Polylopha cassiicola Liu & Kawabe, 1993
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.174871 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6256109 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03951C45-FF9E-E028-8671-F9BB8DD47C1D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Polylopha cassiicola Liu & Kawabe, 1993 |
| status |
|
Polylopha cassiicola Liu & Kawabe, 1993 View in CoL
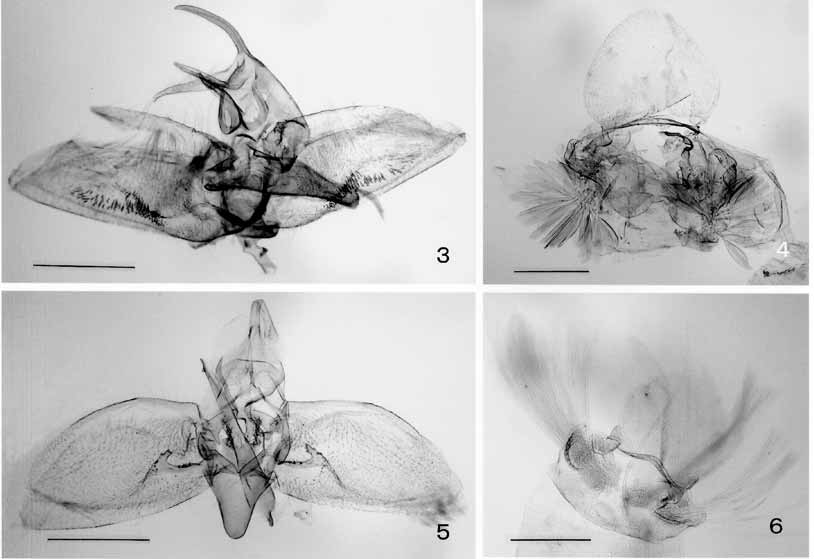
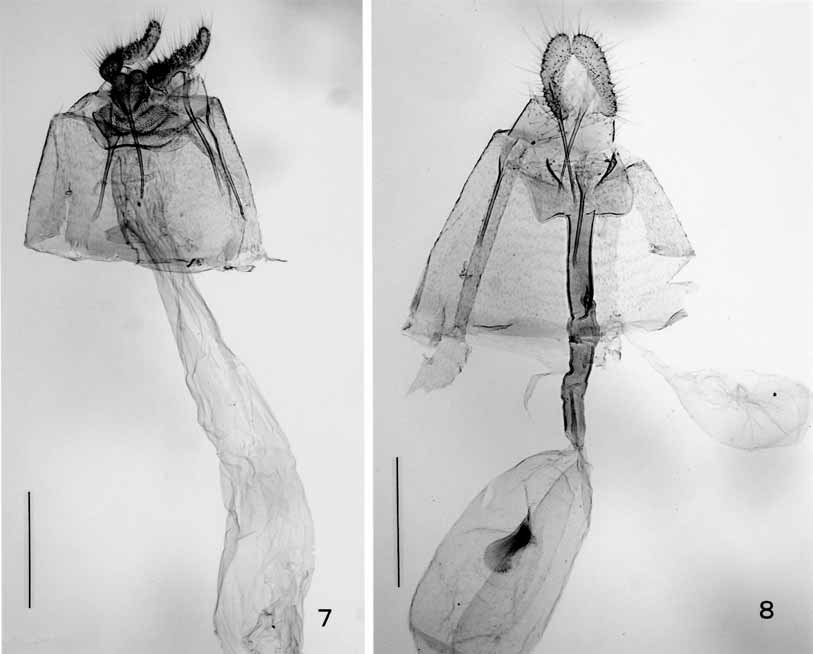
Figs. 2 View FIGURES 1 – 2 , 5, 6 View FIGURES 3 – 6 , 8 View FIGURES 7 – 8
Polylopha cassiicola Liu & Kawabe, 1993: 404 View in CoL , figs. 1–15 (adult, wing venation, ď and Ψ genitalia, larva, pupa); Liu & Li, 2002: 27, color pl. 1, fig. 3, pl. 1, fig. 3, pl. 54, fig. 3, pl. 99, fig. 3 (adult, ď and Ψ genitalia); Brown et al., 2005: 511.
Diagnosis. Sexual dimorphism is not pronounced. Wing expanse is 9–12 mm. The species has a bicolored forewing, with the basal 1/3 dark grayish brown and the apical 2/3 brownish ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1 – 2 ). The male genitalia are characterized by a long aedeagus, valva with a process on sacculus, and large vinculum ( Figs. 5, 6 View FIGURES 3 – 6 ). The female genitalia are characterized by a large rectangular sterigma, a sclerotized ductus bursae and a hornshaped signum with a round top ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 7 – 8 ). The moth is distinguishable from its congeners by these characters.
Material examined. China: Hong Kong, Victoria Peak (400 m), 2ď, 1Ψ, vii.1991, K. Li leg., 1ď, viii.1991, K. Li leg., 1Ψ, viii-ix.1992, A. C. Galsworthy leg., 2ď, v.1993, A. C. Galsworthy leg., 1ď, 2Ψ, vi.1993, A. C. Galsworthy leg., 2Ψ, vii.1993, K. Li leg.; New Territories, 1ď, 2Ψ, 24.ii.2002, M. S. Sterling leg., 2ď, 2002, M. S. Sterling leg. (all BMNH).
Distribution. South China.
Host plant. Lauraceae : Cinnamomum cassia Presl , C. camphora (L.) Presl, C. parthenoxylon (Jack) Meisn. ( Liu & Kawabe, 1993) .
Biology. The adult moths are attracted to light. The larvae bore into the twigs of the host plant ( Liu & Kawabe, 1993).
Remarks. Liu & Kawabe (1993) and Liu & Li (2002) gave only simple line drawings of the adult and genitalia of the species. Therefore I augment those illustrations with photographs.
Polylopha View in CoL is distributed in the Oriental and Australian regions, and seven species have been recorded previously ( Brown et al., 2005). The genus is associated with Annonaceae View in CoL : P. e p i d e s m a Lower, 1901 (= porpacias Meyrick, 1908) feeds on Polyalthia longifolia (Wall.) Benth. et Hook. (Annonaceae) View in CoL ( Diakonoff, 1974; Robinson et al., 2001), P. hypophaea Diakonoff, 1974 on “kalak” [ Miliusa horsfieldii Baill. ex Pierre View in CoL ] ( Diakonoff, 1974), and Lauraceae View in CoL : the present species on Cinnamomum View in CoL spp. The genus is closely related to Lopharcha View in CoL , and the distinguishing character is noted in the remarks for the preceding species.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Chlidanotinae |
|
Genus |
Polylopha cassiicola Liu & Kawabe, 1993
| Nasu, Yoshitsugu 2006 |
Polylopha cassiicola
| Brown 2005: 511 |
| Liu 2002: 27 |
| Liu 1993: 404 |