Herdmania insolita, Monniot & Monniot, 2001
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.5391440 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/F57D87A3-FF55-31B0-EA52-FAFDFC9B1080 |
|
treatment provided by |
Marcus |
|
scientific name |
Herdmania insolita |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Herdmania insolita View in CoL n. sp.
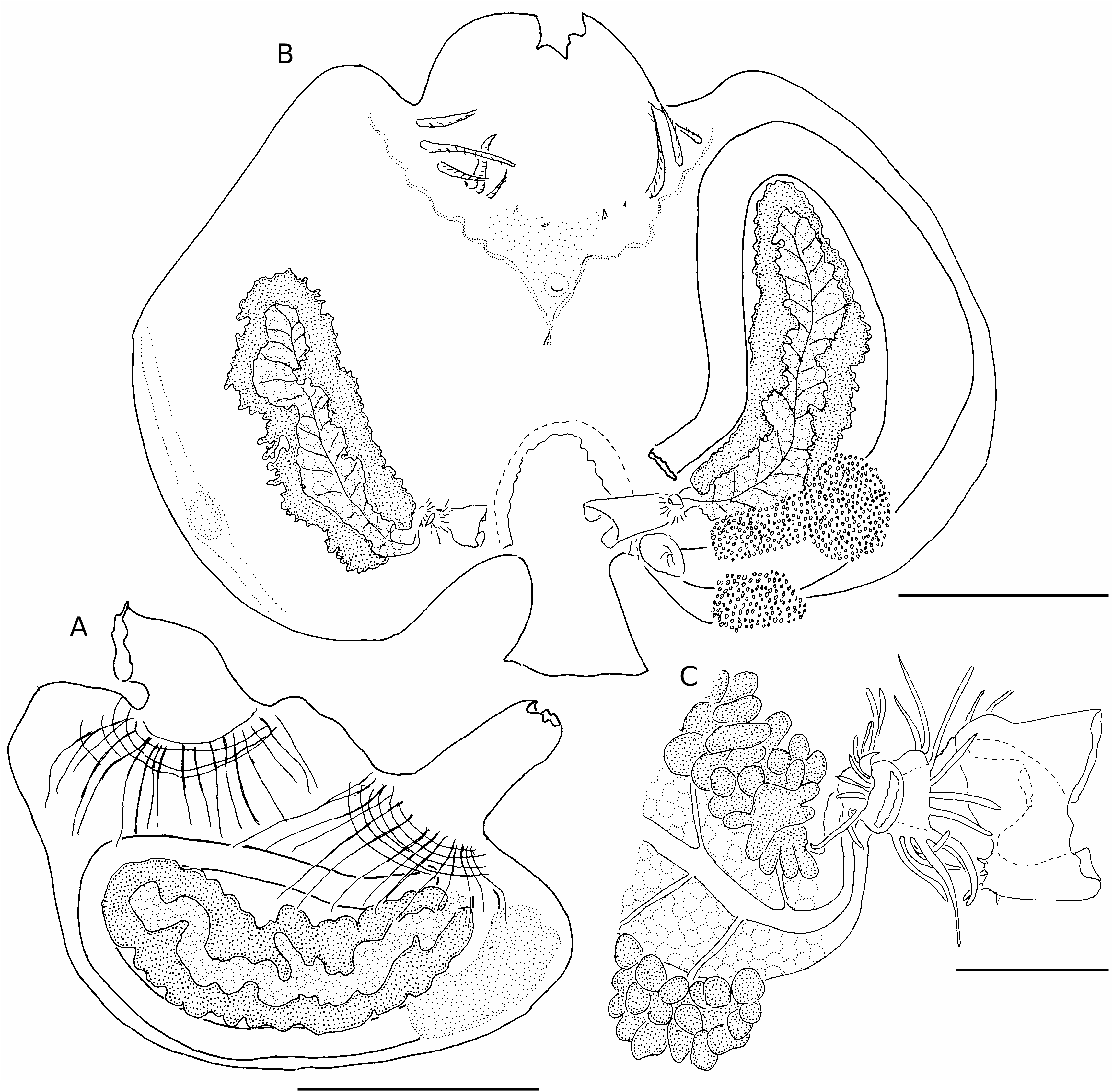
( Figs 102 View FIG ; 103)
Herdmania momus – Monniot F. & Monniot C. 1996: 263, Indonesia (MNHN S2 HER 6).
TYPE MATERIAL. — Federated States of Micronesia. Yap, Colonia, main wharf, 9°30.91’N, 138°07.57’E, 7 m, 4. VI.1996 ( MNHN S2 HER 21).
ETYMOLOGY. — From the Latin insolitus: unusual.
OTHER MATERIAL EXAMINED. — Palau. Koror, Malakal Harbour, Buoy #1, 7°19.88’N, 134°27.50’E, 1 m, 28.I.1998, 2 specimens (MNHN S2 HER 22).
Philippines. Davao, 07°05.89’N, 125°47.58’E, 8 m, 2.IV.1996 ( MNHN S2 HER 17).
DESCRIPTION
Both specimens from Palau and the one from Yap were collected in harbours. The tunic is thin, soft, and semi-transparent. It bears some epibionts on the dorsal part of the body and contains short spicules ( Fig. 103). The siphons form an angle of 90°. One of the specimens contains numerous small patches of red pigment in the dorsal part of the body; the pigment is much less abundant in other specimens.
The muscles are large, strong bundles issuing from each siphon ( Fig. 102A View FIG ). They cross each other but do not extend onto the ventral side, which has no musculature.
The pinnate tentacles are irregular. In one specimen from Palau we counted 16 large tentacles in two orders of size separated by smaller, more irregular ones. In the two other specimens, the dorsal tentacles were not developed. The tentacles contain spicules ( Fig. 103), as do all other organs. There is a large oral velum. The prepharyngeal band draws a deep V. The dorsal tubercle is distinctly protruding. Its opening is horseshoeshaped or forms a C that opens anteriorly ( Fig. 102B View FIG ). The peri-tubercular area is covered with small papillae in two specimens.
The dorsal lamina is long, made of numerous sharp languets.
The branchial sac has eight folds on the right side but only seven on the left, except in one sample where two longitudinal vessels are joined against the endostyle on the left side. In this specimen the formula is:
R.E. 1 3 1 9 2 11 2 13 2 15 2 14 2 13 2 9 2 D.L. D.L. 2 11 2 13 3 15 2 15 2 14 2 13 1 9 1 2 E.L. The folds diminish to join a circular crest around the oesophagus entrance. There are parastigmatic vessels.
The gut forms a straight and open loop ( Fig. 102B View FIG ). The hepatic gland has two lobes made of multiple round papillae. There is one gonad ( Fig. 102B View FIG ) on each side. The ovary, in the centre of the gonad, is sinuous and long. The testis lobes are all around it along its whole length. The sperm ducts join a common axial duct on the ovary ( Fig. 102B View FIG ). The male papilla is surprising; it is enclosed in a tuft of long filiform papillae located on the internal side of the oviduct ( Fig. 102C View FIG ). The female papilla is a long open flange of transparent tissue surrounding the opening of the oviduct and extending out into the cloacal cavity from it. There is a large cloacal velum. Cloacal tentacles were not found.
REMARKS
This species differs from all other Herdmania species in the strange structure of its male genital papillae.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.