Abrderma gracilentum Xing, Shih & Ren
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4205.2.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:87B729D0-2CCE-4BB7-92D1-6CACC63A5973 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6056630 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/EA643831-7D26-FFA9-04EF-24CEBAA2D8F9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Abrderma gracilentum Xing, Shih & Ren |
| status |
gen. nov. |
Abrderma gracilentum Xing, Shih & Ren View in CoL gen. nov.
Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3
Diagnosis. As for the genus due to monotypy.
Etymology. The specific name of “ gracilentum ” refers to the shape of the cerci.
Holotype. CNU-DER-NN2016002, an almost complete specimen.
Type locality and horizon. Daohugou Village , Shantou Township , Ningcheng County, Inner Mongolia, China; Jiulongshan Formation , the latest Middle Jurassic (late Callovian).
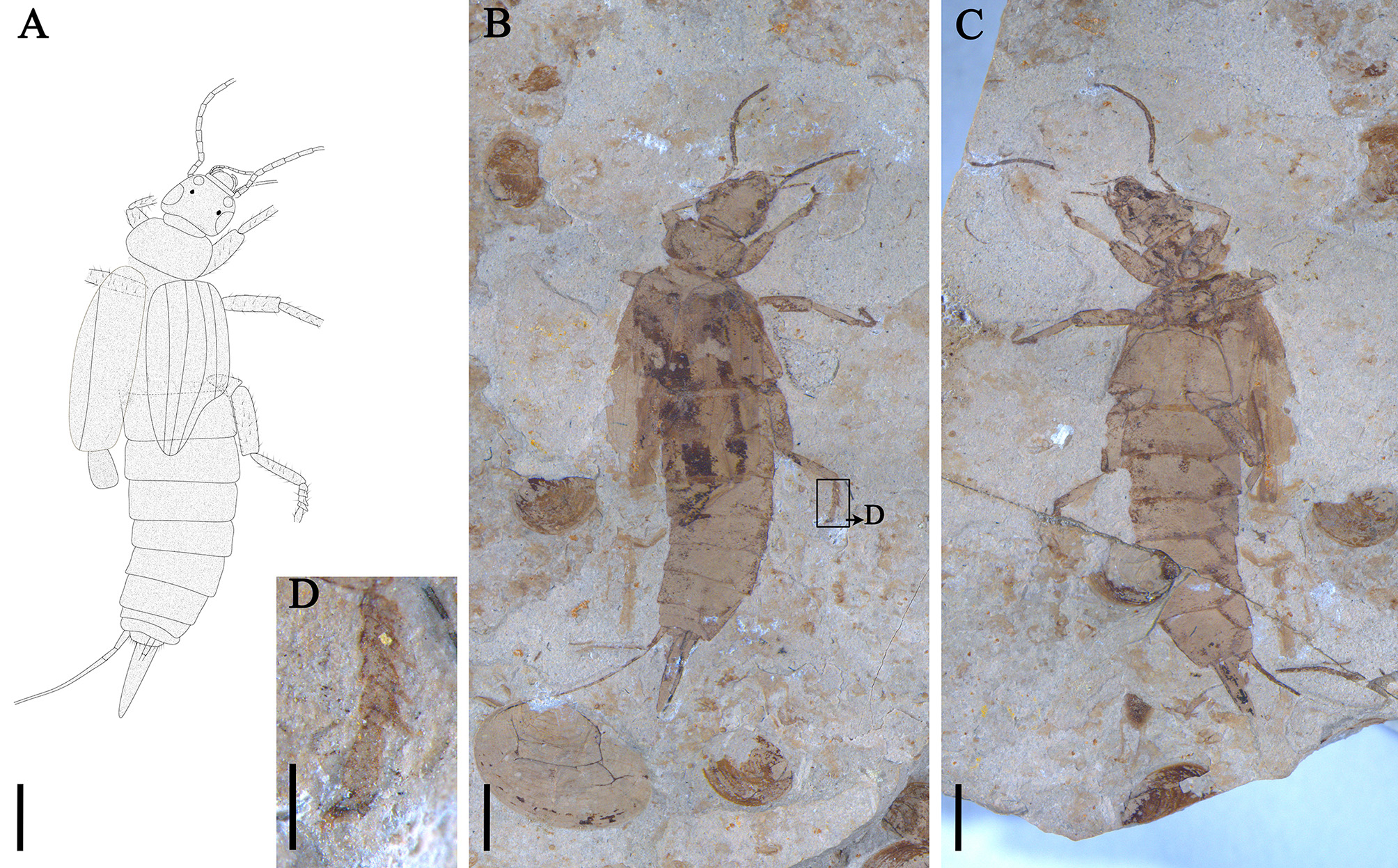
Description: An adult female, dorsal and ventral aspect. Body medium-sized (excluding antenna and cercus) 17.4 mm long, covered with pubescence.
Head: 1.4 mm long, 1.9 mm wide, subtriangular, small. Neck divided into anterior and posterior cervical sclerites, with anterior narrower than posterior. Ocelli present. Compound eye large, prominent and located near posterior margin of head. Mandible with two apical teeth, other teeth not visible. Left maxillary palpus with 11 segments preserved, right palpus preserved but not clear. Labrum semicircular with posterior margin straight. Cypeus approximately rectangular, 1.0 mm long, 0.2 mm wide. Antenna not preserved completely; first antennomere broader than others, pedicel longer than third antennomere.
Pronotum approximately elliptical, 1.3 mm wide, 2.5 mm long; anterior and posterior margins each 2.1 mm wide, both convex; lateral margins rounded. Anterior margin of pronotum broader than posterior margin of head. Scutellum not present.
Tegmen: Longitudinal veins strongly developed, 5.3 mm long, 2.5 mm wide, length/width ratio 2.1. Costal margin slightly arched, sutural margin straight, posterior margin apical. Tegmen extending slightly beyond second abdominal segment. Hind wing impression incomplete , only revealing a little uncovered by the tegmen.
Abdomen 7.7 mm long, 3.3 mm wide; eight abdominal segments; cercus as preserved 4.1 mm long, length ratio of cercus/body 0.2, with segments but not clearly preserved except that second segment of cerci slightly shorter than first segment. Abdomen distally with external ovipositor, 2.4 mm long, slot present at the middle. Pygidium small.
Fore femur thick and short, 1.3 mm long, 0.6 mm wide. Middle femur 1.7 mm long, 0.5 mm wide. Hind femur 2.0 mm long, 0.6 mm wide. Hind tibia 1.7 mm long, 0.3 mm wide. Hind tarsus pentamerous, segments 1‒4 horseshoe-shaped ( Fig 3 View FIGURE 3 D).
Remarks. Perissoderma gen. nov. and Abrderma gen. nov. are assigned to Archidermaptera based on the following characters: ocelli present; tegmina with distinct but much reduced longitudinal venation; cerci long and multi-segmented. In contrast, Neodermaptera do not have ocelli; but have tegmina without venation and cerci forming heavy forceps without segmentation. They are also differentiated from taxa in Eodermaptera, which have venation in the tegmina and short and stout forcipate cerci without segmentation ( Engel, 2003).
These two new genera are assigned to Protodiplatyidae on the basis of the following characters: antenna filiform with 17 to 26 antennomeres, scape enlarged, pedicel at least as long as the third antennomere; ocelli present; abdomen with 8 visible segments in female; prominent, external ovipositor; and cerci long, slender and multi-segmented ( Carpenter 1992, Xing et al. 2016).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |