Parandes fuscus Wang & Chen, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2023.888.2233 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:663C5D99-DCE9-4C17-8C5A-B31950DB09CB |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8246732 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/73FF7C6C-E5DC-4C26-ADCE-0AD06B4FC103 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:73FF7C6C-E5DC-4C26-ADCE-0AD06B4FC103 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Parandes fuscus Wang & Chen |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Parandes fuscus Wang & Chen sp. nov.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:73FF7C6C-E5DC-4C26-ADCE-0AD06B4FC103
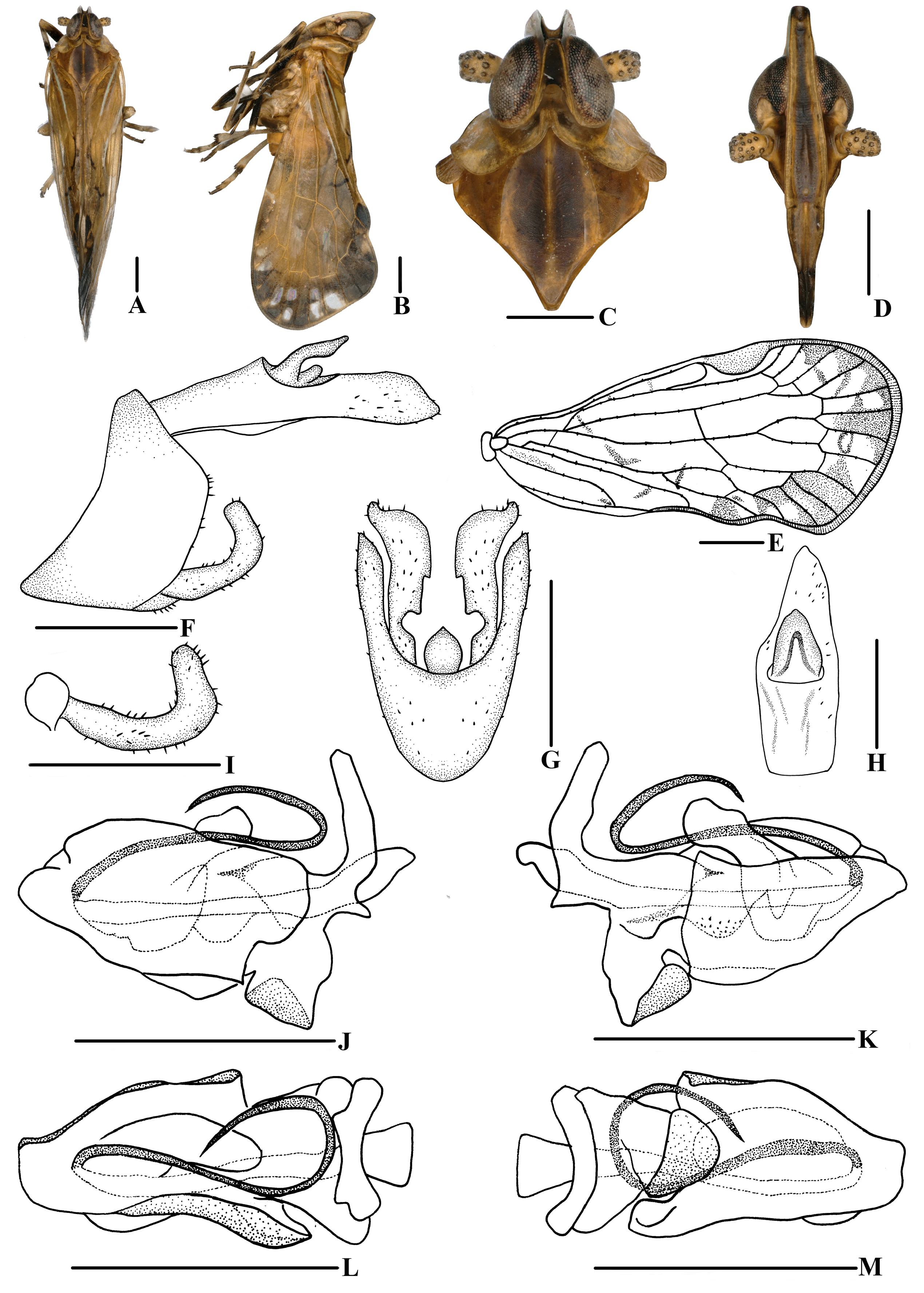
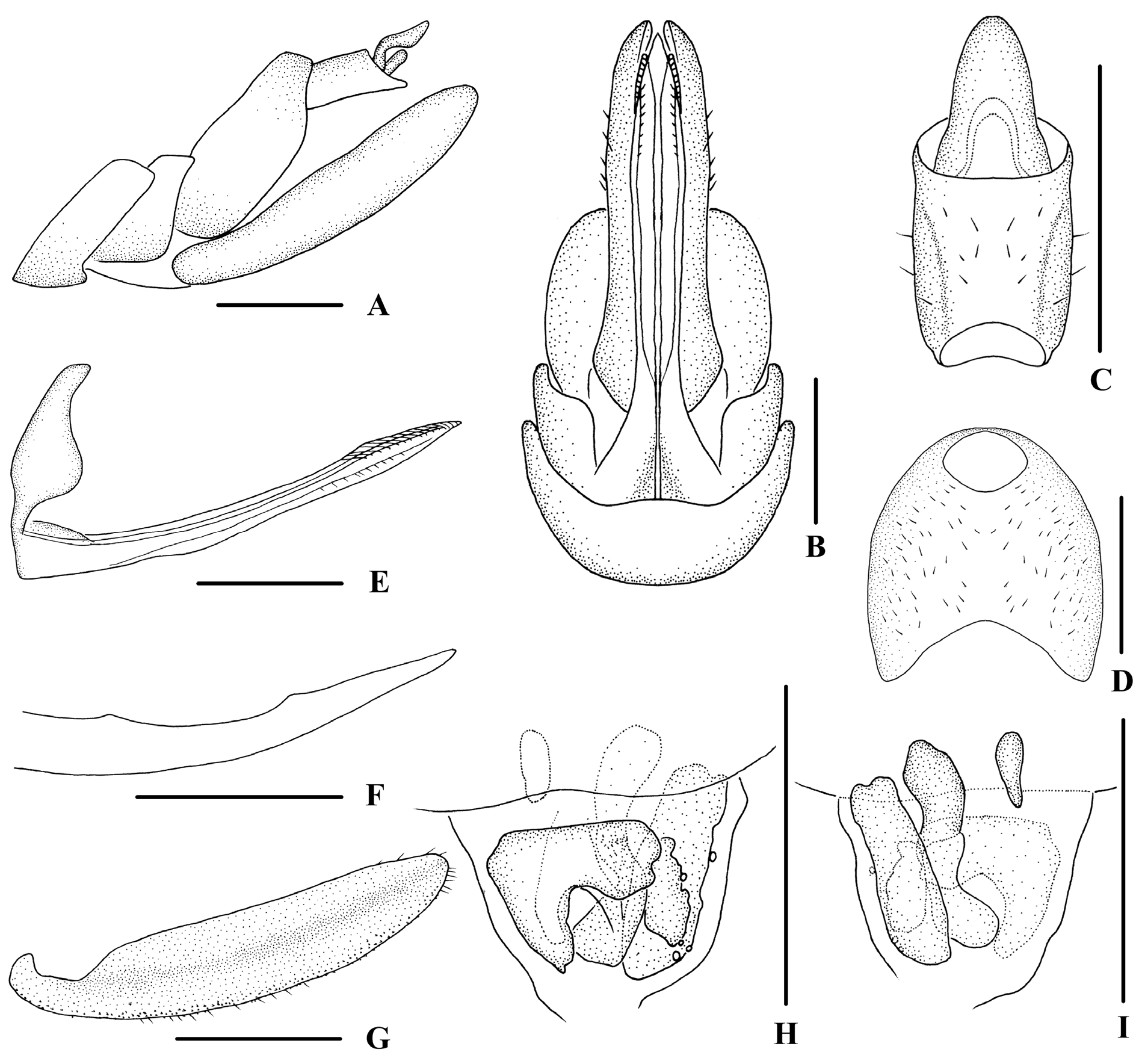
Figs 3–4 View Fig View Fig , 6B View Fig
Diagnosis
The salient features of the new species include the following: apex of forewing dark brown across its entire width apart from a few pale spots ( Fig. 3A, C View Fig ); ventral margin of periandrium with a laminal process near base, bending up to the left ( Fig. 3M View Fig ); basal ⅓ of periandrium with an expanded semi-enclosed structure around the left and right side and ventral margin of periandrium ( Fig. 3J–K, M View Fig ); apex of periandrium with a long spinose process, curved dorsally to the base, then strong bending ( Fig. 3J‒M View Fig ).
Etymology
The specific name is derived from the Latin adjective ‛ fuscus ’, referring to an arcuate dark brown stripe from the apical margin of forewing.
Type material
Holotype CHINA • ♂; Yunnan Province, Mengla County, Menglun Town ; 21.94° N, 101.26° E; 18 Aug. 2014; Ying-Jian Wang leg.; GUGC. GoogleMaps
Paratypes CHINA • 1 ♂; same collection data as for holotype; GUGC GoogleMaps • 1 ♂; Yunnan Province, Mengla County, Menglun Town, Bakaxiaozhai Village ; 21.97° N, 101.22° E; 27 Aug. 2014; Mei-Na Guo leg.; GUGC GoogleMaps • 1 ♀; same collection data as for preceding but 26 Sep. 2015; Qiang Luo leg.; GUGC GoogleMaps • 1 ♀; same collection data as for preceding but 1 Sep. 2017; Yan Zhi leg.; GUGC GoogleMaps • 3 ♂♂, 2 ♀♀; same collection data as for preceding but 13 Jun. 2019; Feng-E Li leg.; GUGC GoogleMaps .
Description
MEASUREMENTS. Body length: male 6.38‒6.82 mm (N = 6), female 6.80‒7.15 mm (N = 4).
COLORATION. General color yellowish brown ( Fig. 3A–B View Fig ). Eyes black brown, margin yellowish brown; ocelli faint red, semi-translucent. Lateral carinae of frons yellowish white; lateral side of head with a long brown spot anterior to the eyes. Antenna yellowish brown. Vertex dark brown. Face and rostrum generally dark brown. Pronotum yellowish brown. Mesonotum with area between lateral carinae darker brown, lateral areas yellowish brown. Forewing semi-translucent, slightly anterior and posterior to fork CuA with a narrow and small irregular puce stripe respectively, posterior to clavus with an elliptical black brown spot, apex of forewing dark brown across its entire width apart from a few pale spots. Stigma black brown. Veins and tubercles concolorous with wing. Hind tibiae yellowish brown. Abdomen yellowish brown ventrally.
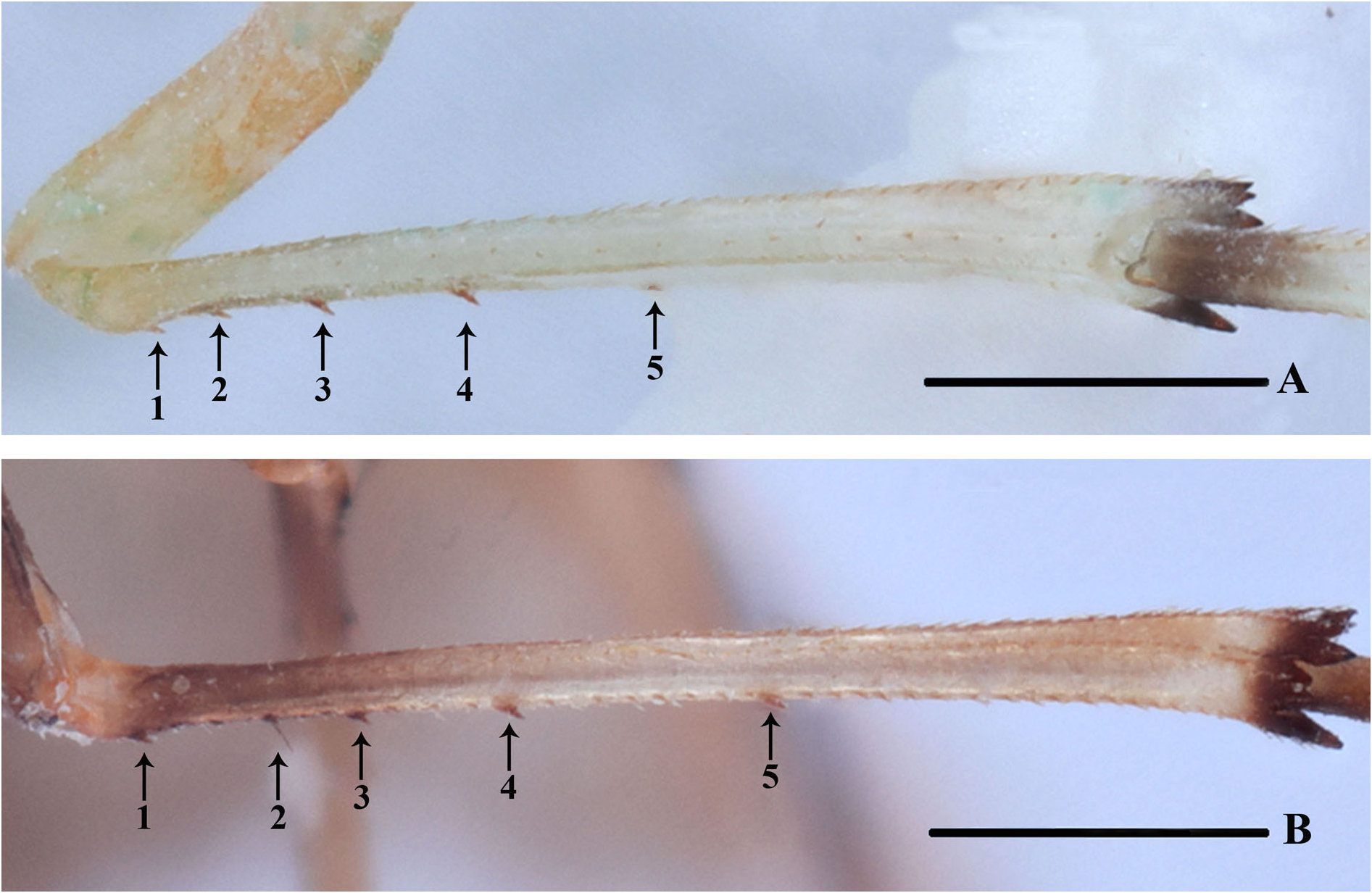
HEAD AND THORAX. Vertex ( Fig. 3A, C View Fig ) 2.1 times as long as wide; anterior margin nearly straightly, posterior margin U-shaped recessed, lateral carina developed, median carina absent. Frons ( Fig. 3D View Fig ) 4.7 times as long as wide, lateral carina developed, base of median carina raised, median carina of postclypeus transparent. Pronotum ( Fig. 3A, C View Fig ) slightly shorter than vertex; posterior margin recessed. Mesonotum 1.1 times as long as pronotum and vertex combined. Forewing ( Fig. 3B, E View Fig ) 2.12 times as long as wide, with twelve apical cells and seven subapical cells; RP 3 branches, MP with 5 terminals: MP 11, MP 12, MP 2, MP 3, and MP 4, fork MP 1 +MP 2 basad of fork MP 3 +MP 4. Hind tibia ( Fig. 6B View Fig ) with five lateral spines; chaetotaxy of hind tarsi: 7/7–8, 2 nd hind tarsus with 2–3 platellae.
MALE GENITALIA. Pygofer ( Fig. 3F–G View Fig ) in ventral view symmetrical; in lateral view, lateral lobes arcuate and extended caudally. Medioventral process linguiform in ventral view, apex pointed. Anal segment ( Fig. 3F, H View Fig ) flat tubular, dorsal margin almost straight, ventral margin curved slightly in lateral view; 2.8 times as long as wide in dorsal view; anal style strap-shaped, not extending beyond anal segment. Gonostyli ( Fig. 3G, I View Fig ) symmetrical ventrally, middle part of inner margin with emarginations; gonostyli in inner lateral view L-shaped. Aedeagus ( Fig. 3J–M View Fig ) with a spinose process. Ventral margin of periandrium with a laminal process near base, bending up to the left; basal ⅓ of periandrium with an expanded semi-enclosed structure around the left and right side and ventral margin of periandrium; apex of periandrium with a long spinose process, curved dorsally to the base, then strong bending, directed dorsocaudad. Endosoma slightly sclerotized, without process.
FEMALE GENITALIA. Tergite IX ( Fig. 4A–B, D View Fig ) moderately sclerotized, without wax plate. Anal segment ( Fig. 4C View Fig ) rectangular, 2.2 times as long as wide in dorsal view, anal style linguiform. Gonapophysis VIII ( Fig. 4E View Fig ) elongate, and slightly curved upwards. Gonapophysis IX ( Fig. 4F View Fig ) with two middle teeth, denticulation unsharp. Gonoplac ( Fig. 4G View Fig ) rod-like, 4.4 times as long as wide in lateral view. Posterior vagina pattern as shown in Figure 4H–I View Fig .
Distribution
China (Yunnan).
Remarks
This species can be distinguished from the other species of the genus by the body color, forewing markings and male genitalia.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.