Leucandra tahuatae, Klautau & Lopes & Guarabyra & Folcher & Ekins & Debitus, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4748.2.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:661CD94A-130B-4BD8-B201-28B079815618 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3704832 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A8A61580-4BAE-4672-8EF9-F6F120C9BF8A |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:A8A61580-4BAE-4672-8EF9-F6F120C9BF8A |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Leucandra tahuatae |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Leucandra tahuatae View in CoL sp. nov.
( Figs 10 View FIGURE 10 , 11 View FIGURE 11 , 12 View FIGURE 12 , Table 10)
Etymology. From the type locality (Tahuata)
Type locality. Matatehoke , Tahuata, Marquesas Island, French Polynesia .
Material examined. Holotype: UFRJPOR 6454 = MNHN-IP- 2018-25 — Matatehoke , Tahuata , Marquesas Island, Station MT01 (9° 53.589’ S– 149° 33.220’ W), depth: 33 m, coll. C. Debitus, 10/IX/2009, P177. GoogleMaps
Diagnosis. Sponge white, tubular, with cortical triactines, large and small choanosomal triactines, and choanosomal and atrial tetractines.
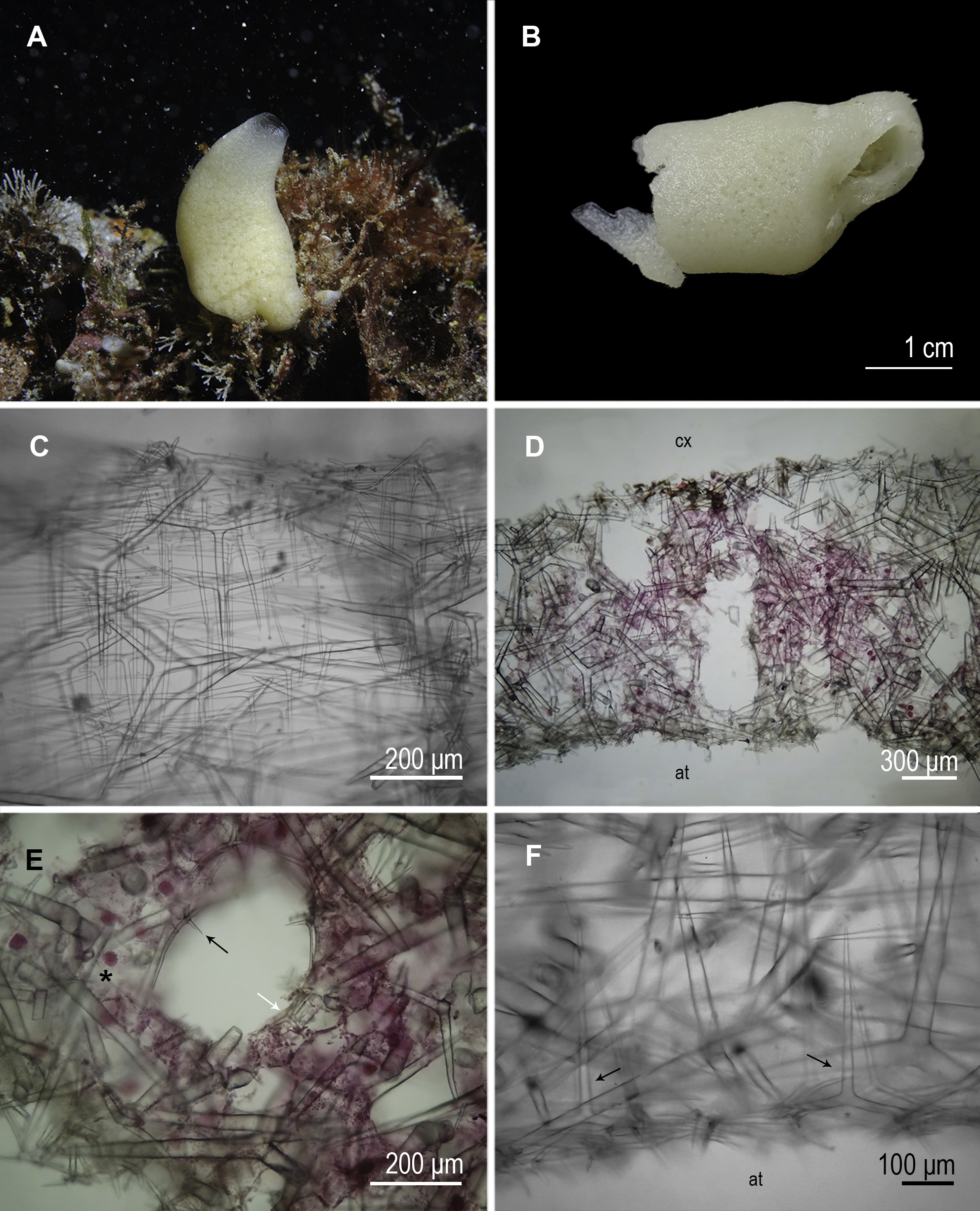
Colour. White alive and beige in ethanol ( Fig 10A View FIGURE 10 ).
Morphology and anatomy. Sponge tubular with apical osculum ( Figs 10A, B View FIGURE 10 ) surrounded by membrane ( Fig 10C View FIGURE 10 ). Surface smooth. Large central atrium. Aquiferous system leuconoid.
The cortical skeleton is composed of tangential triactines ( Figs 11A, B View FIGURE 11 ). In the choanosome there are large triactines (larger than those of the cortex) and small choanosomal triactines and tetractines. Some of these small triactines and the small tetractines surround the choanosomal canals ( Fig 10E View FIGURE 10 ). The subatrial skeleton is composed of triactines that point their unpaired actine to the cortex ( Fig 10F View FIGURE 10 ). The atrial skeleton has tangential tetractines that point their apical actine into the atrium ( Figs 10F View FIGURE 10 , 11C, D View FIGURE 11 ).
Spicules ( Table 10)
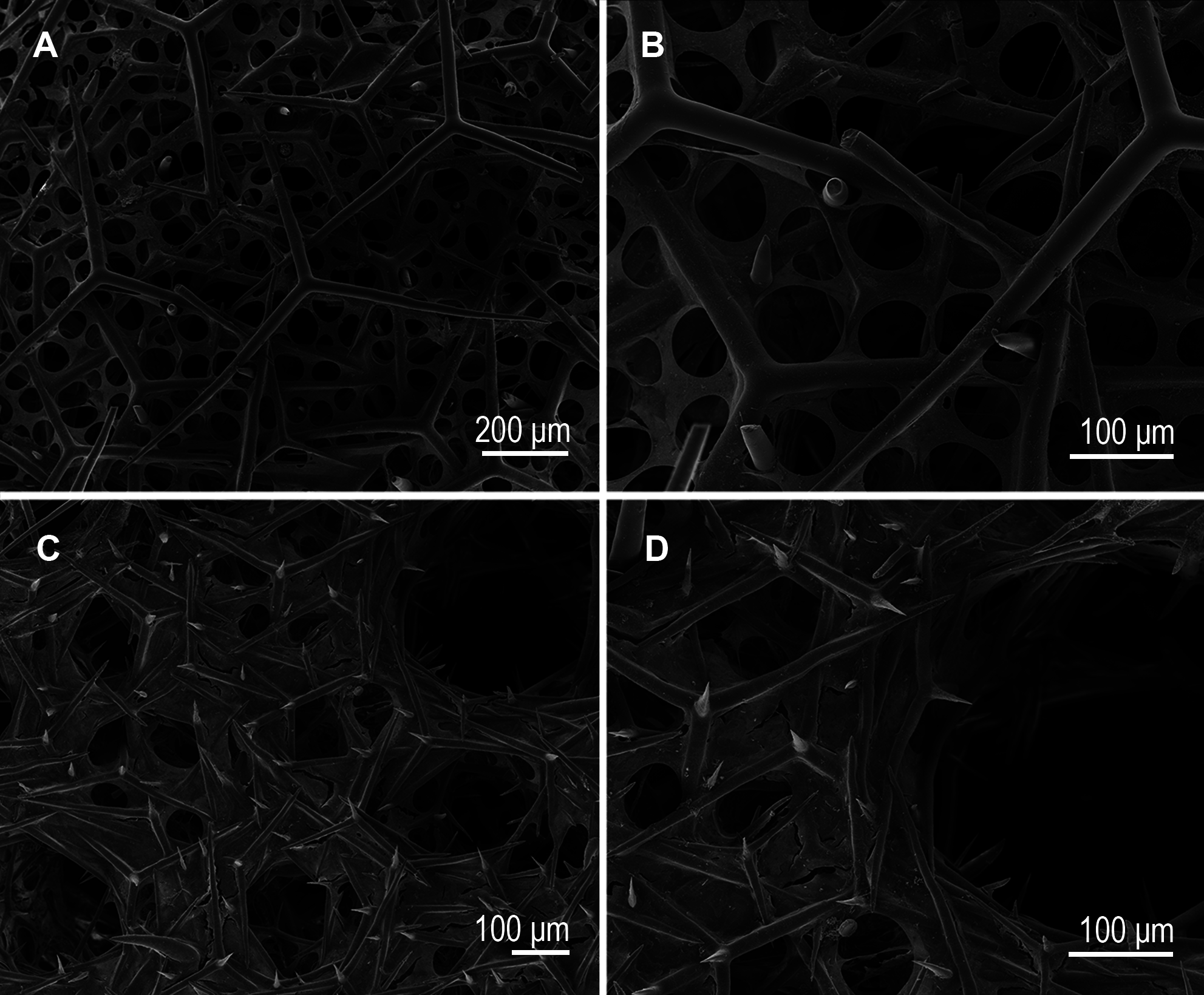
Cortical triactines. Subregular. Actines are slightly conical with sharp tips. Sometimes they are undulated. The unpaired actine is shorter than the paired ones ( Fig 12A View FIGURE 12 ). Size: 449.0/ 32.6 µm (paired), 369.0/ 28.3 µm (unpaired).
Choanosomal large triactines. Subregular. Actines are slightly conical with sharp tips. Sometimes they are undulated. The unpaired actine is shorter than the paired ones ( Fig 12B View FIGURE 12 ). Size: 796.7/ 53.0 µm (paired), 537.8/ 50.3 µm (unpaired).
Choanosomal small triactines. Strongly sagittal, with curved paired actines when they are surrounding the canals. Actines are slightly conical with sharp tips. One of the paired actines is frequently shorter than the other actines ( Fig 12C View FIGURE 12 ). Size: 151.4/ 11.0 µm (paired), 172.1/ 12.6 µm (unpaired).
Choanosomal small tetractines. Strongly sagittal with curved paired actines, as they are find surrounding the canals. Actines are slightly conical with sharp tips. The unpaired actine can present the same length of the paired ones or be shorter. The paired actines are undulated. The apical actine is much shorter and thinner. It is conical, sharp an smooth ( Fig 12D View FIGURE 12 ). Size: 158.1/ 11.7 µm (paired), 184.1/ 13.0 µm (unpaired), 50.9/ 8.9 µm (apical).
Subatrial triactines. Strongly sagittal (T-shaped). Actines are slightly conical with sharp tips. The unpaired actine is longer than the paired ones ( Fig 12E View FIGURE 12 ). Size: 163.6/ 13.2 µm (paired), 261.3/ 16.3 µm (unpaired).
Atrial tetractines. Sagittal. Actines are slightly conical with sharp tips. The basal actines show the same length and they are straight. The apical actine is shorter than the basal ones, conical, sharp and smooth ( Fig 12F View FIGURE 12 ). Size: 214.8/ 14.9 µm (paired), 215.5/ 14.8 µm (unpaired), 50.1/ 8.1 µm (apical).
Ecology. There was algae inside the atrium of this sponge.
Geographical distribution. Marquesas Island, French Polynesia (present work).
Remarks. Most leucandras present diactines in their skeleton but L. tahuatae sp. nov. is part of a small group of this genus without diactines. Another characteristic that differentiates the new species from most leucandras is the presence of a subatrial skeleton. However, sometimes it is very difficult to be sure if a species does not have subatrial skeleton or if its author just did not mention it. Hence, to compare our new species other species of Leucandra , we considered only those with skeleton composed of cortical triactines, choanosomal large and small triactines, choanosomal tetractines, and atrial tetractines. We found only three most similar species to L. tahuatae sp. nov.: L. ramosa ( Burton, 1934) , L. mozambiquensis Van Soest & De Voogd, 2018 , and L. pilula Van Soest & De Voogd, 2018 .
Leucandra ramosa was originally described from Australia. It can be differentiated from L. tahuatae sp. nov. by its greyish-brown colour in ethanol (the new species is white) and by the size of some spicule categories. Cortical triactines: up to 210.0/ 11.0 ( L. ramosa ); 260.0˗ 449.0 ˗700.0/ 25.0˗ 32.6 ˗40.0—paired actine, 180.0˗ 369.0 ˗550.0/ 10.0˗ 28.3 ˗35.0—unpaired actine ( L. tahuatae sp. nov.). Choanosomal large triactines: up to 960.0/ 64.0 ( L. ramosa ); 508.1˗ 796.7 ˗1016.1/ 37.8˗ 53.0 ˗64.9—paired actine, 378.4˗ 537.8 ˗756.7/ 37.8˗ 50.3 ˗54.1—unpaired actine ( L. tahuatae sp. nov.). Choanosomal small triactines: up to 240.0/ 12.0 ( L. ramosa ); 108.0˗ 151.4 ˗202.5/ 9.5˗ 11.0 ˗13.5— paired actine, 129.6˗ 172.1 ˗221.4/ 10.8˗ 12.6 ˗13.5—unpaired actine ( L. tahuatae sp. nov.).
Leucandra mozambiquensis , recently described from Mozambique Channel, can be differentiated from the new species by its external morphology, as it is an “irregular cup-shaped hollow mass” ( Van Soest & De Voogd 2018) while the new species is tubular, and mainly by the presence of tetractines instead of triactines in the subatrial skeleton.
Leucandra pilula , described from Seychelles, is globose, while L. tahuatae sp. nov. is tubular. The former has oxhorn-shaped cortical triactines, while ours has equiangular cortical triactines. Besides, some of their spicule categories have sizes. Cortical triactines: 216.0˗ 281.0 ˗372.0/ 16.0˗ 21.6 ˗28.0—paired actine, 178.0˗ 245.0 ˗326.0/ 15.0˗ 22.7 ˗31.0—unpaired actine ( L. pilula ); 260.0˗ 449.0 ˗700.0/ 25.0˗ 32.6 ˗40.0—paired actine, 180.0˗ 369.0 ˗550.0/ 10.0˗ 28.3 ˗35.0—unpaired actine ( L. tahuatae sp. nov.). Subatrial triactines: 100.0˗ 186.0 ˗303.0/ 11.0˗ 16.6 ˗29.0—paired actine, 94.0˗ 172.0 ˗254.0/ 9.0˗ 17.8 ˗26.0—unpaired actine ( L. pilula ); 116.1˗ 163.8 ˗243.0/ 10.2˗ 13.2 ˗16.2—paired actine, 164.7˗ 261.3 ˗335.1/ 10.8˗ 16.3 ˗21.6—unpaired actine ( L. tahuatae sp. nov.). Atrial tetractines: 136.0˗ 239.0 ˗380.0/ 9.0˗ 17.1 ˗32.0—paired actine, 101.0˗ 186.0 ˗271.0/ 14.0˗ 19.4 ˗32.0—unpaired ac- tine, 45.0˗ 84.0 ˗130.0/ 4.0˗ 8.4 ˗11.0—apical actine ( L. pilula ); 155.0˗ 214.8 ˗325.0/ 13.5˗ 14.9 ˗15.0—paired actine, 150.0˗ 215.5 ˗300.0/ 12.5˗ 14.8 ˗15.0—unpaired actine, 30.0˗ 50.1 ˗67.5/ 6.3˗ 8.1 ˗10.0—apical actine ( L. tahuatae sp. nov.)
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |