Chondracanthus kabatai, Aneesh & Helna & Kumar, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1590/2358-2936e2020014 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10933621 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039387FA-2E16-FF99-FC1B-FCBDFB31F83B |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Chondracanthus kabatai |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Chondracanthus kabatai View in CoL sp. n.
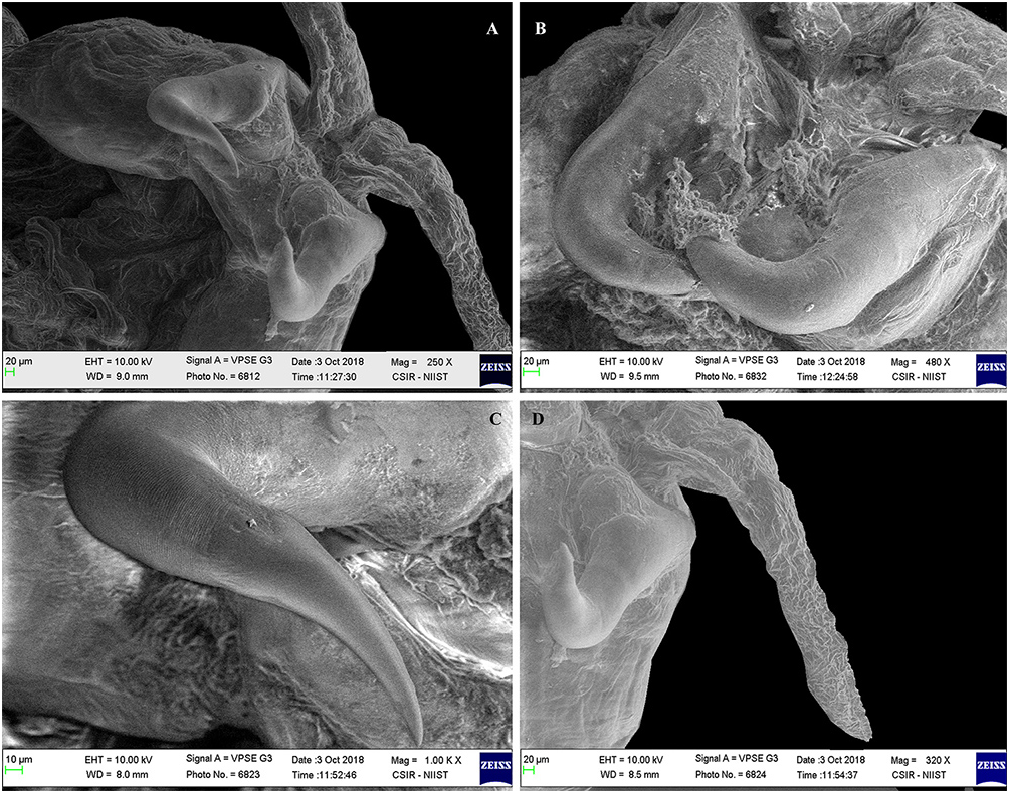
( Figs. 7–14 View Figure 7 View Figure 8 View Figure 9 View Figure 10 View Figure 11 View Figure 12 View Figure 13 View Figure 14 )
Zoobank: urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:E317CB1A-EB5B-4D91-A651-11F124C11168
Material examined: 37 females (30 ovigerous), all with immature/mature males.
Typematerial. Holotype: 1 female (6.5 mm) (ZSI/ WGRC /IR/INV/11728) from Zenopsis conchifer Lowe, Neendakara, Quilon , India, coll. P. T. Aneesh and A. Biju Kumar on 26 February2018 .— Paratypes: same information as holotype, 1 female (8 mm) (ZSI/ WGRC /IR/INV/11729) ; 1 male (0.5 mm) (ZSI/ WGRC /IR/INV/14049) ; 1 female (8 mm) (ZSI/ WGRC /IR/INV/11730) ; 1 female (7.5 mm) (ZSI/ WGRC /IR/INV/11731) ; 1 female (8 mm) (ZSI/ WGRC /IR/INV/11732) .
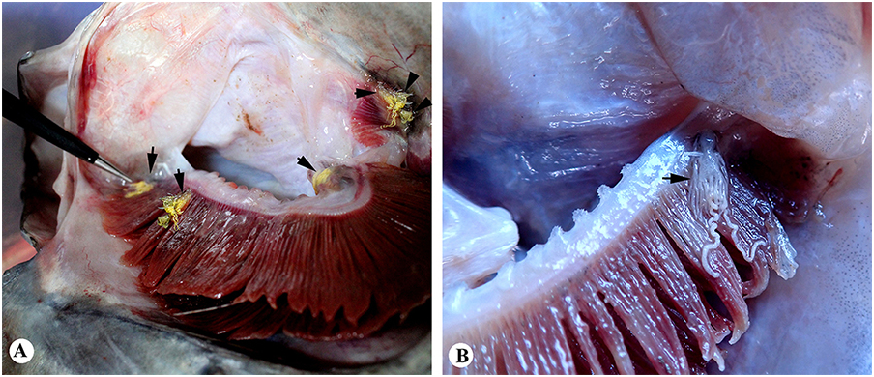
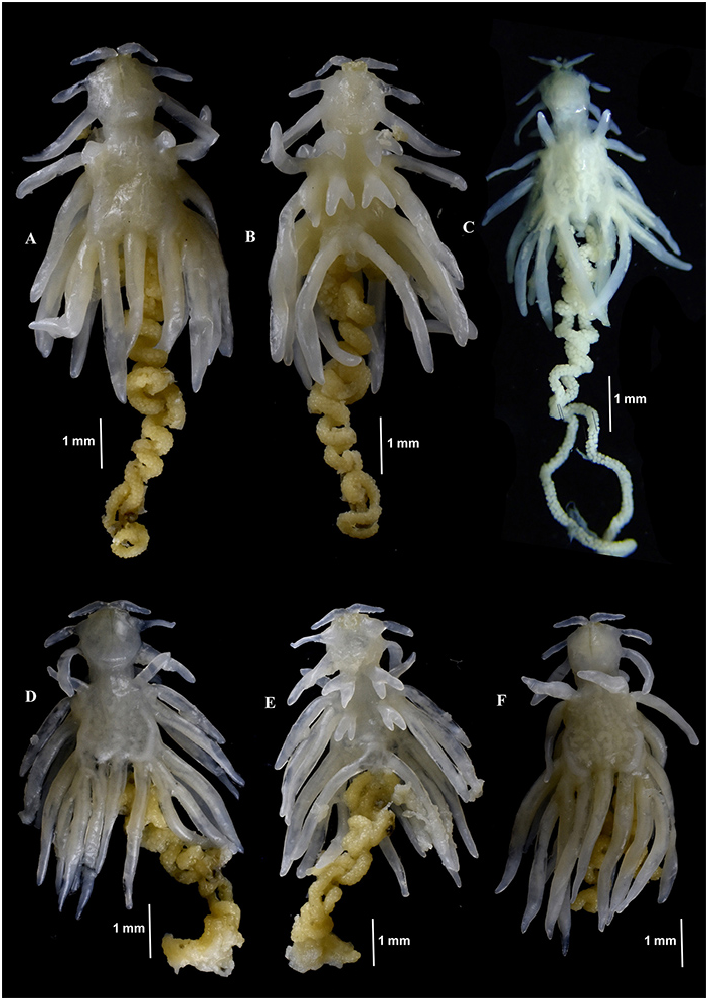
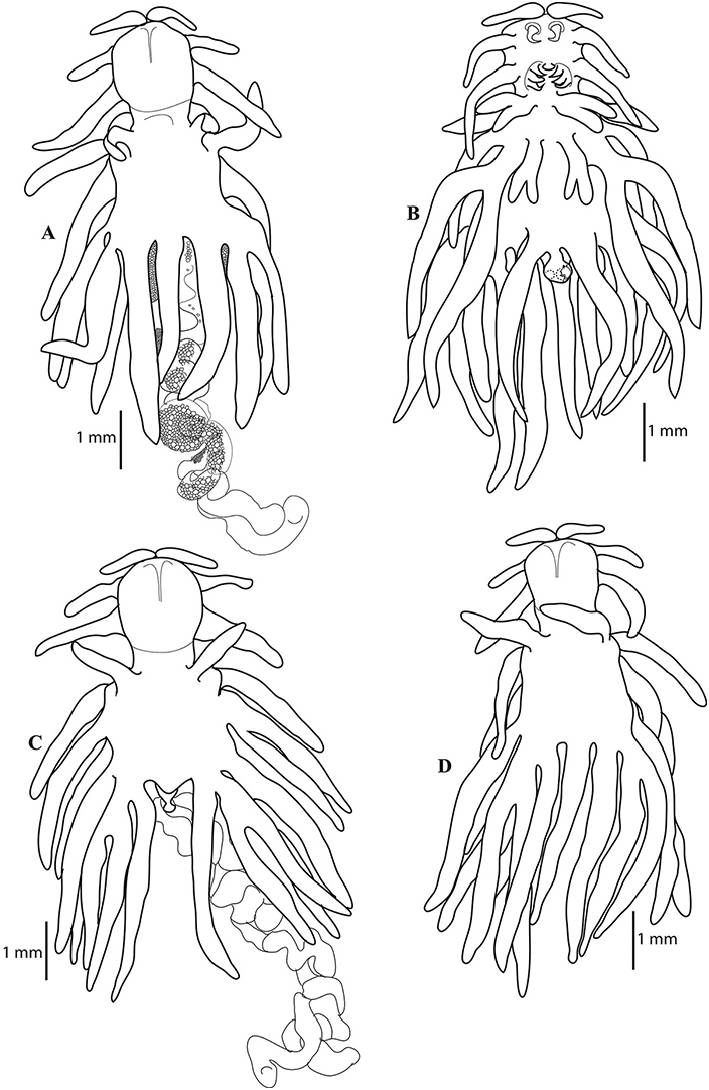
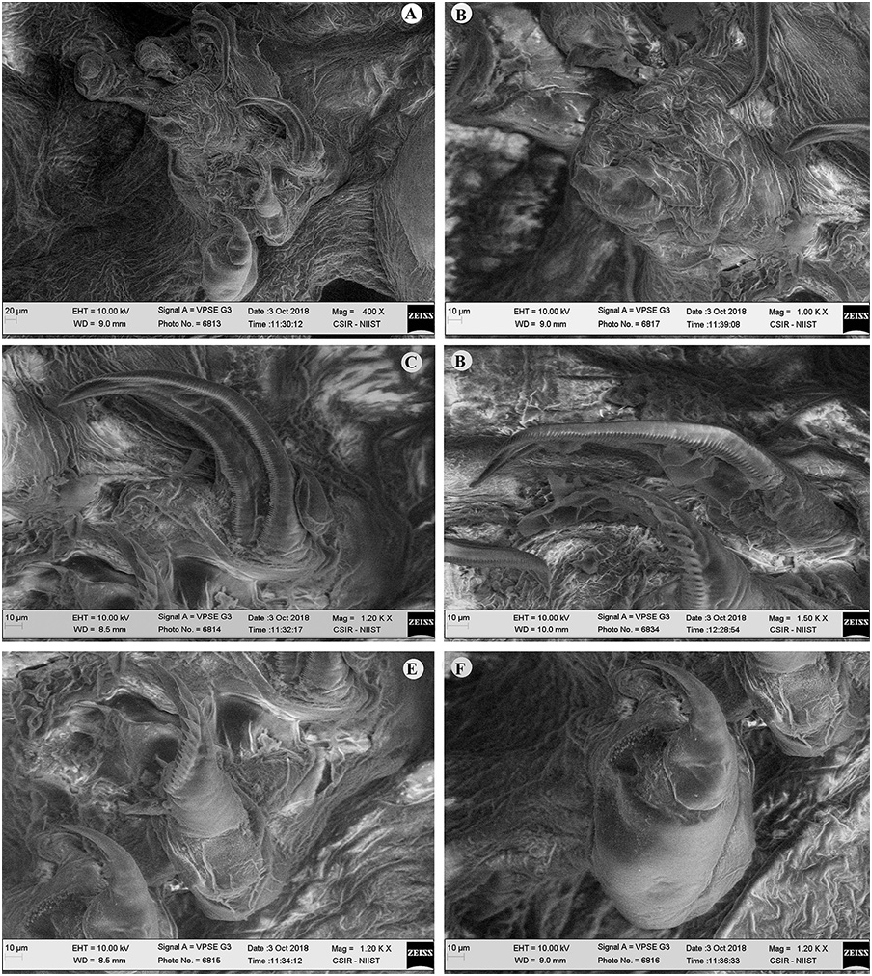
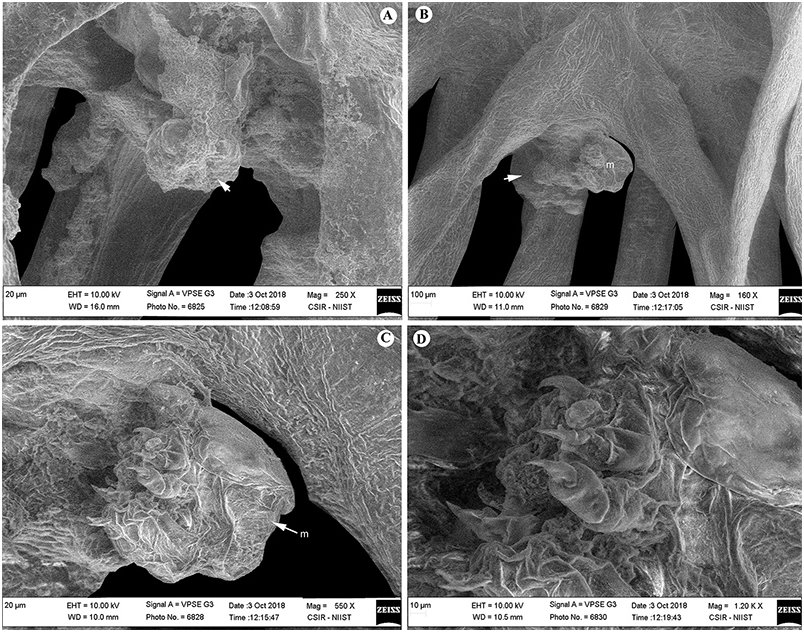
Description. Female ( Figs. 8–14 View Figure 8 View Figure 9 View Figure 10 View Figure 11 View Figure 12 View Figure 13 View Figure 14 ): Body 4.8–8.0 mm length (without egg strings, from anterior margin of head to distal end of longest posterior processes on trunk), unsegmented, divisible into head, short neck, stout trunk and genito-abdomen. Cephalon having cephalosome, as long as wide, with two pairs of elongated and fusiform, pedunculate ventro-lateral processes, the second process about 1.8–2 times longer than process 1. Cephalon dorsally bearing medial longitudinal sclerotized bar. Neck, short and narrow without processes. Trunk much broader, armed with elongated, narrow, fusiform processes; three pairs of anterior, three pairs of posterior and single posteriomedian. Anterior processes including (1) pair of dorsal (1.0– 1.2 mm long), horn-like, on either side close to the lateral margin, directed forward; (2) pair of long (2.1–2.4 mm long), laterally directed, from the lateral margin; and (3) pair of much longer, bifurcate (outer one (3.1–3.2 mm long), inner one much longer (4.2–4.4 mm long)), from the ventral side near to either side of second pair of legs. Posterior processes including (1) pair of ventro-lateral, from the corner (3.5–3.7 mm long); (2) pair at posterior corner, much longer, trifurcate (outer one (3.3–3.4 mm long), middle (3.5–3.6 mm long), and inner (3.9–4.2 mm long)); (3) single, median processes (3.8–4.1 mm long) (much reduced in two specimens ( Fig. 9 c View Figure 9 )) on dorsal side, apparently intersect the lateral processes; (4) a paired, long process on ventral surface (3.5–3.6 mm long), close to either side of median line, just above genito-abdomen. Genito-abdomen (0.25–0.3 mm, long; 0.2 mm wide) globular, longer than wide. Genital complex with pair of setules in midventral region bearing egg strings. Abdomen 2 times wider than long (0.16 mm wide, 0.08 mm long). Caudal ramus conical, directed ventrally and armed with two ventral setae, one dorsal seta and apical conical spinulose papilla.
Egg strings cylindrical, yellow colored, irregularly coiled and extremely longer than trunk; eggs multiseriate. Number of eggs per string ranged from 370 to 440, depending on length of the string.
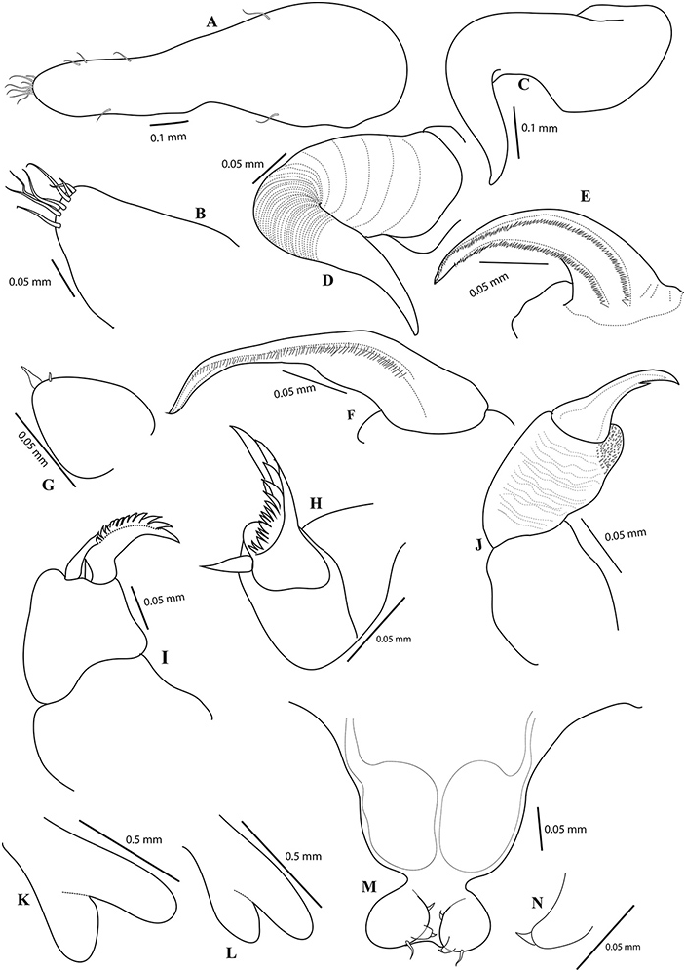
Antennule, cylindrical, unsegmented and fleshy, basally swollen, and distally slender with few marginal setae, apex with 5–6 long and 2–3 short terminal setae. Antenna, usual form with unarmed basal segment; distal segment, strongly curved, heavily sclerotized, marked by band of transverse surface striations at the base, apex, pointed and curved terminal claw. Mandible, distal segment apically curved, with many teeth (118–124) on convex side and 80–86 teeth on concave side. Maxillule, lobate, tipped with two unequal apical spinules.Two-segmented maxilla; first segment unarmed; terminal segment with a robust seta in basal region, and the outer margin claw-like, armed with row of 16–22, 11–16 denticles.Maxilliped, 3-segmented; first segment robust, unarmed; second segment with a patch of minute spinules on inner edge; distal segment, small, ending in curved claw-like structure with small, subterminal hooklet on inner surface. Legs biramous, both rami bearing spinules/ pectinate scales on terminal portion, protopod bearing outer seta. Leg 1 (0.7–0.9 mm long) slightly larger than leg 2 (0.6–0.7 mm long), situated ventrally on trunk region.
Male ( Figs. 13–14 View Figure 13 View Figure 14 ): Body 0.4–0.5 mm long (including caudal rami), 0.23 mm wide, curved ventrally, cephalothorax, more than half length of total body; metasome cylindrical, with indistinct metamerism. Genital segment with pair of ventral genital ridges. Caudal ramus directed posteriorly.
Antennule elongated, with armature formula 1 and 7–8. Antenna, robust, strongly curved, sharp claw. Mandible with 16–20 teeth on convex side and 14–16 teeth on concave side. Maxillule with 2 setae. Maxilla without teeth on terminal process. Maxilliped article 2 with few denticles. Legs bilobate, legs 1 and 2 subequal, with a long lateral seta; endopods reduced to lobes.
Size. Ovigerous female (4.8–8.0 mm length).
Color: White after fixation, with yellow egg sac.
Host: Zenopsis conchifer Lowe. View in CoL
Distribution: Known only from the type locality at Neendakara, Southwest coast, India.
Site of attachment: Attached to the floor of the buccal cavity, over the gill.
Etymology: This species is named in honor of recently deceased Prof. Zbigniew Kabata, one of the pioneer researchers on parasitic copepods of fish and world-renowned fish parasitologist.
| T |
Tavera, Department of Geology and Geophysics |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |