Colocasiomyia pinangae Zhang & Toda, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5278.2.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:697AC989-141D-4A89-8F02-5A4644E303EA |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7907976 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C687D9-FFC3-FFF6-A5C6-FAC3824CE335 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Colocasiomyia pinangae Zhang & Toda |
| status |
sp. nov. |
1) Colocasiomyia pinangae Zhang & Toda View in CoL , sp. nov.
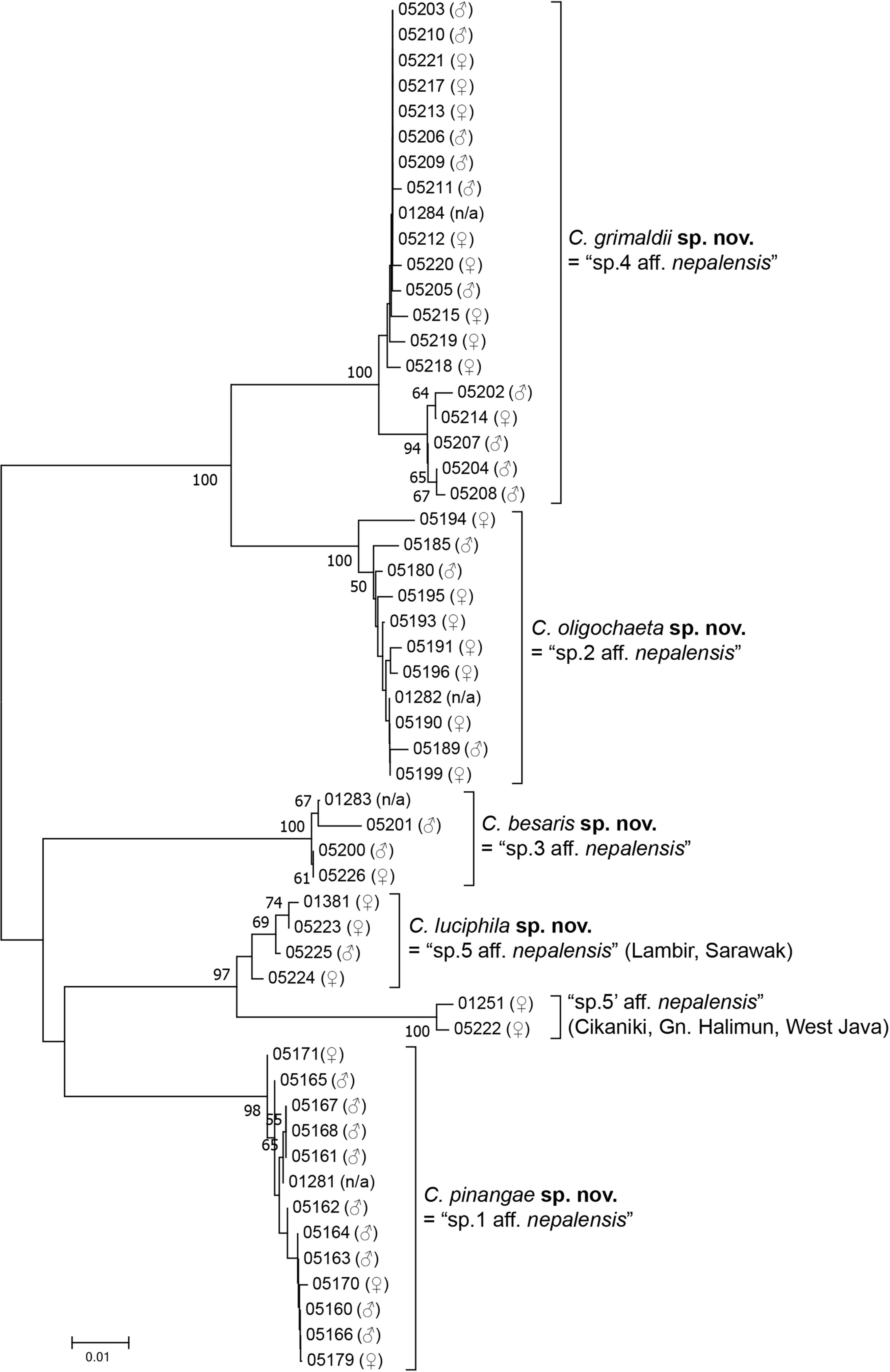
( Figs 2–12A View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 View FIGURE 7 View FIGURE 8 View FIGURE 9 View FIGURE 10 View FIGURE 12 , 14A View FIGURE 14 )
Colocasiomyia sp.1 aff. nepalensis: Sultana et al., 2006: 694 View in CoL ; Fartyal et al., 2013: 768.
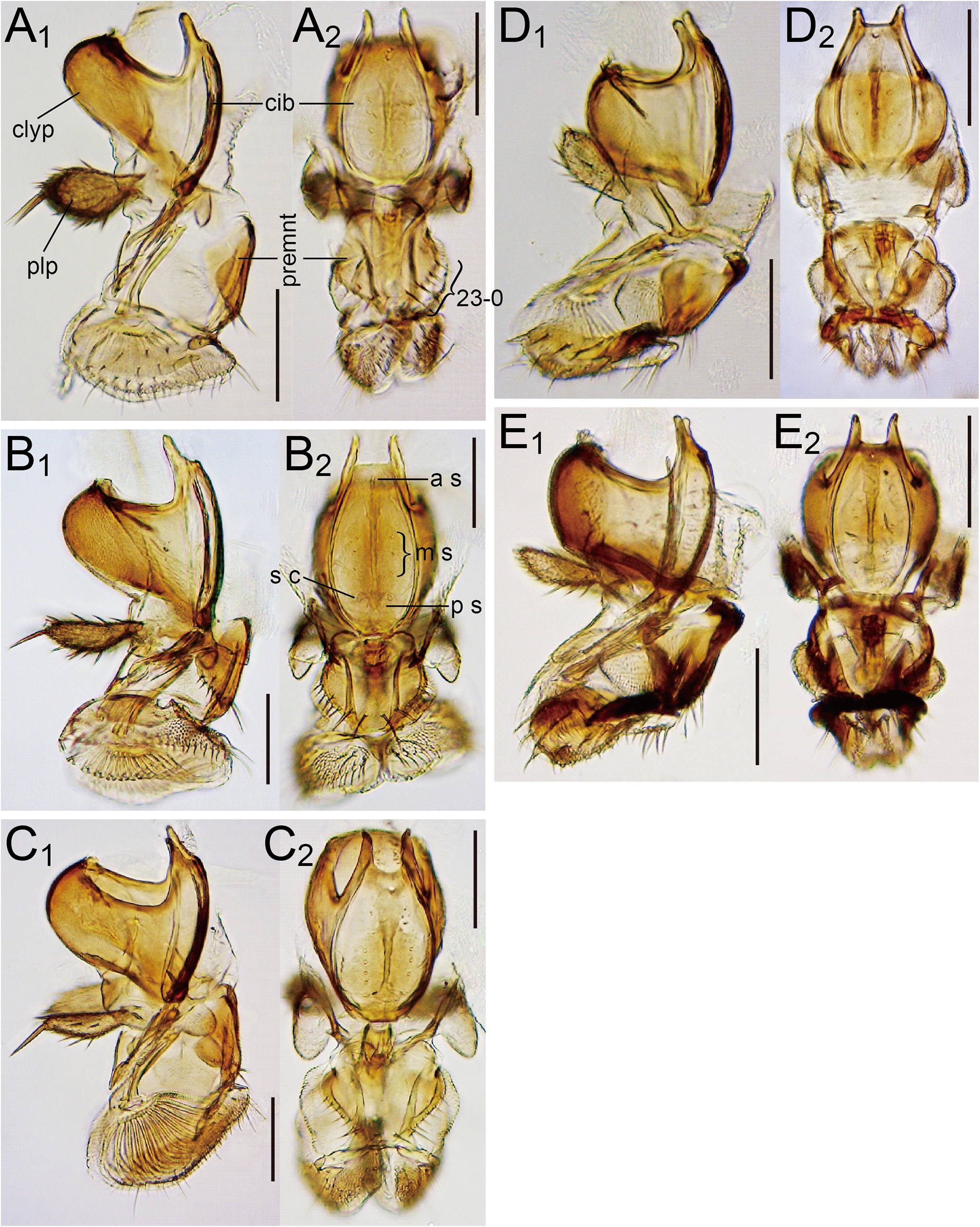
Diagnosis. Surstylus with 5–7 stout, short, peg-like teeth (Fig. 11-1A 2). Pregonites apically round, with coarse serrations on ventral margin (Fig. 11-1A 4). Epigynium with 11–12 sensilla per side near lower posterior margin ( Fig. 12A View FIGURE 12 1 View FIGURE 1 ). Distal, narrow portion of hypogynial valve slightly shorter than basal, broad portion ( Fig. 12A View FIGURE 12 ).
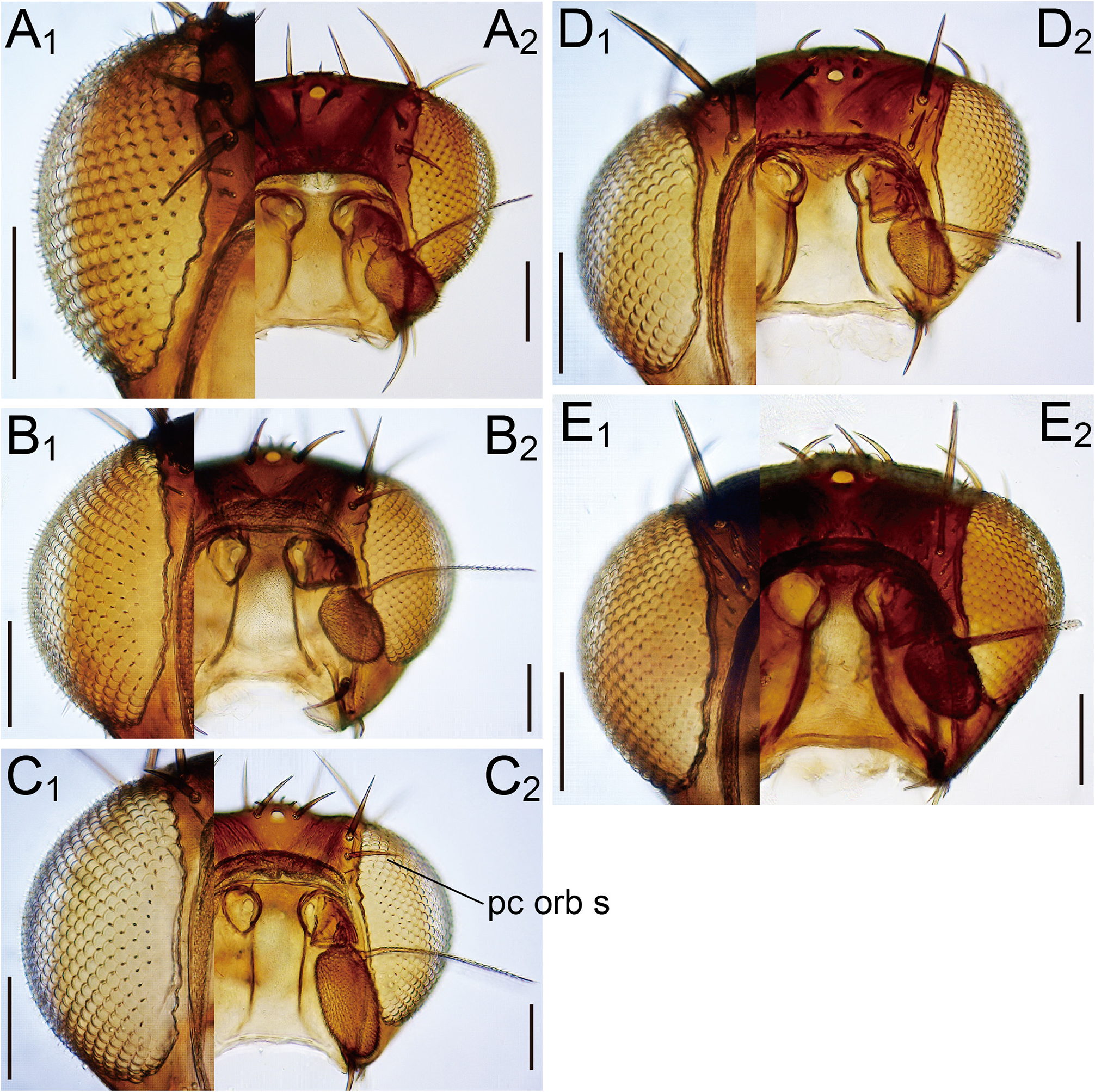
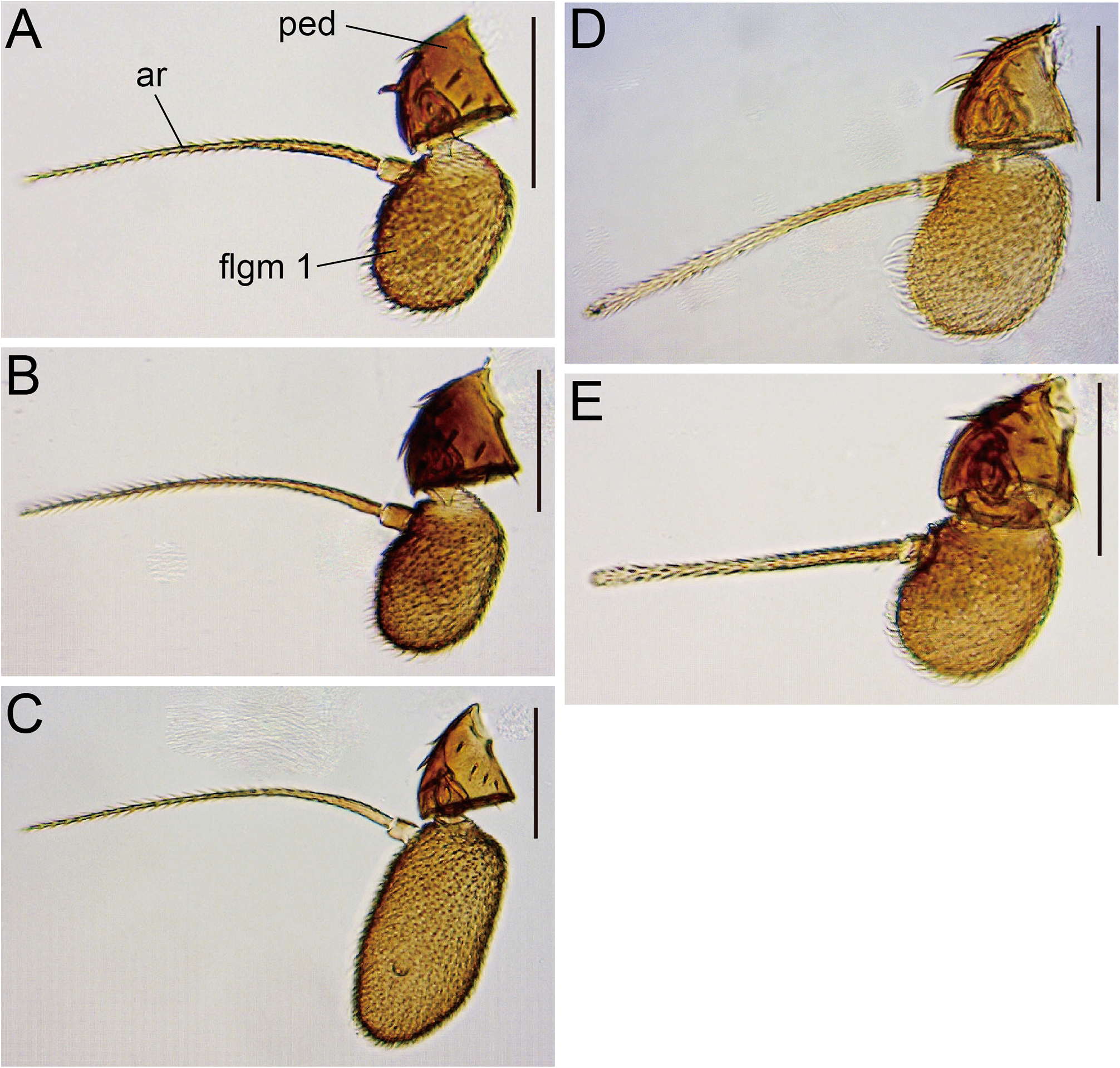
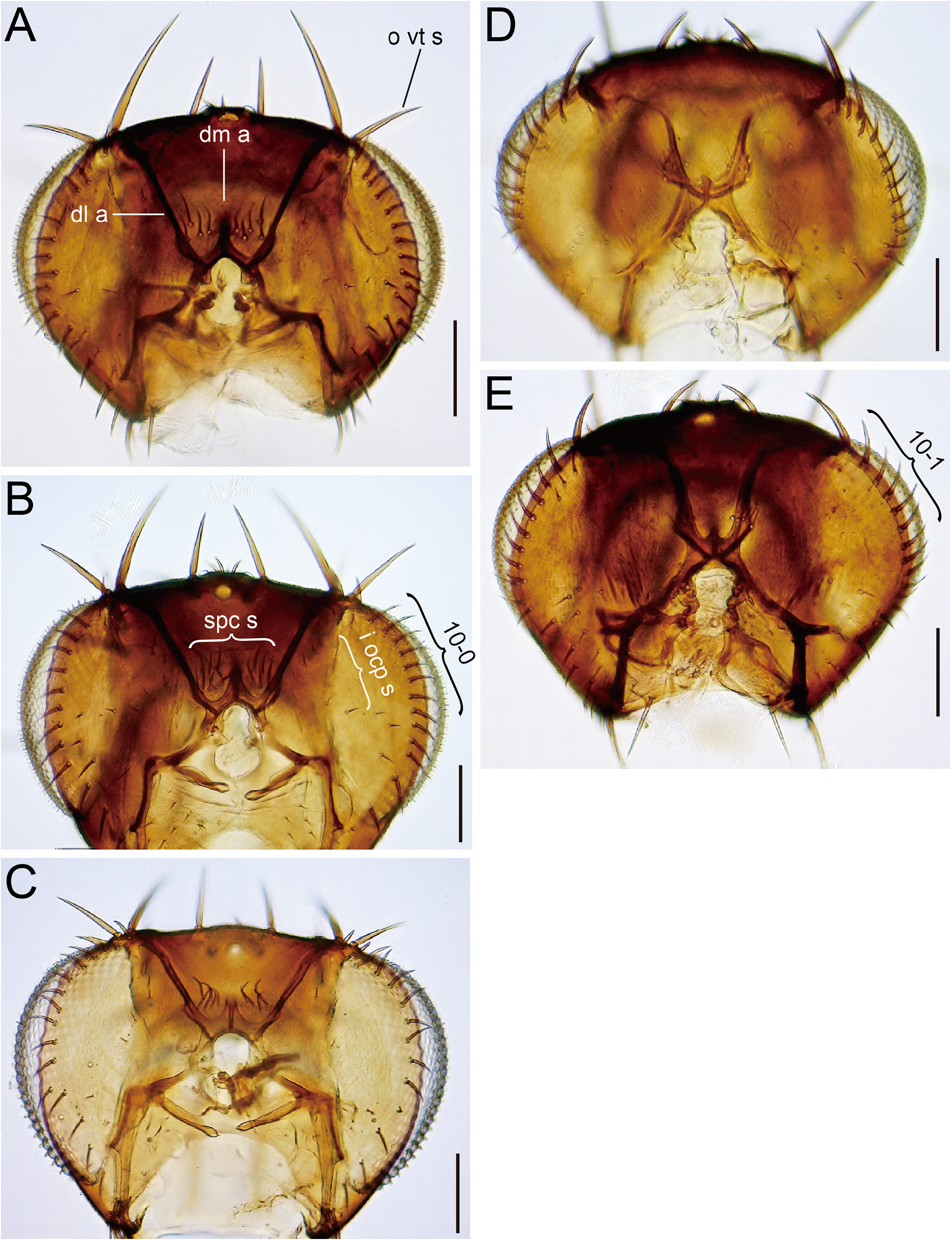
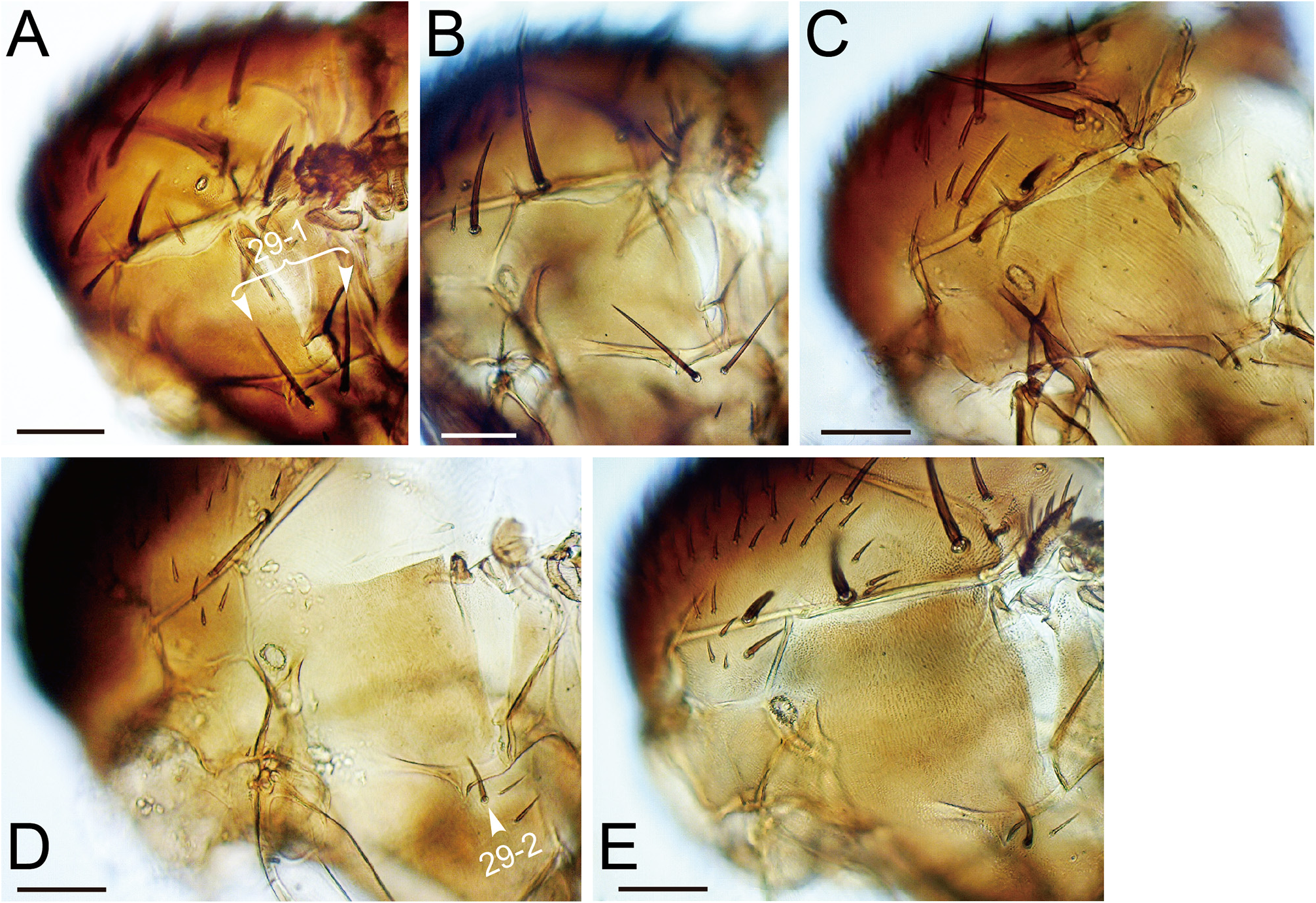
Description (♁ and ♀). Head. Antennal pedicel blackish brown; first flagellomere approximately 1.7 times as long as pedicel; arista approximately 2.1 times as long as first flagellomere ( Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ). Distance between antennal scapes narrower than scape diameter ( Fig. 2A 2 View FIGURE 2 ). Facial carina wider than 1st flagellomere ( Fig. 2A 2 View FIGURE 2 ). Supracervical setae 4–7 and postoculars 17–18 per side ( Fig. 4A View FIGURE 4 ). Cibarial projections at anterolateral corners as long as width of anterior margin; medial sensilla 2–4 per side ( Fig. 5A View FIGURE 5 2 View FIGURE 2 ). Prementum and neighboring lateral membrane with 7–8 setae per side ( Fig. 5A View FIGURE 5 2 View FIGURE 2 ). Labellum with 10 pseudotracheae per side ( Fig. 5A View FIGURE 5 1 View FIGURE 1 ).
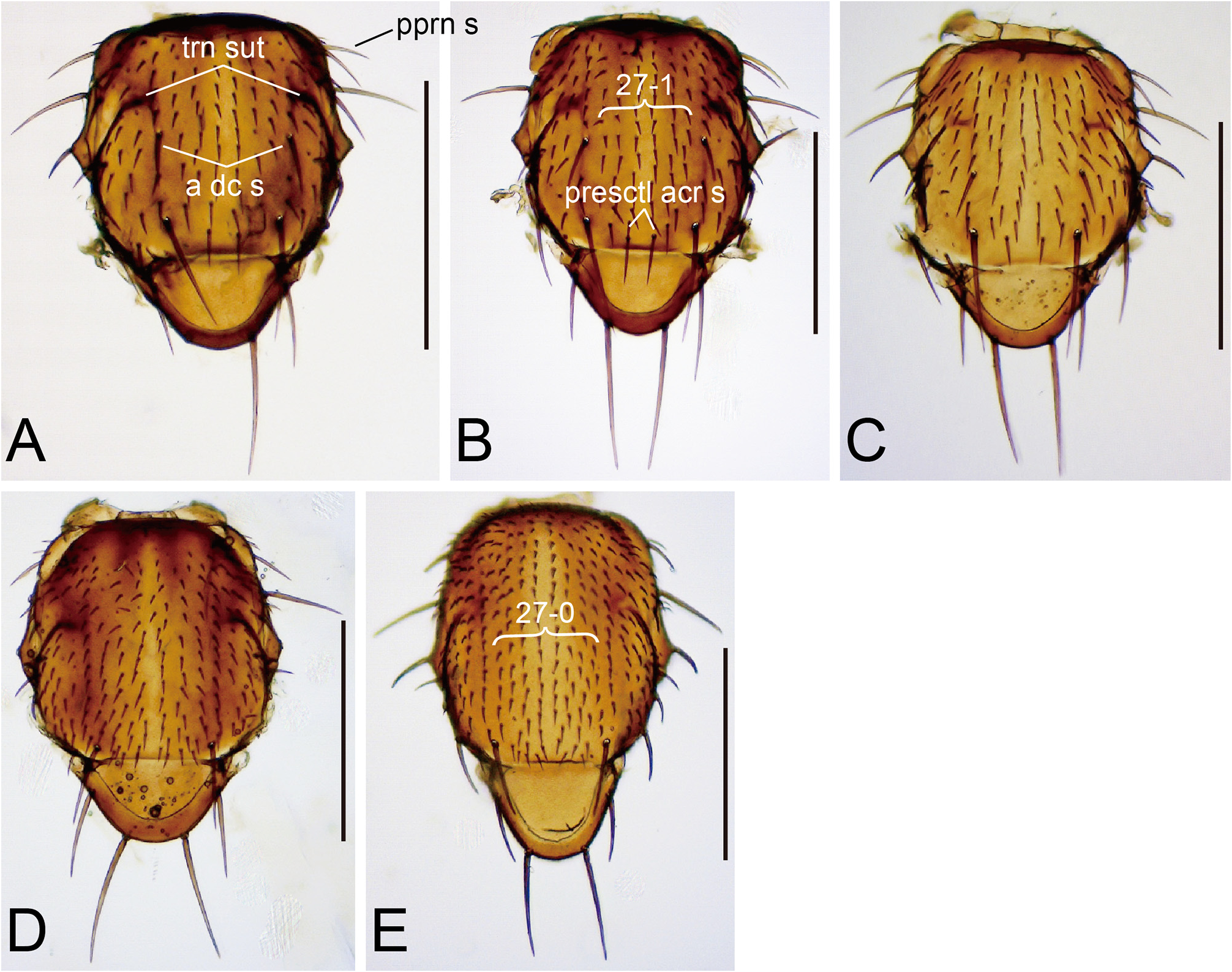
Thorax. Two katepisternal, prominent setae longer than acrostichal setulae ( Fig. 7A View FIGURE 7 ).
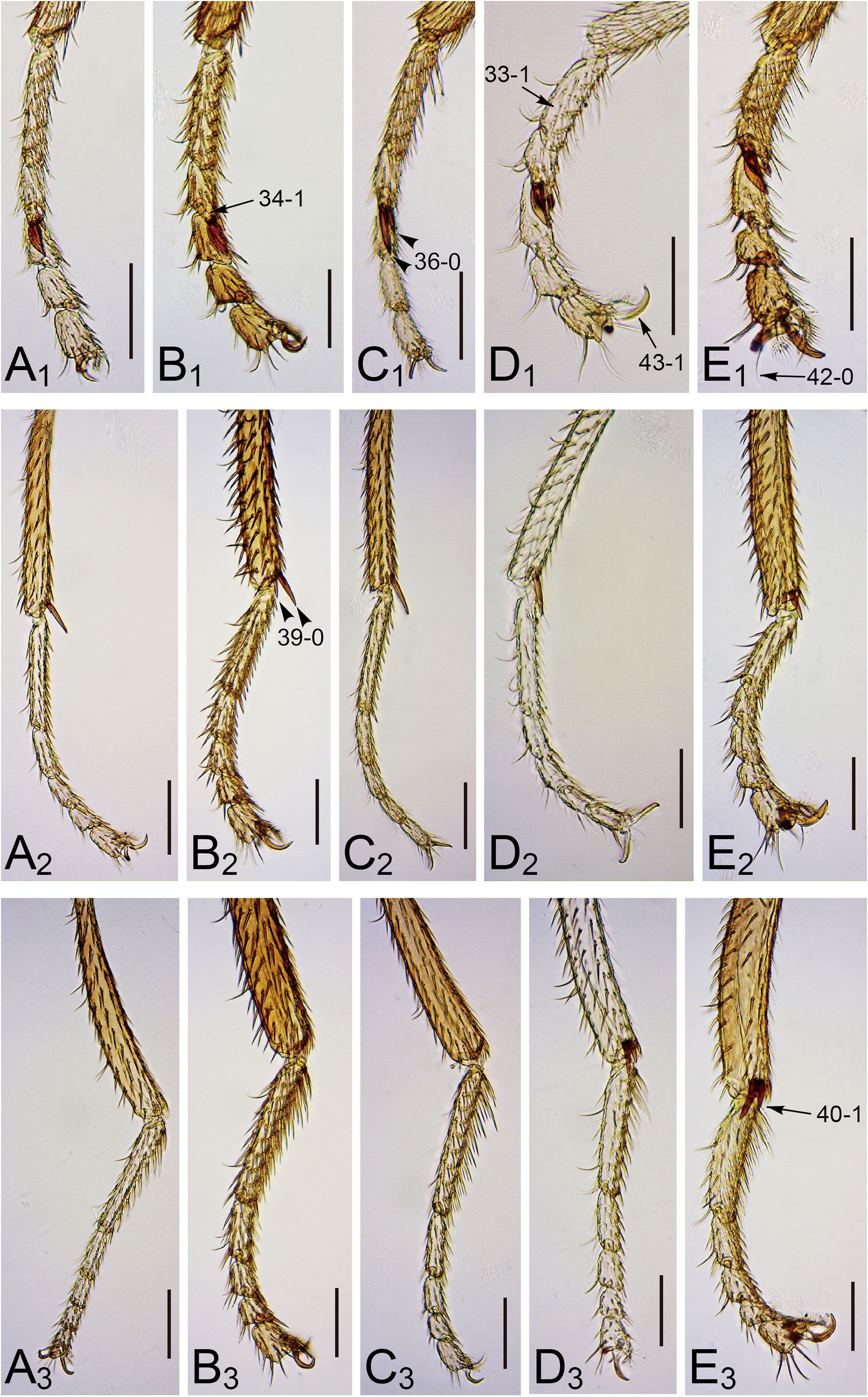
Legs grayish brown, except for fore tibiae and all tarsi pale grayish yellow ( Fig. 14A View FIGURE 14 ). Fore tarsomere I slightly longer than tarsomeres II and III combined; mid I as long as II+III+IV; hind I slightly longer than II+III+IV ( Fig. 9A View FIGURE 9 ). Fore tarsomere II with 1 large and 1 small pegs; latter 1/3 as long as former ( Fig. 9A View FIGURE 9 1 View FIGURE 1 ).
Abdomen. Tergites blackish brown ( Fig. 14A View FIGURE 14 ). Male sternites III and IV as wide as long; V+VI distally deeply bilobed ( Fig. 10A View FIGURE 10 1 View FIGURE 1 ). Female sternites III–V as wide as long; VI wider than long; VII wider than long plate bilobed in distal half ( Fig. 10A View FIGURE 10 2 View FIGURE 2 ). Female tergite VII caudomedially deeply notched.
Male terminalia. Epandrium with 2–4 long setae only on lateral to ventral portion (Fig. 11-1A 1). Cercus nearly entirely pubescent except for small, anteroventral, expanded flap, with approximately 37 setae (Fig. 11-1A 1). Phallal sheath not pubescent (Fig. 11-1A 4).
Female terminalia. Perineal membrane with patch of dense, distinct warts.
Measurements (holotype /range in 6♁ and 5♀ paratypes, in mm): BL (straight distance from anterior edge of pedicel to tip of abdomen) = 1.45/♁ 1.29–1.54, ♀ 1.43–1.62; ThL (distance from anterior notal margin to apex of scutellum) = 0.58/♁ 0.59–0.67, ♀ 0.60–0.67; WL (distance from humeral cross vein to wing apex) = 1.22/♁ 1.25–1.40, ♀ 1.23–1.44; WW (maximum wing width) = 0.60/♁ 0.58–0.66, ♀ 0.59–0.67.
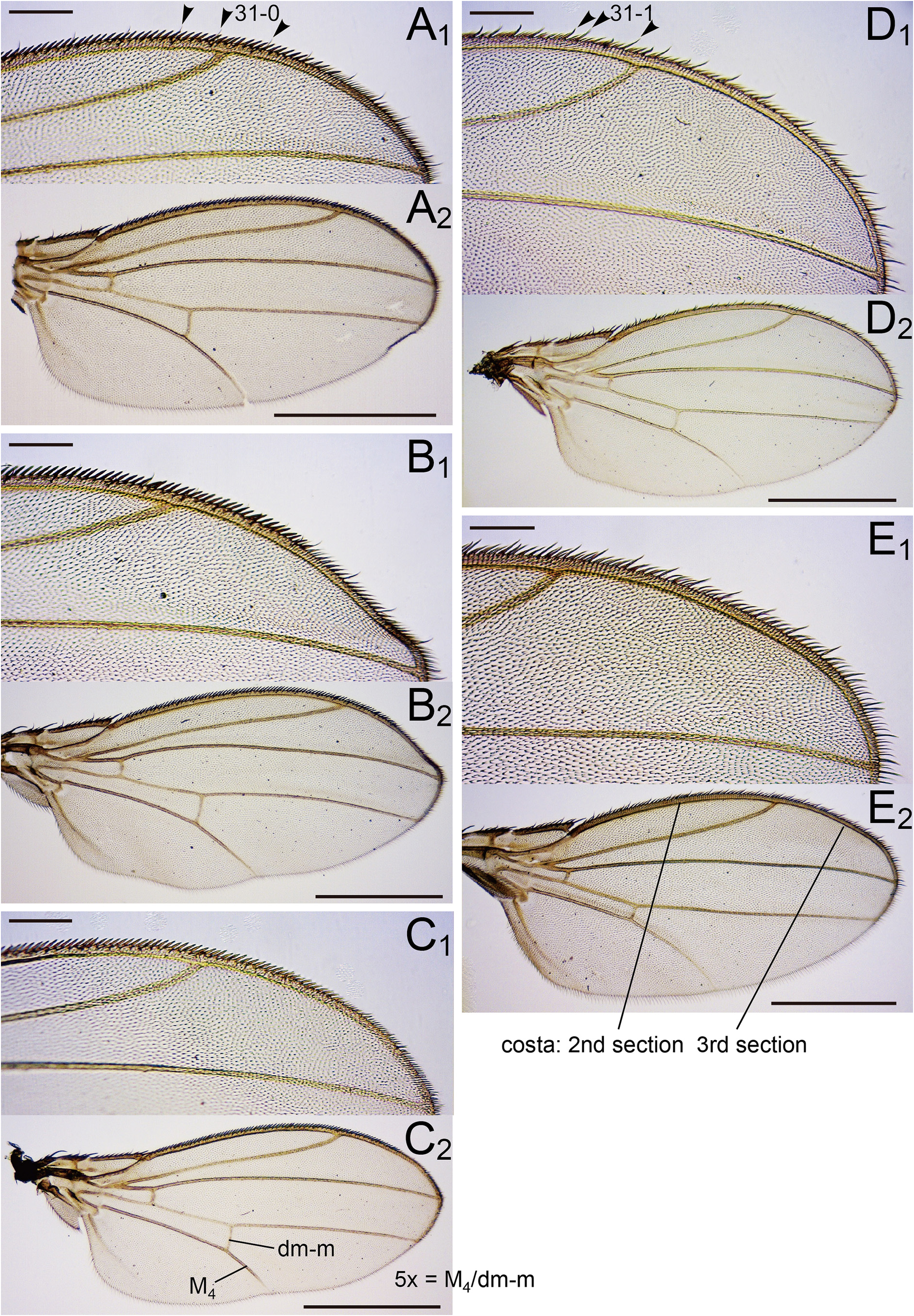
Indices (holotype /range in 6♁ and 5♀, or less if noted, paratypes, in ratio): FW/HW (frontal width / head width) = 0.55/0.53–0.60; ch/o (maximum width of gena / maximum diameter of eye) = 0.36/0.29–0.40; prorb (proclinate orbital seta length / posterior reclinate orbital seta length) = 0.85/0.84–0.97 (2♁, 1♀); rcorb (anterior reclinate orbital seta length / posterior reclinate orbital seta length) = 0.30/0.23–0.40 (3♁, 1♀); vb (subvibrissal seta length / vibrissa length) = 0.33/0.22–0.32; dcl (anterior dorsocentral seta length / posterior dorsocentral seta length) = 0.46/0.44–0.71 (4♁, 4♀); presctl (prescutellar acrostichal seta length /posterior dorsocentral seta length) = 0.42/0.25–0.40 (6♁, 4♀); sctl (basal scutellar seta length / apical scutellar seta length) = 0.54/0.54–0.63 (6♁, 4♀); sterno (anterior katepisternal seta length / posterior katepisternal seta length) = 1.00/0.94–1.26; orbito (distance between proclinate and posterior reclinate orbital setae / distance between inner vertical and posterior reclinate orbital setae) = 0.35/0.32–0.51; dcp (distance between ipsilateral dorsocentral setae / distance between anterior dorsocentral setae) = 0.50/0.57–0.65; sctlp (distance between ipsilateral scutellar setae / distance between apical scutellar setae) = 1.07/0.86–1.03; C (2nd costal section between subcostal break and R 2 +3 / 3rd costal section between R 2 +3 and R 4 +5) = 2.04/1.70–2.16; 4c (3rd costal section between R 2 +3 and R 4 +5 / M 1 between r-m and dm-m) = 1.46/1.30–1.54; 4v (M 1 between dm-m and wing margin / M 1 between r-m and dm-m) = 2.86/2.48–2.78; 5x (M 4 between dm-m and wing margin / dm-m between M 1 and M 4) = 3.18/2.50–3.35; ac (3rd costal section between R 2 +3 and R 4 +5 / distance between distal ends of R 4 +5 and M 1) = 2.63/2.24–3.04; M (M 4 between dm-m and wing margin / M 1 between r-m and dm-m) = 1.11/0.87–1.08; C3F (length of heavy setation in 3rd costal section / length of 3rd costal section) = 0.37/0.37–0.49.
Holotype. ♁ ( MZB), “ Cibodas , West Java, Indonesia, 12.xii.2004, K. T. Takano / ex inflorescence of Pinanga coronata ”.
Paratypes. Indonesia: 24♁, 26♀, same data as the holotype ( MZB, SEHU); 10 ♁, 10♀ (#05160–79), same data as the holotype except for 24.xii.2003 ( KIZ) .
Distribution. Indonesia (West Java).
Remarks. This species resembles C. nepalensis , but can be distinguished from it in having the shorter arista (in C. nepalensis : “2.5× the length of flagellomere I”; Grimaldi 1991), cibarial medial sensilla in parallel rows as wide as sensilla campaniformia (narrower than the latter; “ Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 ” in Grimaldi 1991), two equally long katepisternal setae (“Katepisternum … with 1 large seta”), and two pegs much different in size on the fore tarsomere II (“Tarsal segment on foreleg … bearing a pair of black, spine-like setae; medial one slightly longer”).
Etymology. Referring to the host-plant genus Pinanga .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Colocasiomyia pinangae Zhang & Toda
| Zhang, Guang, Gao, Jian-Jun, Takano, Kohei Takenaka, Yafuso, Masako, Suwito, Awit, Meleng, Paulus Ak & Toda, Masanori J. 2023 |
Colocasiomyia sp.1 aff. nepalensis:
| Fartyal, R. S. & Gao, J. J. & Toda, M. J. & Hu, Y. G. & Takano, K. T. & Suwito, A. & Katoh, T. & Takigahira, T. & Yin, J. T. 2013: 768 |
| Sultana, F. & Hu, Y. G. & Toda, M. J. & Takenaka, K. & Yafuso, M. 2006: 694 |