Premicrodispus (Premicrodispulus) kurganiensis, Khaustov & Khaustov, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.22073/pja.v12i1.77974 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:8980E98A-2D48-43AF-8403-B8385B24EC62 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8109400 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A7F6E478-5D29-45F9-8404-AFD18E7E49B3 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:A7F6E478-5D29-45F9-8404-AFD18E7E49B3 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Premicrodispus (Premicrodispulus) kurganiensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
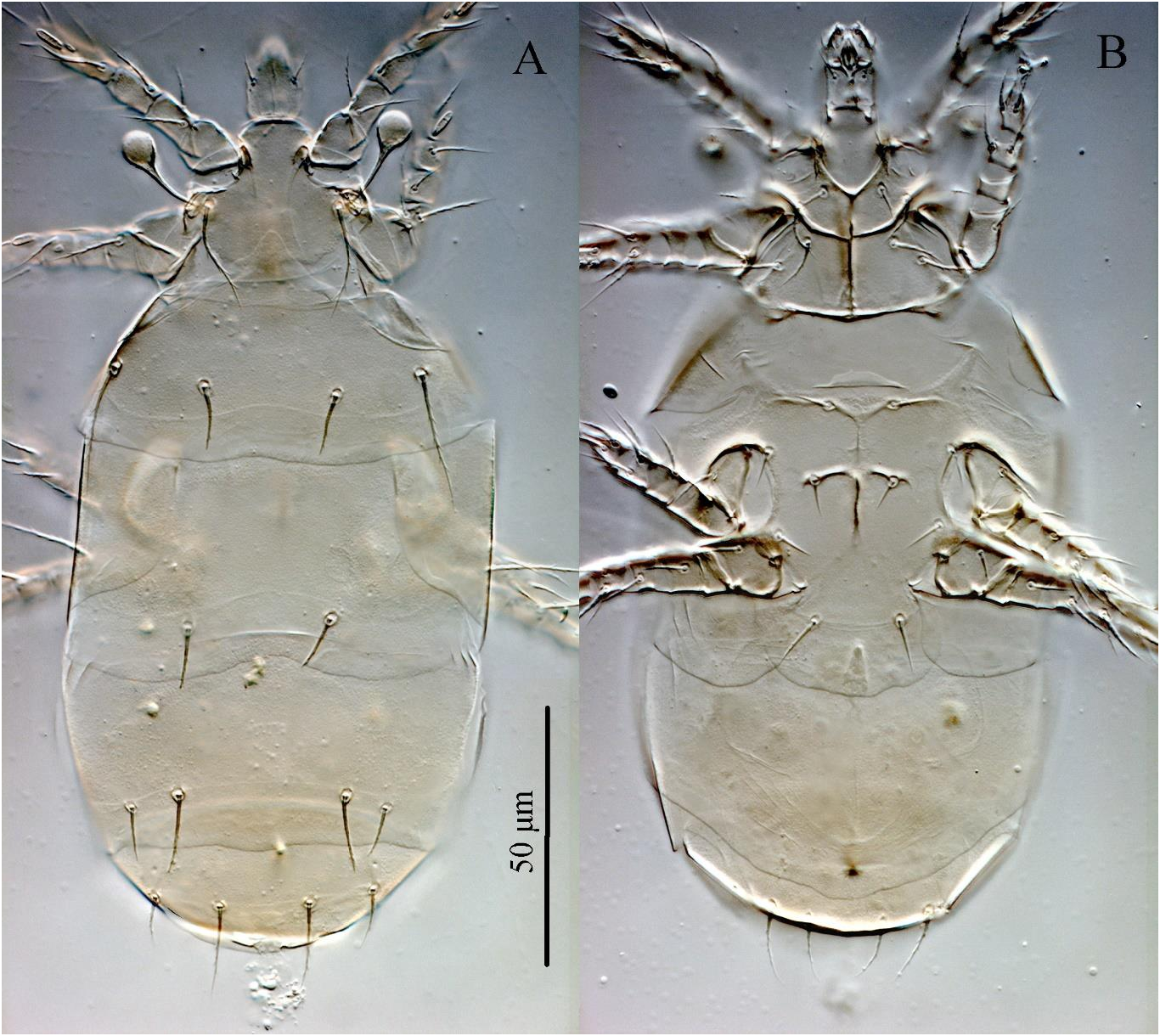
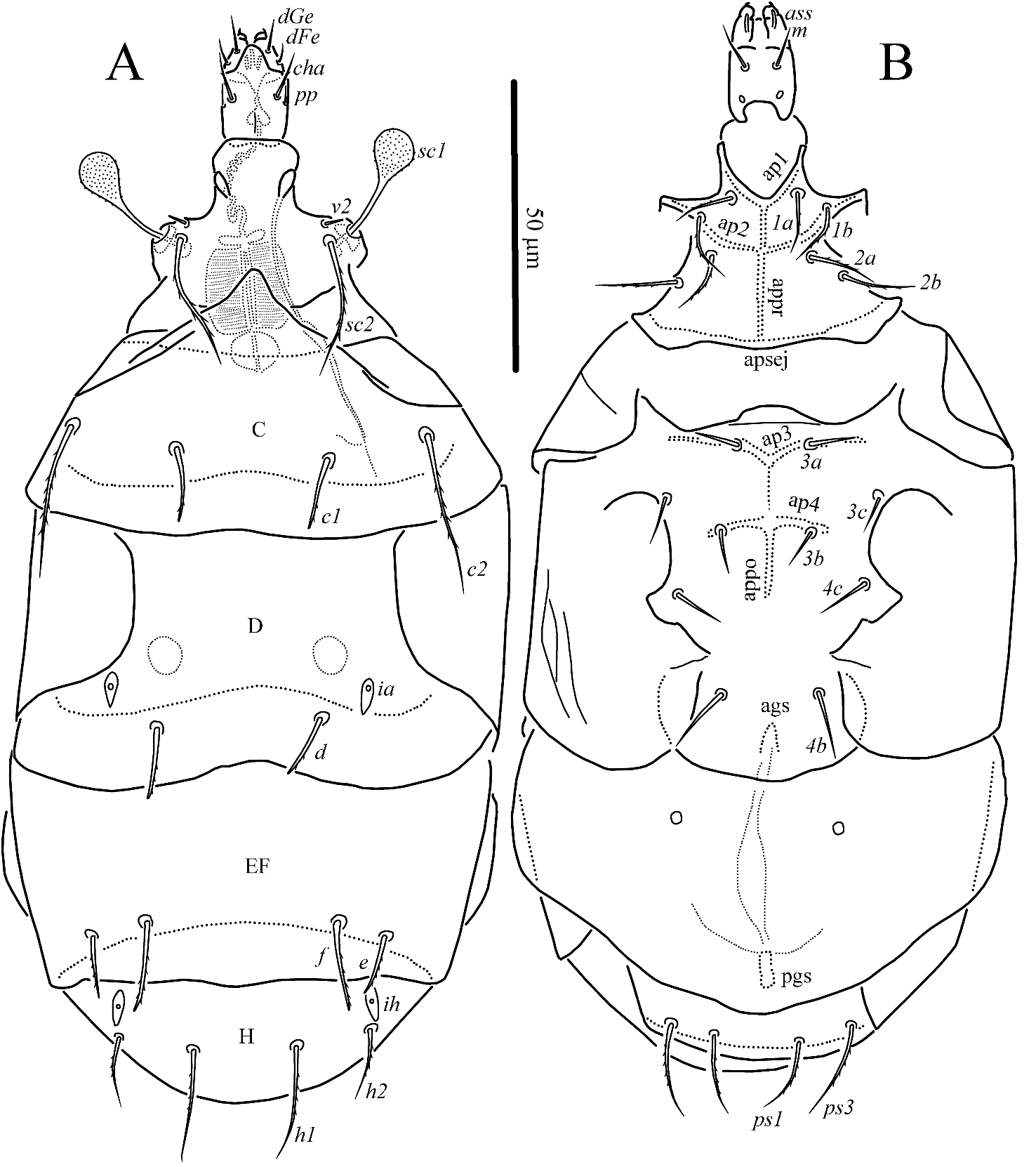
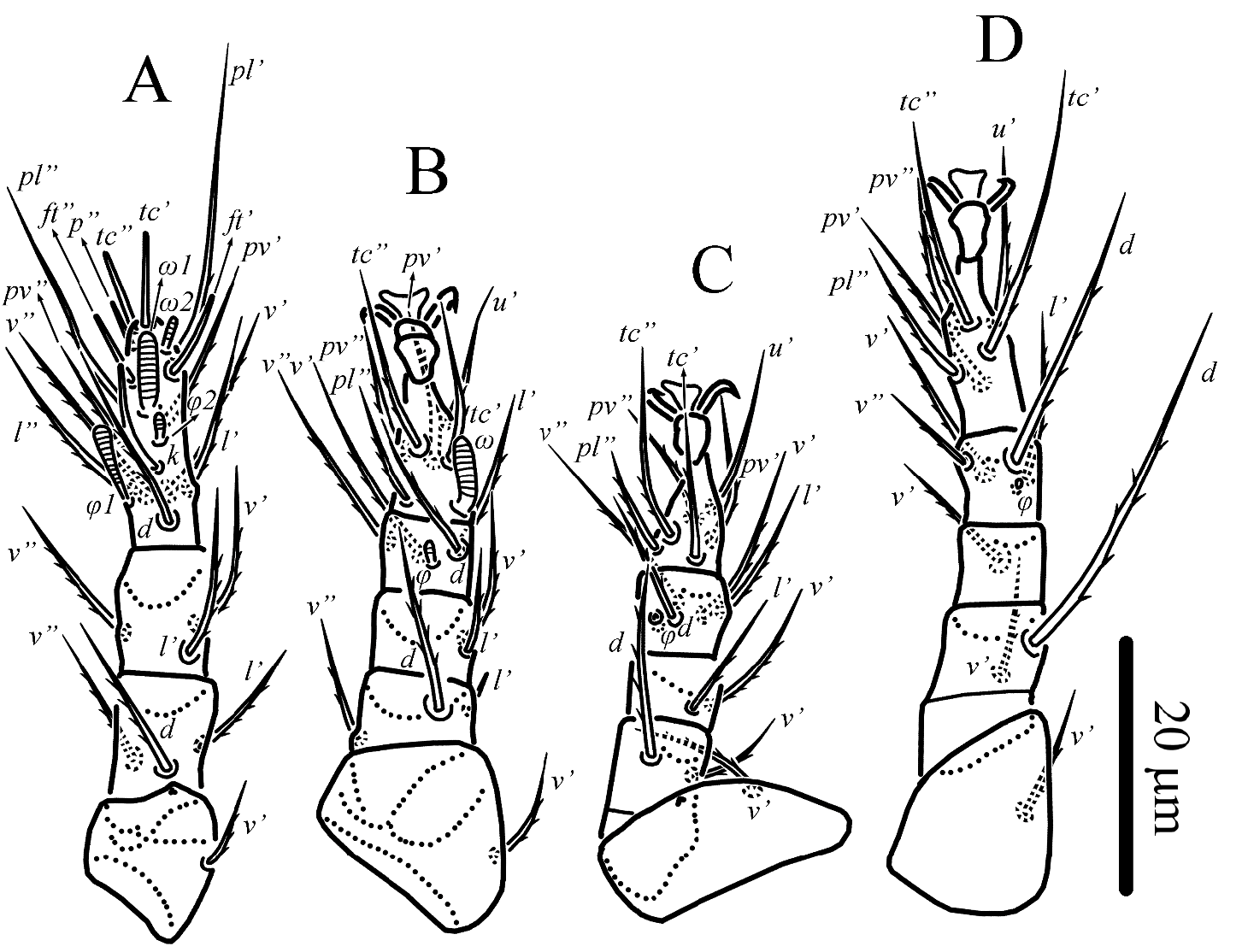
Premicrodispus (Premicrodispulus) kurganiensis sp. nov. ( Figs. 1–3 View Figure 1 View Figure 2 View Figure 3 )
http://zoobank.org/ urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:A7F6E478-5D29-45F9-8404-AFD18E7E49B3
Description
FEMALE – Length of idiosoma 165 (160–175), width of tergite C 80 (75–85).
Idiosomal dorsum ( Figs. 1A View Figure 1 , 3A View Figure 3 ) – Only posterior part of prodorsum partly covered by anterior elongation of tergite C. All dorsal sclerites with very small, hardly visible puncta ( Fig. 3A View Figure 3 ). Trichobothria with long stem, clavate, weakly barbed, with rounded apex. Setae v2 smooth, other dorsal setae weakly barbed; setae v2, c1, d, e, and f blunt-tipped, other dorsal setae pointed. Cupules ia on tergite D and ih on tergite H large, rhombic. Tergite D with a pair of round porous areas. Lengths of dorsal setae: v2 2 (2), sc2 24 (24), c1 13 (13–14), c2 28 (28–30), d 13 (12–13), e 11 (10–11), f 16 (16–17), h1 20 (20–22), h2 12 (12–14). Distances between setae: v2–v2 24 (24–25), sc2–sc2 26 (26– 27), c1–c1 25 (23–24), c1–c2 18 (18–21), d–d 28 (24–28), e–f 8 (8–9), f–f 33 (33–34), h1–h1 17 (17), h1–h2 13 (13–14).
Idiosomal venter ( Figs. 1B View Figure 1 , 3B View Figure 3 ) – All ventral plates with very small, hardly visible puncta ( Fig. 3B View Figure 3 ). Ap1 well developed and joined with appr; ap2 well developed, joined with appr; apsej well developed and joined with appr; sta absent; ap3 well developed, straight, joined with appo; ap4 reaching slightly beyond bases of setae 3b; appo poorly developed in anterior half; apodemes 5 absent. All ventral setae pointed; all setae of anterior sternal plate, ps1 and ps3 weakly barbed, other ventral setae smooth. Setae 4a absent; setae ps2 absent. Anterior margin of posterior sternal plate with short and wide lobe. Ags bell-like, pgs small, elongate-oval. Lengths of ventral setae: 1a 11 (11– 12), 1b 13 (12–13), 2a 11 (11–13), 2b 13 (13–14), 3a 8 (7–8), 3b 8 (7–8), 3c 8 (8–9), 4b 12 (11–12), 4c 8 (8–11), ps1 14 (14–15), ps3 17 (17–18).
Gnathosoma – Length of gnathosoma 16 (16–17), width 12 (11–12). Gnathosomal capsule with poorly developed dorsal median apodeme. Setae cha 9 (9–10) sparsely barbed and pointed; postpalpal setae needle-like; other gnathosomal setae smooth and pointed; setae dFe 4 (4), dGe 6 (6), m 8 (9); palpal solenidion absent, accessory setigenous structure (ass) short, tube-like. Subcapitulum with a pair of round alveolar pits in posterior half. Pharyngeal pumps typical for the genus, tripartite, joined together and situated on long twisted oesophagus.
Legs ( Fig. 2 View Figure 2 ) – Leg I ( Fig. 2A View Figure 2 ). Leg setation: Tr 1 (v’), Fe 3 (d, l’, v”), Ge 3 (l’, v’, v”), TiTa 15(4) (d, l’, l”, v’, v”, k, tc’, tc”, ft’, ft”, p”, pl’, pl”, pv’, pv”, ω1, ω2, φ1, φ2). Lengths of solenidia ω1 6 (6), ω2 2 (2), φ1 6 (6–7), φ2 2 (2); ω1 digitiform, φ1 weakly clavate; φ2 and ω2 baculiform. Setae k and eupathidia ft’, ft”, tc’, tc”, p” blunt-tipped and smooth, other leg setae pointed and barbed. Leg II ( Fig. 2B View Figure 2 ). Leg setation: Tr 1 (v’), Fe 3 (d, l’, v”), Ge 2 (l’, v’), Ti 4(1) (d, l’, v’, v”, φ), Ta 6(1) (pl”, tc’, tc”, pv’, pv”, u’, ω). Solenidion ω 6 (6) digitiform, solenidion φ 2 (2) peg-like. Setae l’ of femur and u’ of tarsus smooth, other leg setae weakly barbed; seta l’ of femur blunt-tipped, other leg setae pointed. Leg III ( Fig. 2C View Figure 2 ). Leg setation: Tr 1 (v’), Fe 2 (d, v’), Ge 2 (l’, v’), Ti 4(1) (d, l’, v’, v”, φ), Ta 6 (pl”, tc’, tc”, pv’, pv”, u’). Solenidion φ hardly visible, located in depression. All leg setae pointed; seta u’ of tarsus smooth, other setae barbed. Femur divided into basi- and telofemur. Leg IV ( Fig. 2D View Figure 2 ). Leg setation: Tr 1 (v’), Fe 2 (d, v’), Ge 1 (v’), Ti 4(1) (d, l’, v’, v”, φ), Ta 6 (pl”, tc’, tc”, u’, pv’, pv”). Solenidion φ hardly visible, located in depression. All leg setae pointed and barbed. Femur divided into basi- and telofemur.
MALE and LARVA – unknown.
Type material
Holotype female, slide ISP T-Mcd-3, Russia, Kurgan Region, Petuknovsky District, vicinity of lake Medvezh’ye , 14 October 2022, salty soil near the lake, 55° 15' 07.7" N, 67° 58' 55.8" E, coll. A.A. Khaustov and V. A. Khaustov; paratypes: 4 females, same data. GoogleMaps
Type deposition
The holotype female is deposited in the collection of ZIRAS ; paratypes are deposited in the collection of the TSUM Z.
Differential diagnosis
The new species is most similar to P. (Premicrodispulus) reductus in having setae c1, d and f blunt-tipped. The new species differs from P. reductus in having setae e blunt-tipped and clearly shorter than f (setae e pointed and subequal with f in P. reductus ) and in having two setae on genu II (one seta on genu II in P. reductus ).
Etymology
The name of the new species kurganiensis refers to its geographical distribution in Kurgan Region.
| ISP |
International Cooperative Project for Description and Deposition of Type Cultures |
| V |
Royal British Columbia Museum - Herbarium |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |