Dothiorella obovata Rathnayaka & K.D. Hyde, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.564.1.2 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7082066 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6258505A-FFA1-8336-F4E3-FDE9FEF86B15 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Dothiorella obovata Rathnayaka & K.D. Hyde |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Dothiorella obovata Rathnayaka & K.D. Hyde , sp. nov.
Index Fungorum number: IF559719; Facesoffungi number: FoF 11668; Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5
Etymology:—In reference to obovate-shaped ascospores.
Holotype:— MFLU 22-0094
Saprobic on dead twig of Pavonia odorata . Sexual morph: Ascomata 195–250 μm high × 170–240 μm diam. (x̄ = 215 × 200 μm, n = 10), immersed to erumpent through host tissue, globose, solitary and scattered. Peridium 34–90 μm wide, 5–7 layers, brown to dark brown cells of textura angularis. Hamathecium comprising 2–4 μm wide, oblong to cylindrical, septate pseudoparaphyses. Asci 60–95 × 12–25 μm (x̄ = 75 × 18 μm, n = 10), 8-spored, bitunicate, fissitunicate, cylindric-clavate to clavate, with a short pedicel, slightly curved, apically rounded with a well-developed ocular chamber. Ascospores 12–17 × 6–10 μm (x̄ = 14 × 8 μm, n = 30), 1–2-seriate, overlapping in the ascus, hyaline to yellowish brown, aseptate when immature, becoming brown to dark brown, 1-sepate at maturity, obovoid, with granular appearance, upper cell is wider than lower cell, straight. Asexual morph: Undetermined.
Culture characteristics:— Conidia germinating on PDA within 24 h. Germ tubes produced from one side of the conidium. Colonies on PDA reaching 2.0– 2.5 cm diam. after 5 days at 25 °C, circular, medium dense, flat or effuse, slightly raised, fluffy to fairly fluffy, aerial, grey colour in top view, black in bottom view.
Material examined:— THAILAND. Trat province (Southern Thailand): on dead twig of Pavonia odorata (Malvaceae) , 3 September 2020, Rashika Sajith (MFLU 22-0094, holotype); ex-type living culture MFLUCC 22- 0058.
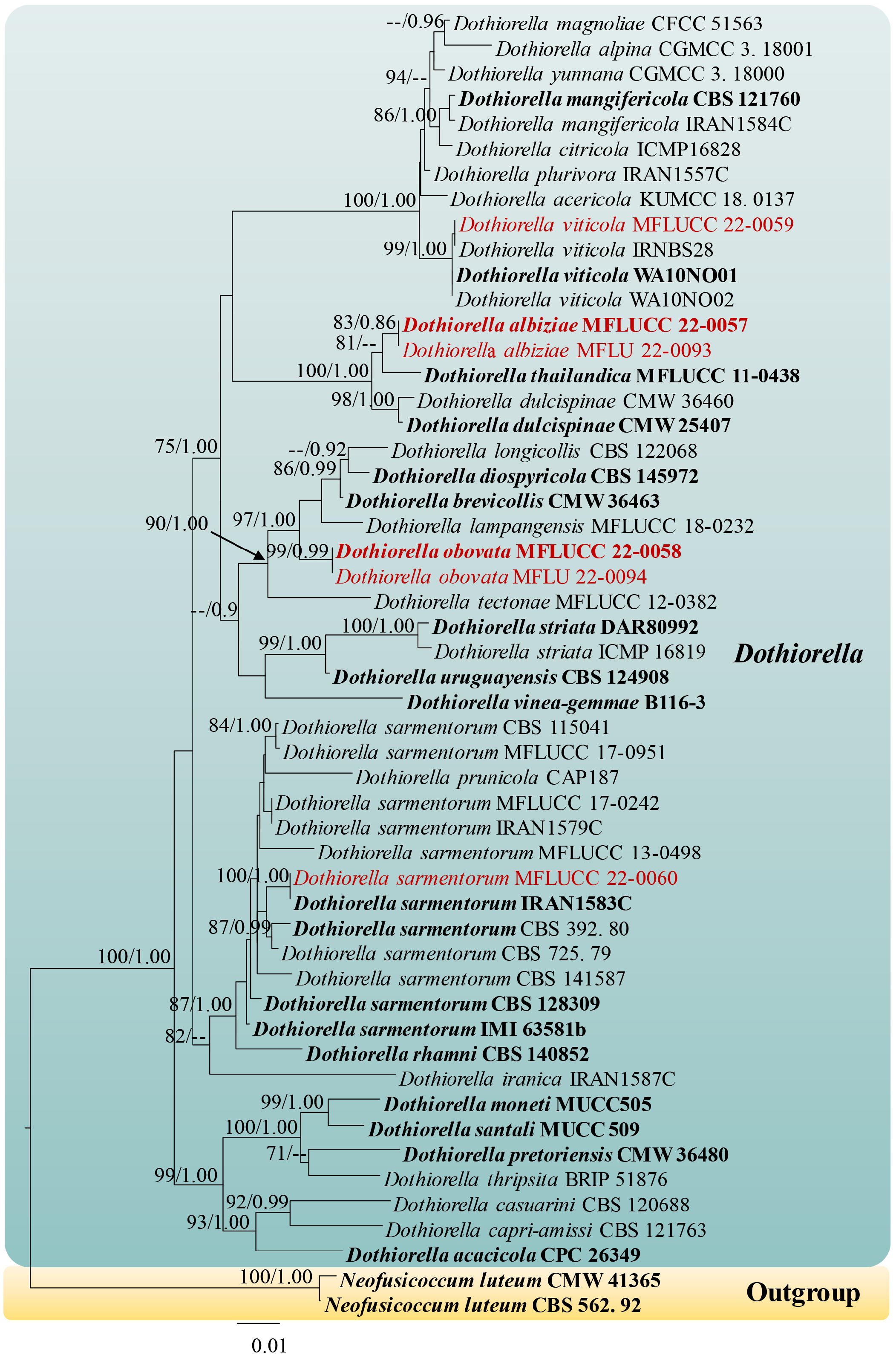
Notes:— Dothiorella obovata fits within the generic concept of Dothiorella by having pigmented, 1-septate ascospores. Morphologically, our new strain (MFLU 22-0094/ MFLUCC 22-0058) is distinguished from other Dothiorella species by having obovate ascospores. Based on multi-gene phylogeny (ITS, LSU, tef 1-α and β-tub), D. obovata constitutes a distant lineage sister to D. brevicollis , D. diospyricola , D. lampangensis , and D. longicollis with relatively high 97% ML bootstrap and 1.00 PP support ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ). Only asexual morphs have been recorded for D. brevicollis , D. diospyricola , D. lampangensis , and D. longicollis , while D. obovata is recorded from the sexual morph. Therefore, we could not compare the morphology of D. obovata with these four species. Base pair differences between D. brevicollis , D. diospyricola , D. lampangensis , D. longicollis and D. obovata (MFLUCC 22-0058) are shown in Table 2 View TABLE 2 . According to distinct morphology and phylogenetic evidence, we established D. obovata as a new species in Dothiorella .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |