Sotoplacidae
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.275670 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6491813 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/E72487C3-DF4A-1E21-FF62-ECF261B2FA07 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Sotoplacidae |
| status |
|
Family Sotoplacidae View in CoL nov. fam.
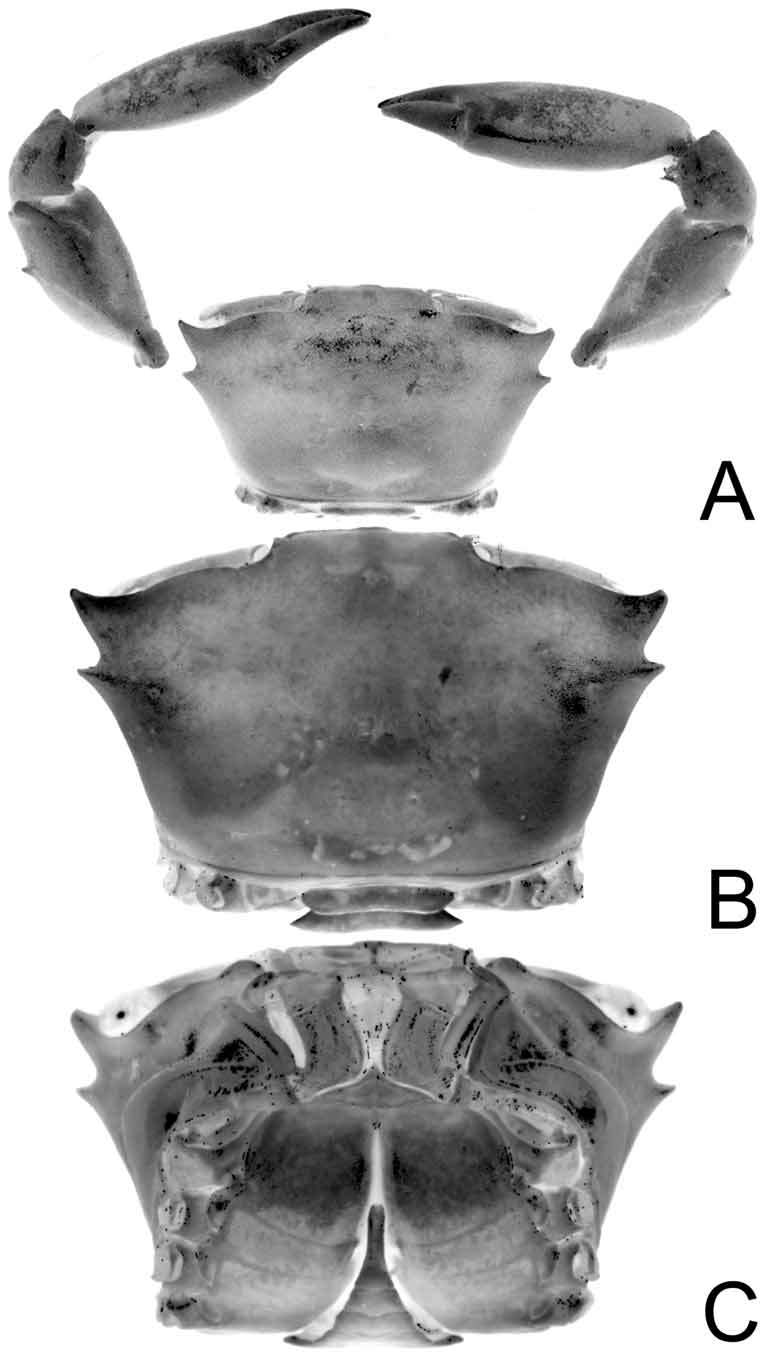
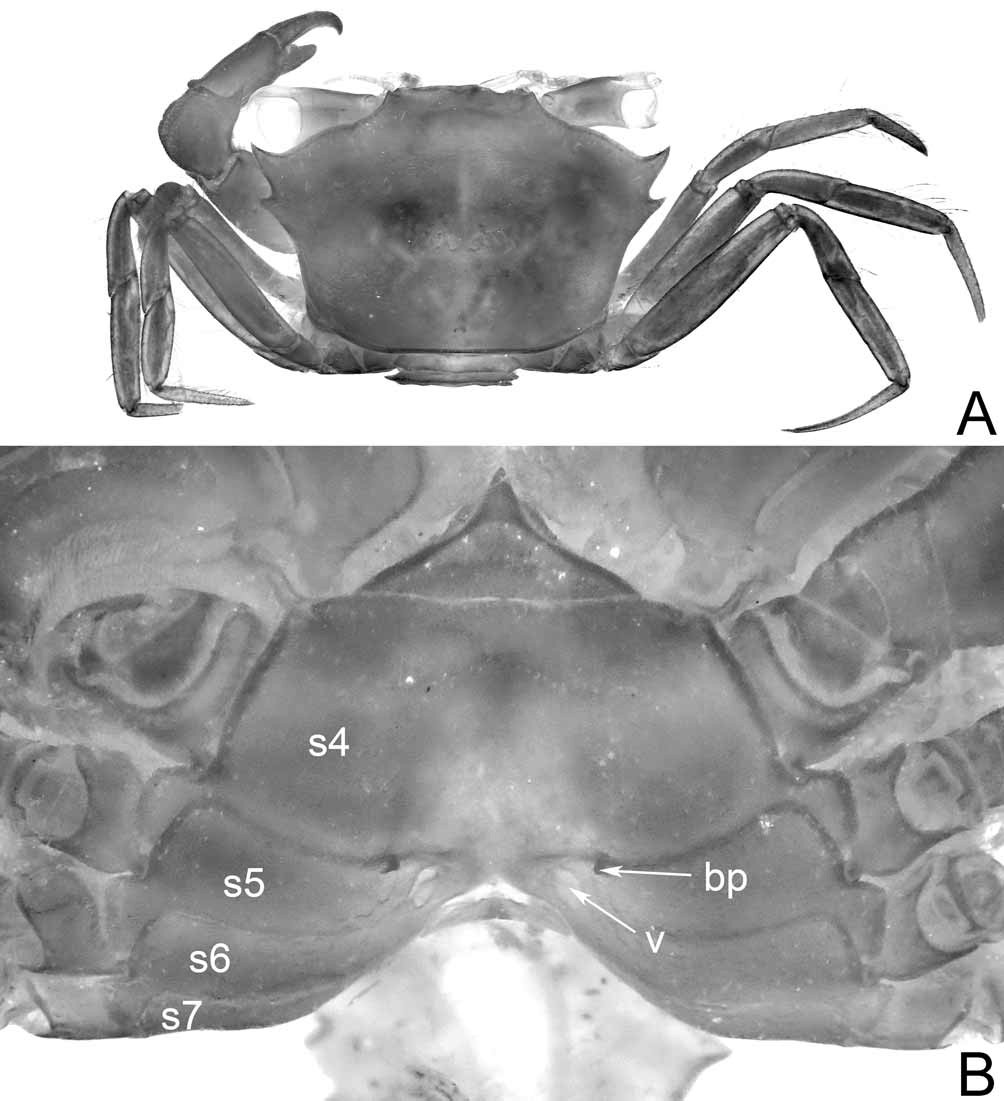
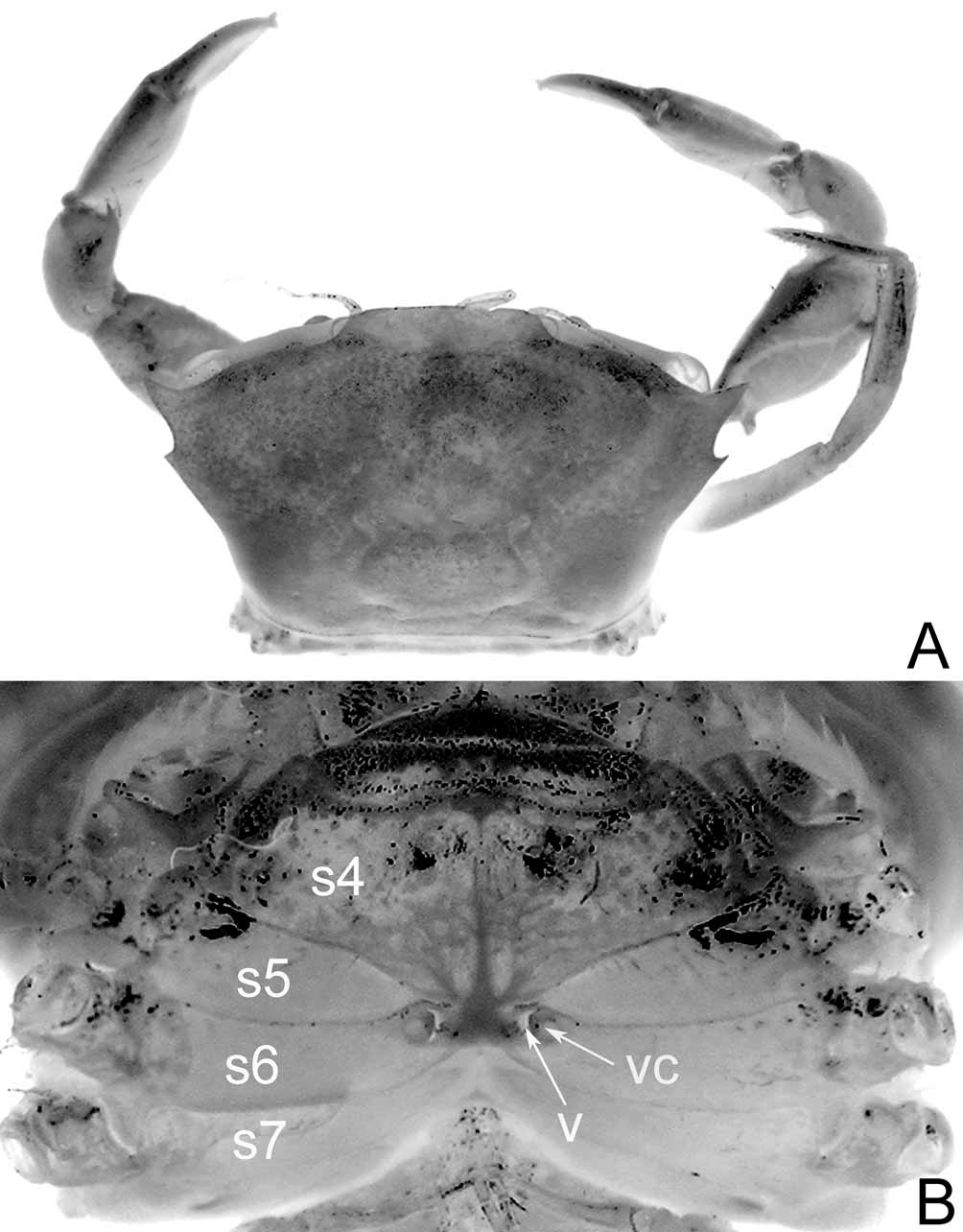
Diagnosis. Carapace transversely rectangular, wider than long, dorsal surface smooth, without clear indication of regions; front wide, with slight median notch; one acute anterolateral tooth posterior to acute, anteriorly oriented outer orbital angle ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 A, B, 7A, 8A; Guinot 1984: fig. 1, pl. 1, fig. A; Almeida et al. 2008: fig. 1). Orbit long, eye basophthalmite long, slightly shorter than front; cornea large, rounded ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 C, 2A, B, 3B). Basal antennal segment immobile, lodged in orbital hiatus, excluding antennal flagellum from orbit ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A, B). Carpus of cheliped with obtuse tooth on inner margin ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 A, 8A); plumose setae on anterior margin of carpus, anterior portion of inner margin of merus (absent in holotype). Dorsal margins of merus, carpus, propodus of ambulatory legs unarmed, dactylus slender, smooth, setose ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 A). Thoracic sternum wide ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 B, C, 5A, 7B, 8B; Guinot 1984: fig. 2A); suture 2/3 complete, straight; 3/4 deep, short, interrupted, only visible laterally; sutures 4/5, 5/6, 6/7, 7/8 interrupted, sinuous ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 B); male sternoabdominal cavity deep, very long, almost reaching suture 2/3, end of cavity marked by short longitudinal median line that reaches suture 2/3 ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 B, C, 5A); surface of sternite 4 adjacent to abdomen prominently swollen, surfaces distinctly convex ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 C, 2B, C); large portion of sternite 8 exposed when abdomen closed, including an area just above anterolateral margin of abdominal somite 3 ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 B, C, 5A). Male abdomen triangular, not T-shaped, all somites free; telson slender, tongue-shaped, much longer than wide, more than twice length of somite 6 ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 C, 3A, 5A; Guinot 1984: fig. 2A); somite 3 slightly transversely wider than somites 1, 2, 4–6; press-button of male abdominal-locking mechanism with tubercle next to thoracic suture 4/5 ( Figs. 5 View FIGURE 5 A, B). Male genital opening coxal. Penis coxo-sternal, long, protected by closed gutter formed by adjoining margins of episternite 7, thoracic sternite 8 ( Figs. 4 View FIGURE 4 , 5 View FIGURE 5 C), not by closed abdomen. G1 long, slender, slightly sinuous, slender part not tapering, with margins appearing subparallel, apex distinctly truncated with several distal large denticles, short protopodite ( Figs. 5 View FIGURE 5 B, 6A–C; Guinot 1984: fig. 2B–D); length of G2 less than one-third of G1, with reduced flagellum, obtuse apex, cup at junction with few, large spinules ( Figs. 6 View FIGURE 6 D–F; Guinot 1984: fig. 2E–G). Female abdomen rounded, not covering outer portions of thoracic sternum, with 6 freely articulated somites, rounded telson; press-button of abdominal-locking mechanism with triangular, pointed tubercle at thoracic suture 4/ 5 in pre-adult females ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 B), absent in adults ( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 B). Vulva vertically elongated, extending across anterior third of sternite 6 along deflected thoracic suture 5/6 close to median axis of thorax; elliptical, obliquely longitudinal, slightly salient sternal vulvar cover along external margin of vulva ( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 B); ovoid vulva, sternal vulvar cover absent in pre-adult females ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 B).
Remarks. A unique combination of characters places Sotoplax as a taxon independent from the most closely related family, the Euryplacidae , by the following: (1) the male sterno-abdominal cavity is deep, long, almost reaching thoracic suture 2/3, the end of the cavity is marked by a short longitudinal median line that reaches thoracic suture 2/3 ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 C, 2B, C, 5A) (cavity not reaching to the anterior portion of thoracic sternite 4 in Euryplacidae [ Fig. 9A View FIGURE 9. A ; e.g. Ng & Castro 2007: fig. 3A; Castro & Ng in press: figs. 3C, 16D], or, without short longitudinal median line that connects to thoracic suture 2/3 if it reaches to the anterior portion of thoracic sternite 4); (2) the surface of thoracic sternite 4 lateral to abdomen of the male distinctly inflated ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 C, 2B, C) (not inflated in Euryplacidae [ Fig. 9A View FIGURE 9. A , B]); (3) the male telson is long, slender, much longer than wide, and more than twice the length of somite 6 ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 C, 2B, C) (shorter, less slender telson never approaching twice length of somite 6 in Euryplacidae [ Fig. 9A View FIGURE 9. A ]); (4) a large portion of thoracic sternite 8 is left exposed when the male abdomen is closed, including an area just above the anterolateral margin of abdominal somite 3 ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 B, C, 5A) (a relatively smaller portion of thoracic sternite 8, if any, is exposed in Euryplacidae [ Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9. A B; e.g. Ng & Castro 2007: fig. 2C; Castro & Ng in press: figs. 16F, 17F, 44G]); (5) the press-button of the male abdominal-locking mechanism has a tubercle next to thoracic suture 4/5 ( Figs. 5 View FIGURE 5 A, B) (the male press-button has a tubercle close but not next to thoracic suture 4/5 [e.g. Ng & Castro 2007: fig. 3A; Castro & Ng in press: figs. 11E, 17D] in Euryplacidae ); (6) the penis is protected by a closed gutter, formed by the margins of thoracic episternite 7 and sternite 8 ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ) (the penis is protected by a concavity along the posterior portion of thoracic episternite 7 but remains exposed [e.g. Castro & Ng in press: figs. 19F, 30F], whereas in the extreme case of Euryplax , additional protection is provided by a part of episternite 7 extending close to, and partially overlapping, but never fusing with thoracic sternite 8, thus not forming a closed gutter [ Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9. A C, D]); (7) the G1 is relatively long and slender, of equal width along the slender part, with a distinctly truncated apex armed with a few denticles ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 A–C) (progressively thinner distally, with a sharp or rounded apex with many denticles in at least the distalmost third portion in Euryplacidae [e.g. Ng & Castro 2007: fig. 4A–C; Castro & Ng in press: figs. 11E, 14A, B, D, E, G, H, J, K]); (8) thoracic sutures 4/5, 5/ 6, 6/7, 7/8 are interrupted ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 A) (suture 5/6 is complete in most Euryplacidae [e.g. Castro & Ng in press: figs. 3G, 19H, 21D], although interrupted in Nancyplax [Castro & Ng in press: fig. 31F, G], Xenocrate [Castro & Ng in press: fig. 39G, H], and new genus being described in Castro & Ng in press); and (9) the sternal vulvar cover in adult females is elliptical and obliquely longitudinal ( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 B) (the sternal vulvar cover is absent in most Euryplacidae , being present as transverse cover along the posterior margin of the vulva in only two species: Heteroplax dentata Stimpson, 1858 [being placed in new genus in Castro & Ng in press] and Psopheticoides sanguineus Sakai, 1969 [Castro & Ng in press: figs. 41G, 36G respectively]).
Differences between the new family, the Euryplacidae , and the remaining 10 families of the Goneplacoidea as defined in Ng et al. (2008) are summarised in Table 1.
Whereas none of the above listed features are by themselves diagnostic, the combination of characters is unique. The dorsal surface of the carapace of Sotoplax , being transversally elongated, with moderately long orbits and eye peduncles, and one anterolateral tooth posterior to each outer orbital tooth, is superficially similar to several genera of Euryplacidae (notably Heteroplax Stimpson, 1858 , sensu lato) and Goneplacidae (namely Goneplacoides Castro, 2007 , and Neogoneplax Castro, 2007 ). The form of the male abdomen, however, particularly the long and tongue-shaped telson, the length of the sterno-abdominal cavity that reaches to almost thoracic suture 2/3, the swollen thoracic sternite 4, large and characteristically shaped exposed part of thoracic sternite 8, the distinctive structure of the G1, and the protection of the penis by a closed gutter, set Sotoplax aside from all euryplacids. In all its other characters, it also cannot be accommodated in any of the other goneplacoid families (Table 1).
Several of the diagnostic characters bear further discussion. The form of the male sterno-abdominal cavity is diagnostic in Sotoplax when compared with all euryplacids. In most euryplacids, even when the male abdomen is distinctly T-shaped with somite 6 and the telson elongated (e.g. Eucrate ), the cavity ends well before thoracic suture 2/3, usually just reaching to the anterior margin of thoracic sternite 4 ( Fig. 9A View FIGURE 9. A ). Even in some unpublished species of Heteroplax sensu lato (to be included in a new genus in Castro & Ng in press) where thoracic sternite 3 is transversely very narrow and the cavity appears to be close to thoracic suture 2/3, there is no longitudinal median line present that leads from the end of the cavity to the suture. The male telson of Sotoplax is highly diagnostic. The tongue-like shape of the male telson is unique ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 C, 2B, C); all euryplacids have distinctly triangular telsons ( Fig. 9A View FIGURE 9. A ). In addition, the length of the male telson of Sotoplax is twice the length of abdominal somite 6. The telson is never as proportionally long, even in euryplacids with T-shaped male abdomens and relatively elongated telsons (e.g. Eucrate ) ( Fig. 9A View FIGURE 9. A ). The exposed portion of thoracic sternite 8 when the male abdomen is closed is not only relatively larger in Sotoplax than in euryplacids, but characteristically “brackets” the antero- and posterolateral margins of the male abdominal somite 3 ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 B, C, 5A). In all euryplacids, even those having part of thoracic sternite 8 exposed (e.g. Euryplax and Trizocarcinus Rathbun, 1914 ; Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9. A B), the exposed part of the sternite 8 never reaches beyond the lateral corner of abdominal somite 3 and the exposed part of thoracic sternite 8 has a characteristic shape.
The coxo-sternal condition of the penis is important. The adjoining margins of the episternite 7 and thoracic sternite 8 of Sotoplax join to form a covered gutter around the penis ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ). Penis protection by the thorax in euryplacids involves a concavity in thoracic sternite 7 (e.g. Castro & Ng in press: figs. 19F, 30F). In Euryplax , which has the most elaborate coxo-sternal modification in the family, episternite 7 is expanded and partially overlaps sternite 8. Episternite 7 therefore appears to touch thoracic sternite 8 but their margins are not joined and most of the penis can still be observed between the sternites ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9. A D). A ventral view of the thorax may give the mistaken impression that thoracic episternites 7 and sternite 8 actually meet ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9. A D), but a lateral view ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9. A C) will show that the penis is sitting in a channel not completely covered and remains visible.
The morphology of the characteristic G1 of Sotoplax is very different from that in euryplacids and other goneplacoids. Although relatively long, it is still proportionately shorter than in euryplacids. More characteristically, the slender part does not taper gradually towards the tip, being of equal width throughout its length, with the tip distinctly truncated ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 A–C). In euryplacids, the G1 tapers gradually or rapidly to a sharp or rounded tip, with the distal part sometimes appearing almost thread-like (e.g. Guinot 1969: figs. 48, 53, 54, 56, 58; Ng & Castro 2007: fig. 4; Castro & Ng in press: figs. 11E, 14A, B, D, E, G, H, J, K).
1. Comparison between Sotoplacidae View in CoL n. fam. and families of the superfamily Goneplacoidea. Genera examined in parentheses. Number of genera per family following Ng et al. (2008) and De Grave et al. (2009).
thoracic sternite 4 continued next page
1. (continued)
abdomen Moderately wide; Moderately wide to Moderately wide; all Very narrow Moderately wide to Very wide, short, Moderately wide; all Moderately wide; all Narrow; all somites Nearly triangular; Narrow;all somites somites 3–5 wide; somites 3–5 somites free;lateral (moderately wide in wide; all somites free triangular, inflated sutures distinct but somites free or 3, 4 free; lateral margins of all somites free; free; lateral margins of completely fused, fused; lateral margins margins of somites 3– some genera);all (but 3–5 fused in because of very large adult somites 3–5 fused; lateral margins somites 3–6 parallel to lateral margins of somites 4–6 nearly only lateral suture of somites 3–6 6 gradually narrowing somites free; lateral Neommatocarcinus ); G1; all somites free; immovable;lateral of somites 4–5 each other; somites 3–6 parallel to each other; lines visible,lateral gradually narrowing to to semicircular telson; margins of somites 4– typically lateral lateral margins of margins of somites 4– gradually narrowing to quadrilateral telson; gradually narrowing triangular telson; margins of somites triangular or narrow somite 6 as wide as 6 abruptly narrowing margins of somites 4– somites 4–6 gradually 5 gradually narrowing triangular telson; somites 5, 6 slightly to narrow,slender, somites 6 slightly 3–6 gradually telson;somite 5 wider long, somite 5 wider from somite 3 to 5 gradually narrowing narrowing from to triangular or somites 5, 6 wider wider than long; elongated telson wider than long,5 narrowing to than long; posterior than long;somite 3 narrow, slender telson; to triangular or somite 3 to broad rounded telson; than long;somite 3 somite 3 wider than with very thin, wider than long; triangular telson; portion of somite 3–5 slightly narrower than somite 6 much longer semicircular telson; telson; somites 5, 6 somites 5, 6 wider slightly wider than somites 2, slightly rounded tip; somites somite 3 wider than somites 5, 6 as wide wider than somites 1, somites 1, 2 than wide, somite 5 as somites 5, 6 wider wider than long; than long; somite 3 somites 1, 2 narrower than somite 5, 6 wider than somites 1, 2 as long; somite 3 2 long as wide; somite 3 than long;somite 3 somite 3 nearly as slightly wider than 1 long;somite 3 only slightly wider wider than somites 1, nearly as wide or wide as somites 1,2, somites 1, 2 slightly wider than than somites 1, 2, 2 slightly wider than which are dorsally somite 2, much which are long, somites 1, 2 placed;telson wider than somite 1 dorsally placed cordiform with basal
teeth
Press-buttons Tubercle at Tubercle close to Tubercle close to Tubercle near thoracic Tubercle near thoracic Tubercle at about Large tubercle near Large tubercle on Tubercle at sternal Tubercle very close Tubercle near thoracic
of male approximately thoracic sternal suture thoracic sternal suture sternal suture 4/5 sternal suture 4/5 posterior third of thoracic sternal suture posterior portion of suture 5/6 to thoracic sternal sternal suture 5/6
abdominal- posterior third of 4/5 5/6 sternite 5 5/6 sternite 5 suture 4/5
locking sternite 5
mechanism
Press-buttons Unknown Tubercle close to Unknown Smalltubercle near Small tubercle on Unknown Unknown Unknown Unknown Conspicuous, Unknown
pre-adult thoracic sternal suture thoracic sternal suture median portion of triangular,pointed
female 4/5 4/5 thoracic sternite 5 tubercle at thoracic
abdominal sternal suture 4/5
locking
mechanism
G1 Long,slender, Short to moderately Long, sinuous, distal Long,slender;slender Long,slender to stout; Short, stout,curved, Rather short, slender; Long,slender or stout; Long,slender; small Long, slender, same Long, slender;small straight,acuminate long,slender, straight, part with short spines apex; many small apex varies among twisted,distal part curved,apex slightly small denticles, denticles, pointed apex width along entire denticles,pointed apex apex moderately pointed denticles along distal genera with many long setae, tapering with small pointed or regularly length;few large apex portion thick,complex apex; denticles tapering apex denticles at conspicuously long truncated apex protopodite
G2 Long (as long as Short (less than 1/3 Long (as long as G1), Short (less than 1/3 Long (as long as G1, Long (about 2/3 G1 Long (much longer Long (longer than Short (less than 1/3 Short (less than 1/3 Long (as long as G1); G1), with long G1 length) to slender G1 length), slightly short in length), slender; than G1), slender; G1), slender; G1 length),slender G1 length),slender, exceptionally short flagellum moderately long expanded tip with Microgoneplax , simple flagellum, long flagellum distinct flagellum (about half reduced flagellum, flagellum
(about 2/3 G1) or long lateral spinule (acute Paragoneplax ), tubular apex from basal part total length) distinct few thin spinules at (longer than G1); with lateral extension in slender;typically long from basal part base of distal cup long flagellum Nancyplax ) flagellum distinct
from and as long as
basal part
Male genital Coxal, large:opens Coxal, large, opens Coxal Coxal,large,opens Coxal, large,opens Coxal, large,opens Coxal, large, opens Coxal,large,opens Coxal,opens just Coxal, large, opens Coxal large,opens just
openings just anterior to just anterior to coxo- just anterior to coxo- just anterior to coxo- just anterior to coxo- just anterior to coxo- just anterior to coxo- anterior to coxo- just anterior to anterior to coxocoxo-sternal sternal condyle of P5 sternal condyle of P5 sternal condyle of P5 sternal condyle of P5 sternal condyle of P5 sternal condyle of P5 sternal condyle of P5 coxo-sternal sternal condyle of P5 condyle of P5 coxa coxa coxa coxa coxa coxa coxa coxa condyle of P5 coxa coxa continued next page 1. (continued)
Penes Coxo-sternal, long, Coxo-sternal, very Coxo-sternal, Coxo-sternal, long, Coxal to coxo-sternal, Coxo-sternal, long, Coxal, long,thick, Coxal,moderately Coxo-sternal, long, Long, protected by Short, protected by protected by convex long,protected by moderately long, protected by concave short to moderately basally thick, in only protected by long, protected by protected by closed channel transversely wide posterior portion of prolongation of protected by posterior portion of long (penis with depression posterior to transversely wide transversely wide prolongation of formed by junction abdominal somite 3, thoracic sternite 7, episternite 7, double prolongation of thoracic sternite 7, calcified portions in a suture 7/8; coxal abdominal somite 3 abdominal somite 3, episternite 7, relatively of sternites 7, 8, not prolongation of transversely wide coxo-sternal plate episternite 7 transversely wide few genera), protected gonopore protected by episternite 7 narrow abdominal by abdominal episternite 7 abdominal somite 3, formed by thoracic abdominal somite 3, by transversely wide concave posterior moderately expanded somite 3, partially by somites
prolongation of sternite 7 plus anterior prolongation of abdominal somite 3, portion of thoracic but not covering penis long groove formed by
episternite 7 extension of thoracic episternite 7 prolongation of sternite 7, expansion junction of thoracic
sternite 8, groove in episternite 7 of sternite 8, large sternites 7, 8 ( Fig.9 View FIGURE 9. A F),
sternite 8 abdominal somite 3 unprotected dorsal
portion slightly
calcified
Female Narrow,triangular, Narrow,triangular, all Unknown Relativelynarrow, all Wide, all somites free; Wide, all somites free; Relatively narrow, all Relatively narrow,all Relatively narrow, all Relatively narrow, Narrow,subquadrate, abdomen all somites free; not somites free,not somites free;not covers outer portions covers outer portions somites free;not somites free; not somites free;not all somites free; not all somites free; not covering outer covering outer covering outer of thoracic sternum of thoracic sternum covering outer covering outer covering outer covering outer covering outer portions of thoracic portions of thoracic portions of thoracic portions of thoracic portions of thoracic portions of thoracic portions of thoracic portions of thoracic sternum,with sternum,with large sternum, with large sternum,but sternite 8 sternum, but sternum,large portion sternum;large sternum;relatively moderately large portion left exposed portion left exposed covered by abdominal practically all of of sternite 8 exposed portion left exposed smaller area left portion left exposed by closed abdominal by closed abdominal somites 2, 3 sternite 8 covered by by abdominal somites by closed exposed by closed
by closed somites 2, 3; sterno- somites 2, 3 abdominal somites 2, 2,3 abdominal somites abdominal somites 2, abdominal somites abdominal cavity 3 2, 3 3 due to relatively
2, 3 extends to suture 2/3 narrow sternum Vulvae Large,circular, Large,circular, Unknown Ovoid,extending Ovoid to round;varies Large, round, Ovoid,extending Large, round, Small, ovoid, Vertically Relatively small, extending across extending across most across anterior third of in size, occupying extending across most across most of sternite extending across extending across elongated, ovoid, occupying anterior half of of sternite 6; bordered sternite 6; sternal various portions of of sternite 6, deflected 6; sternal vulvar cover anterior half of sternite anterior third of extending across anterior half of sternite sternite 6 in contact by wide,non- vulvar cover absent sternite 6; sternal thoracic sternal suture 6 (across most of sternite 6 close to anterior third of 6, relatively close to with suture 5/6, sclerotised margin (except transverse vulvar cover in six 5/6 almost making sternite in Progeryon ); median axis of sternite 6; elliptical, median axis of
very close to with soft centre vulvar cover in two genera contact with suture sternal vulvar cover sternum, elevated, obliquely sternum,slightly median axis of species); margin 4/5; sternal vulvar salient,posterior covered by thick longitudinal sternal elevated;sternal
thorax;non- typically thick, cover absent; margin ( Rhadinoplax ), short, membrane (no sternal vulvar cover in vulvar cover absent, movable operculum elevated with spherical anterior ( Paragalene ), vulvar cover or adults conspicuously
prominences ( Fig.9 View FIGURE 9. A E) absent ( Progeryon ) operculum) elevated margin Female Suture 2/3 Suture 2/3 complete, Suture 1/2 (ridge), 2/3 Suture 2/3 complete, Suture 2/3 complete, Suture 2/3 complete, Suture 2/3 complete, Suture 2/3 complete, Suture 3/4 deep, Suture 2/3 Suture 2/3 complete, thoracic complete, straight; straight; 3/4 short, (concave), 3/4 convex (straight in straight;3/4 deep, concave; 3/4 deep, straight;3/4 deep, concave or straight; interrupted; 4/5, 5/6, complete, straight, straight,3/4 complete; sternum 3/4 not exposed, deep,interrupted;4/5, complete; 4/5,5/6, some genera); 3/4 interrupted,sutures interrupted; 4/5,5/6, interrupted;4/5, 5/6 3/4 deep,interrupted; 7/8 interrupted, 6/7 3/4 deep, 4/5, 5/6, 6/7 4/5, 5/6, 6/7,7/8 5/6, 6/7,7/8 6/7,7/8 interrupted; deep,interrupted;4/5, 4/5,5/6 interrupted 7/8 interrupted,6/7 interrupted,6/7,7/8 4/5,5/6 interrupted, complete; sternites 7, interrupted;4/5, interrupted, 7/8 complete, straight; interrupted;sternites sternites 7, 8 with 6/7, 7/8 interrupted, medially, 6/7 complete complete; median line complete;sternites 7, 6/7,7/8 complete; 8 with median line 5/6, 6/7,7/8 complete;sternites 7, sternites 5–8, 5–8, posterior portion median line 5/6 complete (interrupted in 4 absent 8 with median line sternites 7, 8 with interrupted; 8 with median line posterior portion of of 4 with distinct or (interrupted in some genera),7/8 median line sternites 7, 8 with
4 with median line poorly defined median genera); sternites 7, 8 interrupted;sternites median line
line with median line 7, 8 with median line
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
InfraOrder |
Brachyura |
|
Family |