Kulikovia spp
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.jcz.2022.05.005 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/F15687E3-1C56-FFD0-FFFA-FDBE9FDDCCC0 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Kulikovia spp |
| status |
|
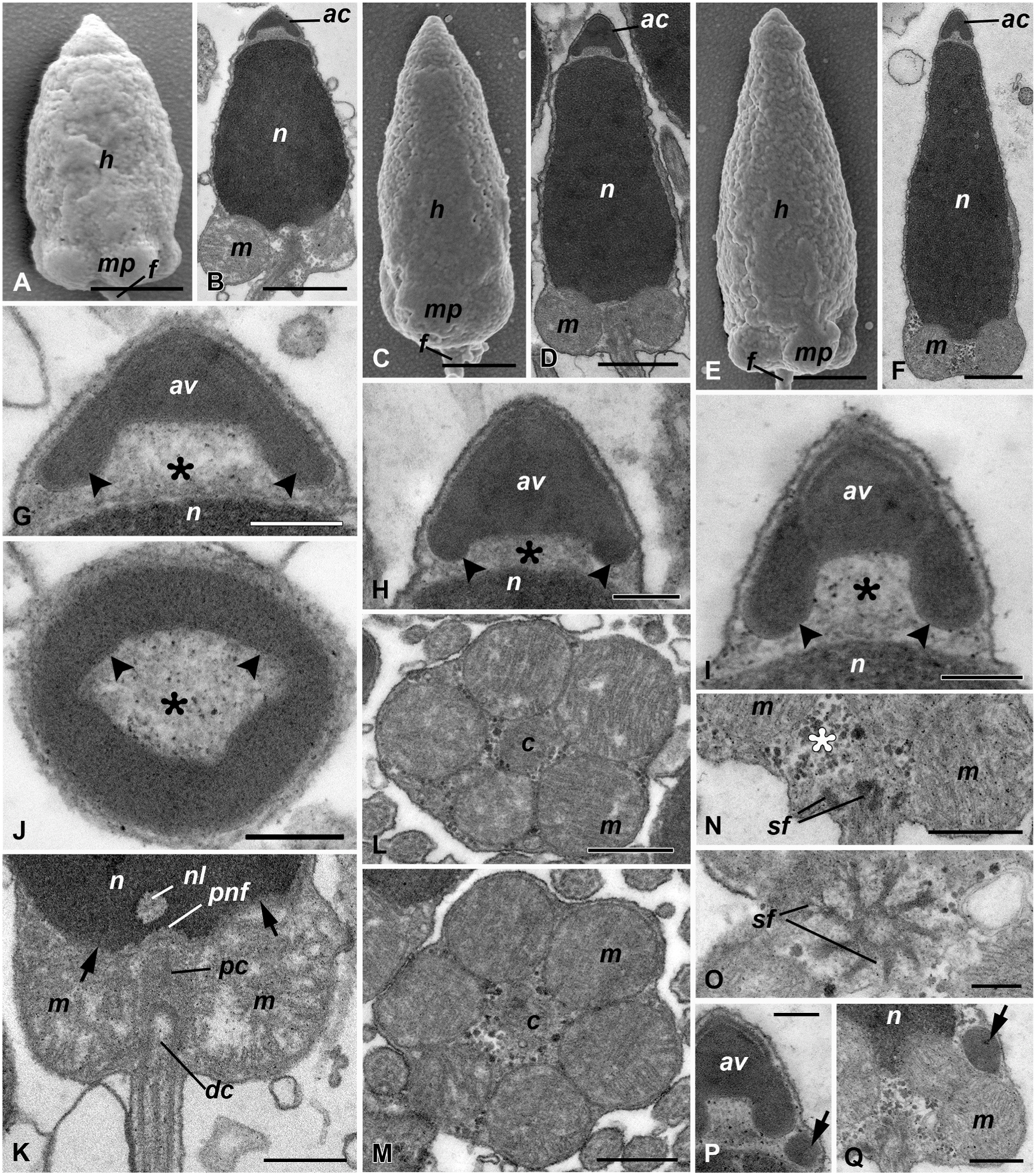
3.2. Sperm morphology in Kulikovia spp .
Unlike M. bella , the spermatozoa of the studied species of the genus Kulikovia have shorter bullet-like sperm heads of the ect-aquasperm type ( Fig. 2A, C, E View Fig ). In sections, each spermatozoon contains an acrosomal complex, a nucleus, and a short midpiece with mitochondria ( Fig. 2B, D, F View Fig ). A morphometric study of the spermatozoal organelles has revealed different sizes of nucleus and acrosomal complex between the studied species and shown their species-specific shapes ( Table 2). Nevertheless, in all studied Kulikovia species, several common general features in sperm organization have been identified: a small, single-vesicle, anteriorly located acrosomal complex, a straight, cone-shaped nucleus, five mitochondria in the posterior region of the nucleus, and a posteriorly oriented flagellum ( Fig. 2A–F View Fig ).
The acrosomal complex in all the species is organized rather simply, and consists in longitudinal sections of a single cone, an electron-dense acrosomal vesicle, and subacrosomal space limited by invagination of the basal part of the acrosomal vesicle and the apical part of the nucleus ( Fig. 2G–I View Fig ). The acrosomal vesicle in all the studied Kulikovia spp . is electron-dense with some heterogeneity in the content. In Kulikovia sp. , it is more visible and represented by the slightly lighter apical part and the electron-denser basal part with a lamellar pattern ( Fig. 2I View Fig ). According to previous studies (Franz´en 1983a; Dohren ¨et al. 2010), the posterior extension of the acrosomal vesicle is an acrosomal ring component that we observed in all the studied Kulikovia species ( Fig. 2G–I View Fig ). In all of the three species, the subacrosomal space has a shape close to a trapezium and is filled with subacrosomal substance of moderate electron density ( Fig. 2G–I View Fig ). In transverse sections, the acrosomal complex has a rounded shape with an electron-dense ring (acrosomal ring component) surrounding the subacrosomal space of moderate electron density ( Fig. 2J View Fig ).
The nucleus contains condensed electron-dense chromatin ( Fig. 2B, D, F View Fig ) but sporadic nuclear lacunae (small regions with diffuse chromatin) can be found ( Fig. 2F, K View Fig ). Despite the different length/width ratios of nucleus in Kulikovia spp . ( Table 2), the nuclear shape is always cone-like; a slight convexity is visible on the anterior surface and several invaginations on the posterior part (posterior nuclear fossa and invaginations hosting mitochondria) ( Fig. 2K View Fig ).
The midpiece in all the studied species consists of five rounded mitochondria ( Fig. 2L View Fig ) with a diameter of ca. 0.9 μm. In all Kulikovia spp ., spermatozoa with six mitochondria were also found ( Fig. 2M View Fig ), but their proportion in the sperm population was no more than 1%. Mitochondria surround the proximal and distal centrioles located perpendicularly to each other ( Fig. 2K View Fig ). The distal centriole has a pericentriolar complex organized by nine satellite fibers ( Fig. 2P, Q View Fig ). Particles of presumptive glycogen are often visible in cytoplasm. Moreover, in Kulikovia sp. , an electron-dense vesicle is often present in the apical cytoplasm near the acrosomal complex ( Fig. 2P View Fig ) or in the midpiece area ( Fig. 2Q View Fig ).
The axoneme in Kulikovia spp . has a typical 9 × 2 + 2 microtubular organization ( Fig. 2M View Fig ), but the length of its flagellum differs from the longest one in Kulikovia sp. by more than 10 μm ( Table 2).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.