Clavinema mariae (Layman, 1930) Yamaguti, 1935
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4185.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:0D054EDD-9CDC-4D16-A8B2-F1EBBDAD6E09 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5626650 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038FB248-FF9B-FF9D-89B9-C68B219D9DD4 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Clavinema mariae (Layman, 1930) Yamaguti, 1935 |
| status |
|
Clavinema mariae (Layman, 1930) Yamaguti, 1935
Synonyms: Philometra mariae Layman, 1930 ; Philometra americana Kuitunen-Ekbaum, 1933 ; Philometra sp. of Arai (1967 partim)
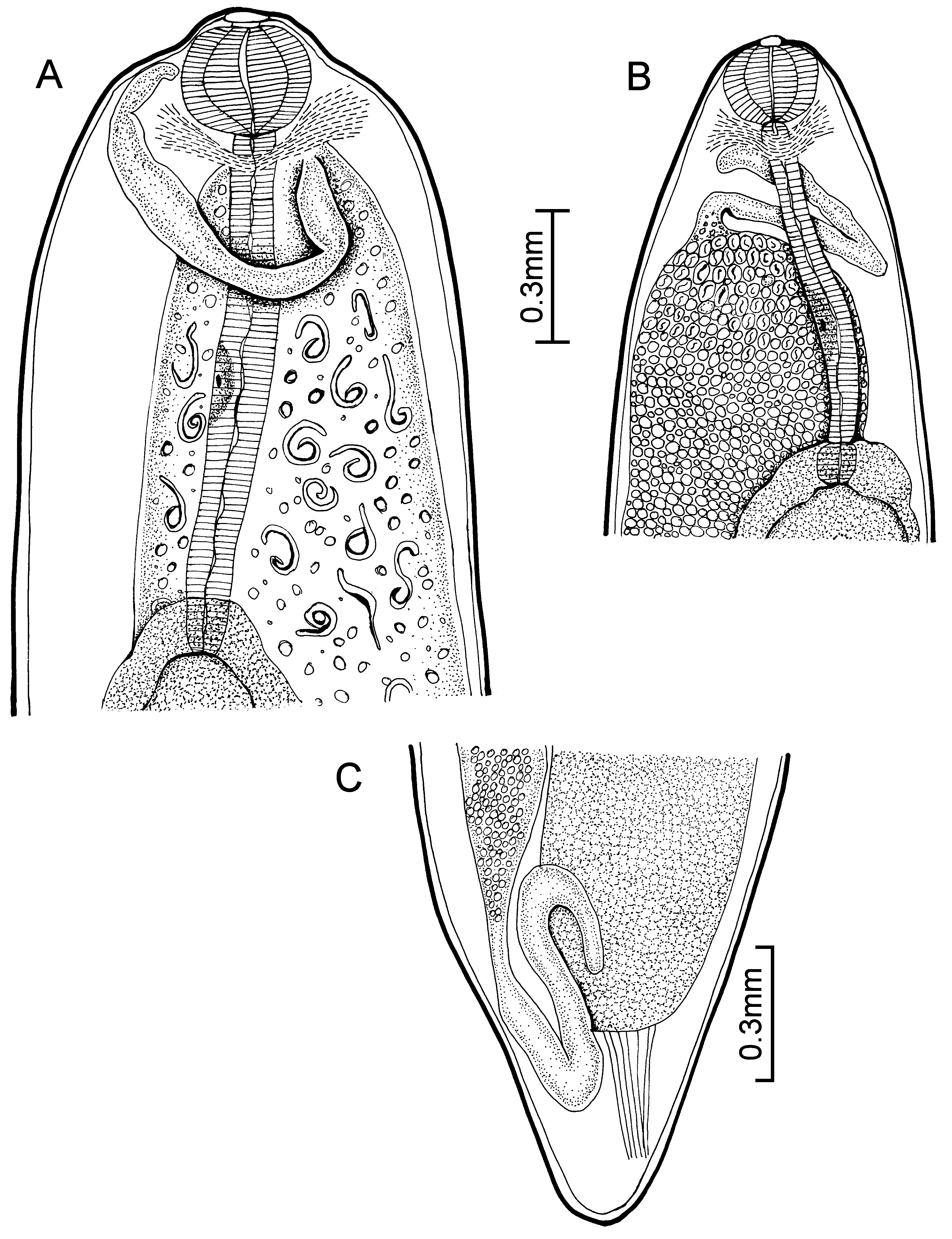
Description (after Margolis & Moravec 1987). With characteristics of the genus. Males unknown.
Females: body of gravid and subgravid worms distinctly narrower in posterior half. Cuticle smooth. 23.6–48.5
long; maximum width 0.74–1.90. Gravid worms with larvae in uteri 33.7–48.5 long; maximum width 0.74–1.49.
Head end rounded, with elevated oesophageal bulb region (0.115 long and 0.322 wide) in larger worms. Mouth
papillae not observed. Mouth slightly depressed. Anterior end of oesophagus forming a conspicuous, strongly
muscular bulb, well separated from posterior cylindrical portion of oesophagus; bulb 0.202–0.326–0.235–0.398.
Small, not well demarcated oesophageal gland situated about middle of posterior portion of oesophagus. Entire
oesophagus including bulb 0.958–1.442 long ( Fig. 29 View FIGURE 29 A). Oesophagus opens into intestine through distinct valves.
Nerve ring encircles anterior end of cylindrical portion of oesophagus, 0.281–0.446 from anterior end ( Fig. 29 View FIGURE 29 A).
Intestine dark and broad throughout, attached by short ligament to ventral body wall near posterior end ( Fig. 29 View FIGURE 29 C).
Uterus containing eggs, developing embryos, and larvae. Larvae 0.300–0.426 long and 0.009–0.018 maximum
width. Vulva absent. Uterus reaches anteriorly to posterior end of oesophageal bulb in gravid worms ( Fig. 29 View FIGURE 29 A) or
near it in subgravid worms ( Fig. 29 View FIGURE 29 B). Anterior ovary tubular, well developed. Posterior ovary directed anteriorly,
its distal end pointing backwards. Uterus reaching posteriorly almost to posterior end of intestine. Posterior end of
body rounded, lacking projections or papillae ( Fig. 29 View FIGURE 29 C).
Sites: body cavity, fins, musculature, subcutaneous
Hosts: Anoplarchus purpurescens (2); Cottus asper (9); Gobiesox maeandricus (1, 2); Parophrys vetulus (3, 4, 7); Pholis laeta (5, 6); Pholis ornata (1, 2); Platichthys stellatus (1, 2, 4, 8); Paraplagusia bilineata (1, 2); Xiphister atropurpureus (1, 2)
Distribution: British Columbia, Pacific
Records: 1. Kuitunen-Ekbaum 1933c (PA); 2. Kuitunen-Ekbaum 1938 (PA); 3. Margolis 1952a (PA); 4. Margolis 1952b (PA); 5. Arai 1967a (PA); 6. Arai 1969 (PA); 7. Margolis 1970 (PA); 8. Lewis 1978 (PA); 9. Margolis & Moravec 1987 (BC, PA)
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SuperFamily |
Dracunculoidea |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SuperFamily |
Dracunculoidea |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |