Pseudorinelepis genibarbis (Valenciennes, 1840)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4658.1.12 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:4CDBDEEA-CE59-4C04-8C4D-0FEA5DC3EB8A |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4323716 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6A28C01F-FFD0-FFFA-FF7C-E3383E33AC44 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Pseudorinelepis genibarbis |
| status |
|
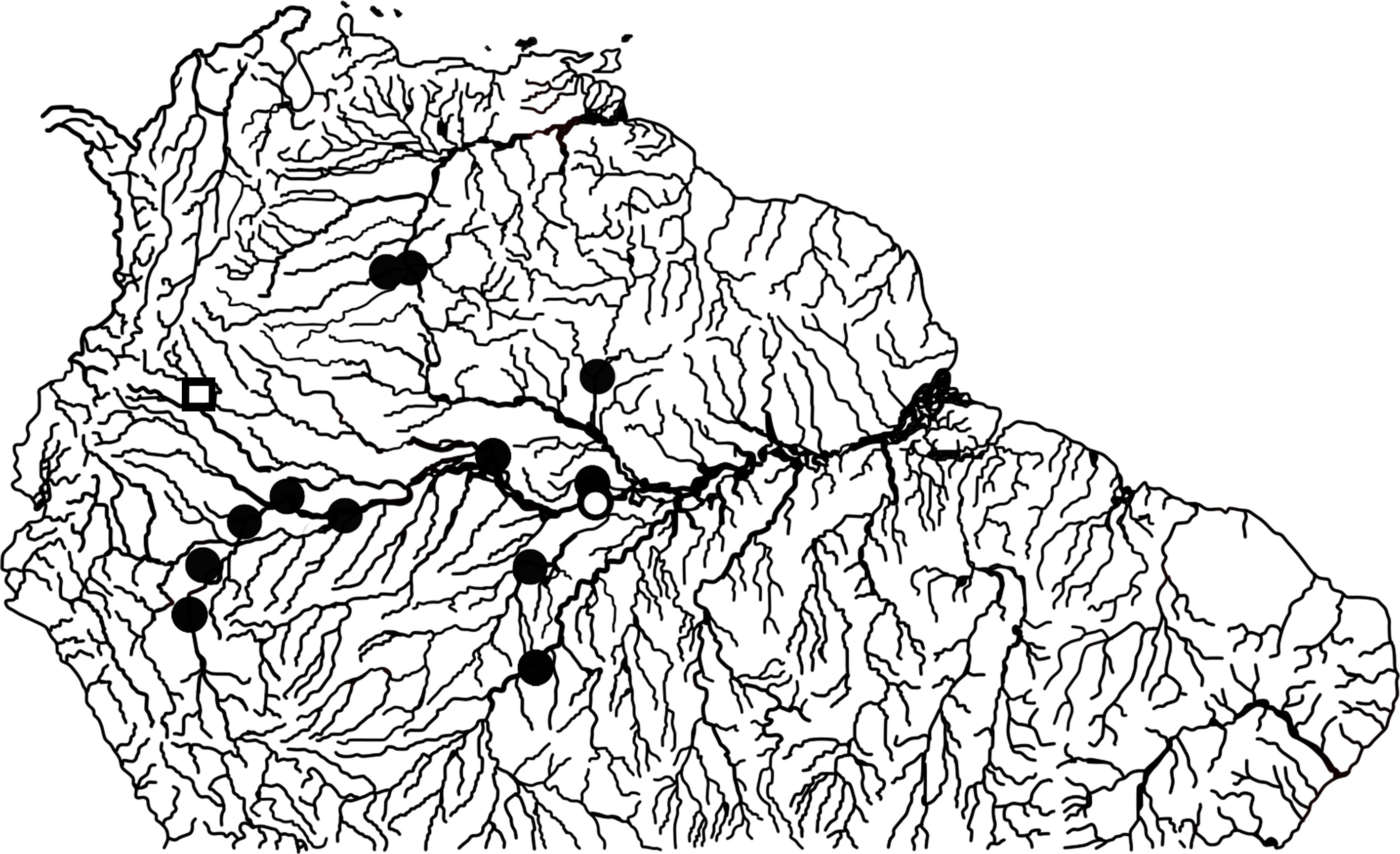
The specimen identified as P. genibarbis is deposited in the ichthyological collection of the Museo de Historia Natural - Universidad de la Amazonía, Colombia ( UAM-P) with the catalog number UAM-P 891. The specimen was captured in the lagoon complex of Peregrinos, at the coordinates 00º 04.556’N 74º 34.601’W at a height of 158 masl, on October 27, 2018.We obtained previous locality records online for others specimens of P. genibarbis ( GBIF and Fishnet2) and combine those records with the map in Armbruster and Hardman 1999 ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ) GoogleMaps .
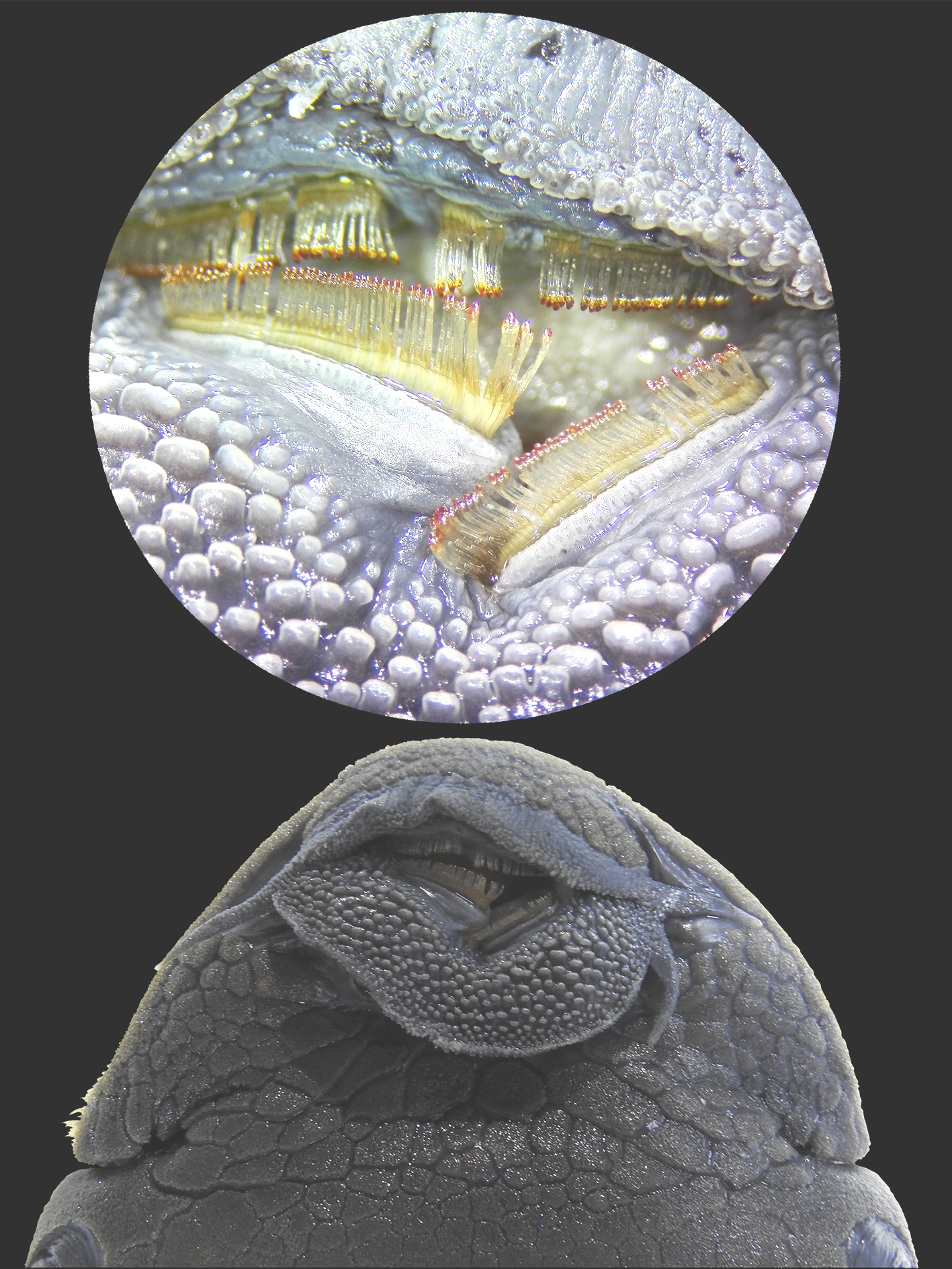
Description: The specimen has a standard length (LS) of 192.7 mm and a weight of 255 gr. It has the abdomen completely covered with plates, no adipose fin, and strongly keeled lateral plates ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ). The body is uniformly brown, including the fins, its coloration turned black after preservation. It has simple eyes lacking an iris operculum. The fin rays are: Dorsal: I, 7; pectoral: I, 6; pelvic: I, 5; anal: I, 5; caudal: I, 14, I. The lateral line comprises 25 lateral plates; plates at below the base of the dorsal fin: 6; post-dorsal plates: 12–16 (12), and post anal plates: 8–12 (8) ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ). Long, slender bifid teeth with small cusps from 49 to 53 per mandibular branch ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ).
Water physicochemical conditions at the capture locality were pH 6.7, conductivity 3 μS/cm and water temperature 24.8 ºC. In general, these waters that drain extremely nutrient poor, old, leached soils, have acid pH (6.6–6.7), high transparency, low conductivity, and a dark color caused by humic acids released by deep organic detritus ( Castellanos 2002, Galvis et al., 2007). These aquatic environments, despite coming from the Andean region, could be considered to be blackwater, poor in minerals, with a low concentration of inorganic nutrients (similar to distilled water) and low primary productivity ( Galvis et al., 2006).
The plant community is composed of submerged vegetation, such as trees, palms, aquatic grasses and shrubs (mainly families Fabaceae , Arecaceae , Malvaceae , Salicaceae and Lecythidaceae ). The ecosystem is partially protected, but there is timber harvesting and cutting of trees for the establishment of houses and crops.
In this note, we add a new collection site for this species, which corresponds to the first record of Pseudorinelepis genibarbis in the Caquetá river basin. Pseudorinelepis genibarbis is a gregarious species that is typically found in small slow streams, floodplain lakes, and large rivers, with the capacity to face anoxic environments in permanent lagoons (Lucero, 2016). The lagoon complex of Peregrinos is a habitat that meets the conditions for the species.
We thank the Centro de Investigación de la Biodiversidad Andino Amazónica of the Universidad de la Amazonia and its director Alexander Velásquez Valencia for linking us to the project “Community Agrotourism for the generation of economic benefits, through the promotion of responsible and sustainable participatory initiatives in the territory with zero deforestation in the Vereda Peregrinos of the municipality of Solano Caquetá ” funded by Visión Amazonia. To Francisco Provenzano and José Iván Mojica for their support and knowledge provided in the field of ichthyology. To the biologist Diego Ossa Calderón, to Lina María Correa who is a project intern and to the local researchers of the Peregrinos community Jorge Eliecer Rojas Quiroz, Aiber Rojas Quiroz, German Guzmán Riofrío and Elicerio Vieda for the collaboration in the field.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |