Begonia hispidissima Zipp. ex Koord. [§ Petermannia
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.24823/EJB.2022.405 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10524591 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FFFE04-FFB7-FFC1-FF94-1075993FFACA |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Begonia hispidissima Zipp. ex Koord. [§ Petermannia |
| status |
|
8. Begonia hispidissima Zipp. ex Koord. [§ Petermannia View in CoL ], Meded. Lands Plantentuin 19: 485 (1898).
– Type: Indonesia, Sulawesi, Minahasa , 10 iv 1895, Koorders, S.H. 16241B (lectotype K [K00076118], isolectotypes B [B100238031], BO, L [ L0701074 ], designated by Smith & Wasshausen [1983: 444]. Figure 6 View Figure 6 .
Perennial, monoecious herb, erect, up to c. 35 cm tall. Stem densely hairy; internodes 2–5.5 cm long, slightly swollen at the nodes, brownish-reddish, densely hairy. Leaves basifixed, alternate; stipules semi-persistent, 5–8 × 2.5–4.5 mm, ovate, with an abaxially slightly prominent midrib, apex narrowed into a bristle projecting up to c. 2 mm, margin entire, cream-coloured, abaxially hairy; petioles 1–3 cm long, terete, not channelled, concolorous with the stem, glabrous; lamina 6.5–9.5 × 3–7 cm, asymmetrical, elliptic, base oblique, slightly cordate and lobes not or just slightly overlapping, apex acuminate, margin serrate to biserrate, adaxial surface green, with red veins, densely hairy, abaxially pale green with red veins, hairy; venation pinnate, secondary veins craspedodromous. Inflorescences protogynous, female inflorescences on node basal to male or separated; female inflorescences 2-flowered, peduncles 1–2 cm long, hairy; male inflorescences racemose-cymose (a thyrse), with up to 3 cymose partial inflorescences, each dichasially or dichasially-monochasially branching with up to 4 flowers, peduncle of partial inflorescence up to c. 15 mm long, bracts caducous. Male flowers: pedicels 10–15 mm long, white-pinkish, glabrous; tepals 2, white to white tinged with pink, 7–11.5 × 6–11.5 mm, ovate to broadly ovate, base slightly cordate, apex rounded, outer surface glabrous; androecium of 38–40 stamens, yellow, filaments up to c. 1 mm long, slightly fused at the very base, anthers up to c. 1 mm long, oblong to narrowly obovate, dehiscing through unilaterally positioned slits that are c.1/2 as long as the anthers. Female flowers: pedicels 8–12 cm long, pale green, pubescent; tepals 5, white tinged pink, subequal, 9.5–16 × 6–12 mm, ovate to elliptic, margin serrulate, and ciliate, outer surface hairy; ovary (excluding wings) 7–13 × 3–4.5 mm, ellipsoid, pale green, hairy, locules 3, placentation axile, placentae bilamellate, wings 3, equal, light green, base mostly cuneate, sometimes rounded, apex truncate to subtruncate, up to 4 mm at the widest point (apically or subapically); style c. 3.5 mm long, basally fused, 3-branched, each stylodium bifurcate in the stigmatic region, stigmatic surface a spirally twisted papillose band, orange. Fruits: peduncles c. 2 cm long, pubescent; pedicels 13–23 mm long, pendulous, slightly recurved; seed-bearing part ellipsoid, 15–17 × 6.5–8 mm (excluding the wings), hairy, dehiscent, splitting along the wing attachment, wings shape as for ovary, up to 10 mm at the widest point (apically or subapically). Seeds barrel-shaped, c. 0.2 mm long.
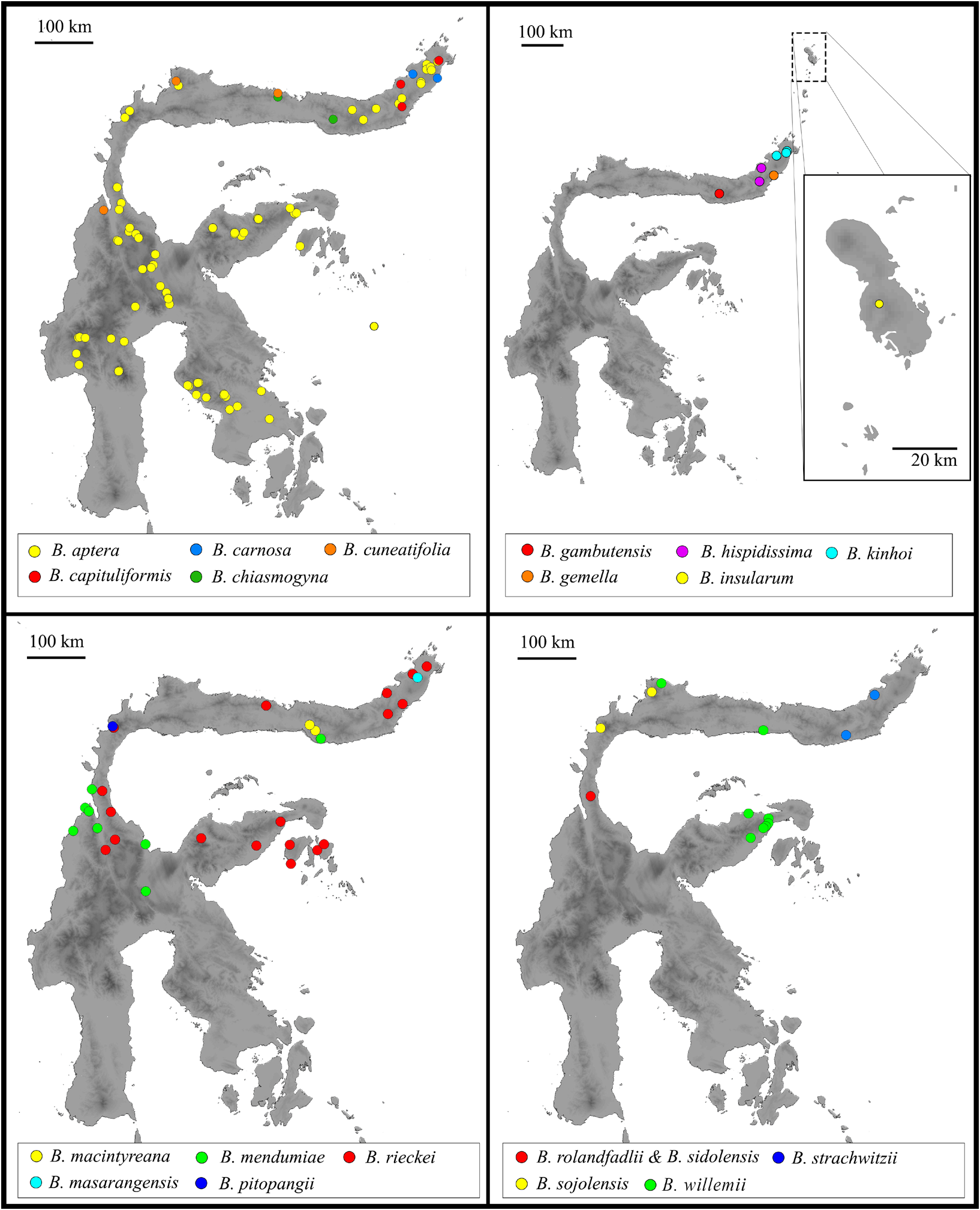
Distribution. Indonesia: endemic to Sulawesi, North Sulawesi Province (central North biogeographical region), Bolaang Mongondow, Minahassa (see Figure 2 View Figure 2 ).
Habitat. Secondary upland forest, on steep slopes, semi-shaded, at 1200–1400 m elevation.
Proposed IUCN conservation category. Data Deficient ( DD). This species is known only from limited collections, including the type specimen in Minahassa and two other collections from Gunung Ambang Nature Reserve (Bolaang Mongondow). The forests in the wider area, especially on Gunung Ambang , are poorly explored. Consequently, we assess this species as Data Deficient ( IUCN Standards and Petitions Subcommittee, 2019).
Additional specimens examined. INDONESIA. Sulawesi. Northern arm of Sulawesi. Eastern North Sulawesi: Bolaang Mongondow, Gunung Ambang Forest Reserve , 2 xi 2016, S. Barber BAAK37, BAAK45, BAAK46 (all BO, E) .
Begonia hispidissima is similar to B. masarangensis in its dense indumentum on the stems and leaves, and the elliptic leaves with serrate to biserrate margin. However, it can be differentiated by several characters such as the male inflorescence thyrse consisting of 2 or 3 partial cymose inflorescences (vs male flowers in simple monochasia) and 2-flowered female inflorescences with 8–12 mm long pedicels (vs 1-flowered with pedicels ≤ 7 mm long).
| DD |
Forest Research Institute, Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |