Quadrimaera yemanjae, Alves & Neves & Johnsson, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4532.4.8 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:9CFCAE32-97F3-46EF-A679-D25B3A3622E8 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5966884 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/FA66D951-FFA3-FF84-FF36-86B56BD8BD4E |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Quadrimaera yemanjae |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Quadrimaera yemanjae sp. nov.
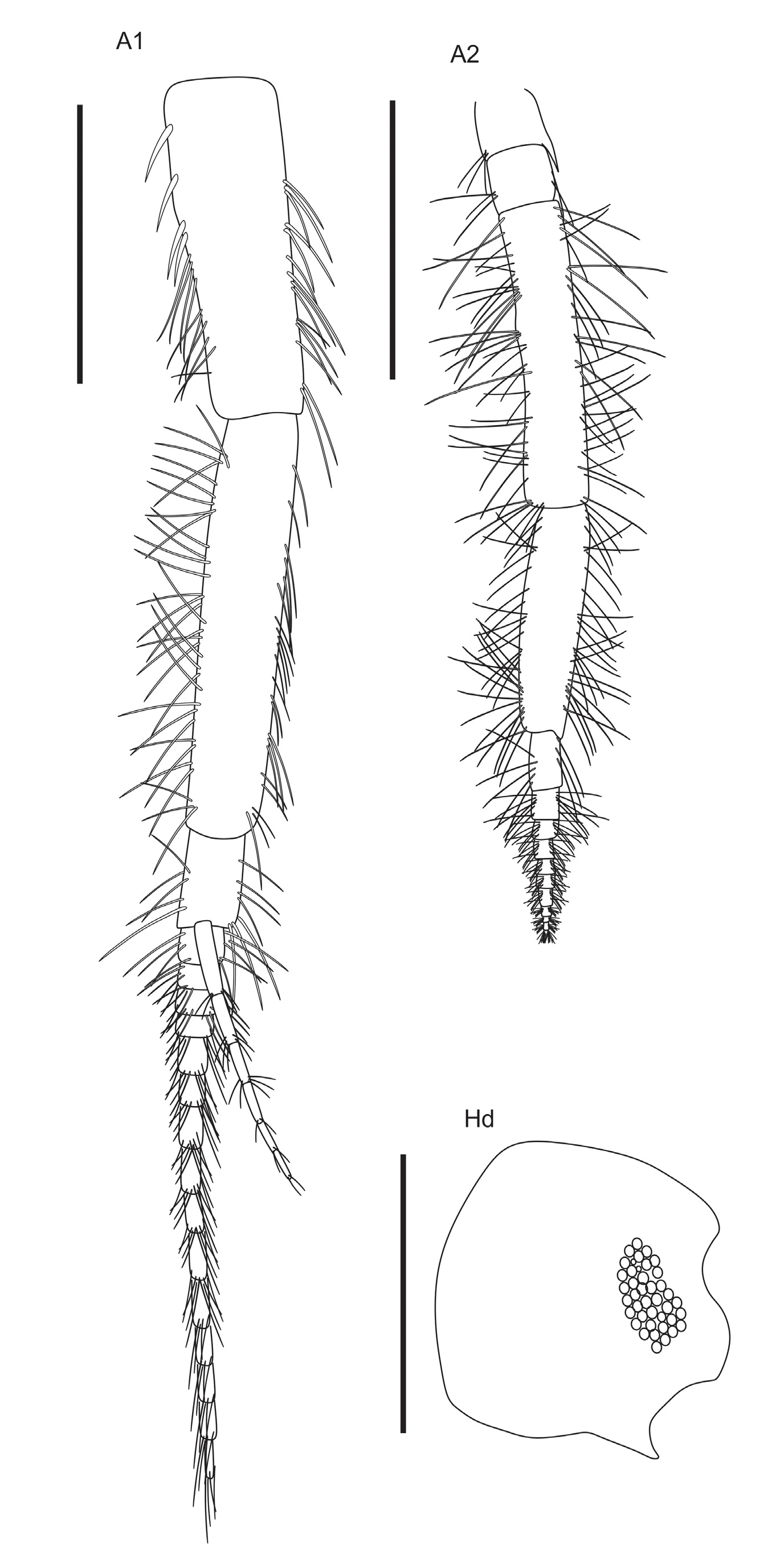
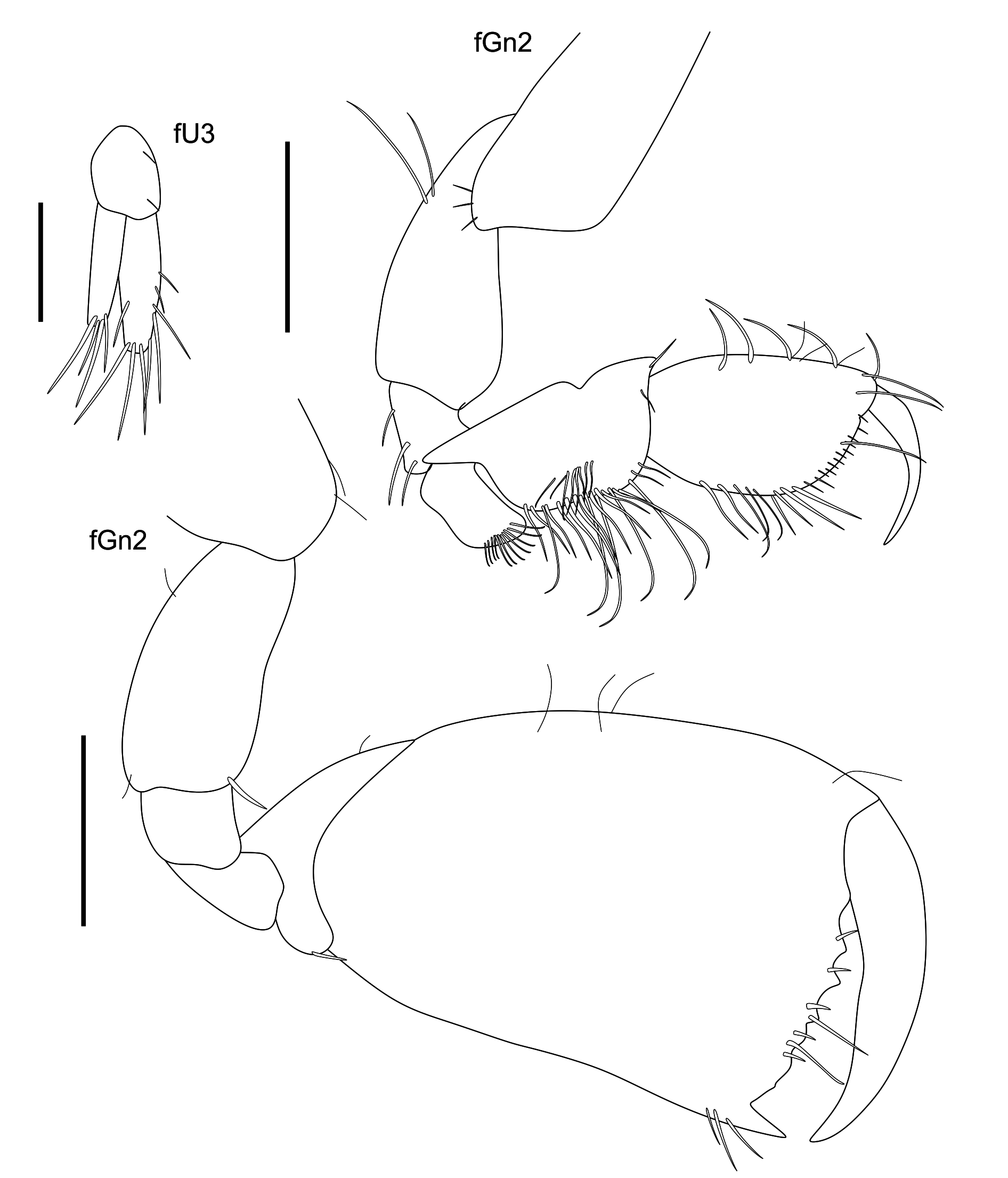
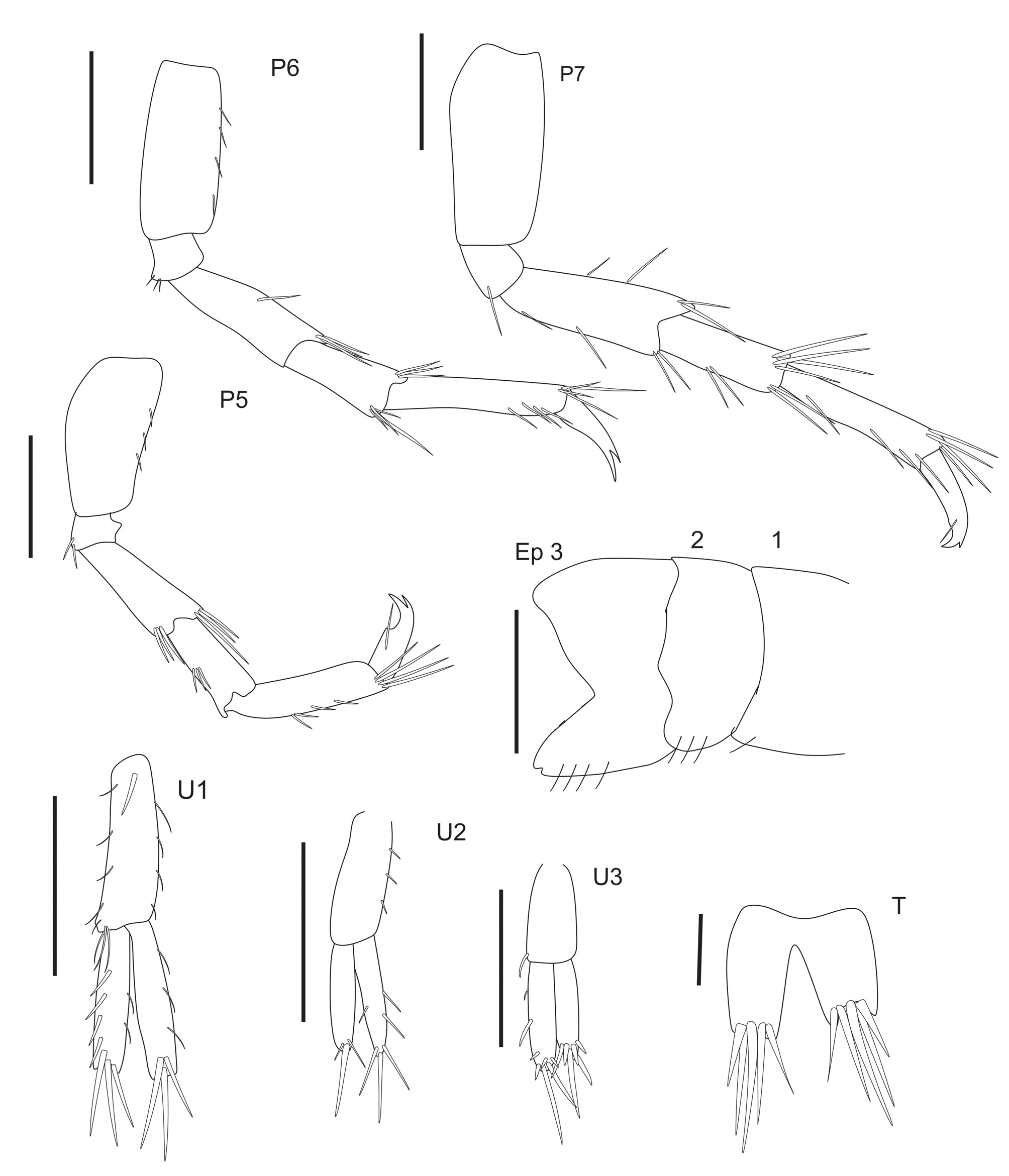
( Figures 2–7 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 View FIGURE 7 )
Examined material. Holotype. Adult male (UFBA 3317), 4.5 mm. Pirangi Beach, RN State, Brazil, (5°59'00.2"S; 35°06'30.1"W). March 2010. Allotype. 1 female ( UFBA 3319 ) 3.9 mm. Pirangi Beach , Rio Grande do Norte State, Brazil, (5°59'00.2"S; 35°06'30.1"W), associated with alga Halimeda opuntia (L.) J.V. Lamour, 1816, intertidal zone (0–2 m of depth) GoogleMaps March 2010. CARNEIRO, P. B. Coll.
Paratypes. Incomplete male ( UFBA 3318 ), 3.5 mm. Pirangi Beach, RN State, Brazil, (5°59'00.2"S; 35°06'30.1"W), associated with alga Halimeda opuntia , intertidal zone (0–2 m of depth) GoogleMaps . March 2010. CARNEIRO, P.B. Coll.
20 females ( UFBA 3319 ), 3.0 to 3.9 mm. All material sampled at Pirangi Beach, Rio Grande do Norte State, Brazil, (5°59'00.2"S; 35°06'30.1"W), associated with alga Halimeda opuntia , intertidal zone (0–2 m of depth). March 2010. CARNEIRO, P.B. Coll GoogleMaps .
Type locality. Pirangi Beach, Rio Grande do Norte State, Brazil (5°59'00.2"S; 35°06'30.1"W).
Etymology. The new species alludes to Yemanjá, a female divinity known as “Goddess of the sea”, a common deity of Afro-Brazilian religions.
Diagnosis. Setose flagellae on antennae 1 and 2. Accessory flagellum 6-articulated. Anteroventral corner of coxa 1 rounded ( Fig 3 View FIGURE 3 ). Article 2 of mandibular palp longer than others ( Fig 4 View FIGURE 4 ). Gnathopod 2 showing transverse palm with 8 concavities. The 3 most proximal concavities are U-shaped and the last is the deepest one ( Fig 5 View FIGURE 5 ).The other 4 distal concavities are elliptical, with the anterior most and the distal most deeper than the others ( Fig 5 View FIGURE 5 ). Dactyl with inner margin regularly ornamented with sparse setae. Bases of pereopods 5–7 slender with pronounced posterodistal lobe ( Fig 5 View FIGURE 5 ). Telson cleft about 75% of its length, each lobe with 2 notches and 5 robust setae.
Description. Antenna 1 setose, 25% longer than antenna 2, peduncle article ratio: 1:1.2:0.2, accessory flagellum 6-articulated, peduncle 32% longer than flagellum with 15 articles. Antenna 2 strongly setose, cone gland reaching about 50% of total length of article 3; flagellum with 11 articles ( Fig 3 View FIGURE 3 ).
Right mandible incisor with 2 teeth; lacinia mobilis with 3 teeth; setae row with 5 plumose setae, being the last one shorter than the others; cylindrical and triturative molar with plumose seta; mandibular palp 3-articulated, ratio of articles: 0.3:1.0:0.5; article 1 subquadrate with distal corner rounded; article 2 with 4 setae; article 3 with 5 slender and long setae ( Fig 4 View FIGURE 4 ). Maxilla 1 inner plate subtriangular, with 8 apical setae; outer plate with 7 pectinate setae; palp 2-articulated, article 1 slightly longer than 2, which bears 8 setae ( Fig 4 View FIGURE 4 ). Maxilla 2 inner and outer plates distally setose ( Fig 4 View FIGURE 4 ). Maxilliped inner plate quadrate with 8 plumose distal setae; outer plate suboval, distal and inner margins with long setae; palp 4-articulated, article 2 with 8 pectinate setae, article 3 with 2 long slender setae ( Fig 4 View FIGURE 4 ).Lower lip of inner lobes with apical setae; outer lobes laterally expanded with apical setae. Upper lip subtriangular, with apical small setae ( Fig 4 View FIGURE 4 ).
Gnathopod 1, coxa 1 with anteroventral corner rounded, slightly produced, ventral margin with small setae; basis robust, longer than ischium and merus together, ischium subquadrate, ventrolateral margin with row of simple setae; merus subequal in length to ischium; carpus subequal in length to propodus and 1.3 times longer than ischium, posterior margin with dense fringe of plumose setae and long and slender simple setae, posteroventral corner with row of plumose setae; propodus not facially setose, anterior and posterior margin with slender simple setae, palm oblique defined by 2 spines, with small setae ( Fig 5 View FIGURE 5 ). Gnathopod 2 coxa 2 subquadrate, anteroventral margin with small setae, basis strong, anterior margin with 3 small setae, anteroventral corner rounded and produced; ischium 0.3 times shorter than merus; carpus reduced, subtriangular with plumose setae; propodus enlarged, palm transverse, palmar margin with 8 excavations: three proximal most are U-shaped defining four acute processes that grow successively in length; a medial and deeper U-shaped excavation defining 2 acute processes; 4 elliptical distalmost excavations forming 3 truncate processes and the last one acute and produced; dactyl robust, inner margin regular with row of minute setae ( Fig 5 View FIGURE 5 ). Pereopod 3, coxa 3 subquadrate; basis slightly longer than ischium and merus together, merus and carpus setose, subequal in length; propodus setose, slightly longer than carpus; dactyl with bifid nail, showing dactylar ungues ( Fig 5 View FIGURE 5 ). Pereopod 4 similar to 3 ( Fig 4 View FIGURE 4 ). Pereopod 5 basis slender, posterior margin with small setae, posteroventral corner rounded; ischium anteroventral corner with 2 simple setae; merus about 0.4 times longer than carpus; carpus elongated, 0.3 times shorter than propodus; propodus subrectangular with anterior margin setose; dactyl with bifid nail showing dactylar ungues with 2 setae ( Fig 7 View FIGURE 7 ). Pereopod 6–7 with slender basis, propodus without tufts of long setae on posterior margin; dactyl with bifid nail ( Fig 7 View FIGURE 7 ).
Epimeral plate 1 posteroventral corner rounded produced, with small setae. Epimeral plate 2 posterior margin sinuous, posteroventral corner rounded, slightly produced ( Fig 6 View FIGURE 6 ). Epimeral plate 3 with 4 stout and small setae, posteroventral corner produced and bifurcated ( Fig 7 View FIGURE 7 ). Uropod 1, peduncle subequal in length to rami, basofacial setae developed; inner ramus subequal in length to outer ramus, dorsal margin with 3 slender setae, tip with 3 long and stout setae; outer ramus ventral margin with 4 stout and setae, dorsal margin with 2 slender setae, tip with 3 stout and long setae ( Fig 7 View FIGURE 7 ). Uropod 2, peduncle subequal in length to rami, rami long and slender with scarce setae ( Fig 7 View FIGURE 7 ). Uropod 3, peduncle subquadrate, shorter than rami (about 0.4 times), rami subequal in length, showing distally 3 strong, long setae and 3 strong, small setae ( Fig 7 View FIGURE 7 ). Telson as long as wide, deeply cleft (about 75%), lobes with 2 distal lobes and stout and long setae ( Fig 7 View FIGURE 7 ).
Female (Sexual dimorphic characters). Gnathopod 1, coxa 1 anteroventral corner rounded, not produced, ventral margin with small setae; basis strong, longer than ischium and merus together, posterior margin with 2
setae; carpus subequal in length to propodus, posterior margin with long and slender simple setae, posteroventral corner with row of simple setae; propodus not facially setose, anterior and posterior margin with slender simple setae, palm oblique defined by 1 spine, with minute setae ( Fig 6 View FIGURE 6 ).
Gnathopod 2 with coxa 2 subquadrate, ventral margin with two setae; basis thinner than in male, anterior margin without setae, anteroventral corner not produced; ischium 0.1 times shorter than merus; carpus reduced, subtriangular with sparse setae; propodus enlarged, anterior margin convex, palm transverse, palmar margin serrate, with seven small excavations, palmar margin defined by strong spine; dactyl robust, inner margin regular without setae ( Fig 6 View FIGURE 6 ).
Uropod 3, peduncle subquadrate, shorter than rami (about 0.3 times), rami with 2 sets of lateral setae, tips beset with strong setae, three longer and three smaller, inner rami 0.3 times shorter than outer one ( Fig 6 View FIGURE 6 ).
Remarks. Quadrimaera yemanjae sp. nov is more related to the species Q. quadrimana ( Dana, 1852) from Fiji IndoPacific Ocean, and Q. cristianae Krapp-Schickel & Ruffo, 2000 from Brazil, by presenting: (1) coxa 1 anteroventral corner rounded and slightly produced; (2) antenna 2 setose; (3) male gnathopod 2 with transverse propodus palm, ornamented, defined by 2 processes, the first one truncated and the other acute ( Ruffo et al. 2000; Krapp-Schickel & Ruffo 2000). Nevertheless, Q. yemanjae sp. nov. is unique by presenting male gnathopod 2 propodus palm with 8 distinctly excavations. The new species also differs from the Brazilian species Q. chelata Senna & Serejo, 2007 by having: (1) plumose setae on ventral margin of the gnathopod 1 carpus; (2) gnathopod 2 propodus palm with 4 U-shaped excavations and 4 elliptical ones; (3) inner margin of dactyl without processes or spines ( Senna & Serejo 2007). On the most, Q. yemanjae sp. nov. differs from the Western Atlantic species: (1) Q. pieteri Krapp-Schickel & Ruffo, 2000 by presenting coxa 1 with rounded anteroventral corner; (2) Q. miranda Ruffo, Krapp & Gable, 2000 and Q. pacifica (Schellemberg, 1938) by the apical lobes of telson with 2 notches ( Krapp-Schickel & Ruffo 2000; Ruffo et al. 2000).
Quadrimaera yemanjae sp. nov. was found associated with calcareous sea grasses Halimeda opuntia , being together with Q. cristianae , Q. pieteri and Q. rocasensis in the same substratum. The new species shows a higher abundance of female organisms in comparison with the other congeners. Until now, Q. yemanjae sp. nov. is only known for the type locality.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |