Symbiopsocus vietnamicus, Ning & Li & Liu, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4759.3.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:517C2CC6-42E4-4361-8C0F-F451FBA9C4DE |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3810315 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/7B0EDA71-811F-FFCE-FF32-FB0DFD6DC306 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Symbiopsocus vietnamicus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Symbiopsocus vietnamicus View in CoL sp. nov.
( Figs 1–4 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 )
Diagnosis. Male paraproct medially with a short scabrous lobe near trichobothrial field. Male hypandrium: dorsal lobe with lateral arm strongly protruding posteriad and with postero-medial region distinctly protruding, forming a pair of boot-shaped processes; ventral lobe lacking denticles, largely divided in two symmetrical parts, distally flattened and with a digitiform, acutely pointed process. Female external valve without posterior lobe.
Description. Male. Measurements. Body length 2.49 mm, length from post clypeus to wing tip 4.01 mm. IO: 0.26 mm, d: 0.36 mm, IO/d=0.72, f1: 0.76 mm, f2: 0.66 mm, f3: 0.51 mm, FWL: 3.21 mm, FWW: 1.19 mm, HWL: 2.40 mm, HWW: 0.80 mm, t1: 0.40 mm, t2: 0.12 mm.
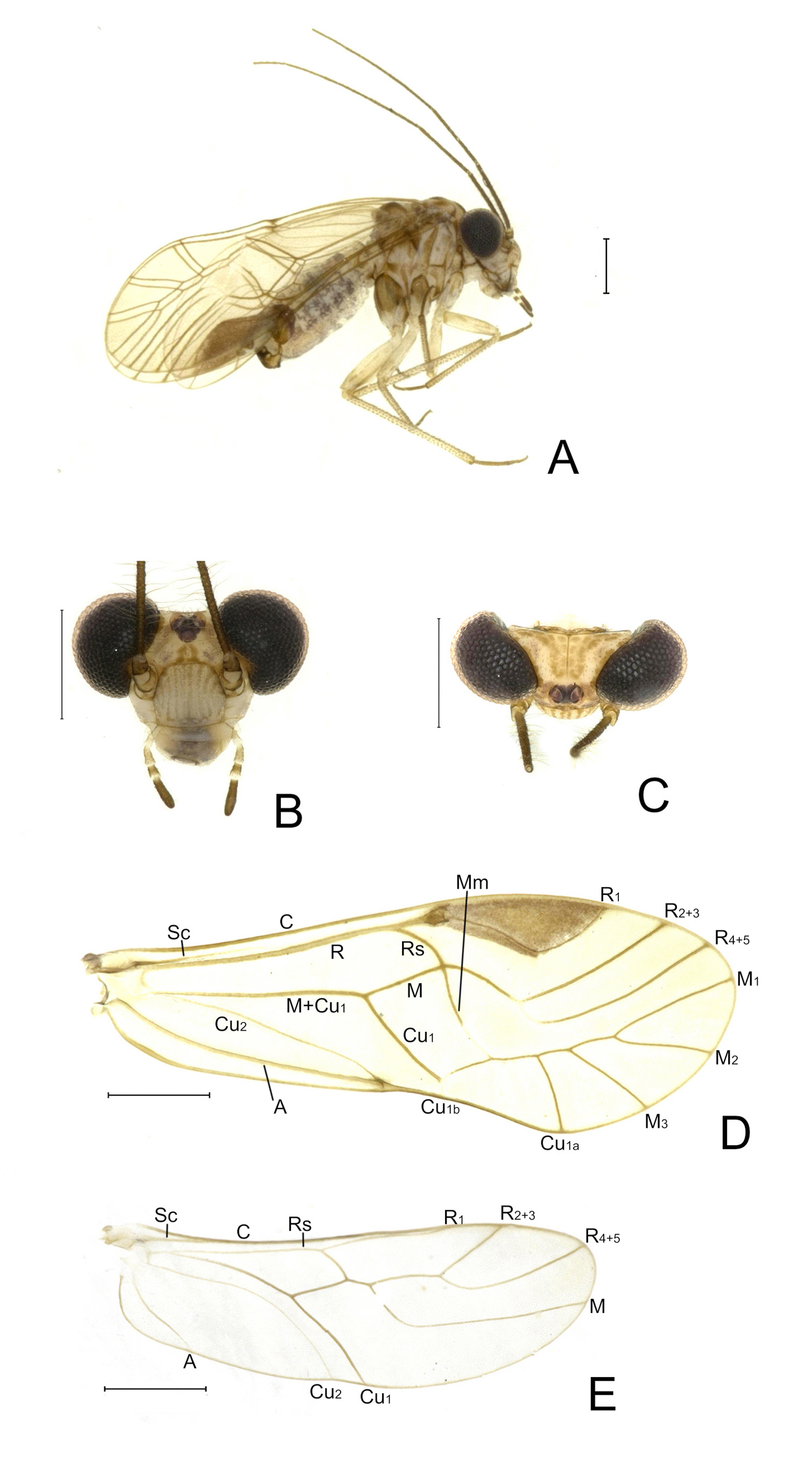
Coloration (in 95% alcohol). Head ( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 B–C) yellow; vertex posteriorly with brownish stripes, which medially extend along ecdysial suture, and laterally extend along inner ocular margin; a dark brown marking present at ocellar region; frons with a U-shaped brownish marking from median ocellus to epistomal suture, and laterally with a pair of small brown markings; postclypeus with eleven longitudinal brownish stripes, anteclypeus yellow laterally and brown medially. Antennae dark brown. Compound eyes black. Mouthparts yellow, but labrum medially brown and terminal segment of maxillary palps dark brown. Thorax brown, but laterally pale yellow along some sutures between thoracic sclerites. Legs pale yellow, but meso- and metacoxae brown, all tibiae pale yellow, with brown setae, entire tarsi pale brown. Forewing ( Fig. 1D View FIGURE 1 ) hyaline, indistinctly smoky brown, with a small brown marking at distal end of vein Cu 2; pterostigma brown; veins brown, but bases of R 2+3 and R 4+5 as well as distal ends of Mm and Cu 1b white. Hind wing ( Fig. 1E View FIGURE 1 ) hyaline, veins brown with Cu 2 white. Abdomen pale yellow, pregenital segments dorsally with a black marking, genital segments brown.
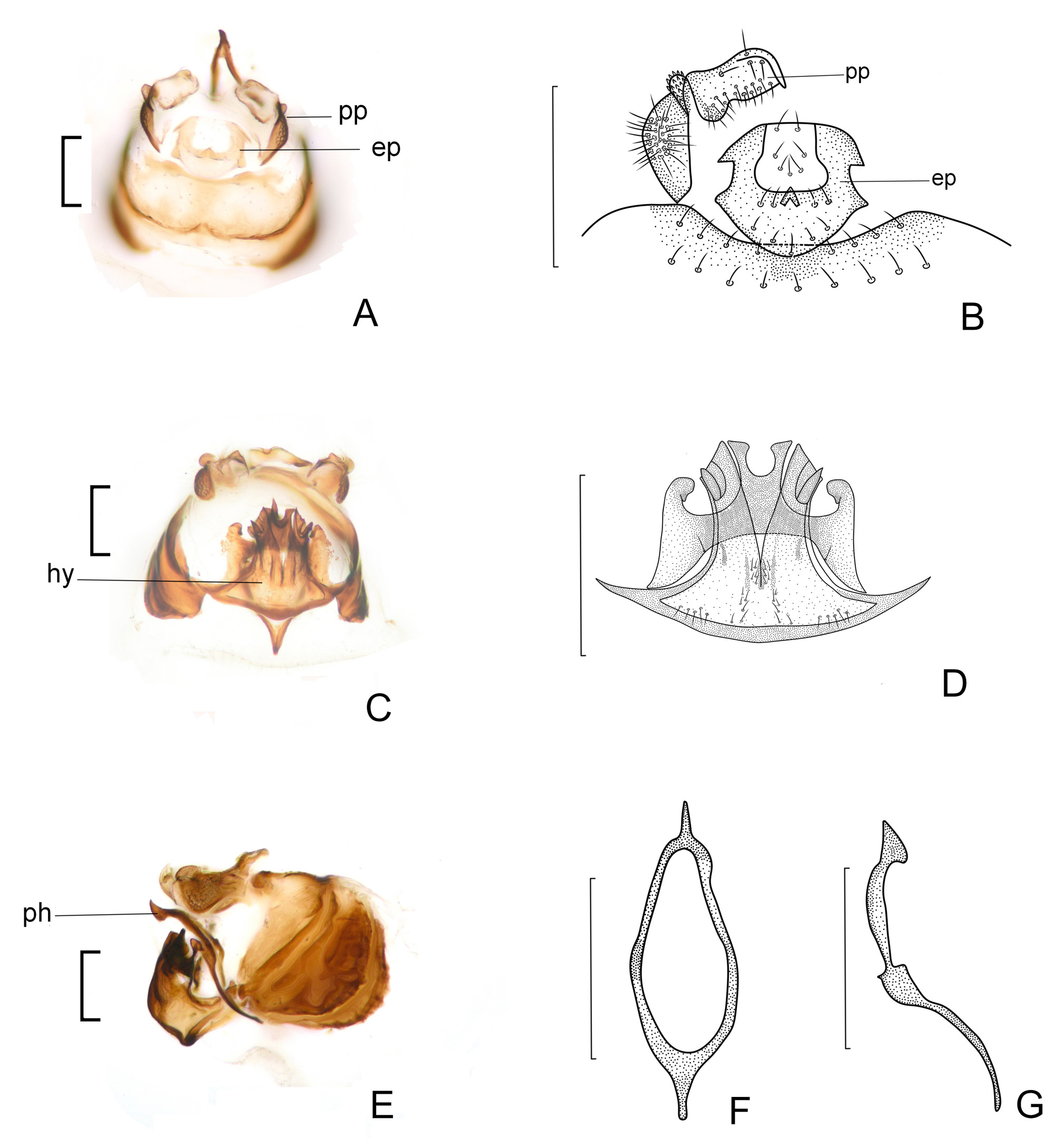
Morphology. Head ( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 B–C) inverted trapezoidal; compound eyes large, ovoid. Forewing ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1 ) membranous, glabrous; Sc ending free in the membrane, Rs and M fused for a short distance or meeting at a point, radial fork with branches diverging at an angle less than 90°; discoidal cell nearly rectangular; M+Cu 1a and first part of Cu 1a together arranged as a nearly continuous, straight line; Cu 1b short; areola postica subtrapeziform. Genitalia ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ): Epiproct ( Figs 3 View FIGURE 3 A–B) nearly circular, sclerotized anteriorly and laterally, antero-laterally and postero-laterally respectively with a pair of subtriangular projections, and antero-medially with a short cone-shaped projection. Paraproct ( Figs 3 View FIGURE 3 A–B) medially with a scabrous lobe distad trichobothrial field. Phallosome ( Figs 3 View FIGURE 3 E–G) slender and rhomboid-shaped, anteriorly protruding into a slender digitiform process, posteriorly protruding into a laterally flattened, subtriangular process. Hypandrium ( Figs 3 View FIGURE 3 C–D) strongly sclerotized, composed of two tiers of lobes; dorsal lobe gradually widened into a pair of lateral arms, distinctly protruding anteriad and posteriad, with sclerotization gradually weakened, and with a projection at tip of anterior protrusions; postero-medial region of dorsal lobe distinctly protruding, forming a pair of boot-shaped processes; ventral lobe lacking denticles, largely divided in two symmetrical parts, distally flattened and with a digitiform, acutely pointed process.
Female. Measurements. Body length 2.74 mm, length from postclypeus to wing tip 4.06 mm. IO: 0.46 mm, d: 0.25 mm, IO/d=1.84, f1: 0.72 mm, f2: 0.65 mm, f3: 0.49 mm, FWL: 3.36 mm, FWW: 1.18 mm, HWL: 2.48 mm, HWW: 0.82 mm, t1: 0.31 mm, t2: 0.09 mm.
Coloration (in 95% alcohol). Similar to male.
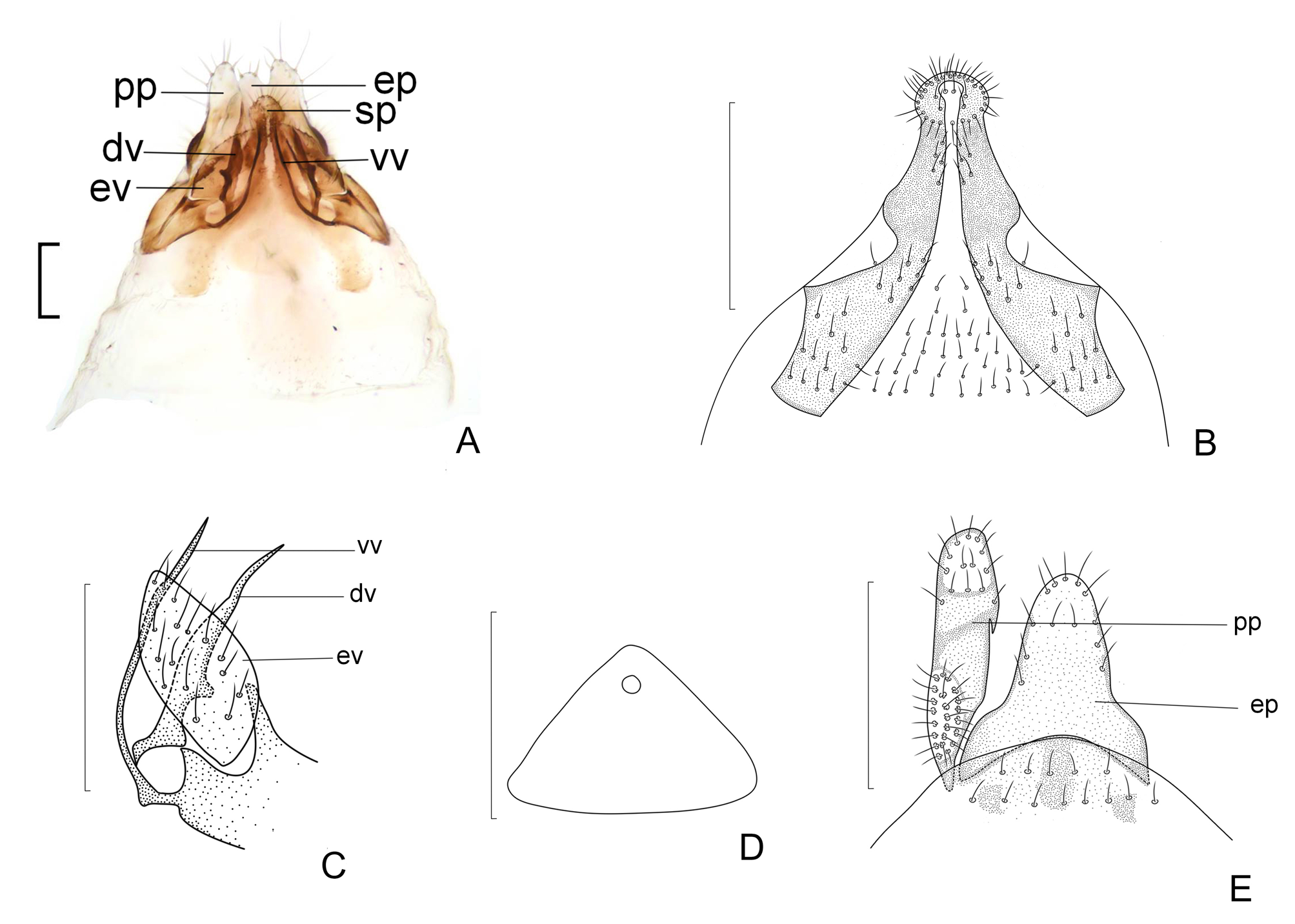
Morphology. Cephalic characters largely similar to the male except for small compound eyes ( Figs 2 View FIGURE 2 B–C). Wings similar to the male. Genitalia ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ): Subgenital plate ( Fig. 4B View FIGURE 4 ), egg guide long, strongly sclerotized marginally and terminally round with long setae; ventral valve ( Fig. 4C View FIGURE 4 ) strongly sclerotized, slender, elongate, acutely tapering at tip; dorsal valve broad with slender distal process, dorsal part strongly sclerotized; external valve near rugby football shape with long setae, lacking posterior lobe.
Type material. Holotype male, VIETNAM: Vinh Phuc Province, Tam Dao [21°23'N, 105°38'E], 21.VI.2011, Wang Guoquan, light trap ( CAU) GoogleMaps . Paratypes: 13 males, 28 females, same collecting site, 20/21/ 23. VI .2011, Wang Guoquan, light trap ( CAU) .
Distribution. Vietnam (Vinh Phuc).
Etymology. The specific epithet “vietnamicus” refers to the country of origin of this species.
Remarks. This new species resembles S. leptocladus Li, 1997 , S. subrhombeus Li, 2002 and S. quadripartitus Li, 2002 in having similar configuration of the male hypandrium (e.g. dorsal lobe with lateral arms protruding posteriad and with postero-medial region separated into a pair of projections, which are curved laterally at tip), it also appears to be similar to S. quadripartitus Li, 2002 in having similar phallosome (i.e. anteriorly and posteriorly both distinctly protruding). The new species can be distinguished from the above species by the ventral lobe of the male hypandrium, distally flattened with a digitiform process. There are six species of Symbiopsocus known with only females, i.e. S. unitus ( Li, 2002) , S. undulates ( Li, 2002) , S. nanyuensis (Li, 1992) , S. magnificus ( Li, 2002) , S. latus ( Li, 2002) and S. changbaiensis ( Li, 2002) . The new species can be distinguished from all these species by the female external valve without posterior lobe.
| CAU |
China Agricultural University |
| VI |
Mykotektet, National Veterinary Institute |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |