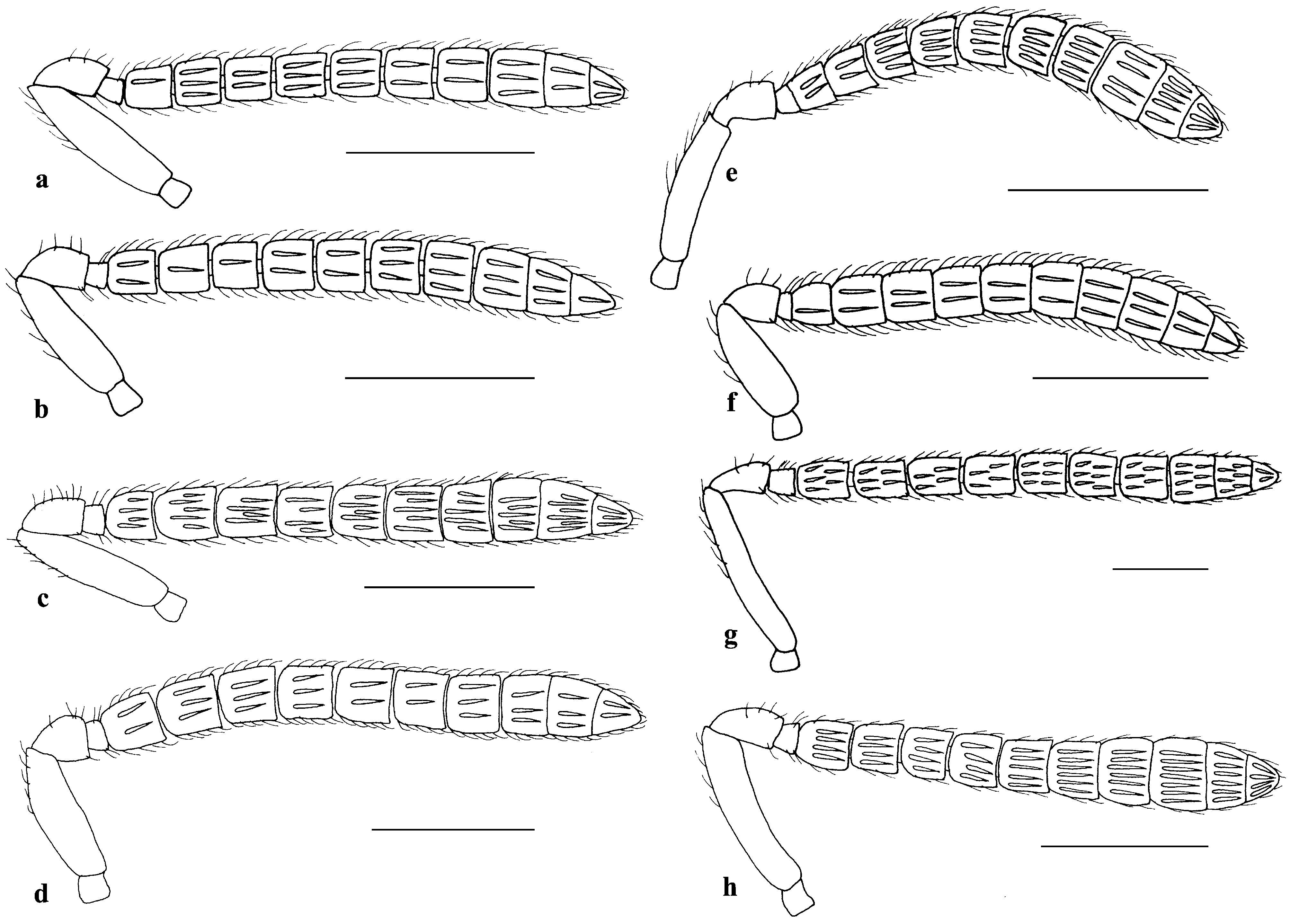
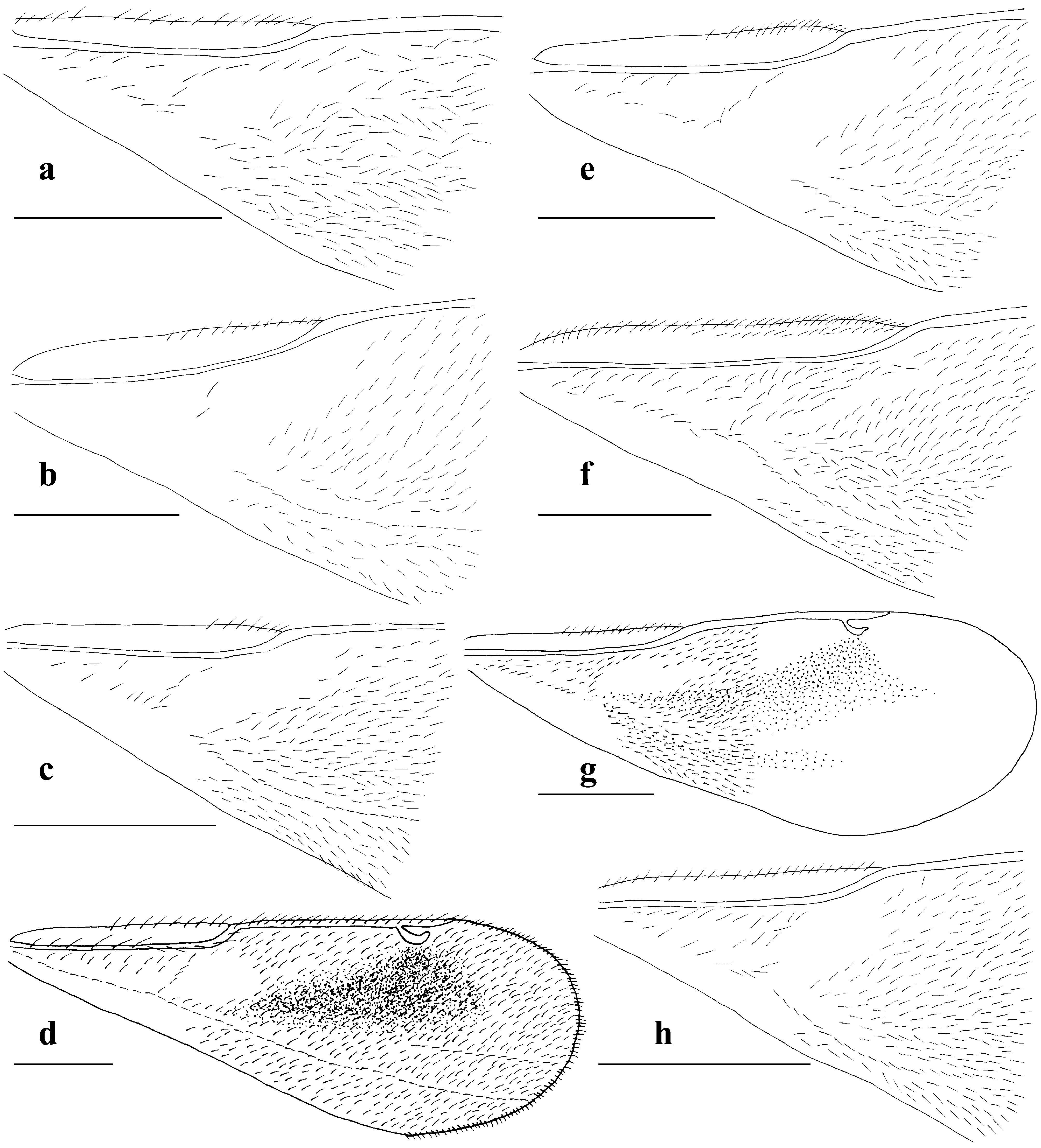
Figs 1b View FIGURE 1 , 5 View FIGURE 5 c–d, 9a–d, 24b
Etymology. The specific name, aciculatus , is derived from the name of associated plant of this species.
Type material. Holotype: ♀ ( BLKU), emerged on 6 May 2009 from a fruit gall of Neolitsea aciculata collected by K. Matsui on 19 April 2009 from Zoushi , Nara, Nara, Japan . Paratypes: 6 ♀ and 1 ♂, same data as the
holotype ( BLKU) ; 4 ♀ and 2 ♂, emerged on 5 May 2009 from fruit galls of Neolitsea aciculata collected by K. Matsui on 19 April 2009 from Zoushi , Nara, Nara, Japan ( BLKU) ; 7 ♂, emerged on 2 May 2009 from fruit galls of Neolitsea aciculata collected by K. Matsui on 19 April 2009 from Zoushi , Nara, Nara, Japan ( BLKU) .
Description. Female. Body length excluding ovipositor sheath 2.5–2.8 mm. Head bluish green with bluish tint. Scape yellowish brown but darker apically; pedicel and flagellum dark brown. Mesosoma bluish green with bluish tint. Fore wing hyaline. All coxae and femora concolorous with mesosoma; all tibiae yellowish brown. Metasoma bluish green with bluish tint ( Fig. 1b View FIGURE 1 ).
Head 2.0× as wide as long in dorsal view; temple 0.2× as long as dorsal length of eye; POL 2.4–2.5× OOL; OOL 1.0–1.3× OD. Head 1.2× as wide as high in frontal view ( Fig. 9a View FIGURE 9 ); eyes separated by 0.9–1.0× their height; malar space 0.3× height of eye; mouth 2.1× malar space; clypeus with apical margin produced, truncate medially.Antenna not clearly clavate ( Fig. 5c View FIGURE 5 ); scape 0.5–0.6× as long as height of eye, not reaching anterior ocellus; combined length of pedicel and flagellum 1.1–1.2× width of head; pedicel 1.4–1.5× as long as wide; anellus 1.1–1.2× as wide as long; F1 quadrate, as long as pedicel; F2–F3 0.9–1.0× as long as wide; F4–F5 0.8–0.9× as long as wide; F6 0.7–0.8× as long as wide; F7 0.6–0.7× as long as wide; each funicular segment bearing longitudinal sensilla arranged in two rows; C3 with a small tuft of micropilosity beneath.
Mesosoma 1.7–1.8× as long as wide; mesoscutum ( Fig. 9b View FIGURE 9 ) with small piliferous punctures; sculpture on mesoscutum transversely reticulate; notaulus shallow; scutellum ( Fig. 9c View FIGURE 9 ) 1.4–1.5× as long as wide; frenal line absent; frenal area indicated by a difference in sculpture from rest of scutellum, smoother and glabrous toward apex; dorsellum with a median carina; propodeum ( Fig. 9d View FIGURE 9 ) with longitudinal striae, smoother medially; lower mesepimeron 1.4× as long as wide. Fore wing 2.2–2.3× as long as wide ( Fig. 24b View FIGURE 24 ); costal cell 7.2–9.0× as long as wide, on upper surface with a setal row in distal half, on lower surface with a setal row that is sparse medially and with scattered setae; basal cell bare; cubital setal line absent; basal setal line with a few setae; speculum widely open below; relative lengths of marginal vein: postmarginal vein: stigmal vein=8.5: 2.0: 1.0. Hind coxa stout, 1.8× as long as wide, with dorsal carina basally; dorsal surface of hind coxa bare in basal half; hind femur 3.8–4.3× as long as wide; hind tibia with longer spur 1.1–1.2× as long as width of hind tibia, 0.4–0.5× length of basitarsus; shorter spur 0.6–0.7× length of longer spur.
Metasoma slightly shorter than mesosoma; posterior margin of metasomal tergum five incised; tip of hypopygium situated at 0.5 length of metasoma; ovipositor sheath as long as metasoma plus 1/3 mesosoma, 2.3–2.4× as long as hind tibia.
Male. Differs from female as follows. Body length 2.5 mm. Antenna stouter than that of female ( Fig. 5d View FIGURE 5 ); scape bluish green; anellus transverse, 2.5× as wide as long; longitudinal sensilla on each funicular segment arranged in one row. Lower mesepimeron 1.1× as high as wide; relative lengths of marginal vein: postmarginal vein: stigmal vein=10.0: 2.2: 1.0. Hind tibia dark green. Metasoma with coppery tint.
Distribution. Japan (Honshu).
Host information. Torymus aciculatus is a parasitoid of an unidentified gall midge ( Diptera : Cecidomyiidae ) that induces fruit galls on Neolitsea aciculata (Blume) Koidzumi (Lauraceae) .
Remarks. Females of T. aciculatus are similar to T. koreanus Kamijo by having the following shared features: scape not reaching anterior ocellus; frenal area indicated by a difference in sculpture from rest of scutellum, with a few setae anterolaterally; dorsal surface of hind coxa bare in basal half; ovipositor sheath 2.3–2.4× as long as hind tibia. However, females of T. aciculatus can be distinguished from T. koreanus by the following features: antenna not clearly clavate (clavate in T. koreanus ); each funicular segment bearing longitudinal sensilla arranged in two rows (one row in T. koreanus ); frenal line absent (present medially in T. koreanus ); propodeum with longitudinal striae, smoother medially (with submedian carinae in T. koreanus ); hind coxa with dorsal carina extending for half length (with complete dorsal carina in T. koreanus ); costal cell on upper surface with a setal row in distal half (becomes double row in distal half in T. koreanus ); basal cell broadly open below (closed below in T. koreanus ); speculum open below (closed below in T. koreanus ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |