Aculodes mongolicus Skoracka et Shi, 2001
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.4620032 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4620052 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B02F61-FFEE-FFBD-7A53-E2C1ABB355CF |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Aculodes mongolicus Skoracka et Shi |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Aculodes mongolicus Skoracka et Shi sp. nov.
Description
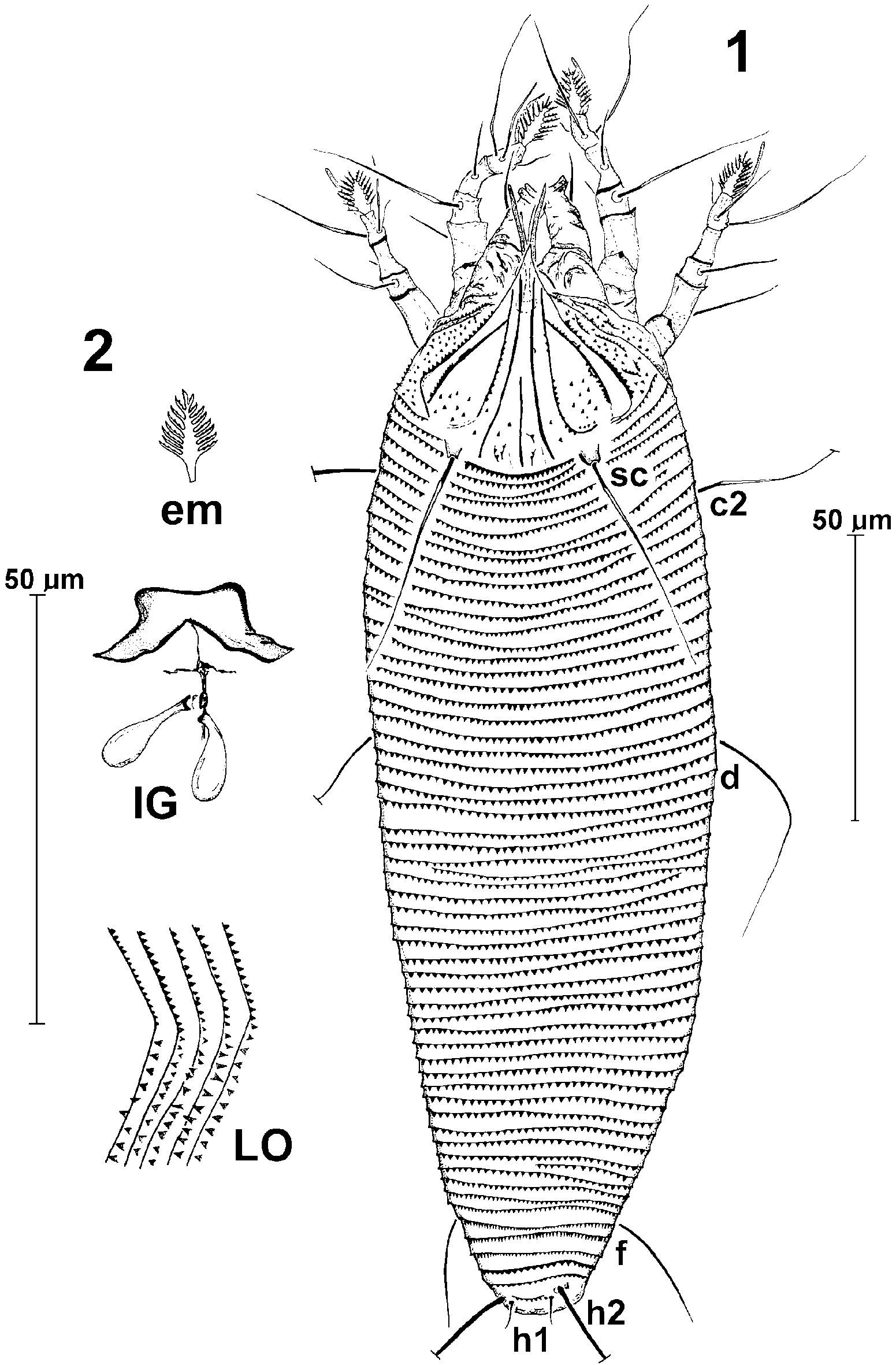
Female ( Figs 15 View FIGURES 12 View FIGURE 12 View FIGURES 56 ) (holotype and 9 paratypes): body length 204 (197257); width 59 (5963); body spindleform. Gnathosoma 22 (2228) long; dorsal pedipalpal genual setae d 12 (1012) long; v setae 2 long; ep seta 4 (34) long; cheliceral stylets 23 (2427) long, almost straight. Prodorsal shield triangular, 46 (4246) long, 43 (4244) wide, with pronounced, elongated and pointed frontal lobe over the gnathosoma; median line present in the posterior ½ part of the shield; admedian lines entire, parallel to each other, in the posterior ½ part of the shield diverging to lateral margins; I submedian lines subparallel to admedian, running laterad just in front of tubercles sc; II submedian lines beginning from 1/3 I submedian lines and forming bows reaching posterior margin of shield. Triangular microtubercles present on the shield, often along lines. Tubercles sc large, located on the rear margin of shield, 4 (4) long, 4 (4) wide, 29 (2629) apart; setae sc 45 (4245) long, projecting to the rear.
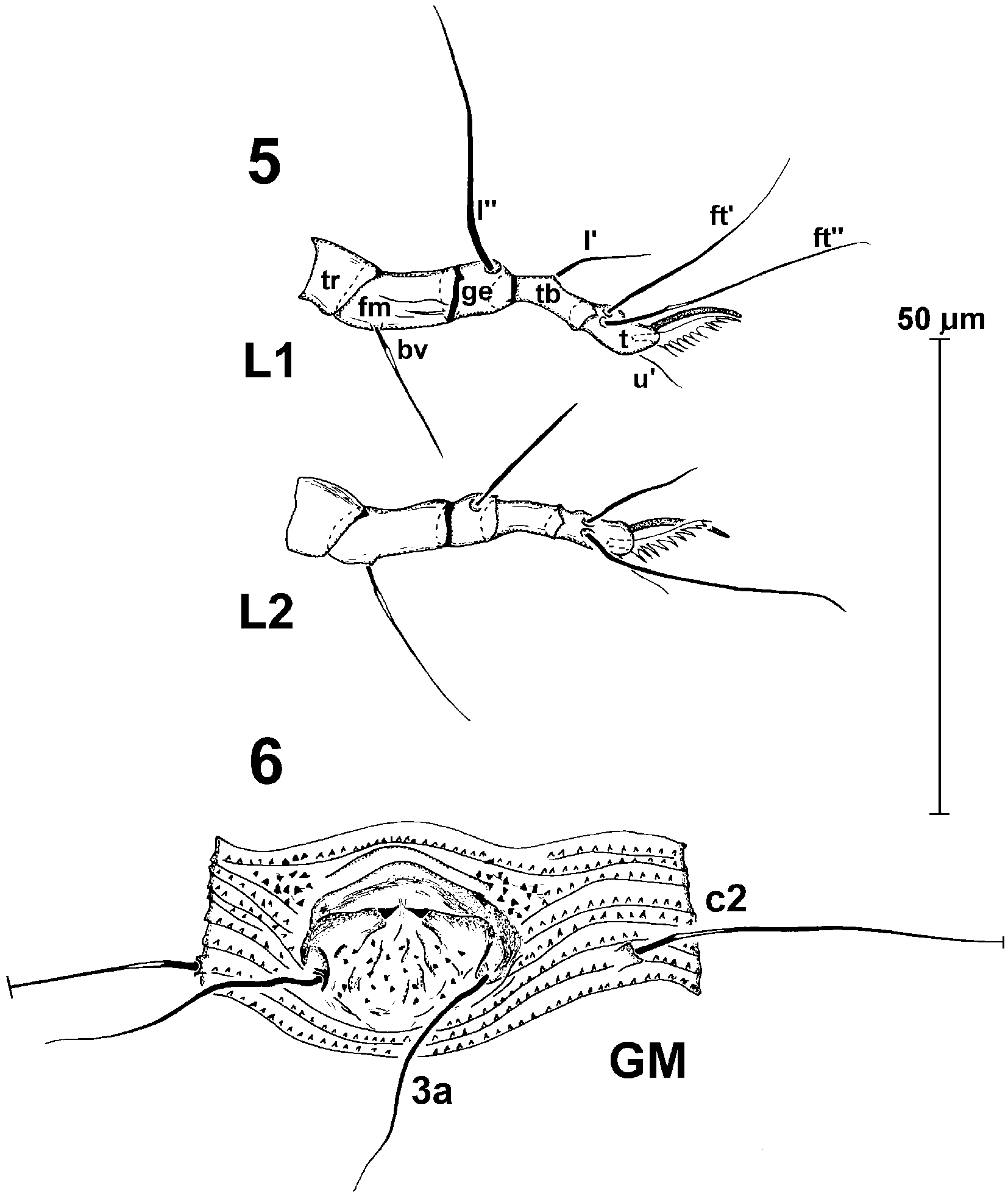
Leg I 37 (3643) long; femur 12 (1012) long, with seta bv 16 (1418) long; position of the seta bv 5 (45) from the ventral, proximal margin of femur; genu 6 (57) long, with seta l’’ 29 (2932) long, position of the seta l’’ 4 (34) from the dorsal, proximal margin of genu; tibia 10 (910) long, with seta l’ 10 (1012) long; position of the seta l’ 5 (45) from the ventral, proximal margin of tibia. Tarsus 7 (89) long, with three setae: ft’’ 30 (2833), ft’ 24 (2429) long, u’ 7 (79) long; tarsal solenidion 10 (1011) long; tarsal empodium simple, 8(78)rayed, symmetrical, 12 (1113) long. Leg II 36 (3640) long; femur 11 (10 12) long, with seta bv 24 (1926) long; position of the seta bv 5 (5) from the ventral, proximal margin of femur; genu 5 (56) long, with seta l’’ 17 (1619) long; position of the seta l’’ 3 (34) from the dorsal, proximal margin of genu; tibia 8 (68) long. Tarsus 8 (78) long, with three setae: ft’’ 29 (2830) long, ft’ 13 (1214), u’ 6 (69) long; tarsal solenidion
11 (1113) long; tarsal empodium 8 (78)rayed, symmetrical, 13 (1113) long.
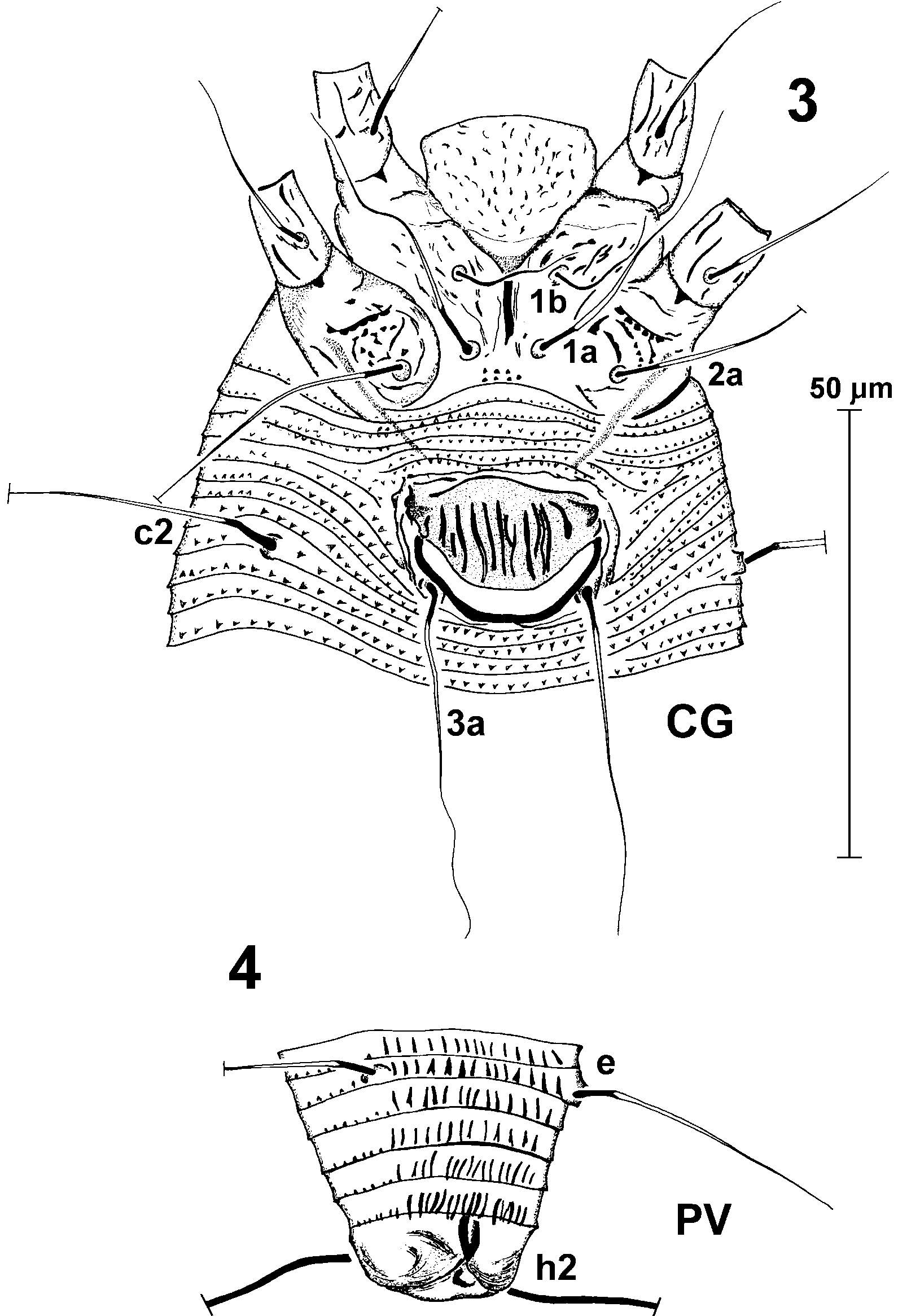
Coxae with a pattern of numerous, short lines, coxae II with triangular microtubercles along lines; tubercles 1b 10 (1012) apart, setae 1b 11 (1016) long; tubercles 1a 9 (810) apart, setae 1a 29 (2433) long; tubercles 2a 25 (2428) apart, setae 2a 48 (4253) long; distance between tubercles 1b and 1a 9 (89), distance between tubercles 1a and 2a 9 (8 9).
Opisthosoma with 64 (5662) dorsal annuli, 74 (6170) ventral annuli, 8 (57) coxogenital annuli. Annuli with microtubercles; dorsal microtubercles triangular, minute, close to each other, located on the margin of annuli; ventral microtubercles triangular but more pointed and larger than dorsal, located at a distance of margin of annuli, from the level of setae f elongated.
Setae c2 46 (4047) long, located on 9th (8th9th) ventral annulus from coxae II; tubercles c2 53 (4958) apart; ventral setae d 61 (5968) long, located on 22nd (20th 22th) ventral annulus; tubercles d 38 (3841) apart; setae e 40 (3038) long, located on 39nd ventral annulus (3340); tubercles e 16 (1518) apart; setae f 27 (2433) long, located on 70th (57rd–66nd) ventral annulus, 5th (5th) annulus from the rear; tubercles f 19 (1825) apart.
Setae h1 5 (45) long, 7 (78) apart; setae h2 72 (7989) long, 10 (1112) apart; distance between h1 and h2 – 3 (23).
Genital parts 14 (1417) long, 24 (2224) wide, genital coverflap with 10 (1011) longitudinal striae; setae 3a 38 (3848) long, 16 (1619) apart.
Male ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 5 6 ) (9 specimens): body length (162209), width (4856), spindleform. Gnathosoma (1924) long; dorsal pedipalpal genual seta d (912) long; v setae (2) long; ep setae (34) long; chelicerae (2026) long, almost straight. Prodorsal shield triangular, (39 43) long, (3844) wide, with pronounced, elongate and pointed frontal lobe over the gnathosoma; pattern of the shield similar to that of a female. Tubercles sc large, located on the rear margin of the shield, (4) long, (4) wide, (2529) apart; setae sc (2938) long, projecting to the rear.
Leg I (3441) long; femur (10) long, with seta bv (1215) long; position of the seta bv (45) from the ventral, proximal margin of femur; genu (56) long, with seta l’’ (2530) long; position of the seta l’’ (34) from the dorsal, proximal margin of genu; tibia (78) long, with seta l’ (1012) long; position of the seta l’ (4) from the ventral, proximal margin of tibia. Tarsus (79) long, with three setae: ft’’ (2630), ft’ (2123) long, u’ (68) long; tarsal solenidion (911) long, slightly curved; tarsal empodium simple, (78)rayed, symmetrical, (1012) long. Leg II (3035) long; femur (10) long, with seta bv (1823) long; position of the seta bv (45) from the ventral proximal margin of femur; genu (56) long, with seta l’’ (1216) long; position of the seta l’’ (3) from the dorsal, proximal margin of genu; tibia (67) long. Tarsus (78) long, with three setae: ft’’ (2328) long, ft’ (1013), u’ (67) long; tarsal solenidion (1012) long, almost straight; tarsal empodium (78)rayed, symmetrical, (1011) long.
Coxae with a pattern of short lines with triangular and subrounded microtubercles; coxae I connecting medially; tubercles 1b (1011) apart, setae 1b (814) long; tubercles 1a (710) apart, setae 1a (1924) long; tubercles 2a (2124) apart, setae 2a (4248) long; distance between tubercles 1b and 1a (8), distance between tubercles 1a and 2a (79).
Opisthosoma with (5156) dorsal annuli, (5562) ventral annuli, (56) coxogenital annuli. Annuli with microtubercles, their size and shape similar to that of female.
Setae c2 (3643) long, located on (8th9th) ventral annulus from coxae II; tubercles c2 (4048) apart; ventral setae d (4464) long, located on (16th19nd) ventral annulus; tubercles d (3135) apart; setae e (2033) long, located on (29th 34th) ventral annulus; tubercles e (1317) apart; setae f (2129) long, located on (51st58th) ventral annulus, (5th) annulus from the rear; tubercles f (1924) apart.
Setae h1 (46) long, (68) apart; setae h2 (5268) long, (1011) apart; distance between h1 and h2 – (23).
Genital parts (1417) long, (2226) wide; setae 3a (2429) long, (1719) apart.
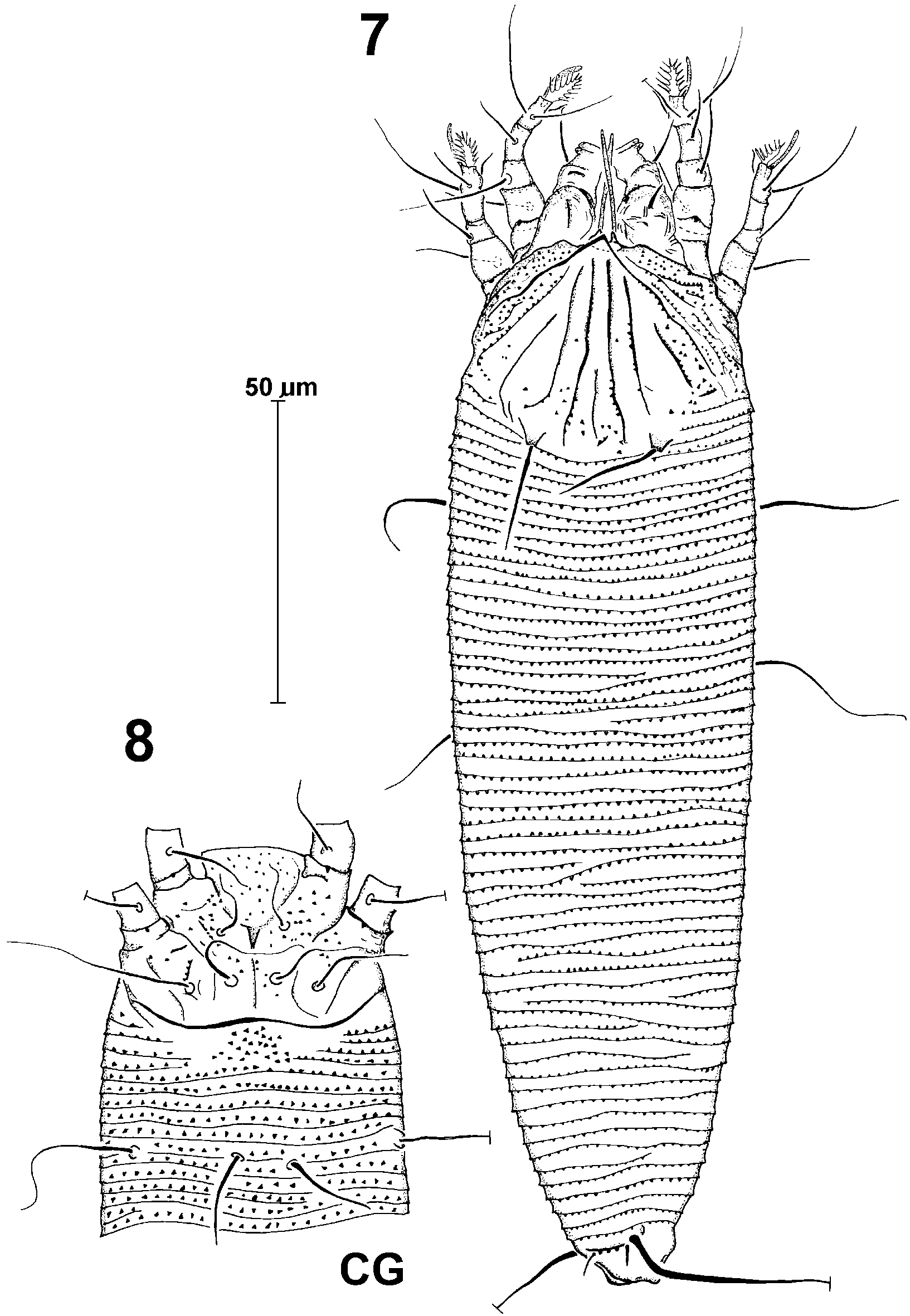
Nymph ( Figs. 7, 8 View FIGURES 7 8 ) (4 specimens): body length (147205), width (4852); spindleform. Gnathosoma (1722) long; dorsal pedipalpal genual seta d (710) long; v setae (23) long; ep setae (3) long; chelicerae (1922) long. Prodorsal shield (3840) long, (3840) wide; triangular, with a little pointed lobe over the gnathosoma; all lines not reaching to posterior margin of the shield; median line only in the rear part of shield; admedian lines parallel to each other, diverging posteriorly the lateral margin of the shield; I submedian lines parallel to admedian; II submedian lines beginning in 1/3 form anterior margin, parallel to lateral marins of the shield; some triangular microtubercles present on the shield. Tubercles of setae sc (34) long, (4) wide, located on rear margin of the shield, (2024) apart; setae sc (1823) long.
Leg I (2832) long; femur (8) long, with seta bv (811) long; position of the seta bv (4) from the ventral, proximal margin of femur; genu (45) long, with seta l’’ (2024) long; position of the seta l’’ (23) from the dorsal, proximal margin of genu; tibia (56) long, with seta l’ (710) long; position of the seta l’ (23) from the ventral, proximal margin of tibia. Tarsus (56) long, with three setae: ft’’ (1725), ft’ (1724) long, u’ (56) long; tarsal solenidion (78) long; tarsal empodium simple, (67)rayed, symmetrical, (810) long. Leg II (2527) long; femur (8) long, with seta bv (1215) long; position of the seta bv (4) from the ventral, proximal margin of femur; genu (45) long, with seta l’’ (1011) long; position of the seta l’’ (23) from the dorsal, proximal margin of genu; tibia (45) long. Tarsus (6) long, with three setae: ft’’ (19) long, ft’ (910), u’ (45) long; tarsal solenidion (810) long; tarsal empodium (67)rayed, symmetrical, (79) long.
Coxae with a pattern of slender microtubercles; coxae I connecting medially; tubercles 1b (1011) apart, setae 1b (8) long; tubercles 1a (8) apart, setae 1a (1518) long; tubercles 2a (2125) apart, setae 2a (35) long; distance between tubercles 1b and 1a (811), distance between tubercles 1a and 2a (78).
Opisthosoma with (5157) dorsal annuli, (4955) ventral annuli. Annuli with dorsal microtubercles triangular, minute; ventral annuli with microtubercles larger and more pointed than ones.
Setae c2 (1928) long, located on (6th 10th) ventral annulus from coxae II; tubercles c2 (4551) apart; ventral setae d (3145) long, located on (14th 21st) ventral annulus; tubercles d (2038) apart; setae e (1626) long, located on (2532) ventral annulus; tubercles e (1216) apart; setae f (1419) long, located on (41st 51st) ventral annulus, (5th) annulus from the rear; tubercles f (1921) apart.
Setae h1 (4) long, (6) apart; setae h2 (65) long, (910) apart; distance between h1 and h2 (2).
Setae 3a (1116) long, (1012) apart.
Larva ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 ) (1 specimen): body length (121), width (43); spindleform. Cheliceral stylets (19) long. Prodorsal shield (33) long, (35) wide; triangular; median and admedian lines similar to that of nymph; I submedian lines present only in the anterior part of shield, II submedian lines not present. Tubercles of setae sc (3) long, (5) wide located at a distance of posterior margin of the shield, (14) apart; setae sc (14) long, converging to each other. Leg I (29) long; femur (9) long; genu (4) long, with seta l’’ (15) long; position of the seta l’’ (2,5) from the dorsal, proximal margin of genu; tibia (4) long, with seta l’ (12) long; position of the seta l’ (2) from the ventral, proximal margin of tibia. Tarsus (5) long, with three setae: ft’’ (18), ft’ (15) long, u’ (5) long; tarsal solenidion (7) long, tarsal empodium 6 rayed, symmetrical, (8) long. Leg II (26) long; femur (6) long, with seta bv (10) long; position of the seta bv (3) from the ventral, proximal margin of femur; genu (3) long; tibia (3) long. Tarsus (5) long; tarsal solenidion (8) long; tarsal empodium 6rayed, symmetrical, (6) long.
Tubercles 1a (8) apart; tubercles 2a (19) apart; distance between tubercles 1a and 2a (7).
Opisthosoma with (37) dorsal annuli, (23) ventral annuli. Dorsal microtubercles triangular but not pointed, minute; ventral microtubercles more rounded, at a distance of the margin of annuli.
Setae c2 (21) long, located on (7th)ventral annulus from coxae II; tubercles c2 (21) apart; ventral setae d (18) long, located on (13 th) ventral annulus; tubercles d (11) apart; setae e (10) long, located on (19) ventral annulus; tubercles e (25) apart; setae f (18) long, located on (30 th) ventral annulus, (5th) annulus from the rear; tubercles f (39) apart.
Setae h1 (5) apart, setae h2 (9); distance between h1 and h2 – (3).
Setae 3a (8) long, (5) apart.
Etymology: The specific name is derived from the country where this mite was found (+ icus, Greek, meaning pertaining to).
Host plant: Hordeum brevisubulatum (Trin.) Link ( Poaceae ).
Relation to host plant: Mites are vagrants on the upper leaf surface.
Type locality: Central Mongolia, Arkhangay Aymag, Horgo Terhiyn Tsagaan Nuur National Park ; foreststeppe zone; 21.07.2000; leg. A. Skoracka; 12 females, 18 males, 5 nymphs .
Material examined: Holotype female, 9 female paratypes, 9 male, 4 nymph, 1 larva paratypes.
Other hosts and localities
Agropyron cristatum (L.) P. Beauv; Poa ochotensis Trin. ; Central Mongolia, Arkhangay Aymag, near bridge over Suman river, rocky riverside; 15.07.2000; leg. A. Skoracka; 46 females, 2 males, 4 nymphs on P. ochotensis , 4 females, 1 male, 3 nymphs on A. cristatum ;
Deschampsia caespitosa (L.) P. Beauv.; CentralNorth Mongolia, Bulgan Aymag, near Bugat locality, meadow steppe near larch and birch forest, elevation 1300 m.; 4.08.2000; leg. A. Skoracka; 3 females ;
Koeleria macrantha (Ledeb.) Schult. , Elymus secalinus (Georgi) Bobr. Central Mongolia, Arkhangay Aymag, Horgo Terhiyn Tsagaan Nuur National Park ; Tarvagatay Mountains , foreststeppe zone, elevation 2500 m.; 19.07.2000; leg. A. Skoracka; 2 females on K. macrantha , 5 females, 4 males on E. secalinus ;
Poa attenuata Trin. ; North Mongolia, Hovsgol Nuur National Park, 25 km NNW from Hatgal locality, elevation 2520 m.; 29.07.2000; leg. A. Labrzycka; 7 females, 1 male, l larva.
Differential diagnosis
Aculodes mongolicus is most similar to Aculodes mckenziei ( Keifer 1944) by triangular prodorsal shield with anterior lobe pointed and the length of sc setae (43 m in A. mckenziei , 45 m in A. mongolicus ). A. mongolicus can be distinguished from A. mckenziei by body shape, which is vermiform in A. mckenziei and more spindleform in the new species. The two species differ also in the length of gnathosoma (35 m in A. mckenziei , 22 m in A. mongolicus ), length of 3a setae (25 m in A. mckenziei , 38 m in A. mongolicus ), length of e setae (26 m in A. mckenziei , 40 m in A. mongolicus ), prodorsal shield pattern (shape of submedian lines) and in the proportion of length of tibia II to tarsus II (0.75 in A. mckenziei , 1 in A. mongolicus ). In addition, dorsal and ventral mirotubercles are similar in shape and dimensions in A. mckenziei , whereas in A. mongolicus ventral microtubercles are larger and more pointed than dorsal ones.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SuperFamily |
Eriophyoidea |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |