Corynoneura tumula, Fu & Liu & Fang & Wang & Wang, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4418.1.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:69DF62CD-87E4-4AD0-A628-189500CB909E |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4504880 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/440687FF-FFAD-CF17-58BC-EABCFD7CAC8A |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Corynoneura tumula |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Corynoneura tumula sp. n.
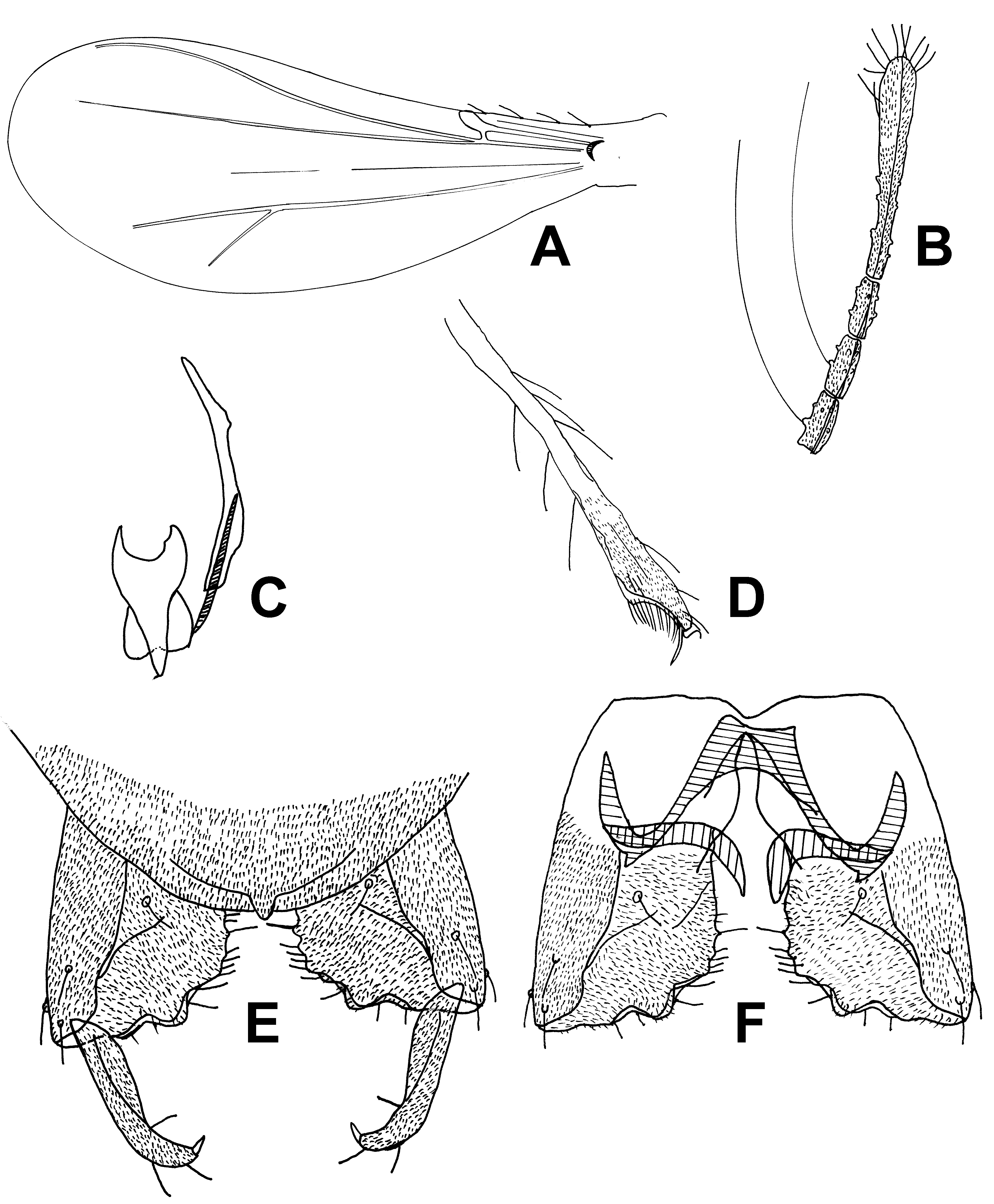
( Figs 3 A–F View FIGURE 3 )
Type material. Holotype male, CHINA: Hubei Province, Enshi Tujia Miao Autonomous Prefecture, Xuanen County, Qizimeishan National Nature Reserve , Banzhuyuan Village , 109°45′6″E, 30°1′12″N, alt. 1220, sweep net, 9.?. 2015, Y.Fu ( HBMY Type no. 16012201w ). GoogleMaps
Paratypes, 1 male, Hubei Province, Enshi Tujia Miao Autonomous Prefecture, Xianfeng County, Zhongjianhe National Nature Reserve , Zhanmahe Village , 109°13′28″E, 29°49′57″N, light trap, 18.? I. 2016, XL.Fang ( HBMY Type no. 17090802HJL ). GoogleMaps
Derivatio nominis. From Latin, tumulus, barrow, hillock, referring to tergite IX with small anal point.
Diagnostic characters. The male imago is characterized by having an antenna with 9 flagellomeres, AR 0.46; anterior margin of cibarial pump strongly concave; anal point present. Superior volsella antero-medially fused and small, with rounded corner. Inferior volsella broad, with dented margin, like double-layer, along the inner margin of gonocoxite and placed caudally.
Male (n=1–2)
Total length 0.78 mm. Wing length 0.49 mm. Total length/wing length 1.6. Wing length/profemur length 2.6.
Coloration. Head dark brown, with black eyes. Thorax dark brown. Legs yellowish. Abdomen: tergites?–? pale yellow, tergites?–? yellow, tergite? brown.
Head. Antenna with 9 flagellomeres, AR 0.46, ultimate flagellomere 103 µm long, ultimate flagellomere slightly expanded apically, with about 9–10 apical sensilla chaetica ( Fig. 3. B View FIGURE 3 ). Temporals absent. Tentorium, stipes and cibarial pump as in Fig. 3. C View FIGURE 3 , tentorium 103 µm long; 12 µm wide; stipes 48 µm long, 5 µm wide. Anterior margin of cibarial pump ( Fig. 3. C View FIGURE 3 ) strongly concave. Clypeus with 6 setae. Length of palpomeres (in µm): 7; 7–10; 10–12; 19; 36–38. Palpomere 5/3 ratio: 3.2–3.6.
Thorax. Dorsocentrals 5. Scutellum with 2 setae. Prealars invisible.
Wing ( Fig. 3. A View FIGURE 3 ). VR 3.0. Cu/wing length 0.55; C 132 µm long; Cu 270 µm long; wing width/wing length: 0.40. Brachiolum without seta, costa with 4 setae.
Legs. Fore trochanter with dorsal keel. Spurs of fore tibia 14 µm long and 7 µm long, of mid tibia 10 µm long and 7 µm long, and spur of hind tibia 10 µm long and 24–26 µm long. Width at apex of fore tibia 17 µm, of mid tibia 14 µm, of hind tibia (a) 36 µm. Width of hind tibia 1/3 from apex (d) 18 µm, elongation length (b) 36 µm, length of maximum thickening (c1) 60 µm, total length of thickening (c2) 85 µm; a/d 2.0; b/d 2.0; c1/d 3.3; c2/d 4.7. Hind tibia expanded, with comb of 13–14 setae, one seta near spur strongly S–shaped ( Fig. 3. D View FIGURE 3 ). Lengths and proportions of legs as in Table 3 View TABLE 3 .
Hypopygium ( Fig. 3. E–F View FIGURE 3 ). Tergite IX and laterosternites IX without long setae. Tergite IX medially concave. Anal point present. Superior volsella antero-medially fused and small, slightly rounded. Inferior volsella broad, with many glandular setae and dented margin along the inner margin of gonocoxite and placed caudally. Phallapodeme slightly curved, 29–36 µm long, joint with sternapodeme placed caudally. Transverse sternapodeme 12–17 µm wide. Small attachment point of lateral sternapodeme with phallapodeme placed and directed caudally. Gonostylus slender and slightly curved tapering, 24–31 µm long, with 3 subapical setae; megaseta 5 µm long. HR 2.0–2.5; HV 2.5.
Distribution. The specimens were collected in subtropical areas in Hubei Province (Oriental China).
Remarks: The new species is similar to C. prominens Fu, Saether et Wang 2009 , both species have small anal point; the sternapodeme inverted U-shaped, but can be separated by the antenna with 9 flagellomeres, AR 0.46, superior volsella with rounded-corner, gonostylus slender and slightly curved tapering in C. tumula sp. n. while C. prominens Fu et al. 2009 has antenna with 8 flagellomeres, AR 0.52, superior volsella triangular, gonostylus strongly curved medially. At present, there are four recorded species with anal point: C. cylindricauda Fu et al. 2009 ,
C. nankaiensis Fu et al. 2009 View in CoL , C. prominens Fu et al. 2009 View in CoL and C. tumula sp. n..
Adult female, pupa and larva: unknown.
TABLE 3. Lengths (in µm) and proportionsof legs segments of male C. tumula sp. n. (n=1–2)
| fe | ti | ta1 | ta2 | ta3 | ta4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p1 | 187 | 223 | 115 | 60 | 31 | 19 |
| p2 | 245 | 221 | 130 | 60 | 34 | 14 |
| p3 | 187–211 | 206–221 | 110–113 | 67 | 26–29 | 14–19 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Orthocladiinae |
|
Genus |
Corynoneura tumula
| Fu, Yue, Liu, Tian, Fang, Xiangliang, Wang, Qian & Wang, Xinhua 2018 |
C. tumula
| Fu & Liu & Fang & Wang & Wang 2018 |
C. nankaiensis
| Fu et al. 2009 |
C. prominens
| Fu et al. 2009 |