Formosatettix strictivertex Deng, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5228.3.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:CF7244F1-F2FA-4435-BD96-5492BC1AF6B8 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7532452 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/3922878E-B771-7941-FF7D-F590FD81D6F9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Formosatettix strictivertex Deng |
| status |
sp. nov. |
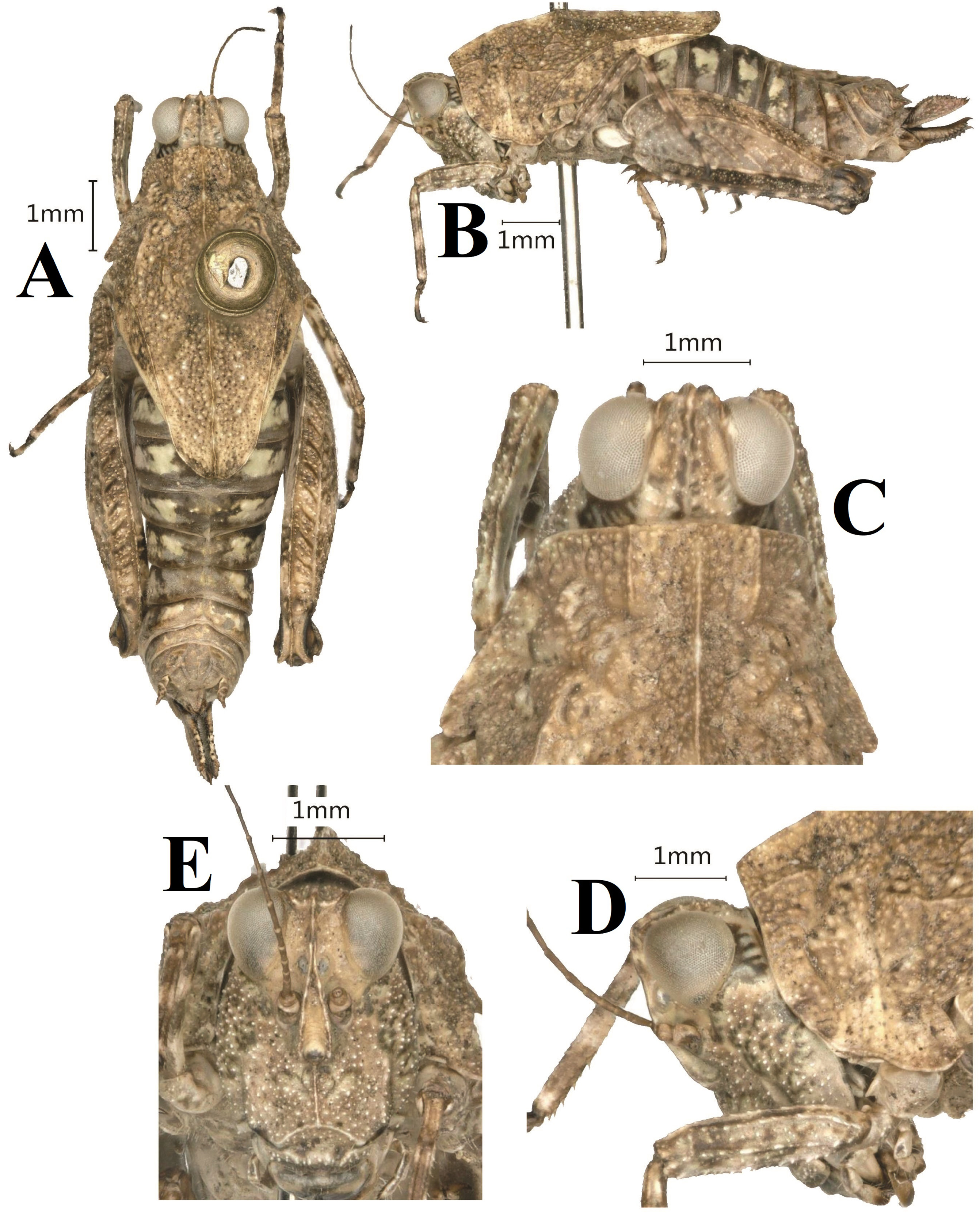
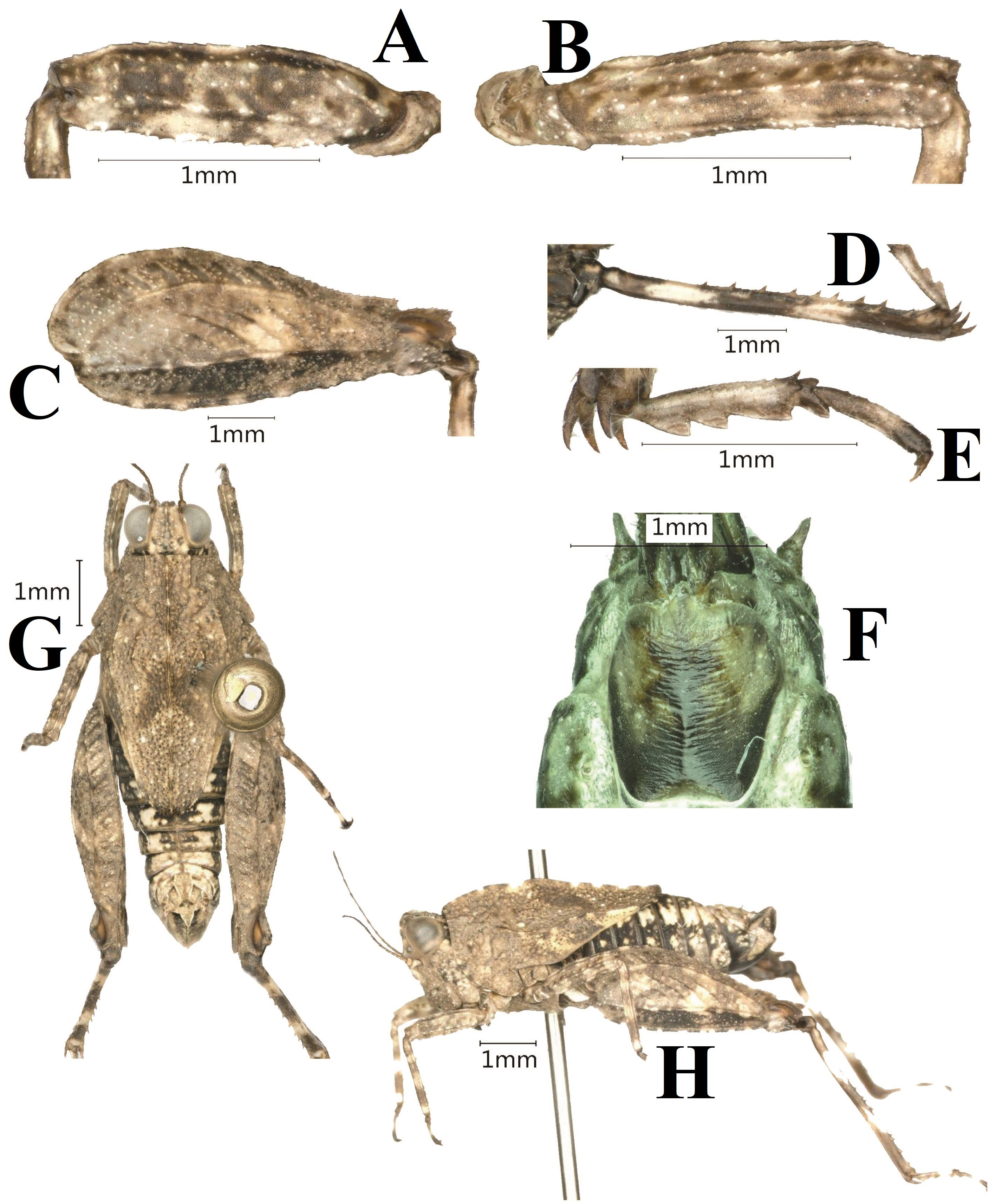
13. Formosatettix strictivertex Deng , sp. nov. ( Figs. 16 View FIGURE 16 , 17 View FIGURE 17 , 24Q View FIGURE 24 , 25D View FIGURE 25 )
Description. Female. Small size, short, body surface interspersed with sporadic short carinae.
Head. Head and eyes not exserted above pronotal surface ( Fig. 16B View FIGURE 16 ). Fastigium of vertex short; in dorsal view, width of vertex between eyes 0.8–1.0 times width of compound eye ( Fig. 16C View FIGURE 16 ); anterior margin of fastigium straight, slightly surpassing anterior margin of eye; median carina visible anteriorly; lateral margins turned backward; vertex uneven with paired fossulae. In lateral view, frontal ridge and vertex forming a right angle; frontal costa straight and not concave between eyes ( Fig. 16D View FIGURE 16 ), protruded anteriorly and broadly rounded between antennal grooves. In frontal view, frontal costa bifurcated above lateral ocelli, longitudinal furrow divergent between antennae, width of longitudinal furrow of frontal ridge narrower than antennal groove diameter ( Fig. 16E View FIGURE 16 ). Antennae short, filiform, antennal grooves inserted below inferior margins of compound eyes, 13-segmented, the 9th and 10th segment are the longest, about 3 times longer than its width. Eyes globose, lateral (paired) ocelli located in lowest third of compound eye height.
Thorax. Pronotum distinctly tectiform, its surface coarse and interspersed with sporadic short carinae between shoulders ( Fig. 16A View FIGURE 16 ). In dorsal view, anterior margin of pronotum truncate; lateral carinae of prozona parallel; humeral angle absent; hind pronotal process broad and short, reaching 1/2 of hind femur and its apex broadly arcuate (apex of hind pronotal process suddenly become narrowly and sharp in individual individual). In profile, median carina of pronotum slightly lamellate and slightly arch-like; lower margin of hind process curved, external lateral carinae of metazona slightly curved, width of infrascapular area is 0.7 mm. Posterior angles of lateral lobes turned downwards, apex of posterior angles obtuse rounded, posterior margins of lateral lobes of pronotum only with ventral sinus and tegminal (upper) sinus absent. Tegmina and hind wings invisible (vestigial hidden under pronotum).
Legs. Fore and middle femora slightly compressed, margins finely serrated, with carinated, ventral margins straight ( Fig. 17A, B View FIGURE 17 ). Hind femora robust and short, 2.6 times as long as wide; with carinated, margins finely serrated ( Fig. 17C View FIGURE 17 ); antegenicular denticles right angle and genicular denticles acute. Outer side and inner side of hind tibia with 5–6 spines ( Fig. 17D View FIGURE 17 ). First segment of posterior tarsi longer than third, three pulvilli of first segment of posterior tarsi are increased in turn, apices of all pulvilli right angle ( Fig. 17E View FIGURE 17 ).
Abdomen. Ovipositor narrow and long, length of upper valvulae 3.0 times its width, upper and lower valvulae with slender saw-like teeth. Length of subgenital plate nearly equal to its width, middle of posterior margin of subgenital plate triangular projecting ( Fig. 17F View FIGURE 17 ).
Coloration. Body dark brown or brown. Fore and middle tibiae with two black bands.C Hind femur brown or dark brown, outer part lower side black (outer part of hind femur with two or three black spots in some of individuals). Hind tibia black, with two light rings in the middle.
Male. Similar to female, but smaller and narrower ( Fig. 17G, H View FIGURE 17 ). Width of vertex between eyes 0.7–0.8 times width of compound eye ( Fig. 17G View FIGURE 17 ); width of infrascapular area is 0.4–0.5 mm. Subgenital plate short, cone-shaped, apex bifurcated.
Measurements (mm). Length of body: ♁ 6.0–6.5, ♀ 9.5–10.5; length of pronotum: ♁ 3.6–4.1, ♀ 4.5–5.0; length of hind femur: ♁ 3.5–4.2, ♀ 4.5–5.0.
Type material. Holotype: ♀, China, Xizang autonomous region, Bomi (Pailong), 30°1ʹ23ʹʹ N, 95°0ʹ20ʹʹ E, 2028 m alt., 14 June 2019, collected by Wei-An Deng, CLSGNU GoogleMaps . Paratypes. 6♁, 13♀, same data, CLSGNU GoogleMaps ; 2♁, 2♀, China, Xizang autonomous region, Motuo ( Motuo county highway), 29°27ʹ40ʹʹ N, 95°26ʹ27ʹʹ E, 670 m alt., 15 June 2019, collected by Wei-An DENG, CLSGNU GoogleMaps .
Diagnosis. New species can be easily distinguished from other species of the genus by width of vertex between eyes 0.8–1.0 times width of compound eye. This new species is similar to Formosatettix gorkhanu s Ingrisch, 2001 from which it differs in width of vertex between eyes 0.8–1.0 times width of compound eye (width of vertex between eyes 2.0 times width of compound eye in F. gorkhanu s); in lateral view, frontal costa straight and not concave between eyes (in lateral view, frontal costa distinctly concave between eyes in F. gorkhanu s); lower margin of hind pronotal process curved (lower margin of hind pronotal process straight in F. gorkhanu s); hind pronotal process broad and its apex broadly arcuate (hind pronotal process narrow and its apex narrowly rounded in F. gorkhanu s).
Etymology. The specific epithet is derived from “ strictivertex ”, meaning vertex is extremely narrow, fastigium of vertex between eyes 0.8–1.0 times width of an eye.
Distribution. P. R. CHINA: Xizang.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Tetriginae |
|
Genus |