Symplecis kibiraensis Varga, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5311.2.8 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:47894874-9E7F-4F66-8B55-C239B4FF2F00 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8094466 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2C4B3962-B237-FFC7-63DF-4AB7FC8DFDA2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Symplecis kibiraensis Varga |
| status |
sp. nov. |
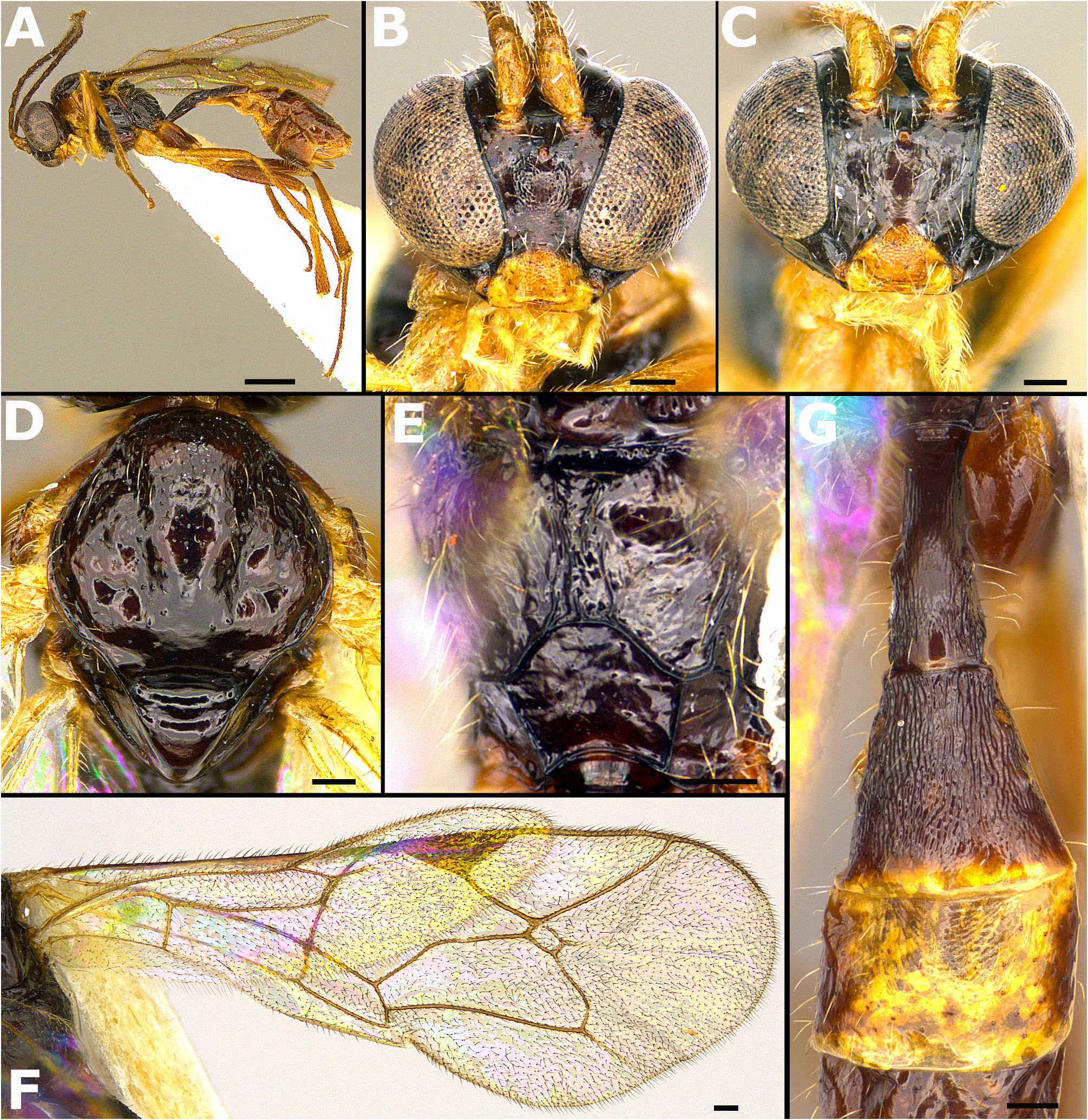
Symplecis kibiraensis Varga , sp. n. ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 )
Material examined. Holotype: ♀, BURUNDI: Kibira National Park , 2.93315° S, 29.50583° E, 2177 m, mixed forest, Malaise trap, bamboo near small meadow, 29.i–12.ii.2010, leg. R. Copeland (deposited in: MRAC) GoogleMaps . Paratypes: 1 ♁, 3 ♀♀, the same locality and date as holotype (deposited in: MRAC, SIZK) GoogleMaps .
Diagnosis. Symplecis kibiraensis sp. n. is characterized by the combination of the following characters: clypeus yellow, almost touching eye (in female) ( Fig. 4B View FIGURE 4 ) or distinctly distant (in male) ( Fig. 4C View FIGURE 4 ); mesosoma largely black except orange pronotum; mesoscutum pubescent ( Fig. 4D View FIGURE 4 ); propodeum with area superomedia not delimited by carinae or carinae indistinct, costulae absent ( Fig. 4E View FIGURE 4 ); fore wing with vein 3rs-m present; hind wing with nervellus not intercepted ( Fig. 4F View FIGURE 4 ); hind coxa from outer side granulate; first metasomal tergite 2.7–3.1× as long as apical width; second tergite longitudinally striae ( Fig. 4G View FIGURE 4 ); ovipositor short, 1.4–1.9× as long as fifth tarsomere of hind tarsus.
Symplecis kibiraensis sp. n. is similar with S matilei in having fore wing with vein 3rs-m present, but differs in having dark mesosoma (largely orange in S matilei ), yellow clypeus (dark brown in S matilei ) and almost indistinct area superomedia (delimited laterally by distinct longitudinal carinae in S matilei ).
Description. Female. Holotype ( Figs 4A–B, D–F View FIGURE 4 ). Body length approximately 3.8 mm. Fore wing 3 mm.
Head ( Fig. 4B View FIGURE 4 ) smooth and sparsely pubescent. Antenna with 19 flagellomeres, first flagellomere 5.0× as long as wide. Face about 0.9× as long as wide, granulate; eyes strongly convergent to clypeus, glabrous. Malar space short, 0.3× the basal width of mandible; subocular sulcus distinct. Clypeus 0.7× as long as wide, almost quadrate, granulate. Mandible bidentate, not twisted. Temples short and strongly narrowed behind eyes (dorsal view). Frons and vertex smooth; length of the ocellar-ocular distance 1.2× maximum diameter of lateral ocellus; occipital carina complete.
Mesosoma ( Figs 4D–E View FIGURE 4 ) smooth and densely pubescent. Propleuron weakly granulate. Pronotum smooth; epomia present reaching mesoscutum. Mesoscutum sparsely, but uniformly pubescent; notauli present, but weak. Scutellum smooth, with carinae present only on basal 0.1; scuto-scutellar groove wide. Mesopleuron smooth; epicnemial carina present; sternaulus deep and long. Metapleuron granulate; pleural and submetapleural carinae present. Propodeum smooth, with only apical transverse carina strong; area superomedia absent, lateromedian longitudinal carina weakly present, but indistinct; apophyses absent.
Legs relatively slender; hind femur 5.5× as long as wide, hind coxa smooth from inner side and granulate from outer side; third tarsomere of hind tarsus 1.2× as long as fifth tarsomere; tarsal claws simple.
Wings ( Fig. 4F View FIGURE 4 ). Fore wing with vein 2 rs-m short, about 0.45× the distance between 2 rs-m and 2 m-cu; vein 3rsm present; vein 1cu-a opposite to M & Rs; hind wing with nervellus not intercepted, vertical; distal abscissa of Cu absent.
Metasoma ( Fig. 4G View FIGURE 4 ) strongly sculptured and sparsely pubescent. First tergite 3.1× as long as apical width, longitudinally striae; carinae indistinct. Second tergite as long as apical width, longitudinally striae. Third tergite weakly granulate on basal 0.5; the remaining tergites smooth. Ovipositor short, about 0.2× as long as hind tibia and 1.4× as long as fifth tarsomere of hind tarsus.
Colour. Body generally black.Head black except clypeus, mandible (except apices), scape and pedicel yellowish. Mesosoma black except pronotum and subtegular ridge orange, and tegula yellow. Legs generally yellowish-brown; fore and mid legs yellow, with tibiae and tarsi weakly darker; hind legs brownish except coxae basally and trochanters yellow. Metasoma with tergites 1–2 black; third tergite largely yellow centrally; the remaining tergites brown. Ovipositor sheaths yellow basally, brown apically. Pterostigma and veins brown.
Variability. Body length 3.0– 3.8 mm. Antenna with 18–19 flagellomeres. Pronotum varying from orange to almost completely dark. Third metasomal tergite varying from almost entirely yellow to brown. Hind legs in one specimen almost completely yellowish (except coxa partly brown).
Male. Generally resembles female, but differs by the smooth face, not divergent eyes and longer malar space ( Fig. 4C View FIGURE 4 ).
Etymology. The new species is named after the type locality, Kibira National Park.
Distribution. Currently known only from Burundi.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |