Cacomantis addendus Rothschild & Hartert, 1901
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5091.1.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:964647F3-9828-4E34-A495-67E03BAFC2EF |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5840626 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E287AE-FFA2-FFBC-86B2-69FCFDB4FC6D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Cacomantis addendus Rothschild & Hartert, 1901 |
| status |
|
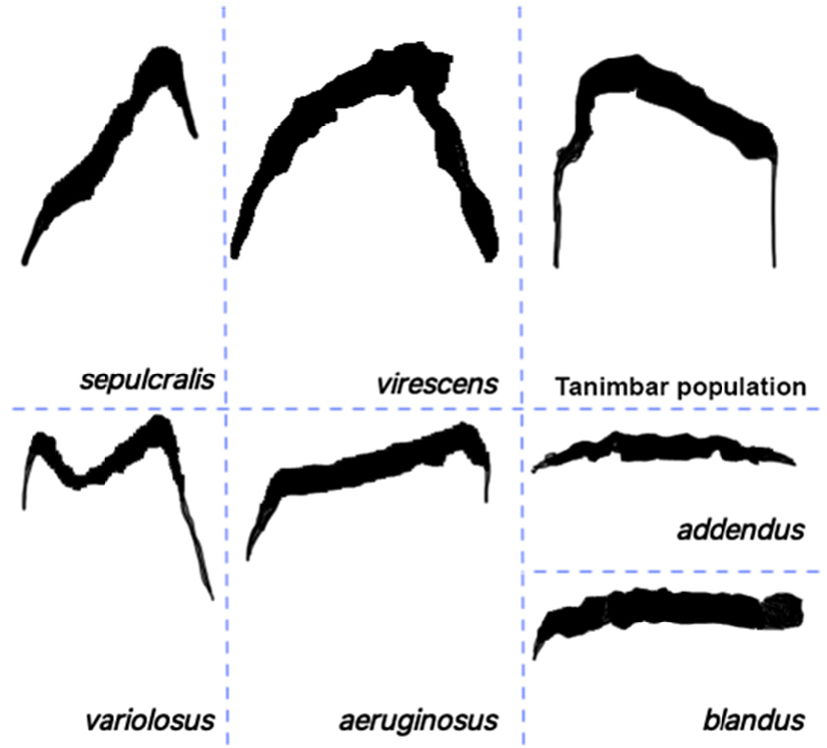
4.6 Cacomantis addendus Rothschild & Hartert, 1901
Range: Solomon Islands, from Buka and Bougainville south to Makira ( San Cristobal).
Diagnosis: main song of one type or blended with a second ‘where’s the tea’ vocalization, elements of the main song long and flattened, resembling those of blandus from the Admiralty Islands , but still longer and slower paced ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ); basic morph of Solomons morphotype (see 3.2.2.(5) above); body medium-sized and tail proportionally long: wing c. 113–123 mm, tail/wing ratio 1.09–1.15 ( Table 2 View TABLE 2 ); barred females with dorsa dully barred black on dark cinnamon, and ventral white heavily barred black and pervasively washed cinnamon; juveniles dark in tone and coarsely mottled and barred black on tawny-cinnamon, extending to very broad rufous barring in outer rectrices. Element length, slow song pace and chimeric character of the main song, where main song and ‘brain-fever’ call run into each other, are unique and render the Solomon population bioacoustically distinct. So does the pervasive rufous wash over the ventrum in barred-morph females and over dorsum and through outer rectrices in juveniles .
Except for Rothschild & Hartert (1901), C. addendus has, until now, been treated as a subspecies of variolosus by all reviewers since Hartert (1925).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |